DPT 745 Week 4 Lecture Notes Pt. 3
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Eye region
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
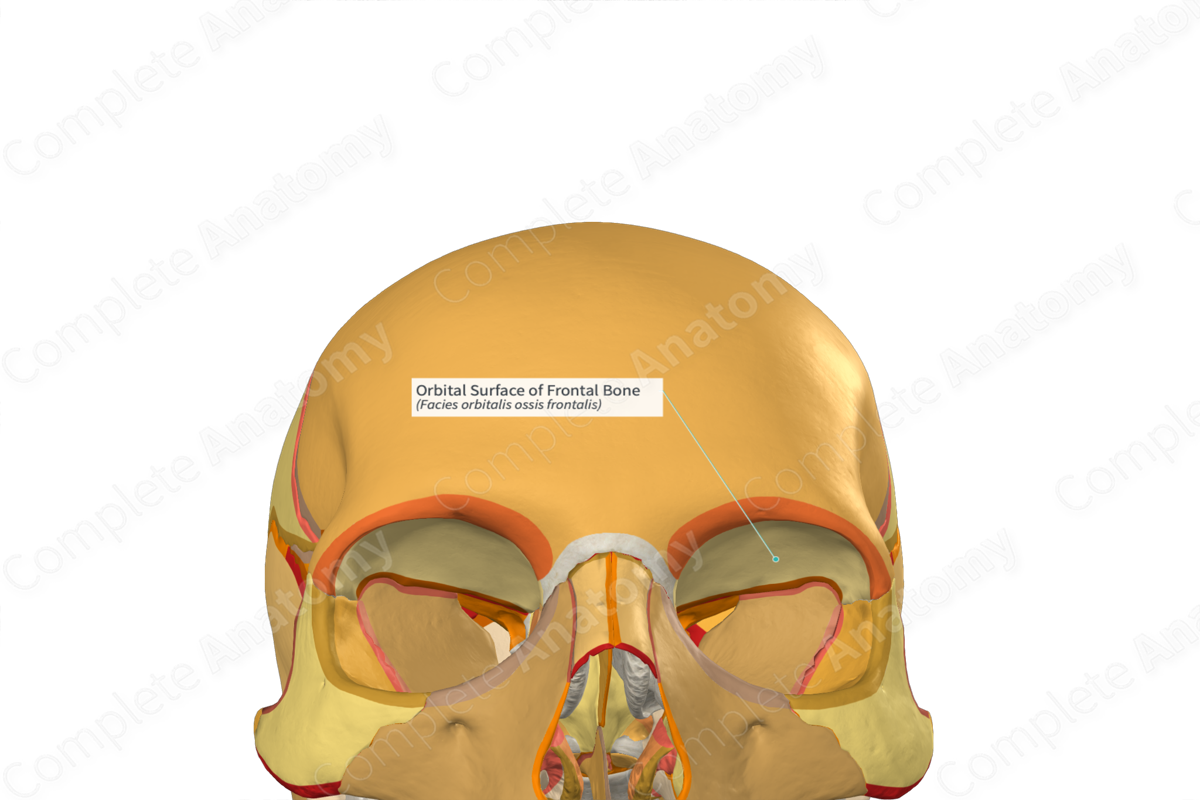
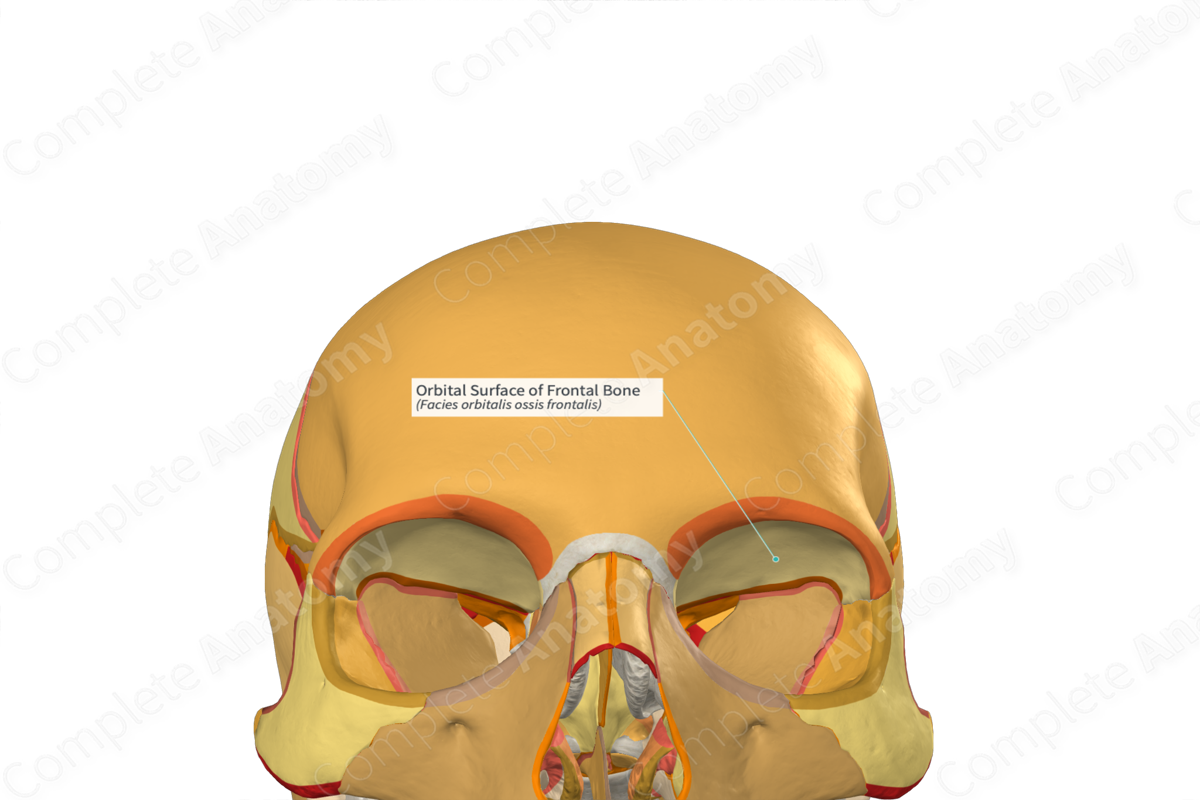
Orbits
Two bony cavities that house the eyeballs and associated muscles, fasciae, vessels, a considerable amount of fat and lacrimal apparatus
frontal
zygomatic
ethmoid
Orbits
• Walls
– Superior wall - orbital plate of the _____ bone
– Lateral wall - _____ bone
– Floor - maxilla
– Medial wall - orbital plate of the _____
