Research methods (qualitative)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Unstructured interview
Opposite to a structured interview - more conversational, more informal, uses open questions, flexible and free flowing.
Questions are not pre set however there may be a an interview schedule containing different topics that the interviewer has to follow and ask questions on.
They are conducted in an informal environment so the interviewee feels comfortable and usually begins with closed factual questions and develops into more personal in depth questions, this aims for a rapport to be gained so that answers can emerge naturally. The interviewer may take the most significant notes but the interviewee feels comfortable is recorded and transcribed.
They are preferred by interpretivists as they are a qualitative source of data allowing verstehen, they are also a primary source of data.
Unstructured interviews (example)
The making of a moonie
Eileen Barker who is an interpretivist wanted to uncover whether the monies were brainwashed or had a choice about belonging to the cult. Moonies were known for mass arranged weddings, there was slot of bad press at the time about the moonies and she wanted to find out how and why people became one. She used unstructured interviews, questionnaires(sample of 20), and overt participant observation, living with the moonies for six years.
Unstructured interviews (PET issues)
PA- flexible for the researcher, meaning they can explore further and not stuck to one structure.
PD- time consuming as venues are needed, training is needed, transcribe this could also lead to high costs.
EA- fully informed consent is gained and confidentiality can be remained.
ED- sensitive topic areas may cause distress such as victims of crime or abuse.
TA-Rapport can be developed leaving interviewee to open up, meaning higher validity.
TD- more unreliable than structured interviews as it isn’t a standardised procedure. Interviewer bias leading to social desirability.
Group interviews
A group of specific participants to answer questions on a topic of interest. Unstructured informal interview.
primary source of data MAINLY used by interpretivists.
Group interviews (evaluation)
advantages
participants may stimulate each others thinking giving more in depth answers.
quicker than individual interviews
useful to get a group response
disadvantages
certain individuals may dominate lessening validity
discussion may divert from topic
peer group may cause pressure leading to social desirability
complex to analyse and transcribe
difficult to manage group due to conflicts
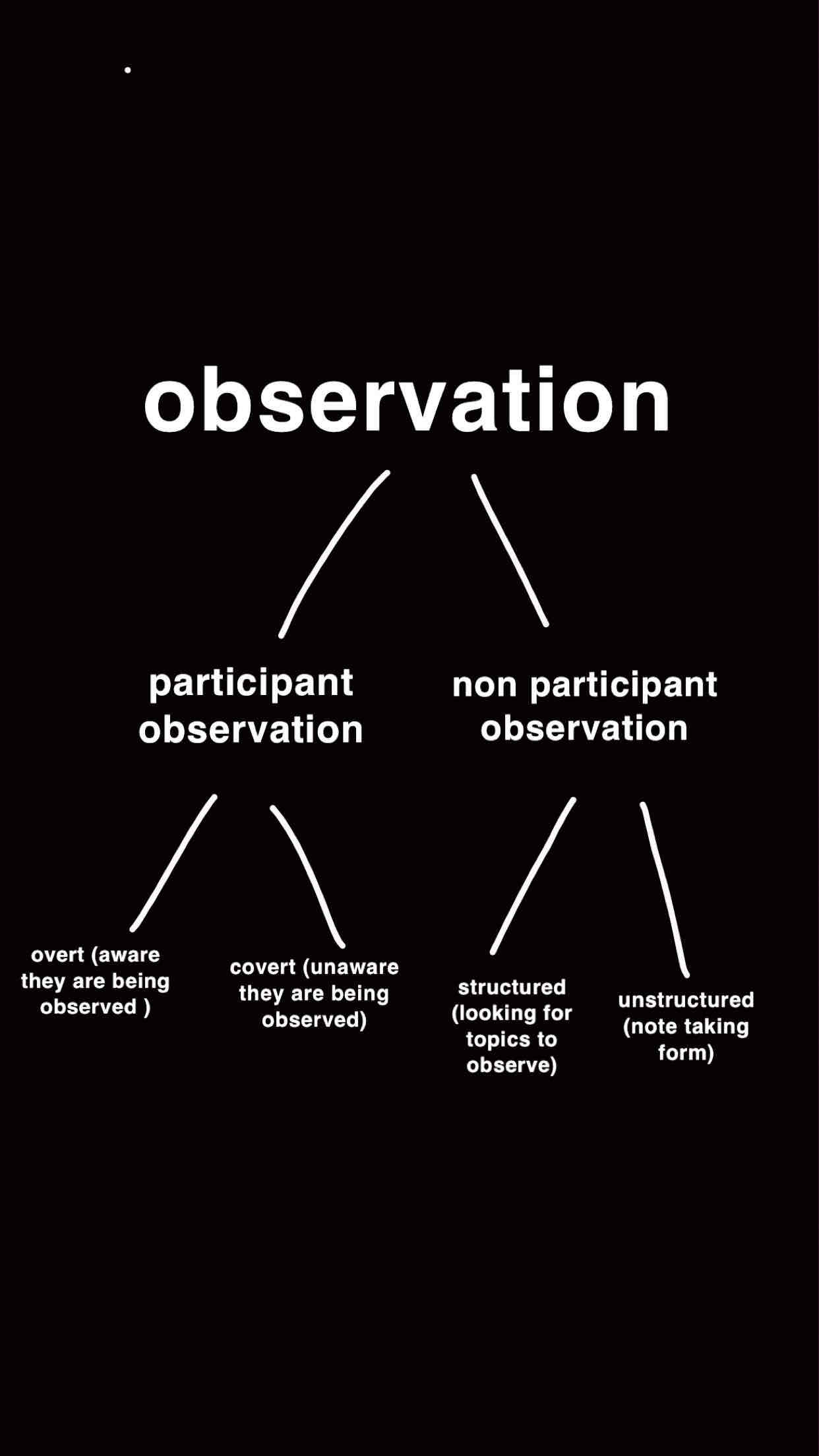
observation
Watching behaviour or getting involved with it. It is a primary source of data.
