BIOL1201 Hamlin test #3
1/293
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
294 Terms
C) binds to receptors on the membranes of other types of yeast cells
In yeast signal transduction, a yeast cell releases a mating factor, which ________.
A) acts back on the same cell that secreted the mating factor, changing its development
B) passes through the membranes of neighboring cells, binds to DNA, and initiates transcription
C) binds to receptors on the membranes of other types of yeast cells
D) diffuses through the membranes of distant cells, causing them to produce factors that initiate long-distance migrations
C) They will mate with each other or with normal mating type a cells, but not with normal mating type α cells.
Yeast cells of mating type a are genetically engineered to produce only mating factor α instead of the normal mating factor a. The gene for the mating factor receptor was unaltered. How will these engineered cells behave in terms of mating?
A) They will only mate with normal mating type a cells.
B) They will only mate with normal mating type α cells.
C) They will mate with each other or with normal mating type a cells, but not with normal mating type α cells.
D) They will only mate each other and not with normal mating type a or α cells.
C) paracrine signaling
Which of the following is a type of local signaling in which a cell secretes a signal molecule that affects neighboring cells?
A) hormonal signaling
B) autocrine signaling
C) paracrine signaling
D) synaptic signaling
D) The target organ must have receptors that recognize and bind the hormone molecule.
Hormones are chemical substances produced in one organ that are released into the bloodstream and affect the function of a target organ. Which of the following conditions is required for the target organ to respond to a particular hormone?
A) Cells in the target organ must modify their plasma membranes to allow the hormone to enter the cytoplasm.
B) The target organ must be the same as the organ that produced the hormone.
C) The target organ must have the opposite mating type of the organ that produced the hormone.