• Contents:
– Eyeball
– Extra-ocular muscles
– Sensory, motor nerves and vascular supply
– Extra-ocular fat
conjunctiva
Lacrimal
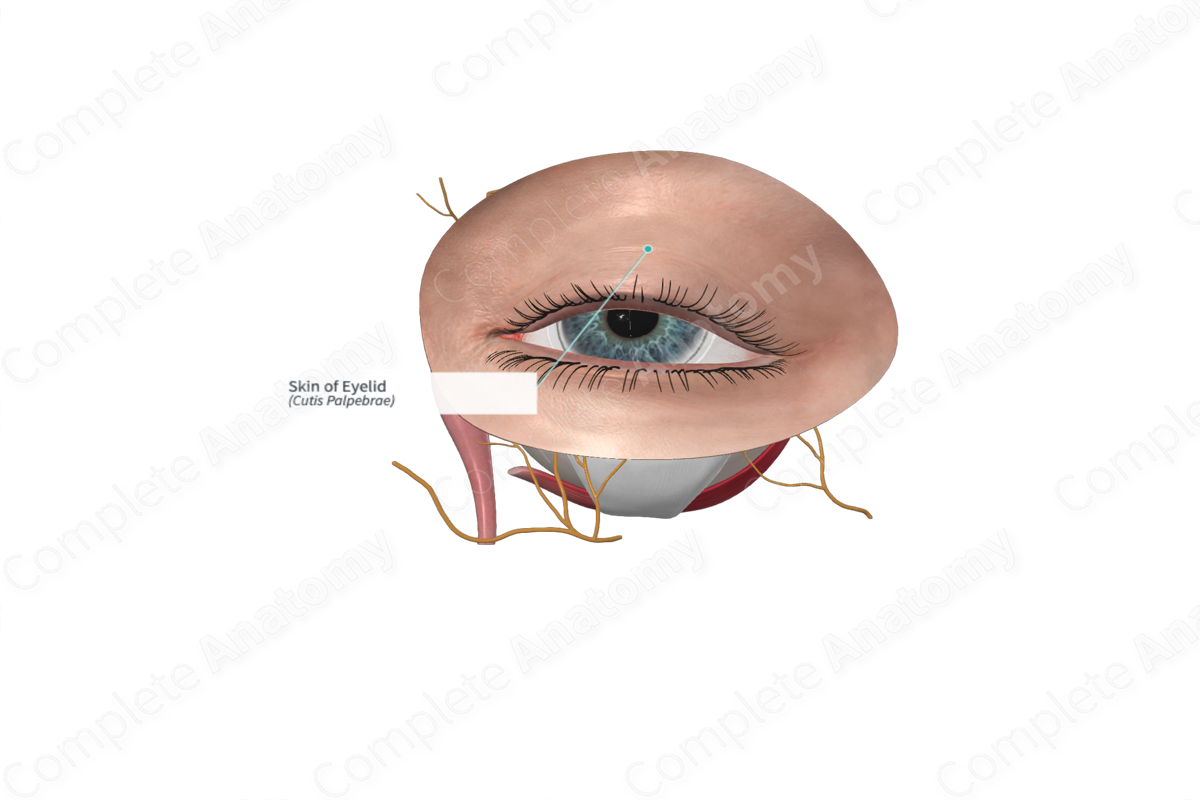
Accessory Eye Structures
• Eyebrows
• Eyelids and eyelashes
• The _____
• _____ apparatus
• Extrinsic eye muscles
Eyelids
palpebrae
_____
• Musculofibrous folds in the front of each eye
• Tarsal plate
• Muscles
– Orbicularis oculi (palpebral part)
– Levator _____ superioris
Conjunctiva
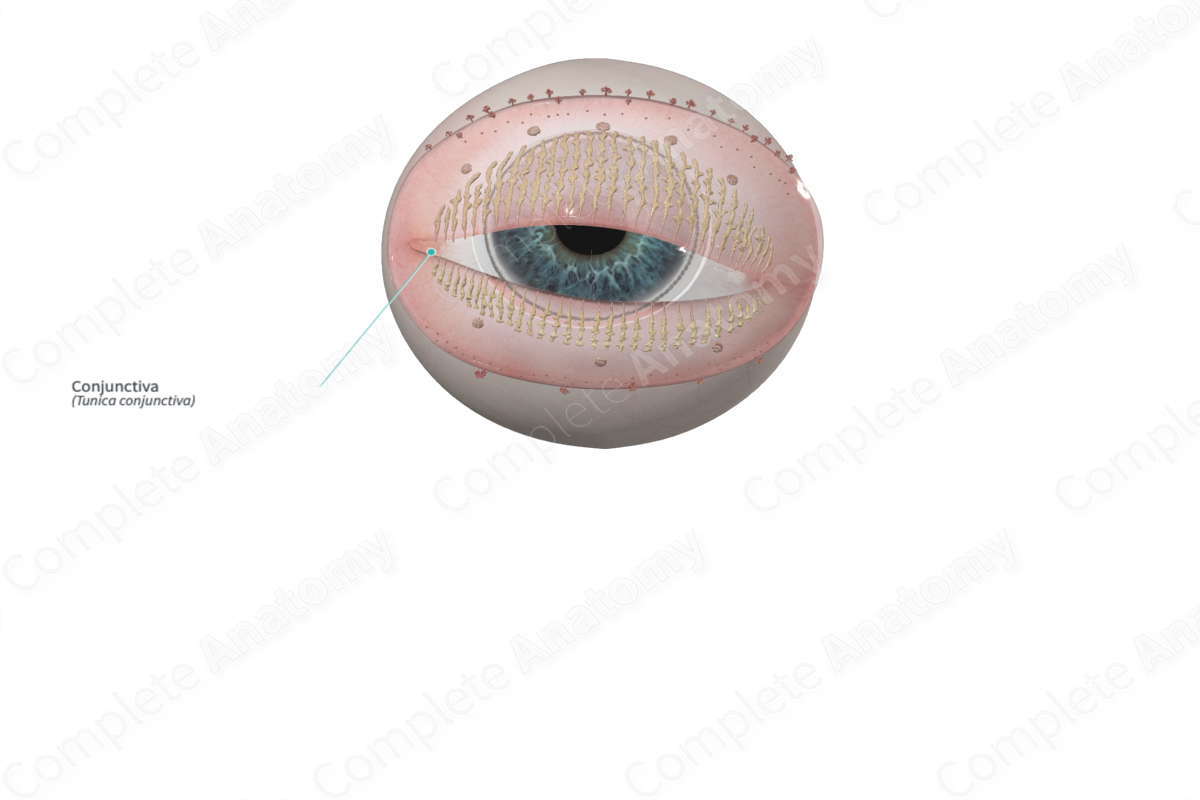
anterior
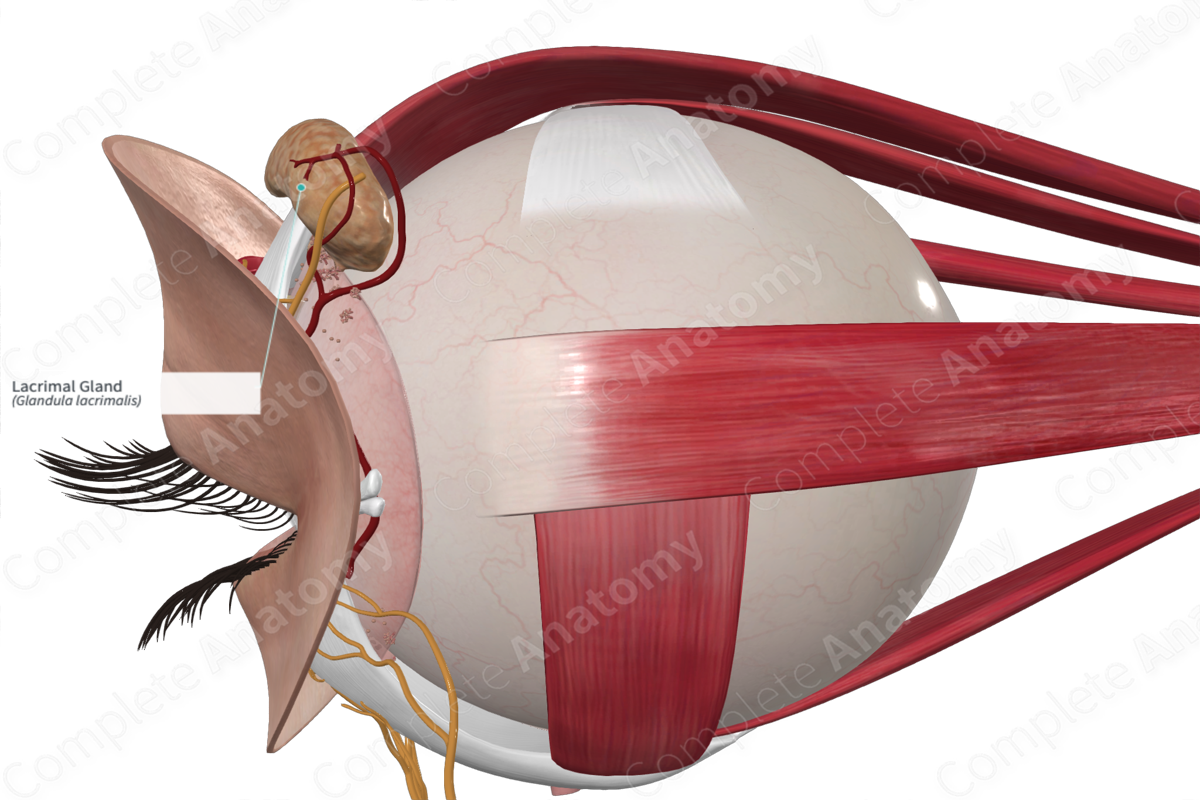
