CHEM 203: Thermodynamics Part 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:55 PM on 12/5/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
* heat always moves from hotter objects to cooler objects, unless energy is supplied to cause the reverse to occur
* for any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe must always increase
* for any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe must always increase
2
New cards
What is a spontaneous process?
a process that occurs on its own (does not refer to the rate of reaction)
3
New cards
What determines the direction of a spontaneous process?
the ^^entropy^^ change
4
New cards
What is entropy?
the dispersal of matter and energy (sometimes defined as a measure of the “disorder”)
5
New cards
At equilibrium entropy of the universe must be ___________,__ and change in entropy of the universe must be ___.
* at a maximum
* 0
* 0
6
New cards
Entropy is a _______ function and is _____________,__ meaning that it depends on _________________.
* state
* extensive
* the amount of substance
* extensive
* the amount of substance
7
New cards
What is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
For any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe must always increase (change always occurs in the direction of maximal probability).
8
New cards
How does volume change of a gas affect entropy?
entropy increases with volume because there are more possible positions for each particle (disorder increases)
9
New cards
How does temperature change affect entropy?
entropy increases with temperature because there are more possible energies for each particle (disorder increases)
10
New cards
Since S increases with T, this implies that in an exothermic reaction heat flows ________ of the system and the entropy of the surroundings _____________.
* out
* increases
* increases
11
New cards
In which phase is entropy the lowest? In which phase is entropy the highest?
* lowest → solid (most ordered)
* highest → gas (most disordered)
* highest → gas (most disordered)
12
New cards