D) The target organ must have receptors that recognize and bind the hormone molecule.
A) Plant hormones frequently travel through the air as a gas.
In which of the following ways do plant hormones differ from hormones in animals?
A) Plant hormones frequently travel through the air as a gas.
B) Animal hormones are only local regulators.
C) Plant hormones commonly travel through the soil from one plant to another.
D) Animal hormones typically travel from the hormone producing cell to an adjacent responding cell through gap junctions.
C) signal molecule
When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway?
A) relay molecule
B) transducer
C) signal molecule
D) response molecule
D) synaptic
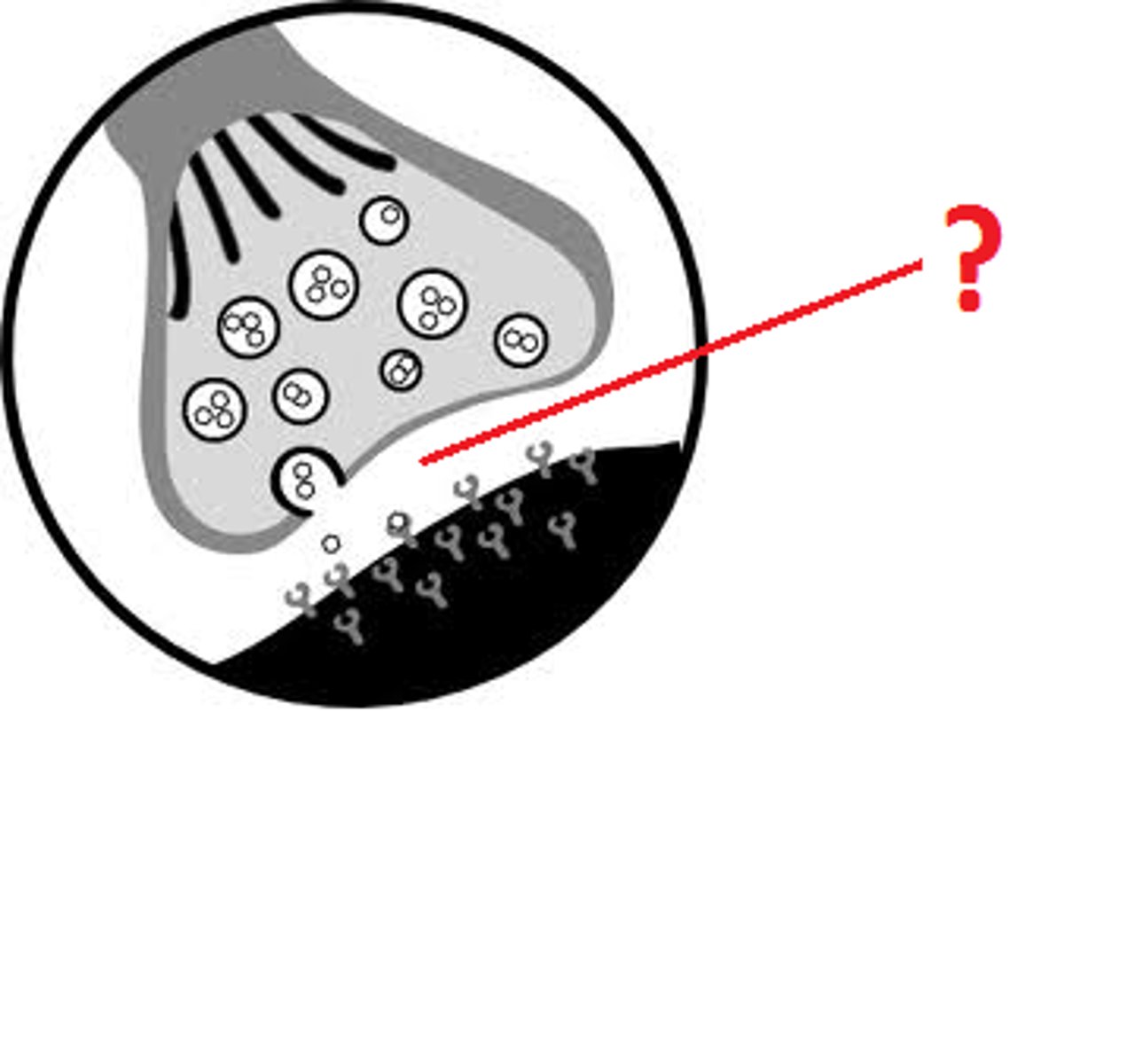
Use the following figure to answer the question.
Which of the following types of signaling is represented in the figure?
A) autocrine
B) paracrine
C) hormonal
D) synaptic
C. Neurotransmitters
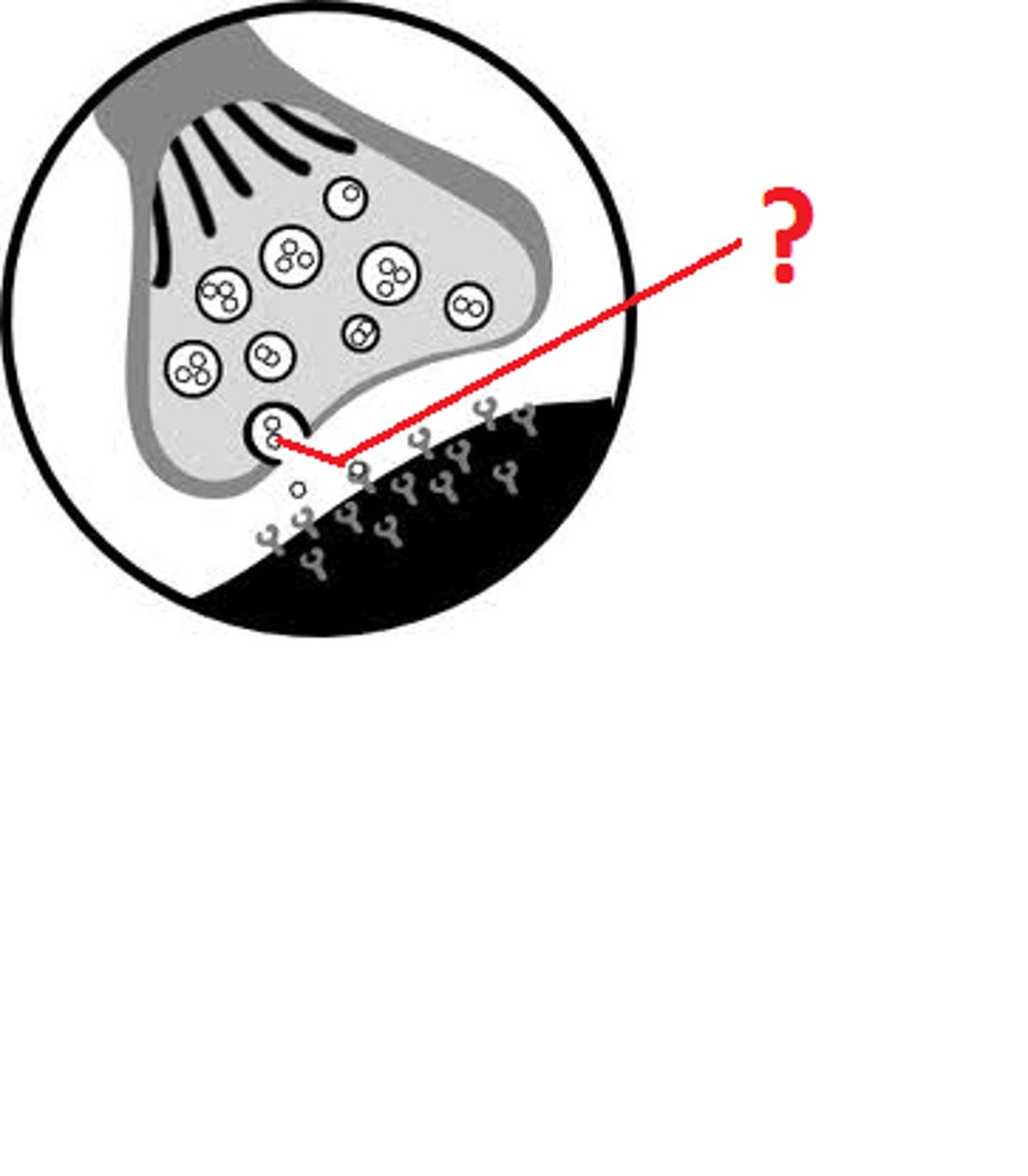
Use the following figure to answer the question.
In the figure, the dots in the space between the two structures represent which of the following?
A) receptor molecules
B)signal transducers
C)neurotransmitters
D) hormones
B) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells.
Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells?
A) Receptor studies indicated that epinephrine was a ligand.
B) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells.
C) Glycogen breakdown was observed when epinephrine and glycogen phosphorylase were combined in a cell-free system.
D) Epinephrine was known to have different effects on many types of cells.
B) A G protein bound to GTP is in its active state.
Which of the following statements about a G protein signaling pathway is true?
A) A G protein-coupled receptor bound to GTP is in its active state.
B) A G protein bound to GTP is in its active state.
C) A G protein bound to GDP is in its active state.
D) Hydrolysis of bound GTP by a G protein activates the G protein.
B) It binds with a receptor protein that enters the nucleus and activates expression of specific genes.