Lacrimal Apparatus
• Gland location - _____ superolateral corner of orbit
Lacrimal papillae
Small hillocks at the medial end of each eyelid
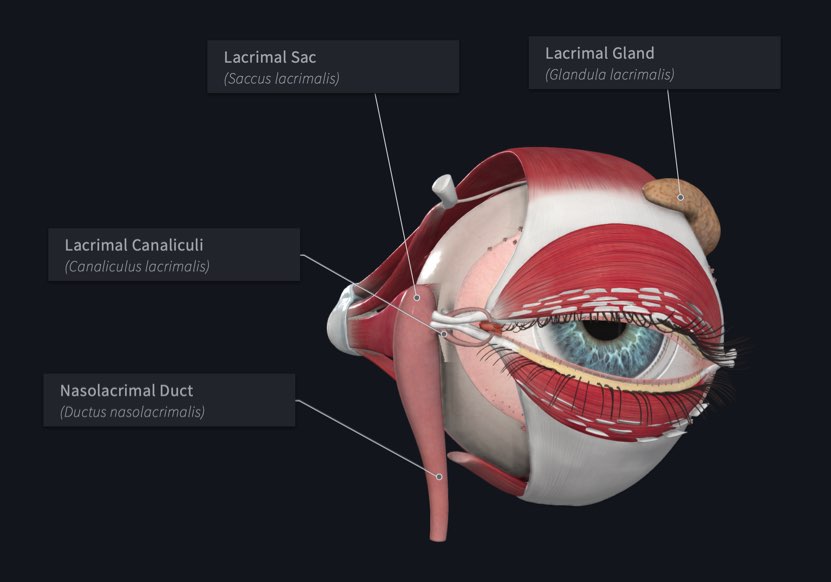
Lacrimal puncta
Openings of the lacrimal canaliculi at the apex of the lacrimal papillae
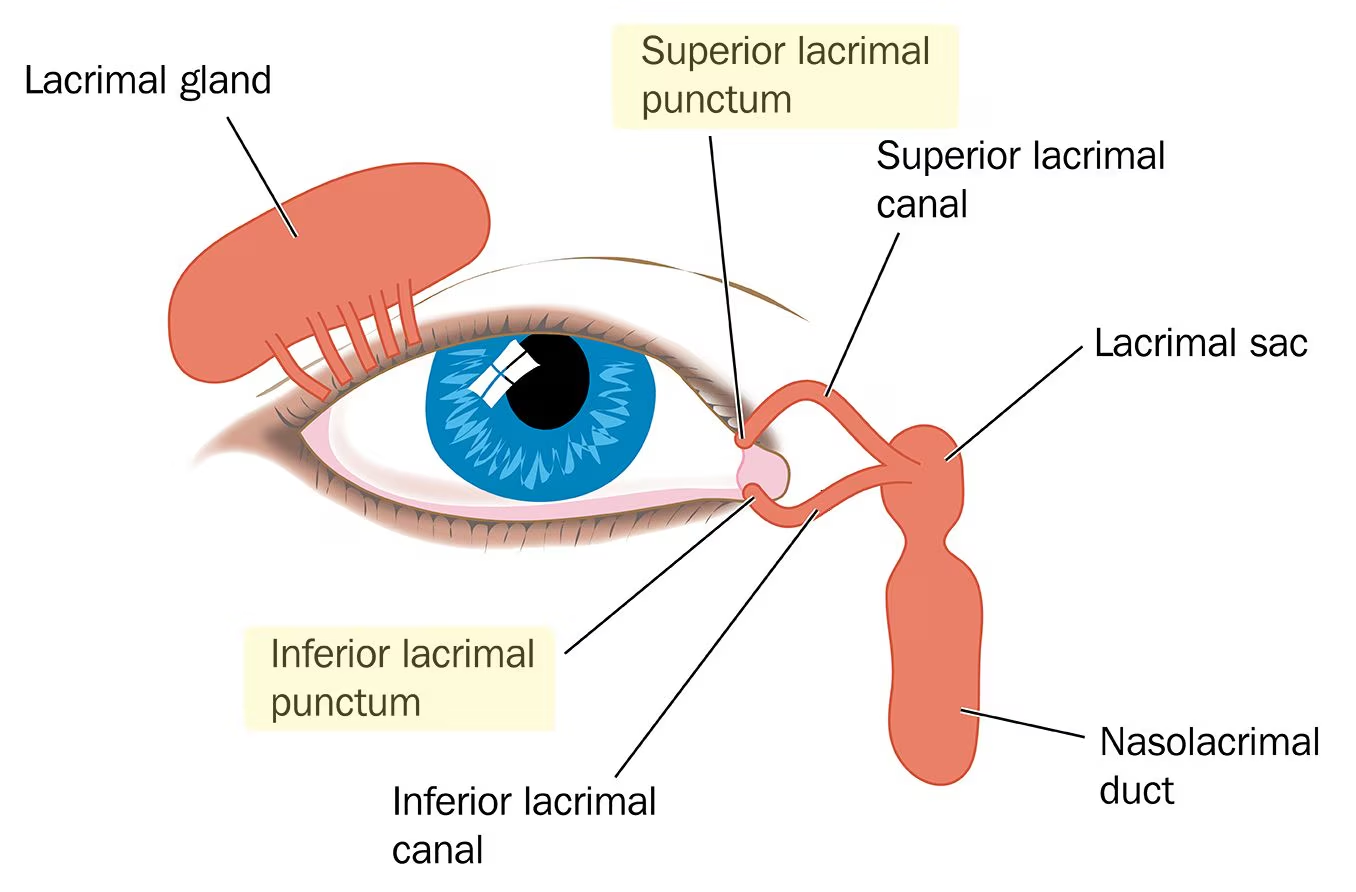
Lacrimal canaliculi
Small ducts that extend from lacrimal puncta to the lacrimal sac
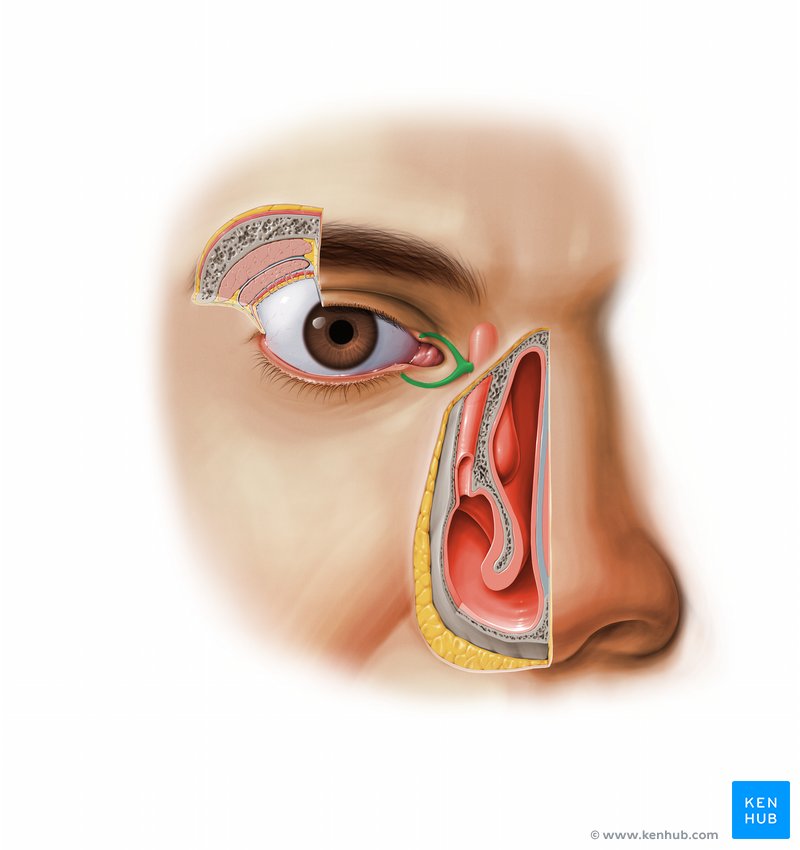
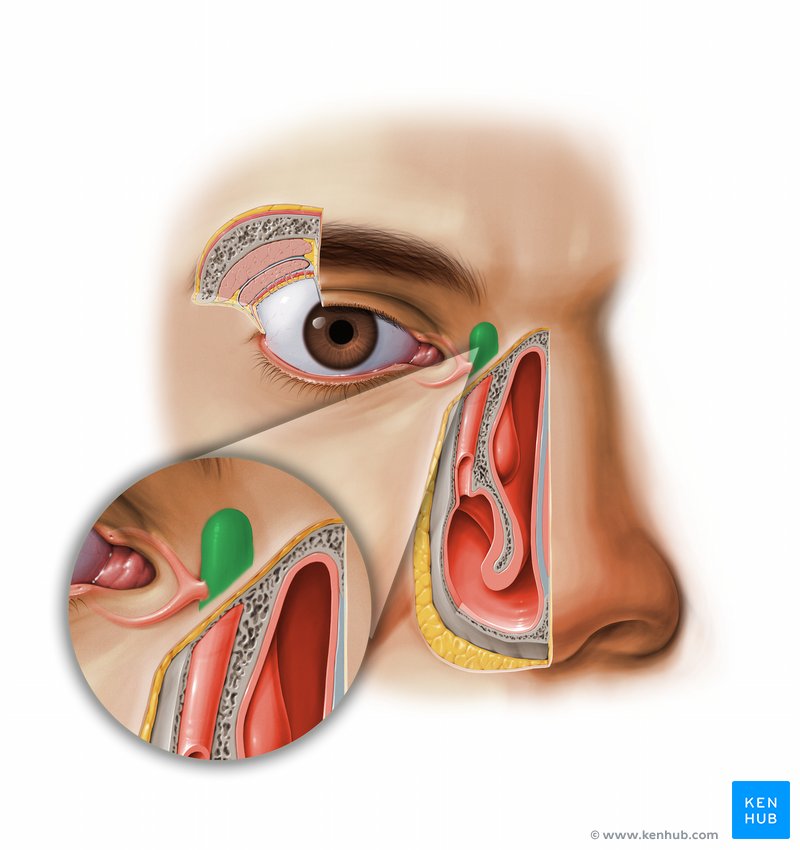
Lacrimal sac
Small sac-like structure at the anterior medial margin of the orbital floor
