L4 Spirometry
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Breathing Variability
Lung measurements
Lung volumes/mechanics can be assessed by using spirometry: closed system; subject inhales and exhales in response to instructor
Spirometry
The measurement of lung volumes and flow
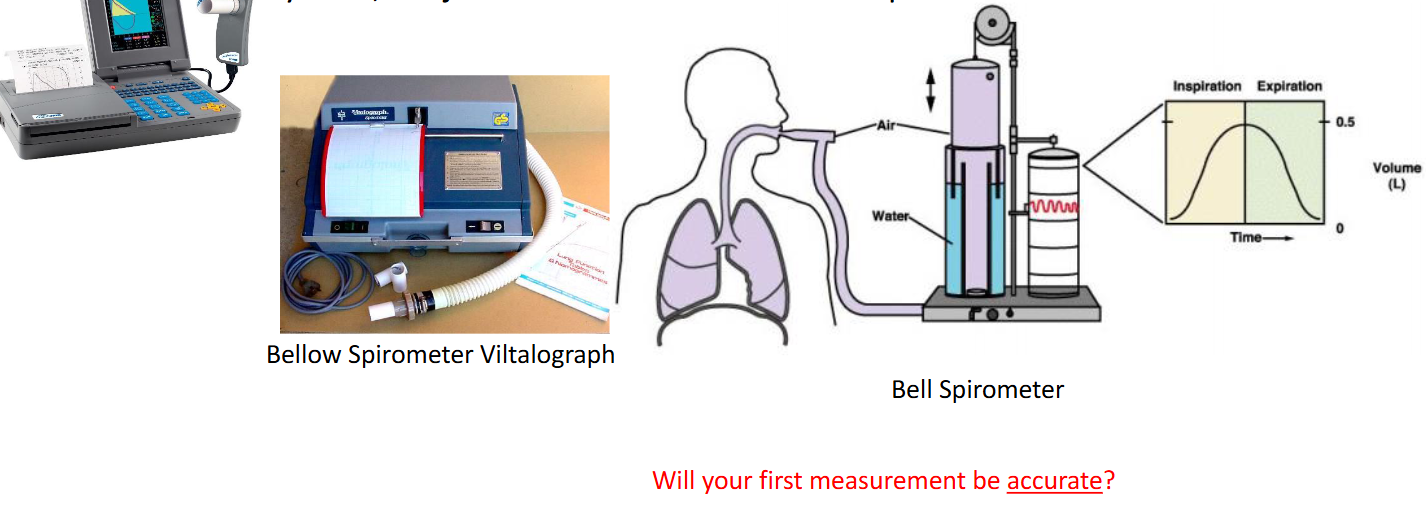
Spirometer - any device used to measure lung volumes and flow
Volume displacement spirometers
water-seal spirometers
bellow spirometer
Gas glow measurement devices (Pneumotachometer)
Pressure differential flow sensor
Peak flow meters
Lung volumes and capacity
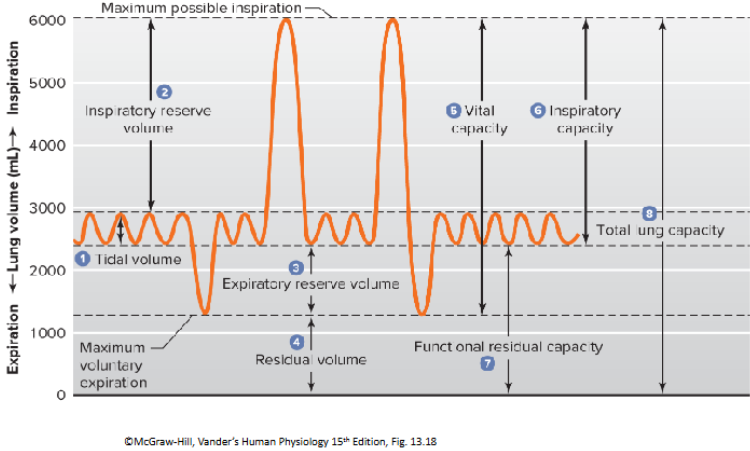
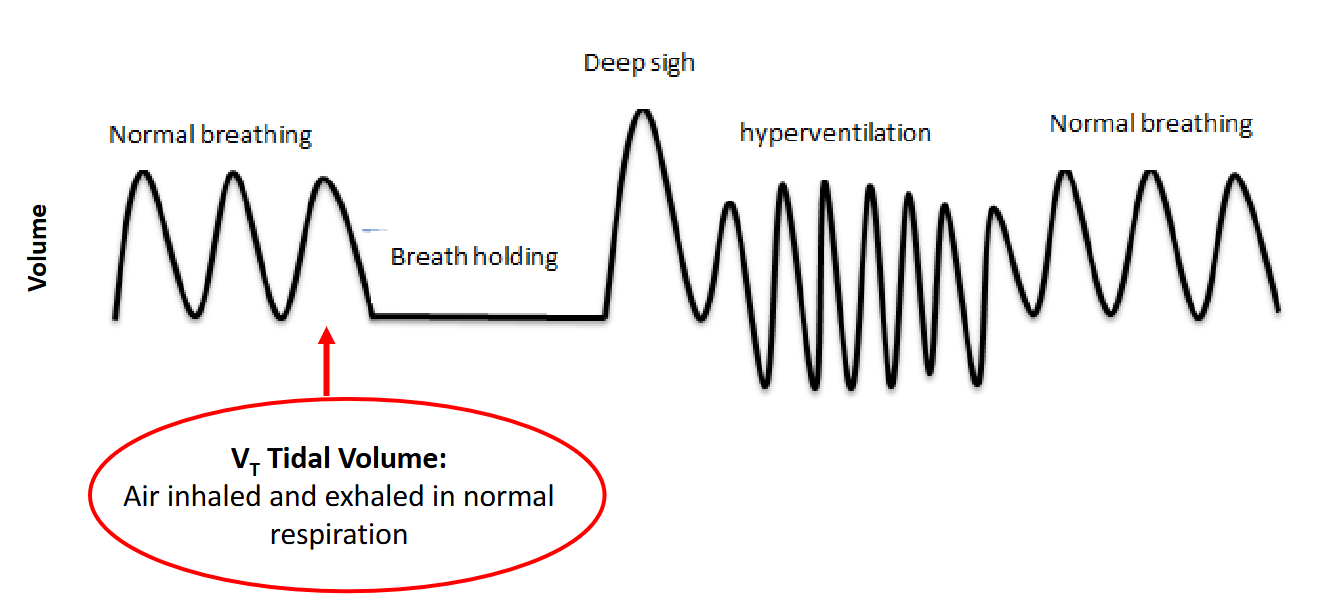
Tidal volume (500ml)
Amount of air inhaled or exhaled in one breath
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) (3000ml)
Amount of air in excess of tidal inspiration that can be inhaled with maximum effort
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) (1200ml)
