Cardiovascular System Part 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What does the cardiovascular system consist of?
Heart: pumps blood, maintains blood pressure
Blood vessels
Blood
What are the types of blood vessels? What are the functions?
Arteries: carry blood AWAY
Veins: returns blood to heart
Capillaries: exchange sites between blood and interstitial fluid
What are the functions of the blood?
Transport gases, nutrients, hormones, metabolic wastes
Regulate pH (acidity levels) and ions
Restrict fluid loss; blood clot
Defend against toxins/pathogens
Stabilize body temperature
How are metabolic wastes removed from blood? Examples?
Removed by kidney
NH4+ (ammonia) and urea
How are nutrients placed in blood?
Digestive system places nutrients in blood
How are hormones placed in blood?
Released/placed by endocrine system
What are the ions that blood regulates?
Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, PO43-
How does blood affect high and low body temperature?
High body temp; blood closer to skin
Low body temp; blood directed to brain, internal organs
What is blood?
Fluid connective tissue
What percentage does plasma and formed elements make up whole blood?
Plasma; 55%
Formed elements; 45%
What is plasma?
Interstitial fluid; containing water, ions, small solutes
gases
dissolved proteins
What are formed elements?
Cells and its fragments
WBCs, RBCs, platelets (cell fragments)
What is hematocrit?
Percentage of whole blood from formed elements
What are the plasma proteins? From most abundant to least adundant?
Albumins
Globulins
Fibrinogen
Hormones
What is the function of albumins in plasma?
MOST abundant
Control recruitment of H2O; osmotic pressure
What are the types of globulins? Functions?
2nd to Most Abundant
Antibodies (immunoglobulins): attack foreign pathogens, proteins
Transport globulins: bind ions, hormones, and lipids
What is the function of the fibrinogens in plasma?
2 to Least Abundant
Blood clotting using insoluble fibrin strands
attracts/works with platelets
What are hormones in plasma?
LEAST abundant
Chemical messengers
What percentage of plasma do the proteins make up?
7%
What are the plasma solutes? What is their percentage of the plasma?
1%
Electrolytes
Organic nutrients
Organic wastes
What are electrolytes (ions) in plasma?
Plasma Solute
Vital for cellular activities
K+, Na+, Cl-, HCO3-, HPO4-
What are the organic nutrients in plasma?
Plasma solutes
Lipids, proteins, carbohydrates
arrive from digestive system
What are the organic wastes in plasma?
Plasma Solutes
Waste from tissues (urea, NH4+)
What is mostly makes up plasma?
Water, 92&%
What is the function of platelets?
Formed Elements
Cell fragments involved in blood clotting
What is the function of RBCs and WBCs?
Formed Elements
RBCs (Erythrocytes): O2 and CO2 transport
WBCs (Leukocytes): bodily defense, immunity
What is most abundant in the formed elements?
Red blood cells
What is hemopoiesis/hematopoiesis? Where is it occur?
Development of formed elements
Occurs in red bone marrow
What are hemocytoblasts?
Stem cells that will differentiate into RBCs and WBCs
What are the two types of stem cells that hemocytoblasts produce?
Lymphoid stem cells
Myeloid stem cells
What do lymphoid stem cell produce? Where do they originate?
Produce lymphocytes only (WBC)
originate in red bone marrow
migrate to lymphoid tissues
What do myeloid stem cells produce?
Produce; RBCs, megakaryocytes (platelets), and all other WBCs
What are the functional aspects of red blood cells?
Large surface area to volume ratio
RBCs form stacks: rouleaux
Flexible
What are RBCs packed with? What does their shape allow for?
Packed with hemoglobin; contains heme carrying O2 and CO2
Shape; allows O2 exchange
What does the rouleaux of red blood cells allow?
Rouleaux (stacks); allow RBCs to transport in capillaries (small vessels)
What is the flexibility of RBCs used for?
To move through narrow capillaries
What occurs to RBCs during development?
RBC characteristics
Lose most organelles
Lack nuclei (anucleate); lack ribosomes
can't make proteins
What is the life span of RBCs?
Less than 120 days (4 months)
will die and be recycled
What is the main function of the red blood cells? What proteins do they use to do this?
Transport respiratory gases
Hemoglobin: protein used to transport gases
How many heme units in one hemoglobin? What is heme?
4 heme units; in 1 hemoglobin
Heme: contains iron
What is oxyhemoglobin? What color?
Heme unit iron and binds to O2 molecule
makes oxygenated blood bright red
What is deoxyhemoglobin? What color?