– It receives the lacrimal canaliculi
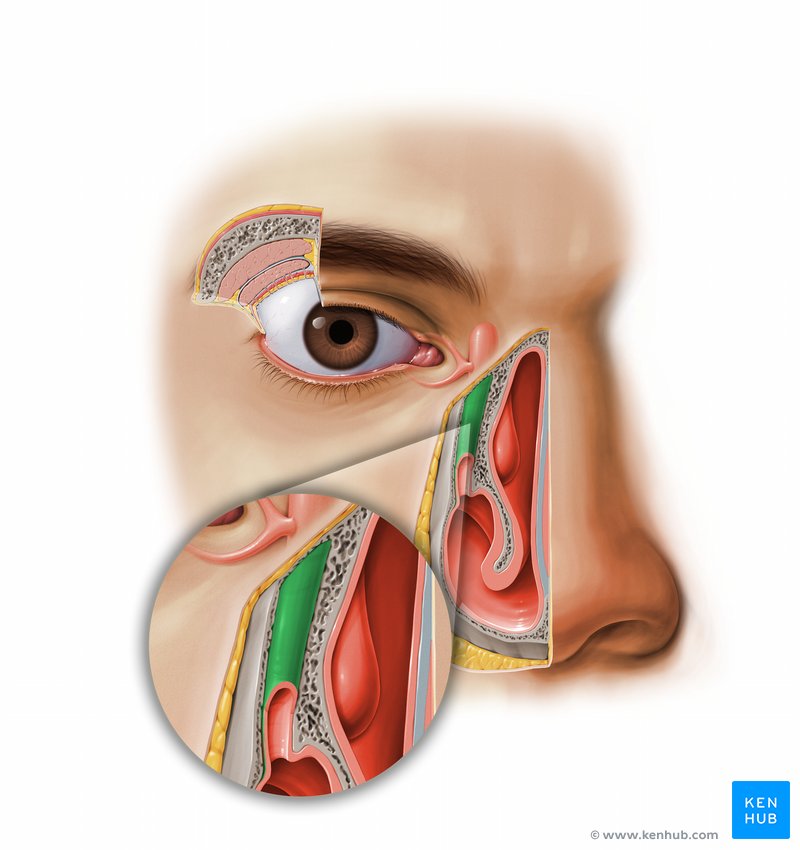
Nasolacrimal duct
Drains the lacrimal sac into the inferior meatus of the nasal cavity
uvea
retina
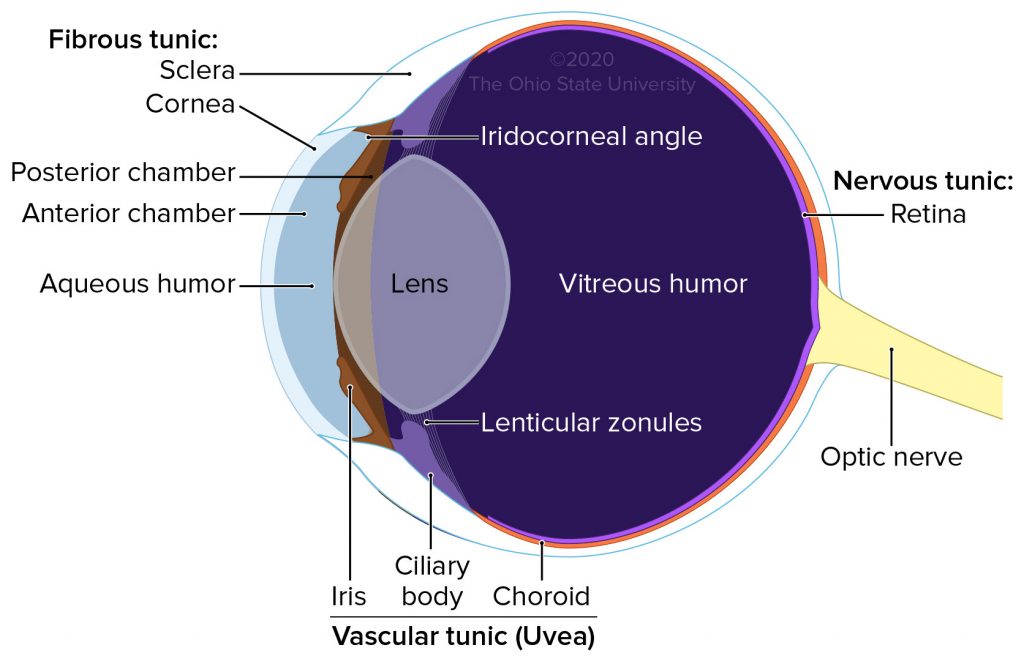
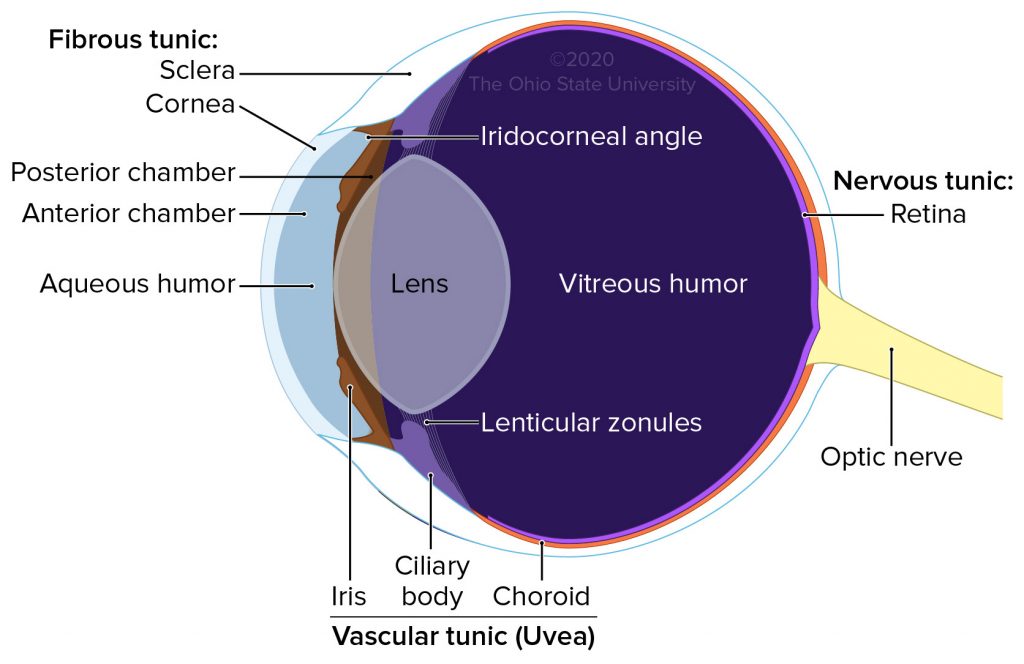
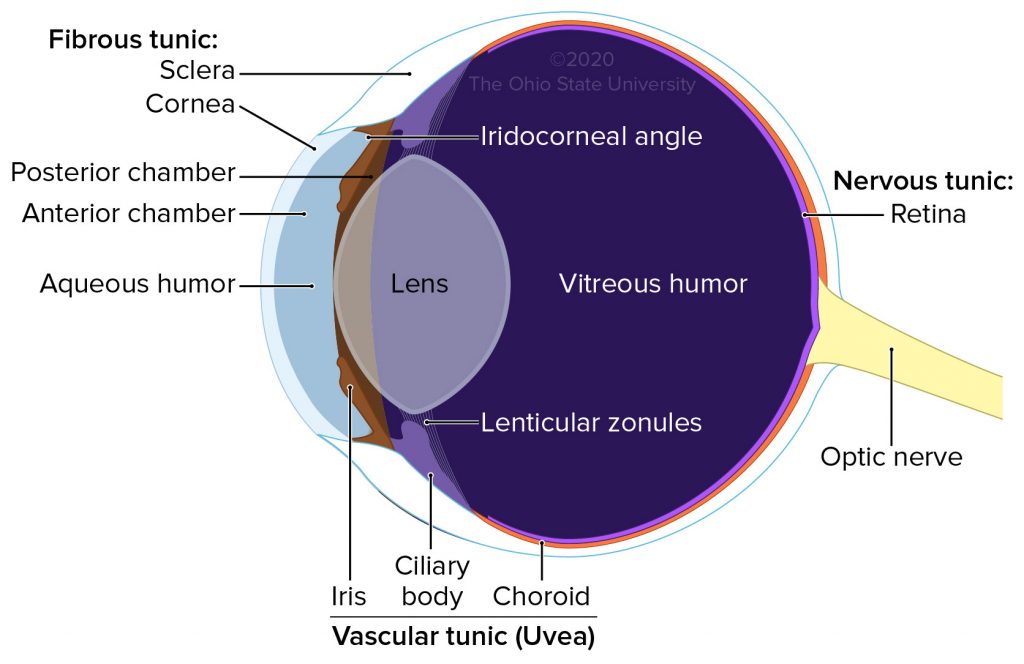
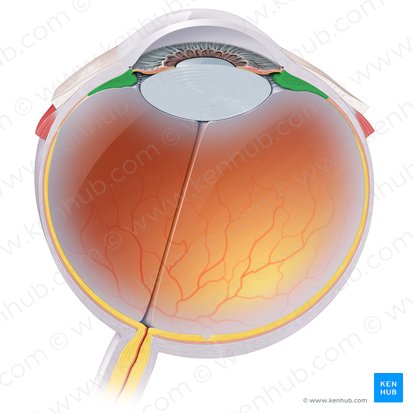
Eyeball
• Peripheral organ of vision
• Composed of three concentric layers of tissue which enclose the lens, vitreous body and aqueous humor
1. External fibrous tunic
