digital design computer basics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
what is the computer divided up into?
input and output devices
what is input
things that send info into your computer
what is output
things where info is coming out from your computer
what are examples of input devices?
mouse, microphone and webcam
what are examples of output devices?
the monitor, little printer, and speakers
what is the outershell of the computer?
a case and its primary function is to keep the inside of the motherboard/computer nice and safe from the things that are on the outside
what are some facts about the outershell?
it was vents on the front and back of the motherboad that keeps the system cool
what is power supply?
take power from the electrical outlet and spread it out all over your computer system and gives power to all individual parts
expansion slots
allows to connect peripheral video cards
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
comes in hertz, always processing info; the brains of the computer which oversees all of its functions
what 2 companies make CPUS
AMD and Intel
heat sink
helps keep your cpu cool
What is a fact about RAM?
the more storage capacity your RAM has the more things you can do at the same time: multitask
what is the graphic card
converts image data to a form that can be viewed on a monitor
CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)
acts as an internal battery to ensure info is still stored when the computer is turned off; for BIOS battery: retains your date, time and vial settings
fan
cools the internal components
hard disk
primary storage medium for most programs and documents
IDE (integrated drive electronics controller)
interfaces the hard drive, floppy disk drive and CD-ROM
motherboard
main circuit board which all other components are connected
ports
interfaces for additional components
RAM (random access memory)
allows quick access to recently viewed data
ROM (read only memory)
fireware used in almost all Electonics
BIOS (asic input output system)
stores info when your computer is turned off
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
high speed connection from graphics card to computer
OS (operating system)
not really a hardware but software which allows basic functioning of the computer
real time clock
synchronize all computer components
whats on the right side of the motherboard?
there are 6 serial ATA or SATA ports on the board. It connects hard drive/cd-rom or dvd-rom drives
red e serial ata
designated for hooking up external drives
pin configurations
used for USB cables and most of the time it comes with ribbon cables
speaker
used to give you notifications from the BIOS: also tells you if there is problems
IDE controller
for older style hard drives or cd rom drives
jumper
works in conjunction with your battery and BIOS
16 x pci express slot
used by graphic card
dual channel ddr2 memory
supports up to 800
what does power LED and hard drive LED have in common
they have a polarity, so you have to get those right or LEDs in front of the case so they dont show up or turn on
what is a bit
comes from binary digit 0 or 1 and it is located by the letter B and its always capitalized
what is bits for seconds
indicates the rate on which info can be transferred
what is a byte
groups of 8 bits and provide a more readable representation of data such as character encoding schemes
what is an example of a byte
ASCII or Unicode
what is bytes for
reading and writing data
how to view different sizes of icons on the computer
this pc/view/icons
list some examples of the different types of icon sizes
extra large icons, large icons, medium icons and small icons
what are some different ways to format the files
list, details, tiles and content
what are some different ways of sorting the files
name, type and total size
how to open downloads
this pc/downloads
what is in the control panel
system and security, network and internet, hardware and sound, programs, user accounts, appearance, clock and region and ease access

what is this
graphic card
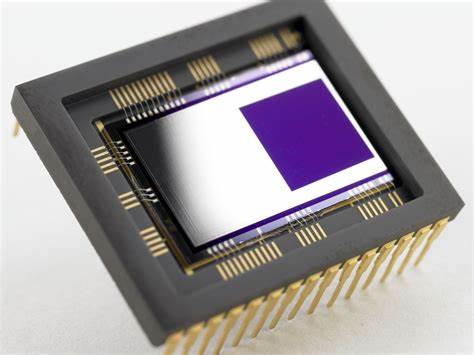
what is this
CMOS
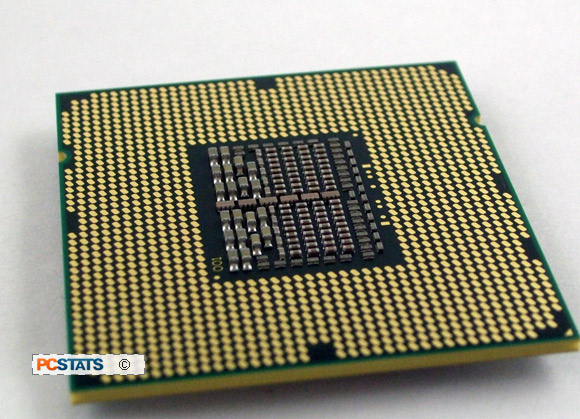

