Period 3 elements and oxides - part 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Draw the trend in first ionisation across period 3
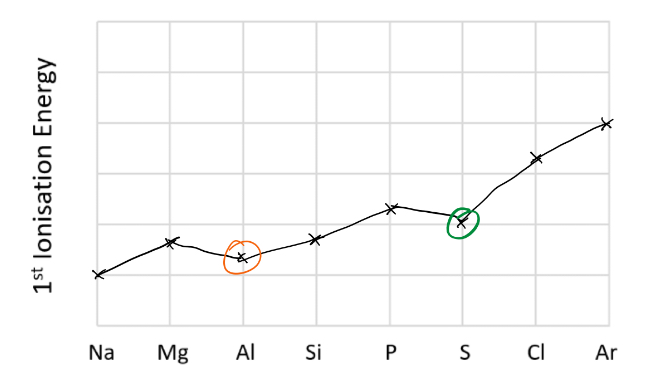
Explain the decrease in first ionisation energy from Mg to Al
Jump to 3p sub shell which is further from nucleus
Explain the decrease in first ionisation energy from P to S
3p3 to 3p4, electron must pair up in orbital so light repulsion makes easier to remove
Draw the trend in melting and boiling points across period 3
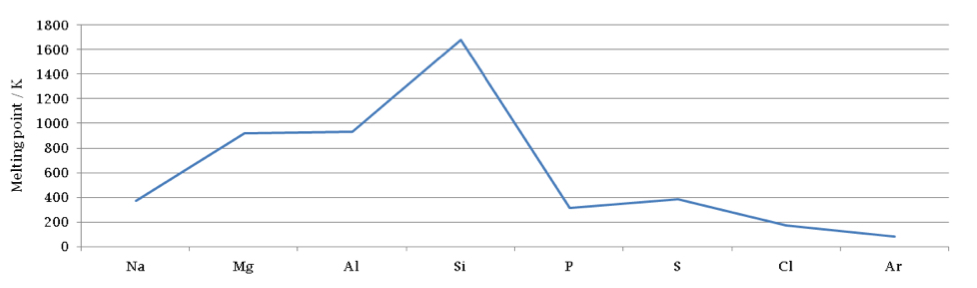
Explain the increase in melting point from Na to Al
Cations increase in charge, cations decrease in size, more delocalised electrons means stronger electrostatic forces
Explain the high melting point of Si
Strong covalent bonds between atoms requires a lot of energy to overcome
Explain the trend in melting point from P to Ar
Slight increase from P to S as molecules contain more electrons so stronger Van der Waals forces, decrease from S to Ar as number of electrons decreases
Which period 3 elements conduct electricity, and what is the trend in those that do?
Na, Mg and Al only, Al3+ has more delocalised electrons so is best
Metal and water —> ?
Metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Metal + steam —> ?
Metal oxide + hydrogen
Flame test for Na
Yellow
Flame test for Mg, Al, Si
Bright white
Flame test for P4
Very white
Flame test for S8
Blue
Reaction of Na2O with water + equation
Dissolves, Na2O + H2O —> 2NaOH
pH of solution formed when Na2O dissolves in water
13
Nature of sodium oxide
Basic
Reaction of MgO with water + equation
Slightly soluble, MgO + H2O —> Mg(OH)2
pH of solution formed when MgO reacts with water
9
Nature of magnesium oxide
Weakly basic
Reaction of Al2O3 with water + pH of solution formed
Insoluble
Reaction of SiO2 with water + pH of solution formed
Insoluble, 7
Describe the difference observed when SO2 vs SO3 reacts with water
SO2 dissolves while SO3 dissolves and reacts violently
pH of solution when P4O10 or SO2 reacts with water
3
pH of solution formed when SO3 reacts with water
0/1
Reaction of Na2O with acid
Na2O + 2H+ —> 2Na+ + H2O
Reaction of MgO with acid
MgO + 2H+ —> Mg2+ + H2O
Reaction of Al2O3 with acid
Al2O3 + 6H+ —> 2Al3+ + 3H2O
Reaction of Al2O3 with alkali
Al2O3 + 2OH- + 3H2O —> 2Al(OH)4 -
Nature of aluminium oxide
Amphoteric
Reaction of SiO2 with alkali
SiO2 + OH- —> SiO3 2- + H2O
Conditions needed for SiO2 to react with alkali
Hot and conc NaOH
Reaction of P4O10 with alkali
P4O10 + 12OH- —> 4PO4 3- + 6H2O
Reaction of SO2 with alkali
SO2 + 2OH- —> SO3 2- + H2O
Reaction of SO3 with alkali
SO3 + 2OH- —> SO4 2- + H2O