2. Middle vascular tunic – _____
3. Internal nervous tunic - _____
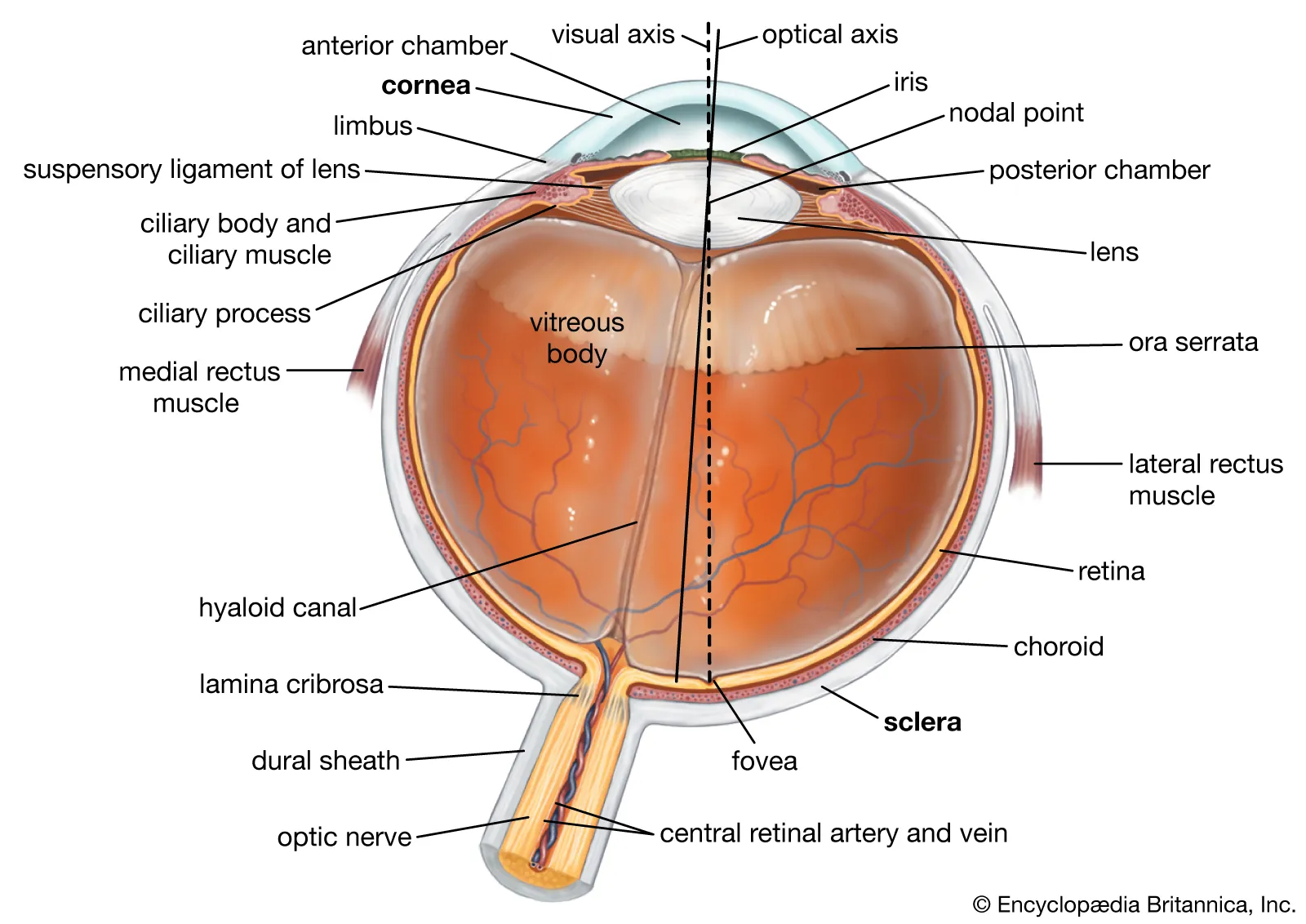
External fibrous tunic
Composed of cornea and sclera
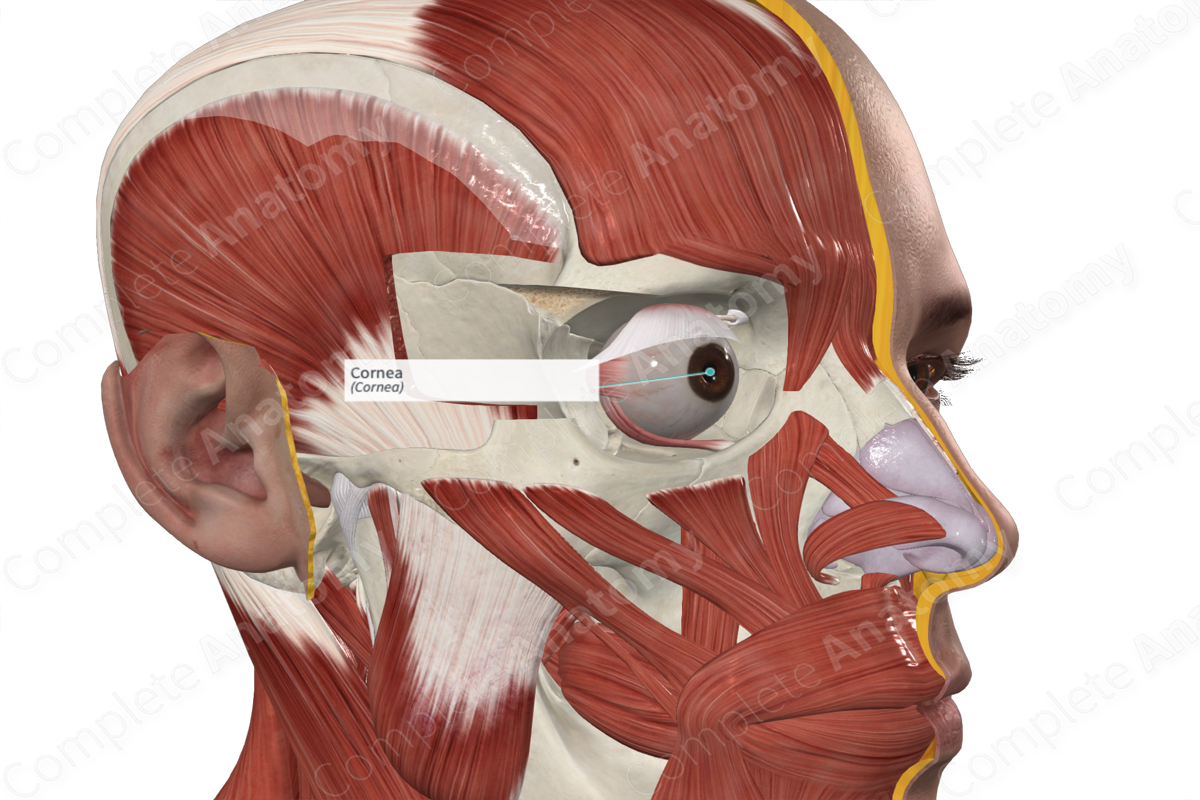
• Cornea
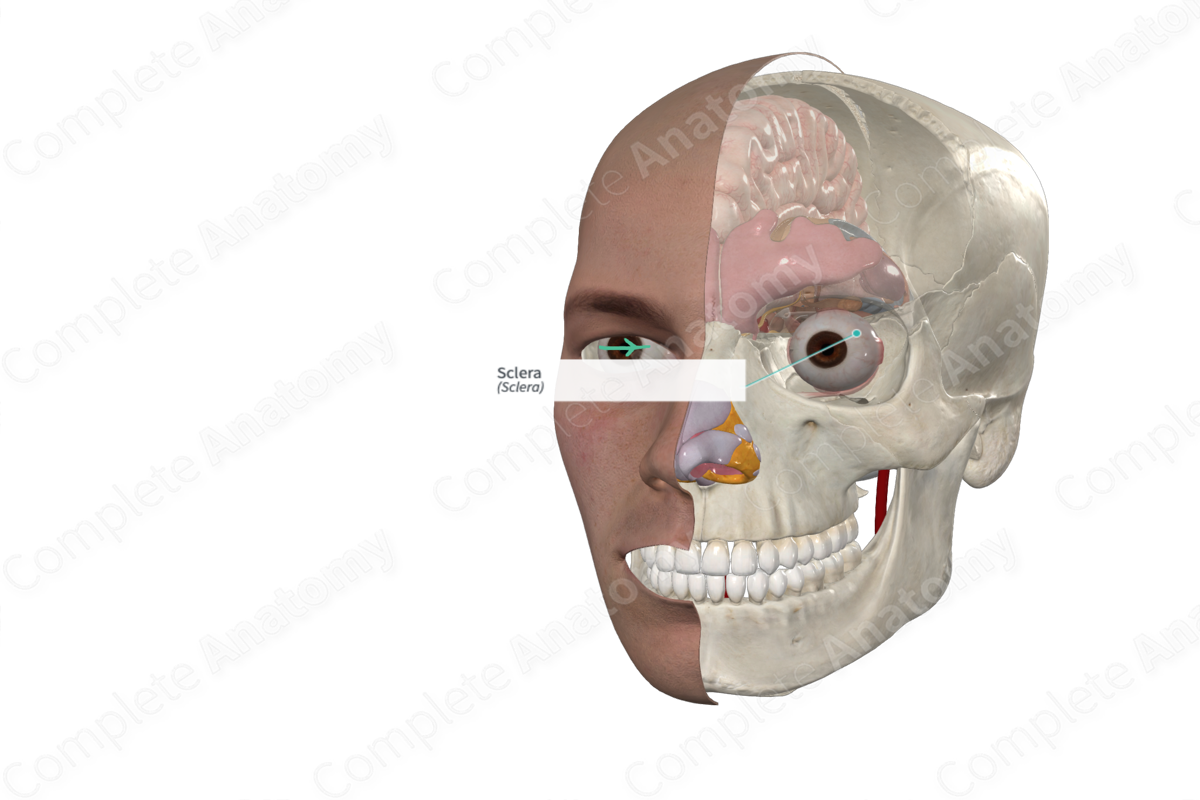
• Sclera
Cornea
Anterior transparent portion of the fibrous tunic, it is responsible for most of the light refraction that occurs in the eye
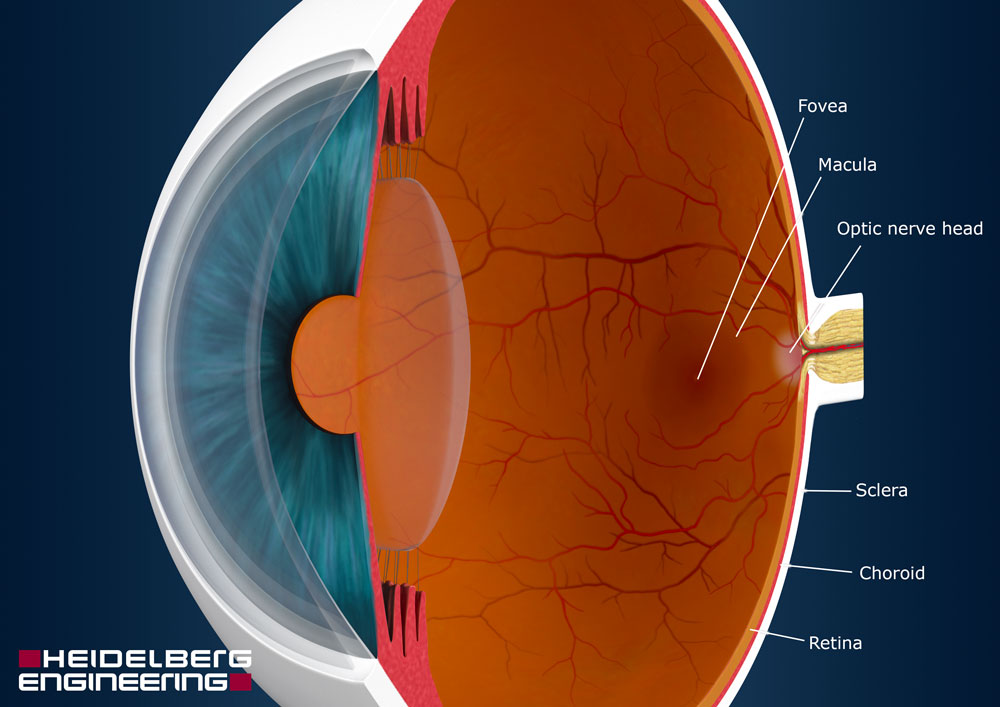
Sclera
Posterior opaque (white) part of the fibrous tunic. It receives the tendons of the muscles of the eyeball.