what is this
CPU
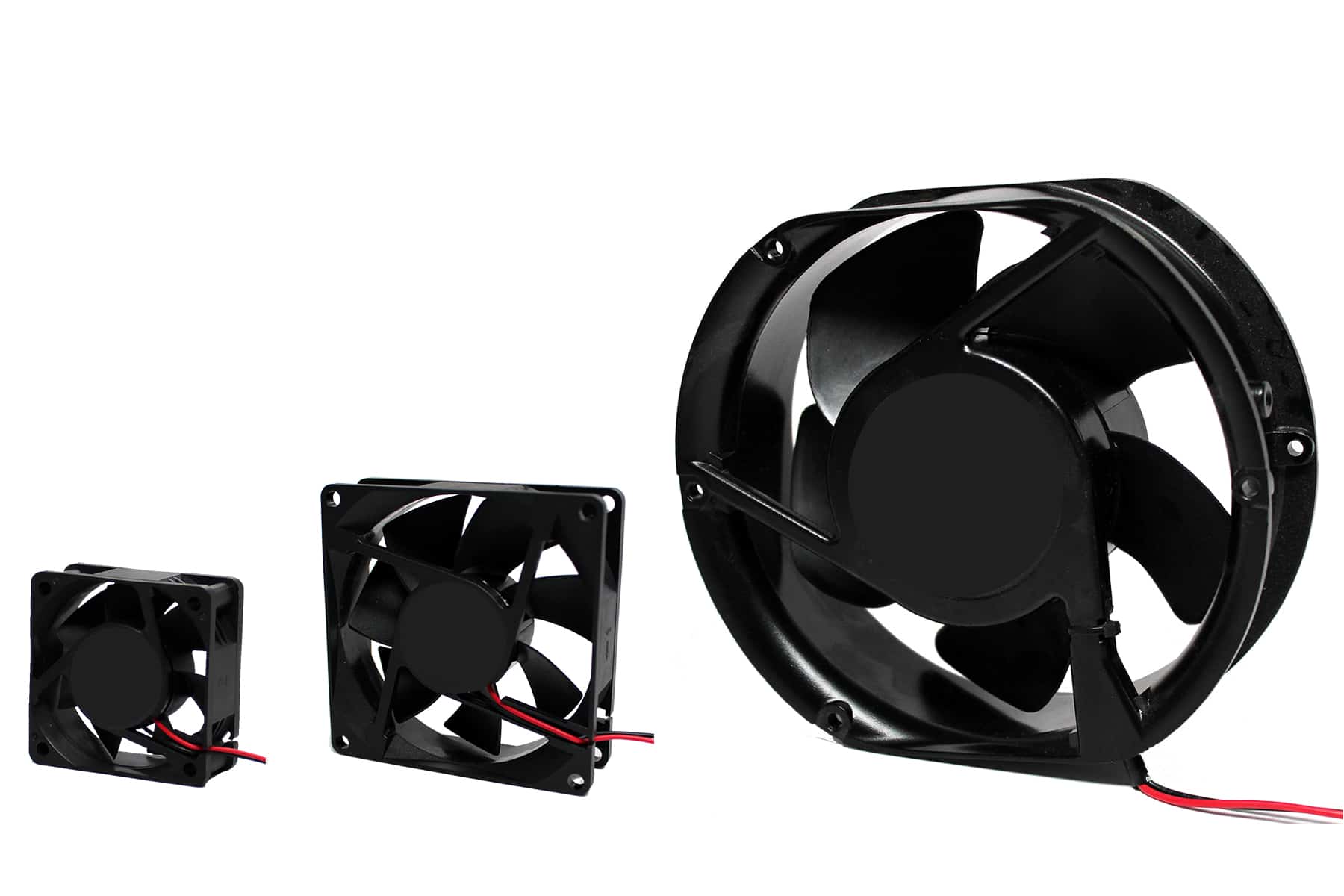

what is this
Fan
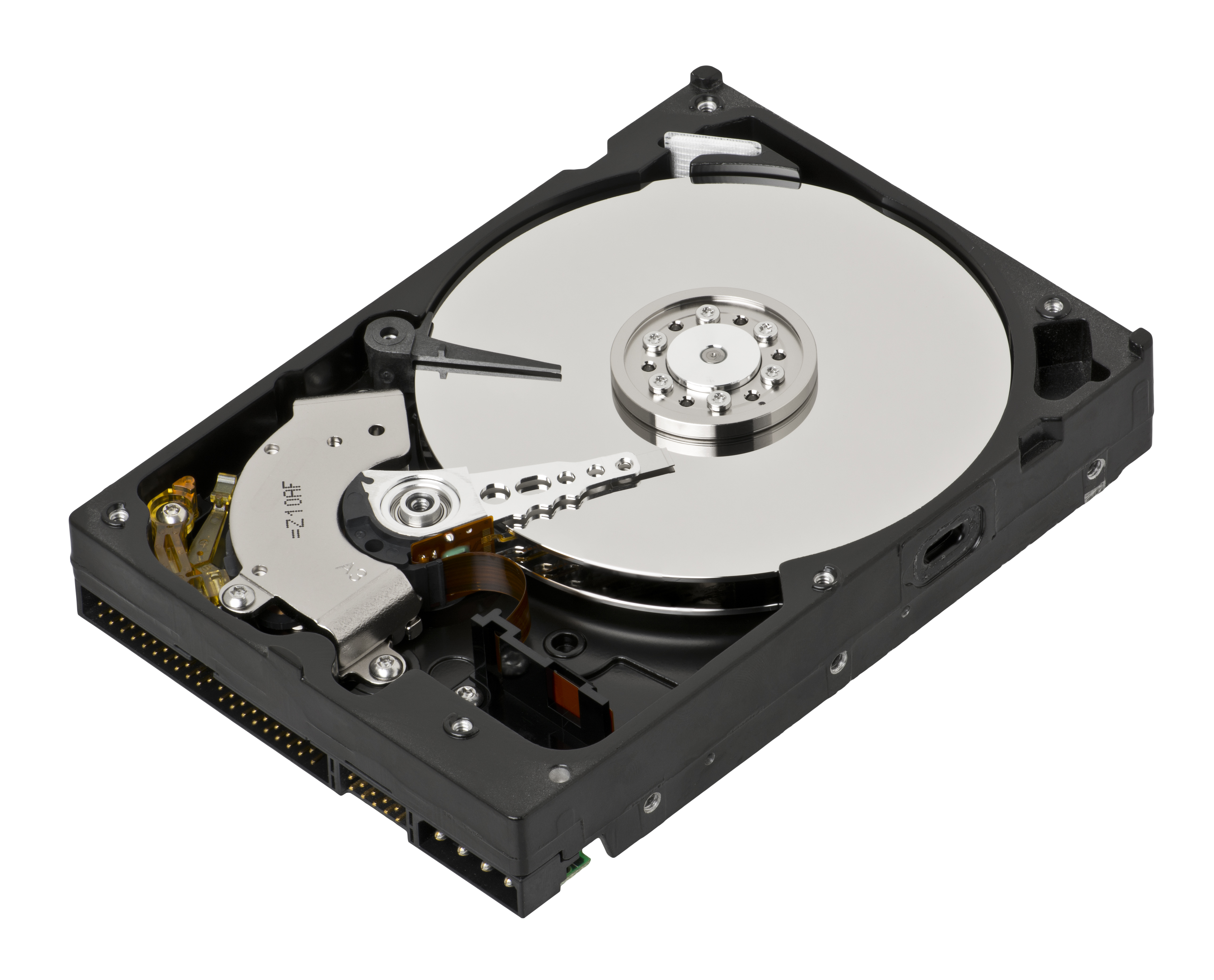

what is this