What is the most likely mechanism by which testosterone functions inside a cell?
A) It acts as a signal receptor that activates tyrosine kinases.
B) It binds with a receptor protein that enters the nucleus and activates expression of specific genes.
C) It acts as a steroid signal receptor that activates ion channel proteins in the plasma membrane.
D) It coordinates a phosphorylation cascade that reduces spermatogenesis.
A) integrins
Scientists have found that extracellular matrix components may induce specific gene expression in embryonic tissues such as the liver and testes. For this to happen, there must be direct communication between the extracellular matrix and the developing cells. Which kind of transmembrane protein would most likely be involved in this kind of induction?A) integrins
B) fibronectins
C) actin microfilaments
D) receptor tyrosine kinases
D) receptor tyrosine kinases
One of the major categories of receptors in the plasma membrane functions by forming dimers, adding phosphate groups, and then activating relay proteins. Which type does this?
A) G protein-coupled receptors
B) ligand-gated ion channels
C) steroid receptors
D) receptor tyrosine kinases
B) The transcription of certain genes would decrease.
Which of the following statements describes a likely effect of a drug designed that inhibits the cellular response to testosterone?
A) The cytoplasmic levels of cAMP would decrease.
B) The transcription of certain genes would decrease.
C) The cytosolic calcium concentration would increase.
D) The activity of G proteins would decrease.
B) at the cytosolic surface
Many G protein-coupled receptors contain seven transmembrane α-helical domains. The amino end of the protein lies at the exterior of the plasma membrane. Loops of amino acids connect the helices either at the exterior surface or on the cytosolic surface of the membrane. The loop on the cytosolic side between helices 5 and 6 is usually substantially longer than the others. Where would you expect to find the carboxyl end of the protein?