Middle vascular
_____ _____ Tunic - Uvea
• Choroid
• Ciliary body
• Iris
Choriod
Brown coat that lines the posterior two thirds of the sclera

Ciliary body
Thickening of the vascular tunic at the level of the corneoscleral junction
– Gives rise to ciliary processes, which produce aqueous humor and give attachment to the suspensory ligaments of the lens
– Contains the ciliary muscle, which is responsible for accommodation
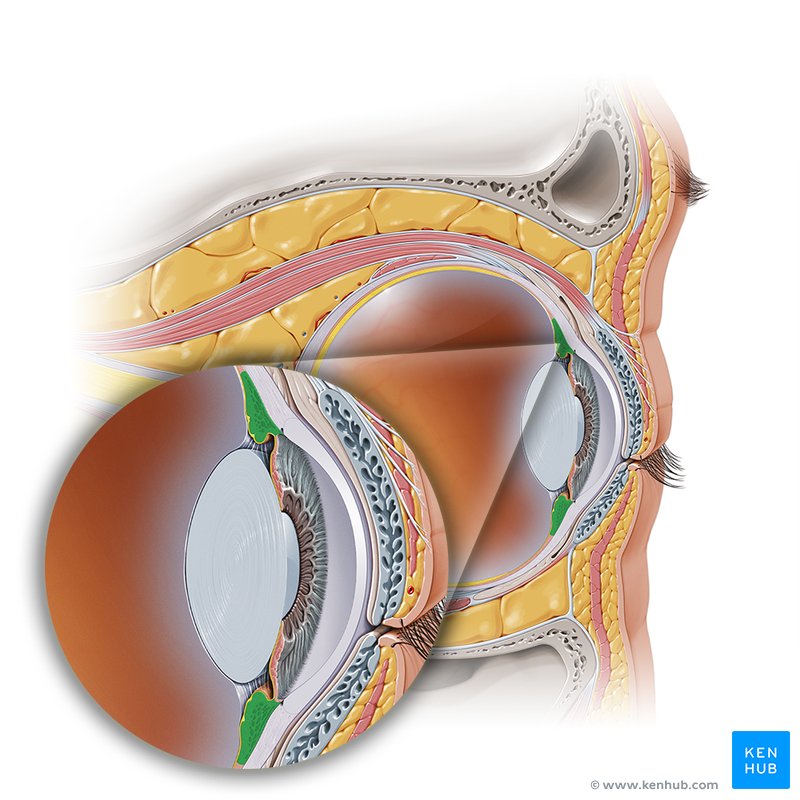
Iris
Divides the space between the cornea and lens into anterior and posterior aqueous chambers
– Pigment cells responsible for color
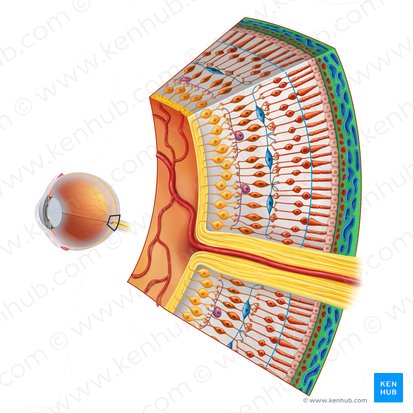
Internal nervous tunic
Innermost layer which contains special receptors cells upon which is projected an inverted image of objects seen
– Rods
– Cones
• Incomplete layer – posterior and lateral walls of inner eye only
Rod cells
Sensitive to light, crucial for low light conditions
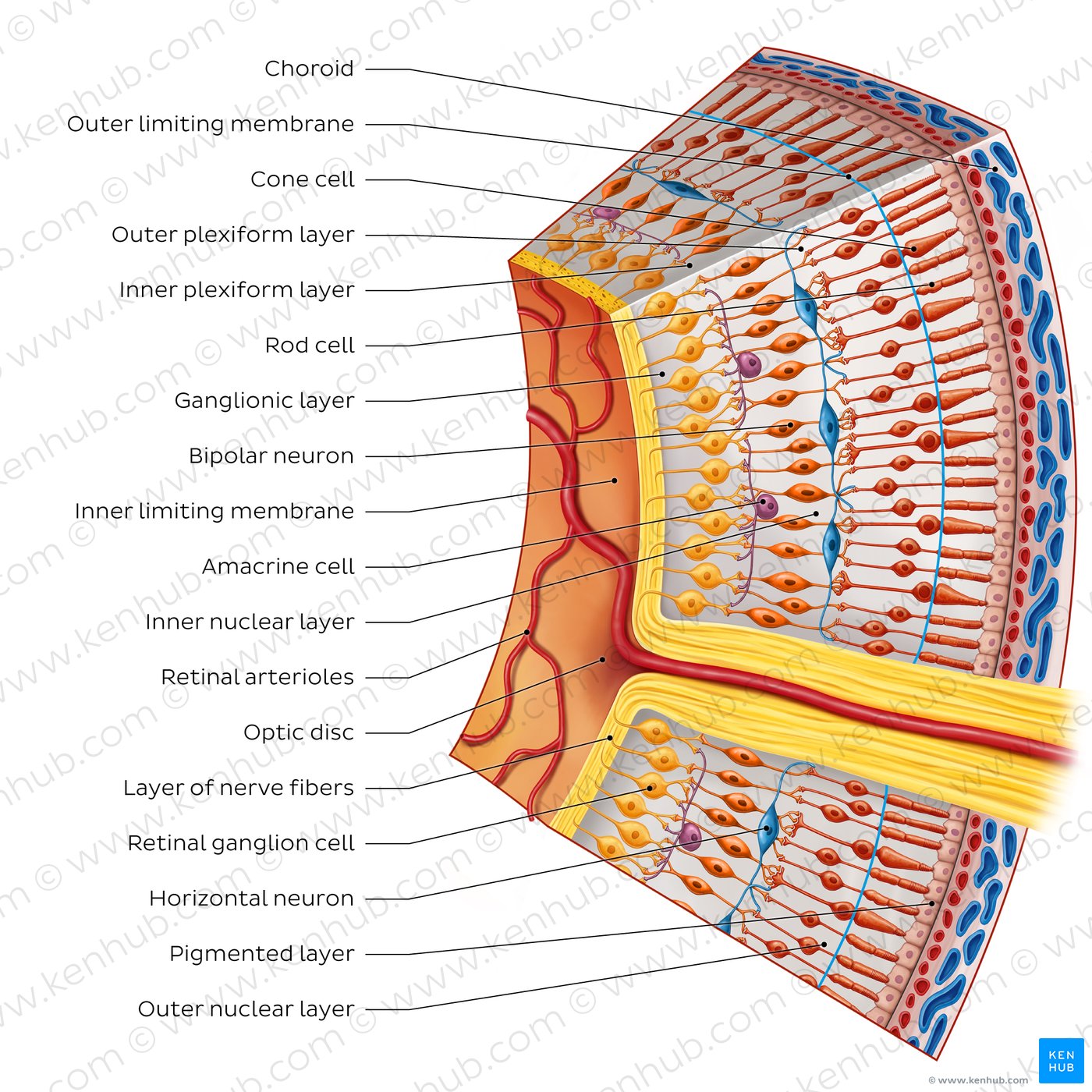
Cone cells
Enable color vision, crucial for detail
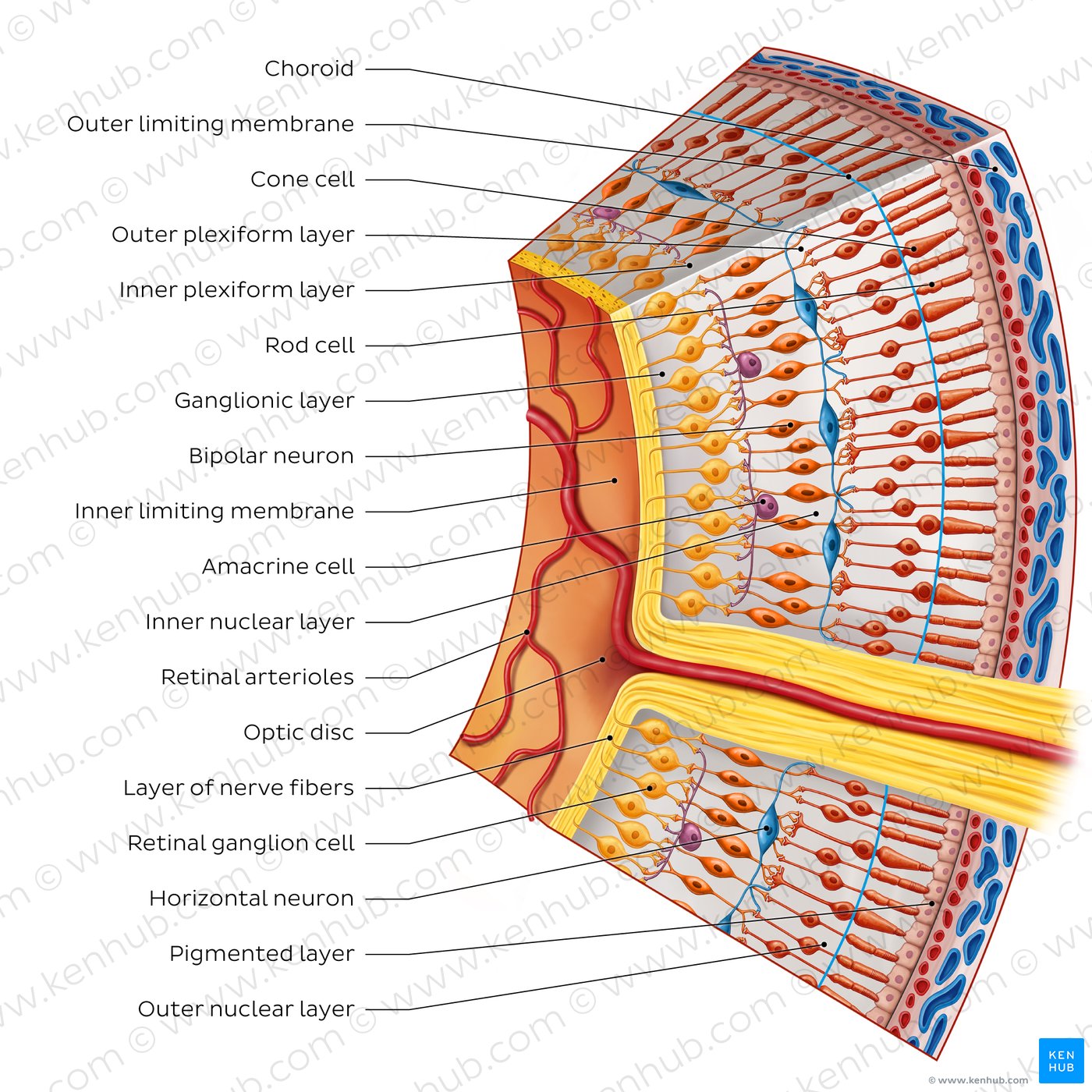
Retina
A light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye that plays a crucial role in vision
Lens