hard disk
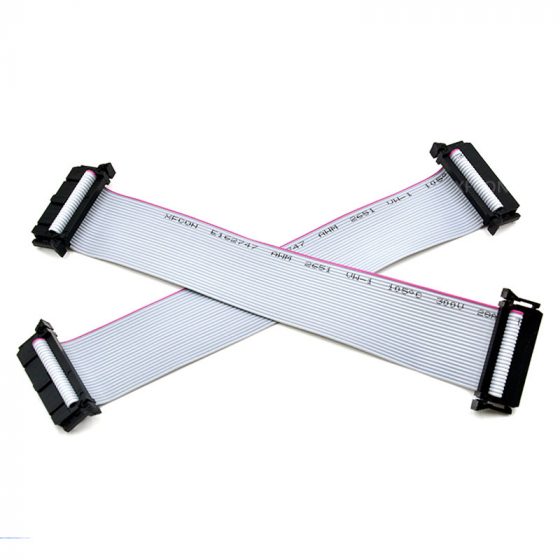

what is this
IDE
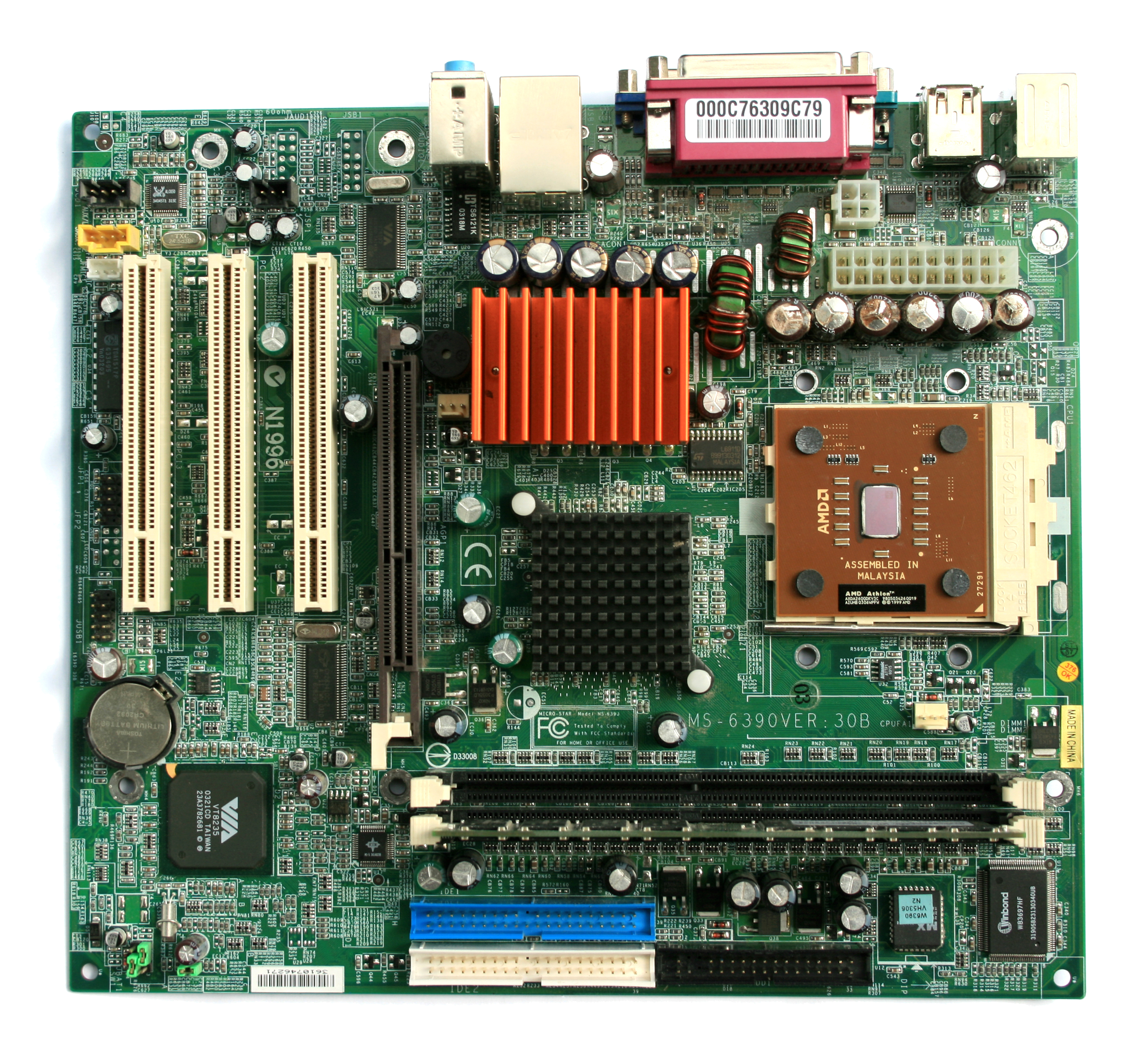

what is this
motherboard