A) at the exterior surface
B) at the cytosolic surface
C) connected with the loop at H5 and H6
D) embedded in the phospholipid bilayer of the membrane
D) at the loop between H5 and H6
Many G protein-coupled receptors contain seven transmembrane α-helical domains. The amino end of the protein lies at the exterior of the plasma membrane. Loops of amino acids connect the helices either at the exterior surface or on the cytosolic surface of the membrane. The loop on the cytosolic side between helices 5 and 6 is usually substantially longer than the others. Where would a coupled G protein most likely interact with this receptor?
A) at the amino end
B) at the carboxyl end
C) along the exterior margin
D) at the loop between H5 and H6
C) ligand-gated ion channel
Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane?A) receptor tyrosine kinase
B) G protein-coupled receptor
C) ligand-gated ion channel
D) steroid receptor
B) Intracellular receptors for testosterone are present only in target cells.
Why does testosterone, a lipid-soluble signaling molecule that crosses the membranes of all cells, affect only target cells?
A) Only target cells retain the appropriate genes regulated by testosterone.
B) Intracellular receptors for testosterone are present only in target cells.
C) Only target cells possess the cytosolic enzymes that transduce the signal from testosterone to adenylyl cyclase.
D) Only in target cells is testosterone able to initiate the phosphorylation cascade leading to activated transcription factor.
A) It would not be able to activate G proteins on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
If an animal cell suddenly lost the ability to produce GTP, what might happen to its signaling system?A) It would not be able to activate G proteins on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
B) It would be able to carry out reception and transduction but would not be able to respond to a signal.
C) It would use ATP instead of GTP to activate G proteins on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
D) It would not be able to activate receptor tyrosine kinases.
B) The receptor may be inside the nucleus of a target cell.
Which of the following statements is true of steroid receptors?
A) The receptor molecules are themselves lipids or glycolipids.
B) The receptor may be inside the nucleus of a target cell.
C) The unbound steroid receptors are quickly recycled by lysosomes.
D) Steroid receptors are typically bound to the external surface of the nuclear membrane.
B) If the patient's cancer cells have excessive levels of HER2.
Particular receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) that promote excessive cell division are found at high levels in various cancer cells. HER2 is an RTK that is present at excessively high levels in some breast cancer cells. Herceptin is a protein that binds to HER2 and inhibits cell division. Herceptin may be an effective treatment for breast cancer treatment under which of the following conditions?
A) If injection of HER2 in the patient's cancer cells stimulates cell division.
B) If the patient's cancer cells have excessive levels of HER2.
C) If the patient's genome codes for the HER2.
D) If the patient has excessive levels of other RTKs in cancer cells.
D) receptor tyrosine kinase activity
Which of the following activities would be inhibited by a drug that specifically blocks the addition of phosphate groups to proteins?
A) binding of G proteins to G protein-coupled receptors
B) ligand-gated ion channel signaling pathways
C) adenylyl cyclase activity
D) receptor tyrosine kinase activity
C) Steroid hormones are lipid soluble, so they can readily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
The receptors for steroid hormones are located inside the cell instead of the membrane surface like most other signal receptors. How do steroids gain access to their receptors?
A) Steroid hormone receptors undergo conformational changes that relocate them on the membrane surface.
B) Both steroid hormones and their receptors are produced by the same cells.
C) Steroid hormones are lipid soluble, so they can readily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
D) Steroid hormones first bind to a steroid activator and this complex is transported across the cell membrane by a steroid transport protein.
A) a lipid-soluble signal
Not all intercellular signals require transduction. Which one of the following signals would be processed without transduction?
A) a lipid-soluble signal
B) a signal that is weakly bound to a nucleotide
C) a signal that binds to a receptor in the cell membrane
D) a signal that binds to the extracellular matrix
B) The physical form of the signal changes as it passes from the cell membrane to the ultimate intracellular target.
What does it mean to say that a signal is transduced?
A) The signal enters the cell directly and binds to a receptor inside.
B) The physical form of the signal changes as it passes from the cell membrane to the ultimate intracellular target.
C) The signal is amplified, such that even one signal molecule evokes a large response.
D) The signal triggers a sequence of phosphorylation events inside the cell.