Transparent structure enclosed in a capsule and suspended between the posterior chamber and vitreous body by the ciliary zonules
Posterior chamber of eye
A narrow space located behind the iris and in front of the lens and its supporting structures
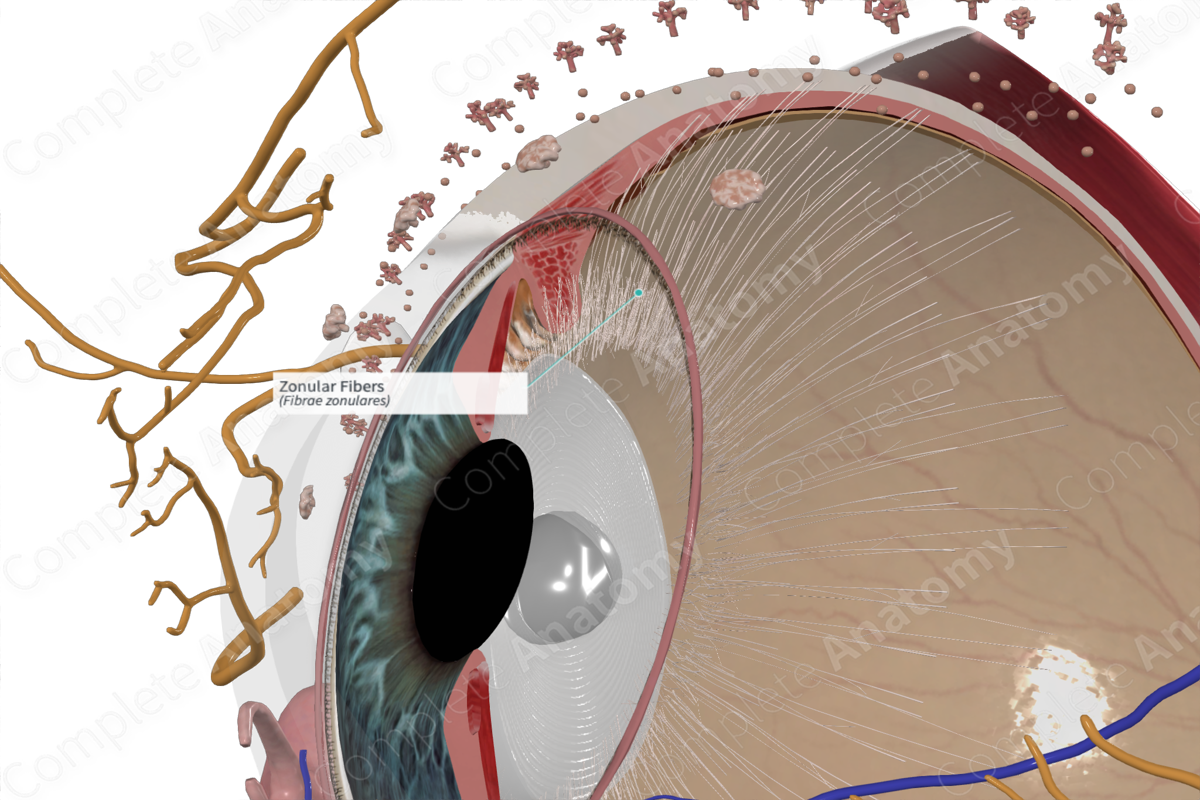
Zonular fibers
Tiny, thread-like fibers that act like suspensory ligaments, holding the lens of the eye in place and allowing it to change shape for focusing
Ciliary body
A ring-shaped structure in the eye, located behind the iris, that plays a crucial role in vision and eye health
Aqueous humor
Clear fluid produced by ciliary processes (in the posterior chamber)
– It passes through the pupil to the anterior chamber
– Produces nourishment for the cornea and lens
Vitreous humor
Clear fluid that fills the vitreous body (posterior to the lens)
Ophthalmic
facial
cavernous
Vascular Supply of Eye
• _____ artery from the internal carotid artery
• Venous drainage primarily to _____ vein and _____ sinus
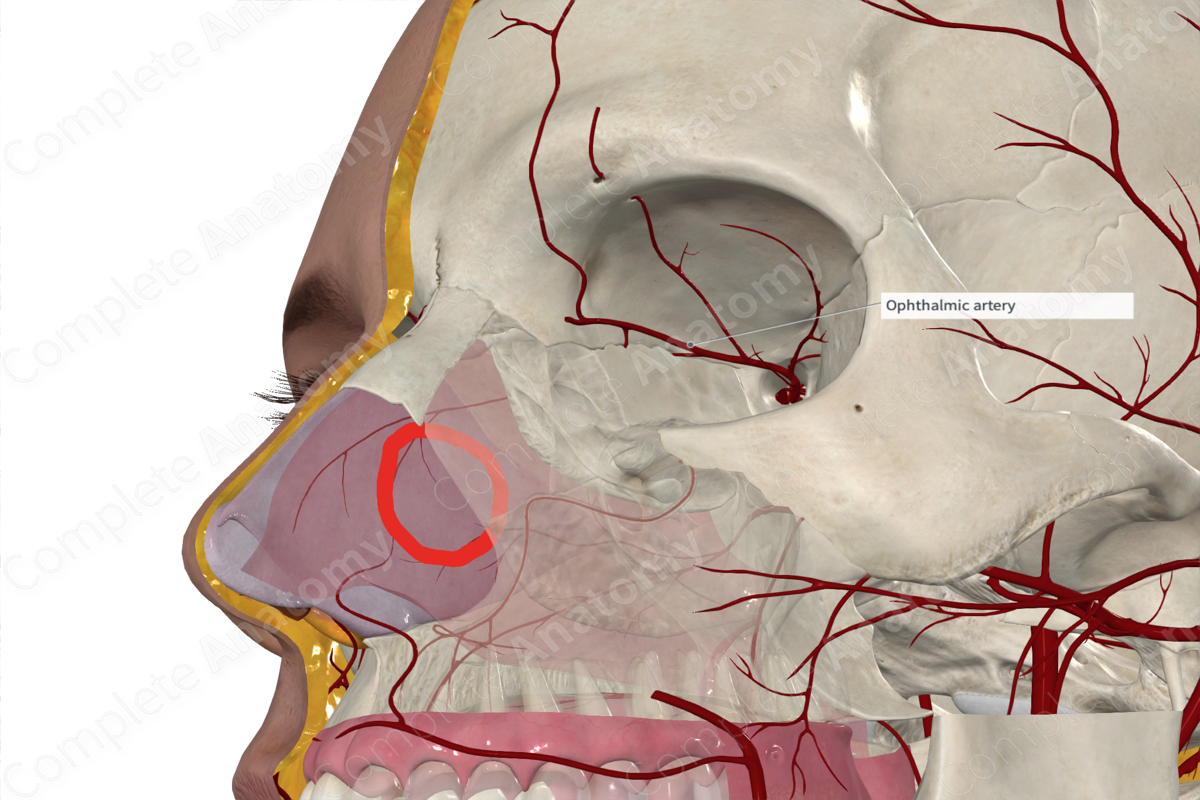
Opthalmic artery
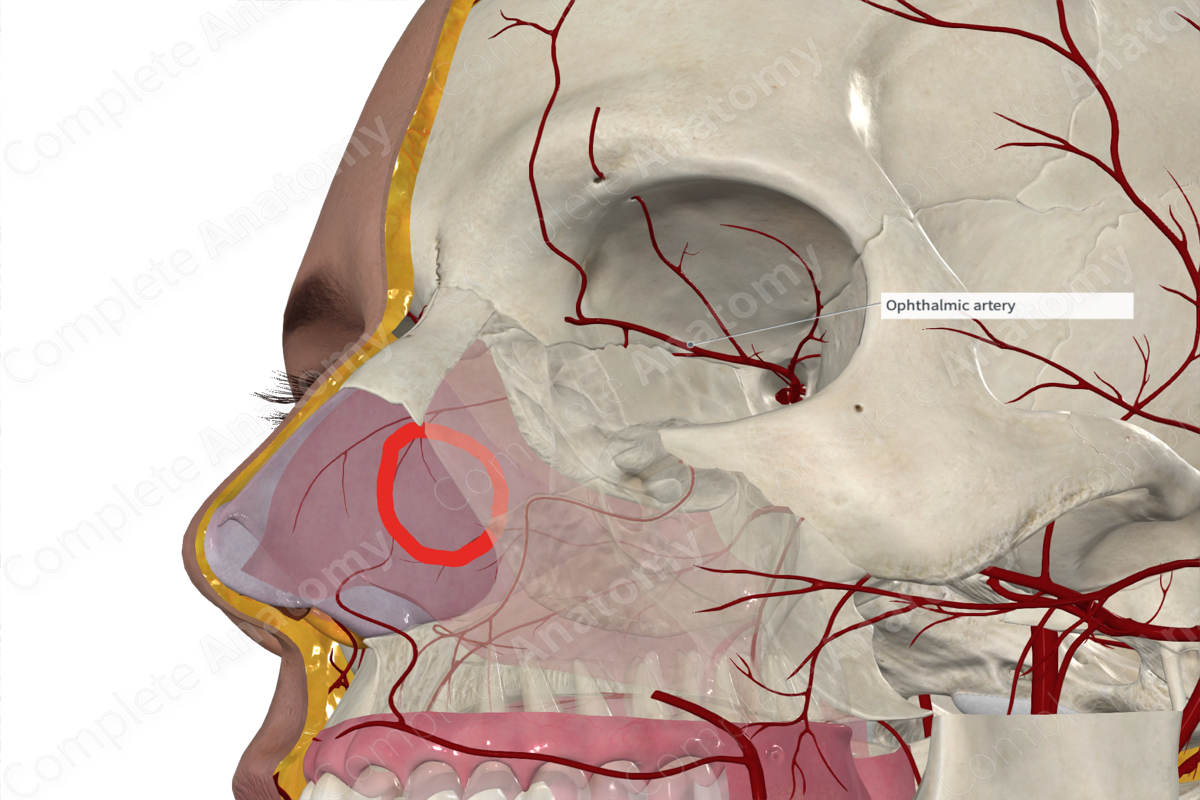
common tendinous ring
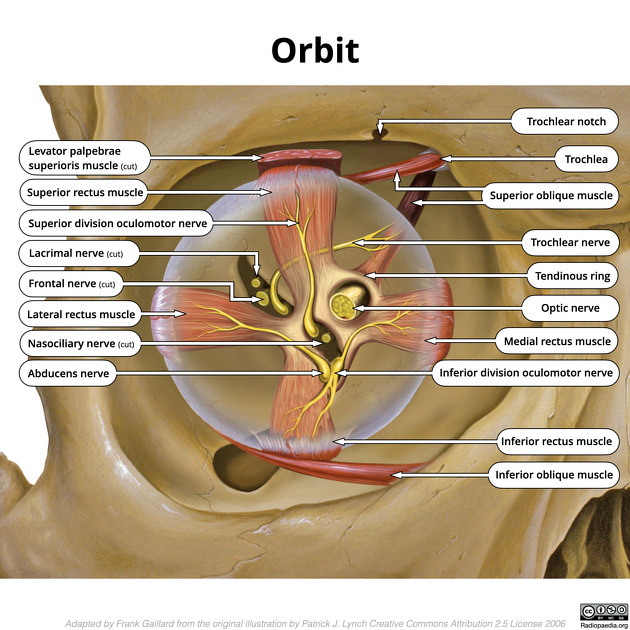
Extra-ocular Muscles
1-4. Rectus muscles