there are two types of observation (image)
the main things to consider when observing is
getting in ( accepted )
staying in
getting out (leaving safely and ethically)
The hawthorne effect (behavioural changes due to knowing behind watched.
structured v unstructured observation (evaluation)
structured observation are preferred by positivists and unstructured are preferred by positivists. Structured observation produces quantitative data whereas unstructured observation produces qualitative data.
Structured observations are quick and cheap, requiring little training however, the data may lack meaning due to schedule.
Unstructured observations allow the interviewer to not be constrained by checklists and categories, allowing more in depth answers so that they can gain verstehen. However, they are difficult to analyse and also difficult to replicate, making them unreliable.
participant observation ( definition, overt and covert)
when a researcher immerses themselves into a way of life of a group and becomes one of them to understand their behaviour (aka ‘going native’)
overt PO - group are fully aware of the research meaning consent is gained, making it more ethical but can lower validity due to the hawthorne effect.
covert PO - group are unaware of the research meaning there is no consent or permission involved, making it less ethical but more valid as they will act as they normally do.
overt PO (PET issues)
overt
PA- flexible (can explore areas of interest)
PD- getting in, staying in, getting out
EA- consent gained, right to withdraw, ethically better than covert
ED- research could disturb balance in the life of group, researcher may become over involved making getting out dangerous or difficult.
TA- verstehen can be gained
TD- risk of the hawthorne effect lowering validity
covert PO (PET issues)
PD- inflexible(can’t ask too may questions), time consuming.
EA- ethically justifiable if issue is in interest of the public or media.
ED- no consent gained, distress can be caused to the group after the research. Can be stressful for the researcher.
TA- gives a real insight into the way of life of a group - gaining verstehen due to no risk of the hawthorne effect.
TD- unrepresentative
overt participant observation (example)
tribe - bruce parry
joined the hamar tribes to see their way of life. These were indigenous tribes that had little contact with the modern world.
Bruce parry could gain insight into the way of life and really gain verstehen for example, he wanted to learn more about the whipping of women in the tribe so he could ask them about it and learn why they do it.
He joined in with different practices and cultural norms such as drinking cows blood and jumping the cattle, this allowed him to form bonds, making his data more valid.
he stayed with the tribe for a month.
covert PO (PET issues)
the secret policeman - mark daly
Mark daly wanted to see if the police system was racist due to the 1999 report claiming that the institution was racist.
He trained to be a policeman and after five months of training he became a fully openrational PC for eight weeks.
He worked undercover using technology filming equipment, he wasn’t allowed to make racket comments or influence anyone to say anything racist. He had to laugh at racist jokes.
conclusions - the majority of officers he met were non prejudiced with the intent of doing their job properly. But there was a minority of people who held the police service back.
They used racist slurs comfortably, believing in the idea that different ethnicities should be treated differently.
Expressive documents
three types of documents - public, personal and historical. Public documents are in public domain includinv government reports, articles, photos, auto/biographies and records. Personal documents are made my somebody for themself; diaries, photos, paintings and letters. Historical documents are from the past such as any of the above.
Documents are used to gain insight into a persons experiences and life to gain verstehen, to find out about past experiences such as war and to find out about a tragic event such as abuse or suicide in a more sensitive way (ethically)
main issue with documents.
CRAM
credibility - is it believeable, sincere and honest
representativeness - does it reflect the views of all
authenticity- is jt genuine
meaning - has the meaning changed. Will the researcher interpret it as intended.
examples of documents
eyewitness accounts from the battle of somme - what it was like to be a soldier in the war and how it affects their mentality.
ann franks diary - hiding and living through the holocaust as a jew and what fear she lived in. Not intended to be published.
a child called it - autobiography about child abuse, helps understand what it was like to live through abuse and go to school and forms of abuse.
Documents (PET issues)
PA- cheap as it already exists
PD- researcher needs to be skilled at assessing CRAM
EA- ethically sound
ED- may be consent issues (personal)
TA- verstehen achieved, valid depending on authors intentions
TD- difficult to make generalisations
what is centuries of childhood (documents)
Phillips Aires a french historian wanted to learn about the status of childhood in the medieval times. He studies historical paintings which were easily accessible through gallery’s and museums.
He found that the idea of childhood didn’t exist in medieval times and childhood did not emerge as separate to adulthood until the 20th century.
problems either his research was that it was ppen to subjective interpretation.