Chapter 4 p2 - Conductors, Electronic Devices
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
A/C:
flows in both directions
60 cycles per second
hertz defined as one cycle per second
electricity alternates at frequency of 60 hertz (cycles) per second in US
D/C:
flows in one direction
battery flow from negative to positive electrodes
DC – Electrons flowing in only one direction. Represented by:
a straight line
can also be pulsed, but doesn’t lose current
Resistance is measured in ohms, named after the physicist:
George Simon Ohm
discovered the Inverse relationship between current and resistance
current increases, resistance decreases
Ohm is the:
electrical resistance equal to the resistance between two points along a conductor that produces a current of 1 ampere when a potential difference of 1 volt is applied
Ohm’s law is the:
potential difference (voltage) across the total circuit or any part of that circuit, is equal to the current (amperes), multiplied by the resistance
V = I*R
V = volts, I = current (amps) R = resistance
An alternating current (A/C) is described as:
electrons flowing alternately in opposite directions
represented by a sinusoidal line produced by a generator
The amount of resistance of current in a conductor depends on four things:
material
length
cross-sectional area
temperature
Resistance is a useful and important part of the process of:
x-ray production
semiconductors:
materials that will conduct electricity but not as well as conductors and that will insulate but not as well as insulators
conductors:
materials with an abundance of free electrons that allow a relatively free flow of electricity
Examples of electrical conductors:
water, gold, copper, steel
Examples of electric insulators:
rubber, glass, oil, diamond, dry wood
Semi-conductors devices:
op-amp
resistors
capacitator
diodes
transistors
ICs
