2153 IC3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is blood pressure
The arterial pressure in the systemic circulation between the aortic valve and the arterioles
reference to the ARTERIAL system
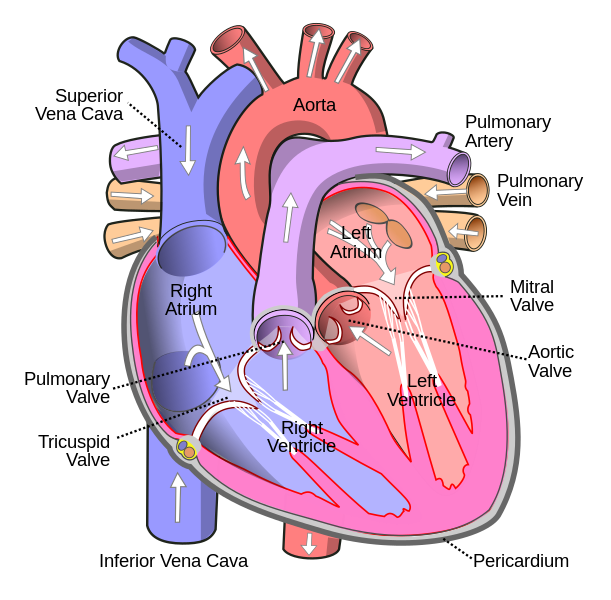
why is blood presssure important
ensures efficient and fast circulation of blood and sufficient exchange of fluids at the capillaries to meet metabolic requirements of tissues
what are the 2 forces required at the capillaries
for good perfusion (rate of flow of blood through tissue):
hydrostatic pressure
needs high enough presssure for blood to exit from capillaries to nearby tissues so pressure in capillaires » tissues
pressure comes from arterial pressure of BP
osmotic pressure
dependent on the proteins present; more proteins present in blood due to albumin than the tissues
Arteriole end: hydrostatic pressure > osmotic pressure : encourages filtration out of the capillary
Venous end: osmotic pressure > hydrostatic pressure : encourages reabsorption back, pull fluid back from interstitial to capillary
net filtration pressure is higher at arteriolar end than venous end = more fluid filtered out than reabsorbed back in
what are some causes of edema
insuficient albumin in the blood : need albumin for osmotic pressure so that fluid returns back. if insufficient e.g. not eating enough, leaking kidneys, fluid cant return back to circulation
how is high pressure generated
heart pumps at great force
valves in the heart for directional flow and allows generation of pressure to stay intact
arterial valve for pressure maintenance in arterial system by closing off the aorta and arteries from the ventricle. mitral valve prevents backflow from ventricle to aorta which allows pressure to be generated within the ventricle
circulatory system maintains high pressure in the arteries
thick walls, low resistance in the arteries —> allows pressure to be maintained and rapid blood flow
arterioles at the end of arteries have high resistance - like a stopper!
can you explain systolic and diastolic pressure
systolic
heart contracts
AV open
what is mean arterial pressure (blood pressure)
cardiac output x total peripheral resistance
7 phases of the cardiac cycle
Atrial Contraction: Atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles.
Isovolumetric Contraction: Ventricles contract, increasing pressure but no blood is ejected yet.
Ventricular Ejection: Ventricles contract further, forcing blood into the arteries.
Isovolumetric Relaxation: Ventricles relax, but no blood enters yet.
Rapid Ventricular Filling: Blood rapidly fills the ventricles.
Reduced Ventricular Filling: Remaining blood enters the ventricles.
Atrial Relaxation: Atria relax, preparing for the next cycle.