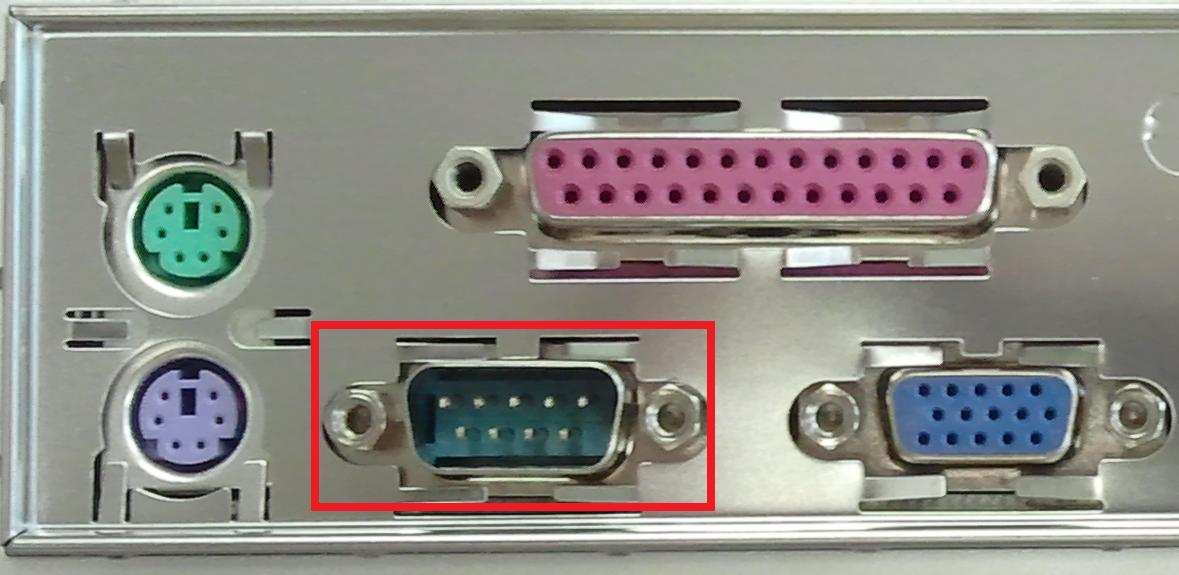
what is this
ports

what is this
power supply

what is this
RAM

what is this
sound card
what are the 3 ways to eject a USB/ memory stick
my pc/c diskc/manage/eject, click on eject button in the task bar, and the task bar