How does mixing of gases affect entropy?
gases always mix, so entropy will always increase with mixing
13
New cards
How does number of moles affect entropy?
increasing the number of moles increases entropy
14
New cards
What is the 3rd law of thermodynamics?
The entropy of a perfect crystalline solid at 0 K is defined to be 0 J/K
15
New cards
What is standard entropy?
The entropy of 1 mole of a substance at standard state conditions
16
New cards
At constant temperature and pressure, delta G equals?
delta G = delta H - T \* delta S
17
New cards
If delta G is negative, the forward process is ____________
spontaneous
18
New cards
If delta G is positive, the forward process is _____________
non-spontaneous
19
New cards
If delta G is 0, the process is _____________
at equilibrium
20
New cards
What does delta G represent?
the maximum energy available to do work
21
New cards
A system at equilibrium can do no ________
work
22
New cards
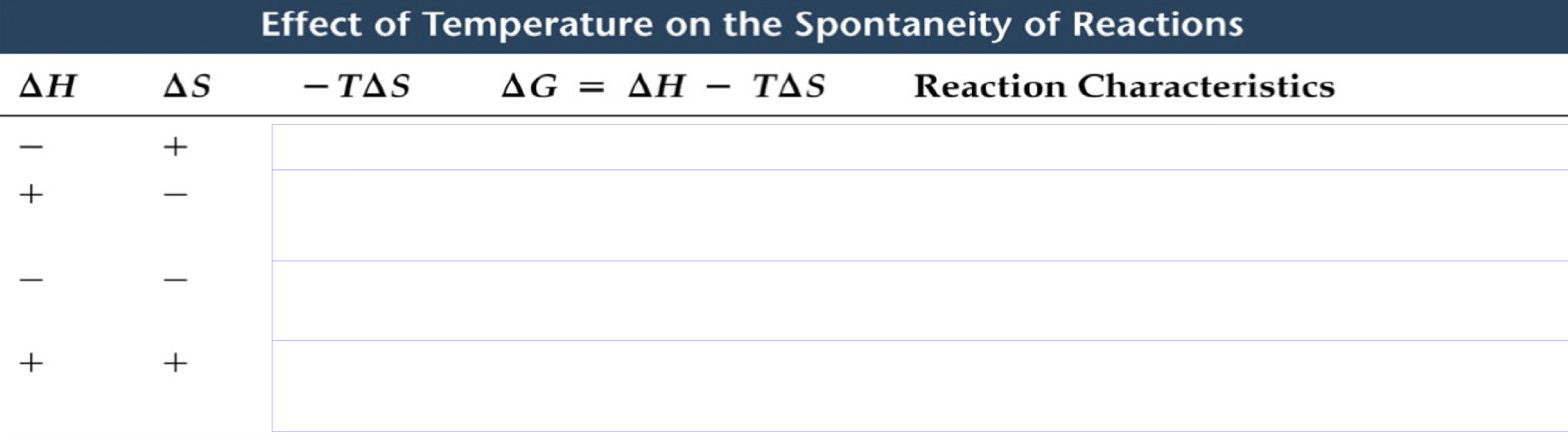
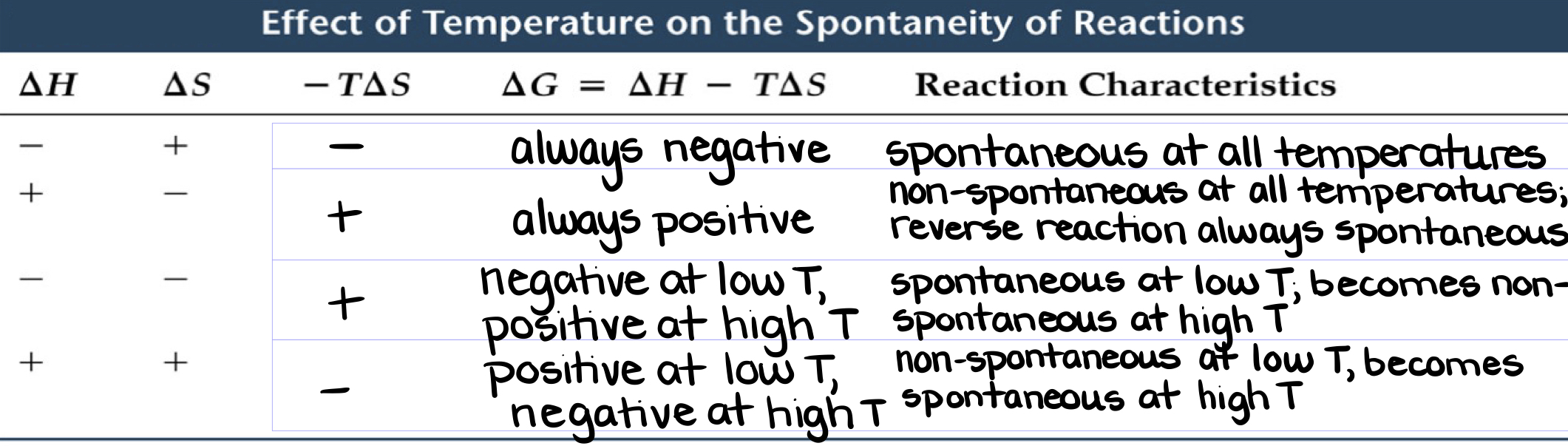
Fill out this table
23
New cards
What does exergonic mean? What does endergonic mean?
* exergonic → -delta G
* endergonic → +delta G
* endergonic → +delta G
24
New cards
For a system **at** **equilibrium** at constant temperature and pressure delta G equals ____
0
25
New cards
What are standard free energies of formation?
the value for the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the most stable forms of its elements
26
New cards
At **standard state conditions**, if free energy change is less than 0, K is ____________
greater than 1
27
New cards
At **standard state** conditions, if free energy change is greater than 0, K is ___________
less than 1
28
New cards
At **non-standard state** conditions, if free energy change is less than 0, then Q is ________ than K and the reaction is ______________
* less
* spontaneous
* spontaneous
29
New cards
At **non-standard state** conditions, if free energy change is greater than 0, then Q is ________ than K and the reaction is ______________
* greater
* non-spontaneous
* non-spontaneous