A closed (complete) pathway composed of wires and circuit elements through which electricity may flow:
an electric cicuit
In an electric circuit, closed means _____, and open means _____.
complete; broken
Series Circuits are calculating for:
the current (amps)
Electronic devices in radiography:
battery
capacitor
diode
protective devices (fuses and circuit breakers)
resistor or rheostat
switch
transformer
Battery:
produces electrons through a chemical reaction
stores an electric charge long term
provides an electric potential.
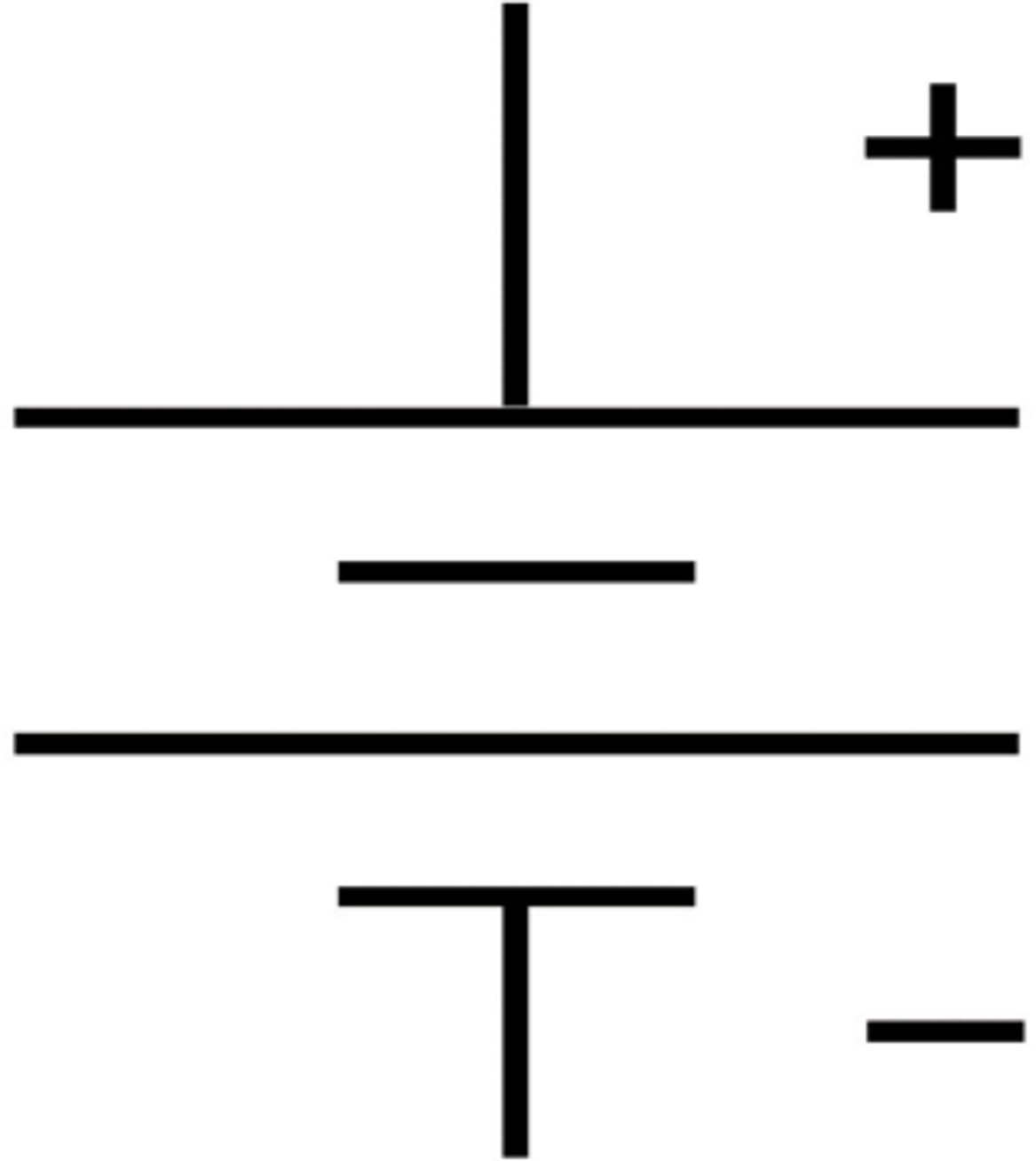
Capacitor:
temporarily stores an electric charge.
cannot produce more electrons
stores charge temporarily
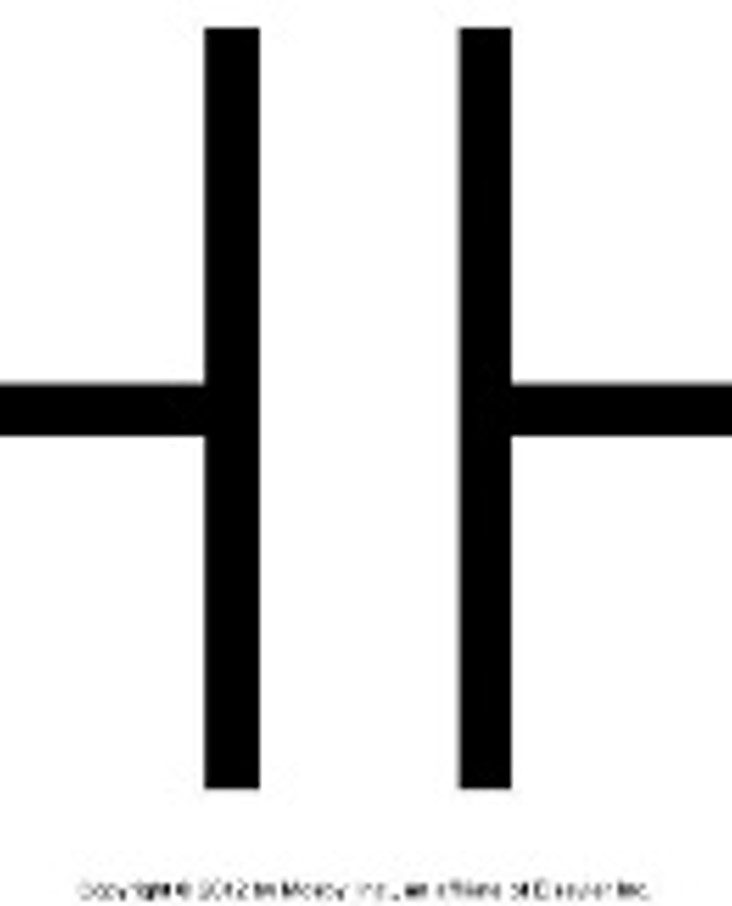
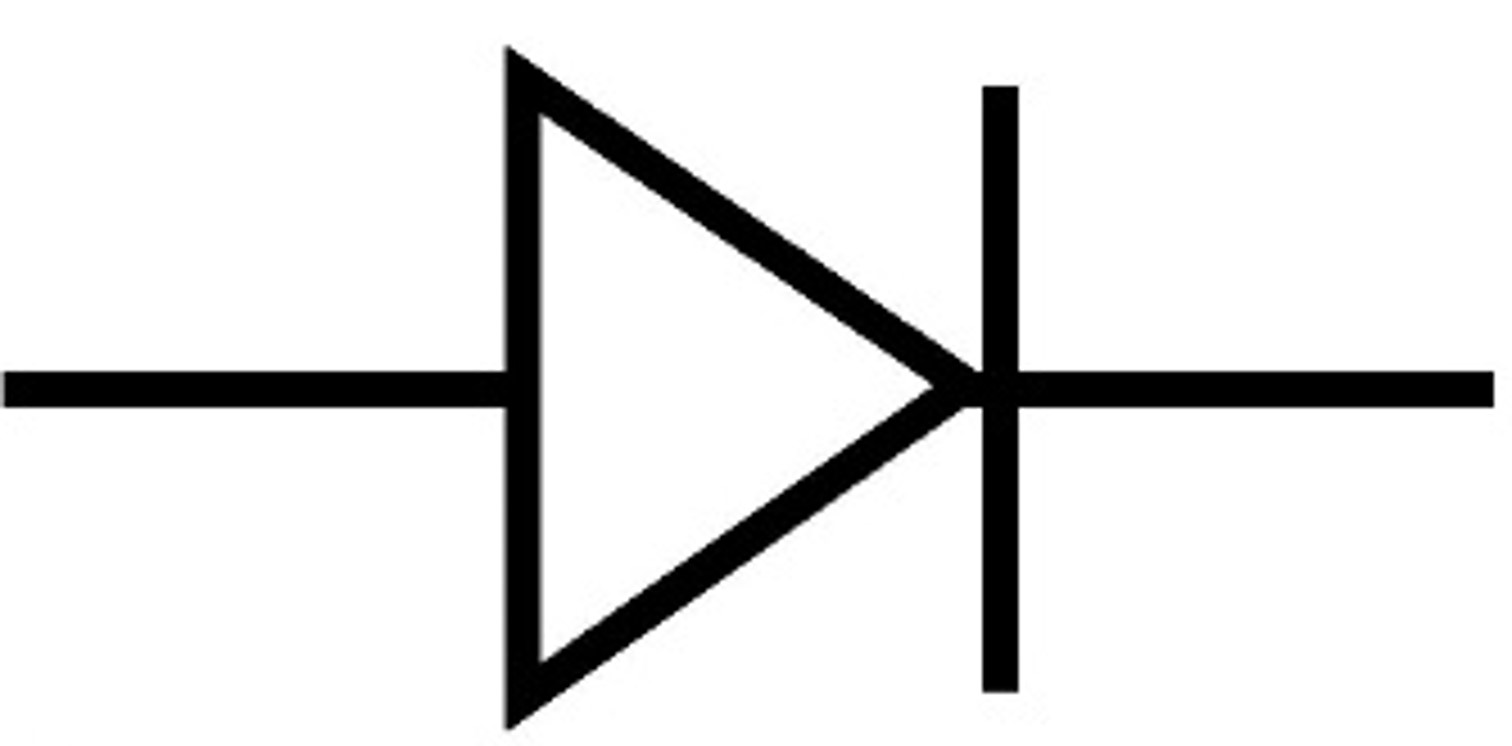
Diode:
a “one-way valve” device; allows electrons to flow in only one direction
Fuses (protective devices):
emergency devices that break or open the circuit if there is a sudden surge of electricity to the circuit or device.