Amount of air in excess of tidal expiration that can be exhaled with maximum effort.
Residual volume (RV) (1200ml)
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after maximum expiration; keeps alveoli inflated between breaths and mixes with fresh air on next inspiration.
Vital capacity (VC) (4700ml)
Amount of air that can be exhaled with maximum effort after maximum inspiration (ERV + TV + IRV); used to assess strength of thoracic muscles as well as pulmonary function
Inspiration capacity (IC) (3500ml)
Maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal tidal expiration (TV + IRV)
Functional residual capacity (FRC) (2400ML)
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after normal tidal expiration (RV + ERV)
Total lung capacity (TLC) (5900ml)
Maximum amount of air the lungs can contain (RV+ VC)
Lung volume measurements
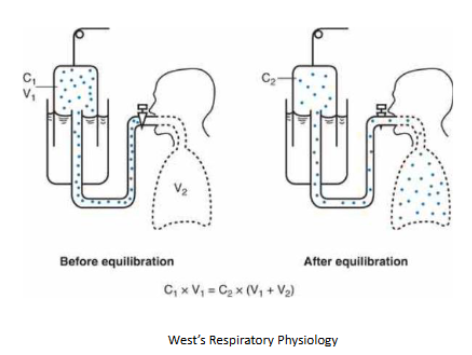
TLC, FRC and RV cannot be measured using a spirometer, because this only measure volumes that can be inspired or expired.