A) activation of receptor tyrosine kinases
Which of the following processes generally requires protein phosphorylation? A) activation of receptor tyrosine kinases
B) activation of steroid hormone receptors
C) activation of G protein-coupled receptors
D) activation ligand-gated ion channels
A) conformational changes to each protein in the series
A signal transmitted via phosphorylation of a series of proteins is generally associated with which of the following events?A) conformational changes to each protein in the series
B) binding of a hormone to an intracellular receptor
C) activation of a ligand-gated ion channel
D) production of ATP in the process of signal transduction
C) insufficient ATP levels in the cytosol
Which of the following is the most plausible explanation for why an animal cell would be
unable to reduce the Ca2+ concentration in its cytosol compared with the extracellular fluid? A) inactivation of calcium-gated ion channels in the cell membrane
B) excessive transport of calcium from the cytosol into the endoplasmic reticulum
C) insufficient ATP levels in the cytosol
D) insufficient levels of protein kinase in the cell
A) It modifies a G protein involved in regulating salt and water secretion.
How does the toxin of Vibrio cholerae cause profuse diarrhea?A) It modifies a G protein involved in regulating salt and water secretion.
B) It modifies adenylyl cyclase and triggers excess formation of cAMP.
C) It signals IP3 to act as a second messenger for the release of calcium.
D) It modifies a ligand-gated ion channel.
A) protein kinase activity
Which of the following results would most likely be an immediate result of a growth factor binding to its receptor?
A) protein kinase activity
B) adenylyl cyclase activity
C) cAMP activity
D) phosphorylase activity
C)phosphodiesterase
The activity of adenylyl cyclase is essentially the opposite of which of the following enzymes?
A) protein kinase
B) protein phosphatase
C)phosphodiesterase
D) phosphorylase
B) cAMP
Caffeine is an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase. Therefore, the cells of a person who has recently consumed coffee would have increased levels of which of the following molecules?
A) phosphorylated proteins
B) cAMP
C) adenylyl cyclase
D) activated G proteins
C) phospholipase C
An inhibitor of which of the following enzymes could be used to block the release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum?
A) serine/threonine kinases
B) phosphodiesterase
C) phospholipase C
D) adenylyl cyclase
D) Protein kinase A activation is one possible result of signal molecules binding to G protein- coupled receptors.
Which of the following statements is true of signal molecules?
A) When signal molecules first bind to receptor tyrosine kinases, the receptors phosphorylate a number of nearby molecules.
B) In response to some G protein-mediated signals, a special type of lipid molecule associated with the plasma membrane is cleaved to form IP3 and calcium.
C) In most cases, signal molecules interact with the cell at the plasma membrane, enter the cell, and eventually enter the nucleus.
D) Protein kinase A activation is one possible result of signal molecules binding to G protein- coupled receptors.
C) GTPase activity and hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
Which of the following is a correct association?
A) kinase activity and the addition of a tyrosine
B) phosphodiesterase activity and the removal of phosphate groups C) GTPase activity and hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
D) adenylyl cyclase activity and the conversion of cAMP to AMP
C) activates or inactivates other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them
Protein kinase is an enzyme that functions in which of the following ways?
A) as a second messenger molecule
B) as a receptor for various signal molecules
C) activates or inactivates other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them
D) activates a G protein
A) hydrolysis of cGMP to GMP
Viagra causes dilation of blood vessels and increased blood flow to the penis, facilitating erection. Viagra acts by inhibiting which of the following events?A) hydrolysis of cGMP to GMP
B) hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
C)dephosphorylation of cGMP
D) formation of cGMP from GTP
C) serine and threonine
Which of the following amino acids are most frequently phosphorylated by protein kinases in the cytoplasm during signal transduction?
A) tyrosines
B) glycine and histidine
C) serine and threonine
D) glycine and glutamic acid
D) They inactivate protein kinases to turn off signal transduction.
What role do phosphatases play in signal transduction pathways?
A) They transfer a phosphate group from one protein in the pathway to the next molecule in the series.
B) They activate protein kinases by phosphorylation.
C) They amplify the second messenger cAMP.
D) They inactivate protein kinases to turn off signal transduction.
C) blocks G protein activity in liver cells
If a pharmaceutical company wished to design a drug to maintain low blood sugar levels, one approach might be to design a compound that does which of the following?
A) activates epinephrine receptors in liver cells
B) increases cAMP production in liver cells
C) blocks G protein activity in liver cells
D) increases glycogen phosphorylase activity in liver cells
D) increases phosphodiesterase activity in liver cells
If a pharmaceutical company wished to design a drug to maintain low blood sugar levels, one approach might be to design a compound that does which of the following?