fuse - wire in glass, melts if current rises excessively
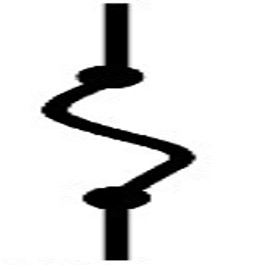
Circuit Breaker- internal switch tripped open:
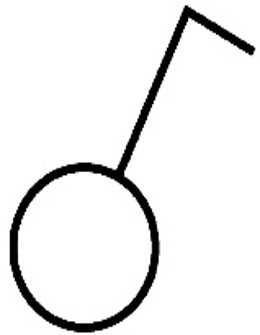
Resistor:
inhibits the flow of electrons, thereby precisely regulating the flow of electricity through that part of the circuit where it is placed

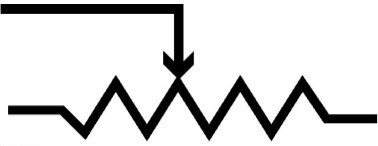
Rheostat:
is simply an adjustable or variable form of resistor
Switch:
a device that opens a circuit (breaks the pathway)
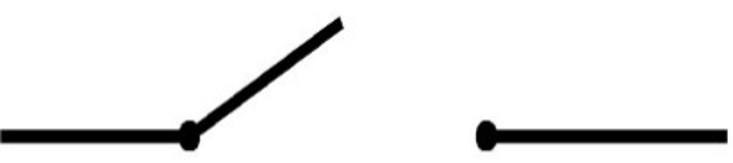
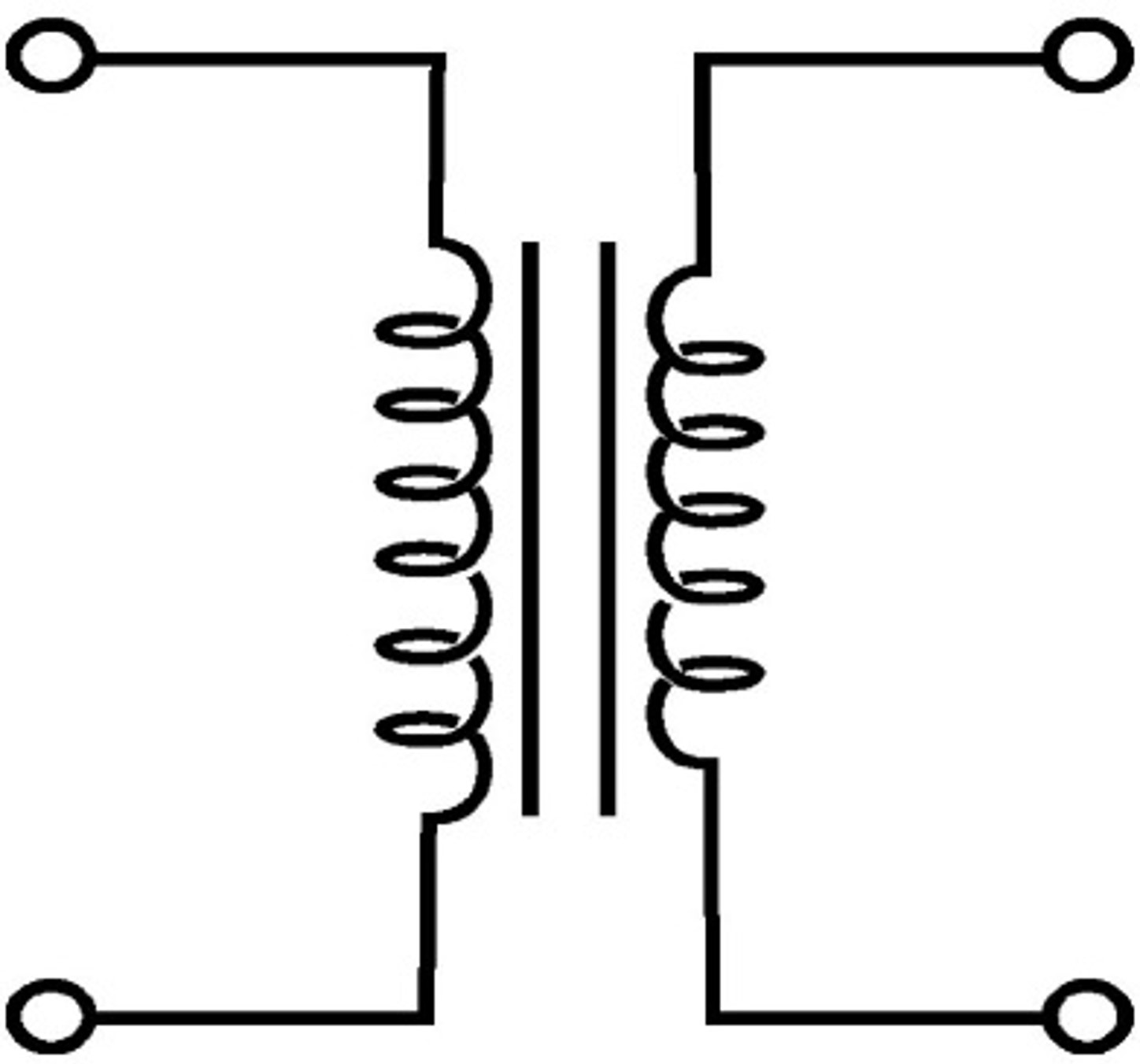
Transformer:
a device that can increase or decrease voltage by a predetermined amount
What happens to the positively charged objects when grounded?
they take on electrons from the earth
What happens to the negative charged objects when grounded?
they give up electrons to the earth until neutral