How do we measure TLC, FRC and RV?
Gas (e.g. helium, virtually insoluble in blood) dilution technique using a known concentration of helium - determine FRC
Lung volumes and capacities can vary based on lots of factors:
Age
Fitness
Posture and weight
Gender
Ethnicity (Nope)
Height
Ventilation
Movement of air in and out of the lungs.
The volume of air entering or leaving each minute is minute volume: Total Ventilation (Minute Ventilation, VE)

Effect of breathing patterns on ventilation
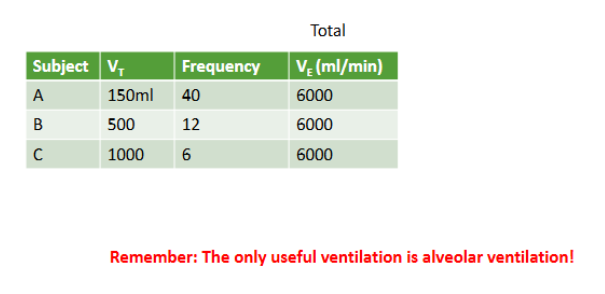
Alveolar Ventilation
Volume of fresh gas entering the respiratory zone each minute

Lung volumes
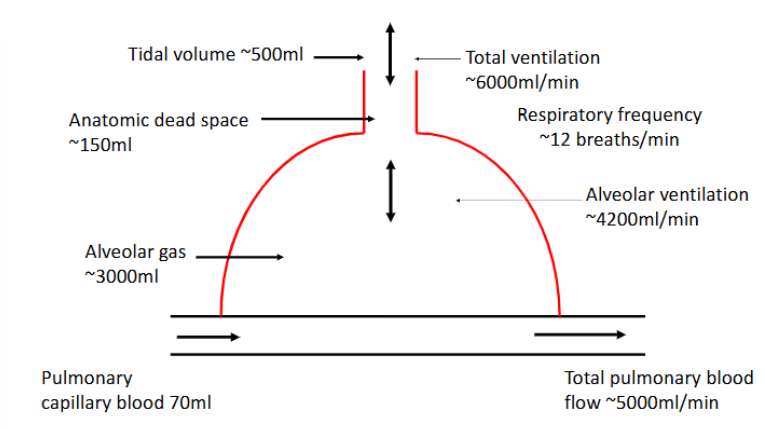
Estimation of alveolar ventilation
No gas exchange occurs in dead space
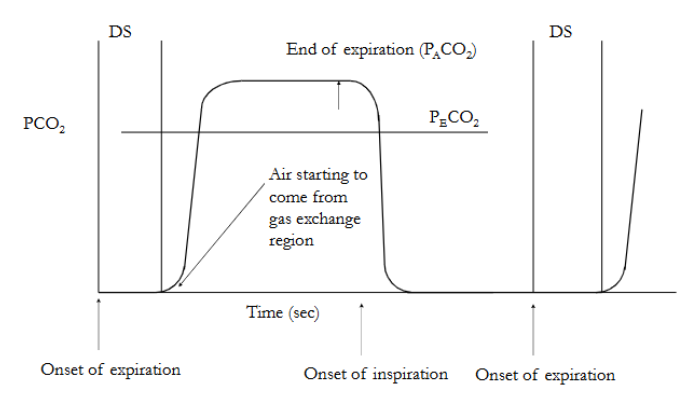
All the expired CO2 comes from the alveolar gas and non from the dead space region
Atmospheric PCO2 =~0mmHg (0.04%)
Therefore, at end inspiration PCO2 is approximately zero since all CO2 comes from gas exchange region
PCO2 can be measured at the mouth by rapid CO2 analyser.
Alveolar Ventilation