– Superior (CN III)
– Inferior (CN III)
– Medial (CN III)
– Lateral (CN VI)
– All 4 muscles originate from a ___ ___ ___ that surrounds the optic canal and superior orbital fissure.
– They then extend anteriorly to insert into the anterior portion of the sclera.
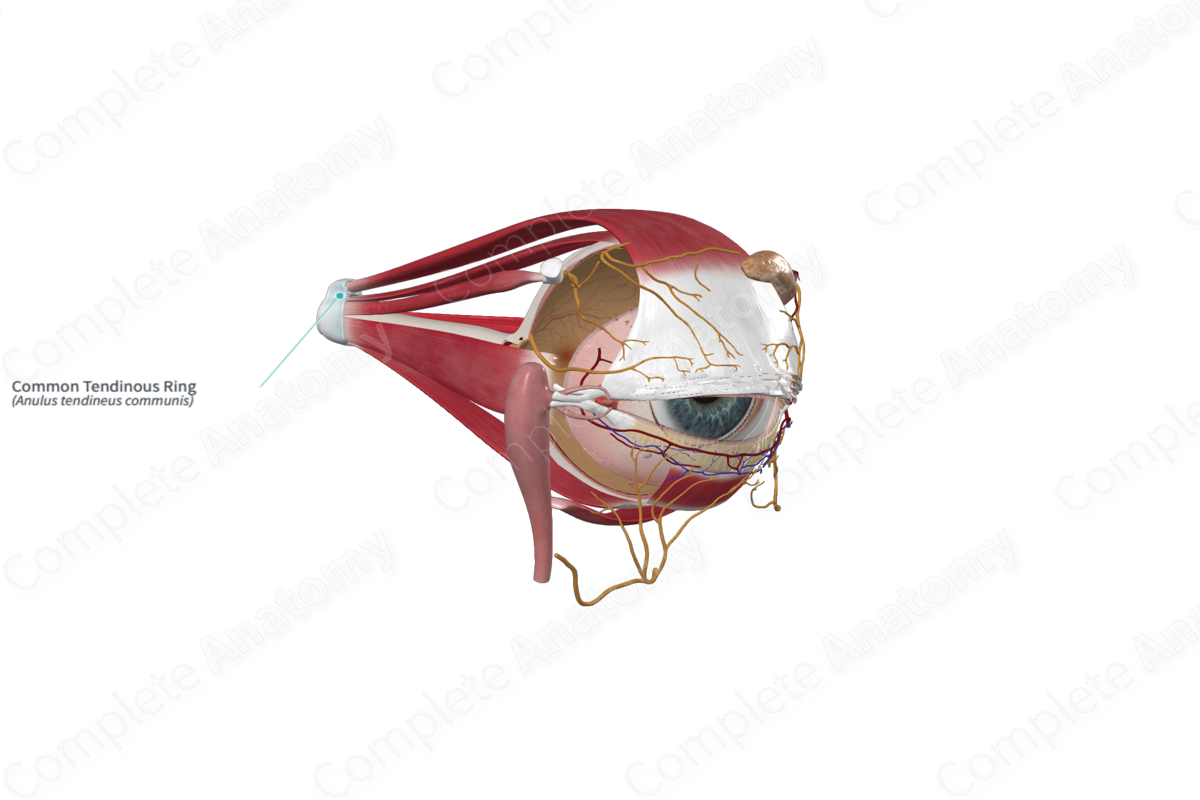
sphenoid, trochlea, Trochlear
oculomotor
Extra-ocular Muscles
5. Superior oblique
– Originates from _____ bone, passes through the _____ (cartilaginous sling) and inserts on the posteriorlateral aspect of the sclera
– innervation – T_____ n. – CN IV
6. Inferior oblique
– Originates from the anteromedial aspect of the floor of the orbit and inserts into the posterolateral aspect of the sclera
– innervation – O_____ n. – CN III
Optic
Opthalmic
Sensory Nerves of the Orbit
• _____ (CN II)
• _____ nerve (CN V1)
Macula lutea
Back of retina, place of highest visual acuity
Optic disc
No rods or cons, resulting in a “blind spot”
Bulbar conjunctiva
The transparent mucous membrane that covers the sclera and extends to the edge of the cornea
Vitreous body
Largest chamber in eye containing fluid
Hemianopsia
A visual field defect where half of the visual field is lost in one or both eyes