Hemoglobin not bound to O2; carying CO2
lack of oxygen, dark red
What happens at the end of RBC life?
Hemolysis: plasma membrane ruptures
What is the function of spleen?
Macrophages recycles destroyed RBCs; engulfing
What is erythropoesis? Where does it occur?
Formation of RBCs
From myeloid stem cells of red bone marrow
What can fatty yellow bone marrow convert to?
Convert to red bone marrow when sustaining blood loss
How are WBCs (leukocytes) different from RBCs?
Contains nuclei and organelles
NO hemoglobin
What are the 5 types of white blood cells? From most to least abundant?
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
Neutrophiles
Lymphocytes
Monocytes —> become macrophages
Eosinophils
Basophils
What are the 2 types of WBCs?
Granular leukocytes
Agranular leukocytes
What are the granular leukocytes?
Granular leukocytes: contains granules (vesicles and lysosomes)
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
What are the agranular leukocytes?
Agranular leukocytes: non visible granules (no vesicles/lysosomes)
Monocytes (macrophages)
Lymphocytes
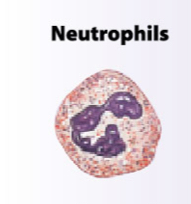
What is the function of neutrophils?
Phagocytic cells engulfing (endocytosis) pathogens in injured tissue
kills own cells
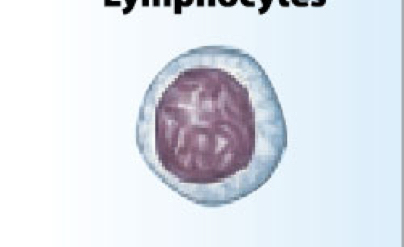
What is the function of the lymphocytes?
Produce antibodies (immunoglobulins); seek foreign substances (antigens)
cells of lymphatic system
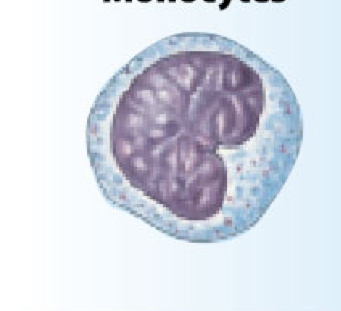
What is the function of the monocytes (macrophages)?
Engulf debris; recycle RBC in spleen
enter tissue become macrophages
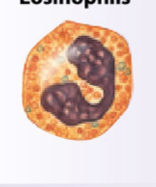
What is the function of eosinophils?
Phagocytic cells engulfing antibody labeled materials and parasitic infections

What is the function of basophils?
Release histamine and cause inflammation (brings blood)
allergies
What are antigens?
Substances that may illicit an immune response
if recognized by corresponding antibodies
What are antibodies?
Seek and destroy foreign antigens
YOUR antibodies will not destroy YOUR antigens
What are surface antigens?
On plasma membrane; recognized as self or normal by immune system (antibodies)
How is blood type determined? What are the 4 types?
Determined by surface antigens
Type A
Type B
Type AB
Type O
What is the antigen and antibody of Type A blood?
Antigen A
Antibodies; Anti-B (seeking antigen B)
What is the antigen and antibody of Type B blood?
Antigen B
Antibodies; Anti-A (seeking antigen A)
What is the antigen and antibody of Type AB blood?
Antigen A and B
No antibodies in plasma
universal recipient
What is the antigen and antibody of Type O blood?
No antigens on surface
universal donor
Antibodies; seeking both Anti-A and Anti-B
can ONLY receive type O
What are surface antigens also known as?
Surface antigens; agglutinogens
What are antibodies also known as?
Antibodies; agglutinins
What is agglutination? How does this happen?
Agglutination: clumping of RBCs
antigens of another blood type exposed to antibodies
What is an example of agglutination?
Giving type A blood to someone who is type B
What is the reaction of agglutination called? What can it cause?
Cross reaction: forms clumps blocking blood vessels cutting blood supply
hemolysis
What is the Rh blood group?
Another type of blood (like Type A/B)
Rh group; based on presence or absence of Rh surface antigen on RBCs
What is Rh positive? Its antigen and antibody?
Presence of Rh surface antigen
no Rh antigens in plasma
What is Rh negative? Its antigen and antibody?
Absence of Rh surface antigen
contains Rh antibody in plasma
What will happen if an Rh negative person is given Rh positive blood?
Antibodies (immune system) will attack blood
Agglutination
NOT vice versa
What will happen if an Rh positive person is given Rh negative blood?
No antibodies will attack; LACK antibodies
Can receive both Rh + and -