A) increases glycogen phosphorylase activity in liver cells
B) activates adenylyl cyclase in liver cells
C) stimulates G protein activity in liver cells
D) increases phosphodiesterase activity in liver cells
A) cAMP
Consider this pathway:
epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP
The second messenger in this pathway is ________. A) cAMP
B) G protein
C) adenylyl cyclase
D) G protein-coupled receptor
D) Elevating cytosolic concentrations of cyclic AMP
Sutherland discovered that the signaling molecule epinephrine is responsible for which of the following events?A) Stimulating glycogen synthesis.
B) Decreasing blood glucose levels.
C) Interacting directly with glycogen phosphorylase.
D) Elevating cytosolic concentrations of cyclic AMP
D) Adenylyl cyclase is activated after the hormone binds to the cell and before phosphorylation of proteins occurs.
Which of the following is true during a typical cAMP-mediated signal transduction event?
A) The second messenger is the last part of the system to be activated.
B) A hormone activates the second messenger by directly binding to it.
C) The second messenger amplifies the hormonal response by attracting more hormones to the cell being affected.
D) Adenylyl cyclase is activated after the hormone binds to the cell and before phosphorylation of proteins occurs.
C) 3, 1, 5, 2, 4
Put the steps of the process of signal transduction in the order they occur.
A conformational change in the signal-receptor complex activates an enzyme.
Protein kinases are activated.
A signal molecule binds to a receptor.
Target proteins are phosphorylated.
Second messenger molecules are released.
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 3, 1, 2, 4, 5
C) 3, 1, 5, 2, 4
D) 1, 2, 5, 3, 4
C) They control gene expression.
What is a primary function of transcription factors?
A) They regulate the synthesis of DNA in response to a signal.
B) They convert ATP into cAMP.
C) They control gene expression.
D) They regulate the release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum.
D) Estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each with different responses.
At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogen and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects?
A) Estrogen is produced in very large concentration by nearly every tissue of the body.
B) Each cell responds in the same way when steroids bind to the cell surface.
C) Estrogen is kept away from the surface of any cells, not able to bind it at the surface.
D) Estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each with different responses.
B) large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facilitate cascade effects
What are scaffolding proteins?
A) microtubule arrays that allow lipid-soluble hormones to get from the cell membrane to the nuclear pores
B) large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facilitate cascade effects
C) relay proteins that orient receptors and their ligands in appropriate directions to facilitate complex formation
D) proteins that enter the nucleus of a cell to regulate transcription
C) amplify the original signal many times
Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because they ________.
A) are species specific
B) always lead to the same cellular response
C) amplify the original signal many times
D) counter the harmful effects of phosphatases
D) The G protein would always be active.
A mutation that knocks out the GTPase activity of a G protein would have what effect on a cell?
A) The concentration of available GTP would decrease.
B) The number of G proteins in the cell would increase.
C) The G protein would be inactivated by a G protein-coupled receptor/signal molecule complex.
D) The G protein would always be active.
B) C. elegans undergoes a fixed and easy-to-visualize number of apoptotic events during its normal development.
Why has C. elegans proven to be a useful model for understanding apoptosis?
A) C. elegans does not naturally use apoptosis, but can be induced to do so in the laboratory.
B) C. elegans undergoes a fixed and easy-to-visualize number of apoptotic events during its normal development.
C) C. elegans has large cells wherein apoptosis is easily observed without the aid of a microscope.
D) As C. elegans ages, its cells die progressively until the whole organism is dead.
C) The cell's DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell shrinks and forms blebs, and the cell's parts are packaged in vesicles that are digested by specialized cells.
Which of the following statements describes the events of apoptosis?
A) The cell dies, it is lysed, its organelles are phagocytized, and its contents are recycled.
B) The cell's DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell dies, and it is phagocytized.
C) The cell's DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell shrinks and forms blebs, and the cell's parts are packaged in vesicles that are digested by specialized cells.
D) The cell's nucleus and organelles are lysed, and then the cell enlarges and bursts.
B) a form of cancer in which there is insufficient apoptosis
If an adult person has a faulty version of the human analog to ced-4 of the nematode, which of the following is most likely to result?
A) activation of a developmental pathway found in the worm but not in humans
B) a form of cancer in which there is insufficient apoptosis
C) formation of molecular pores in the mitochondrial outer membrane D) excess skin loss
A) It prevents the caspase activity of ced-3 and ced-4.
In the nematode C. elegans, ced-9 prevents apoptosis in a normal cell in which of the following ways?
A) It prevents the caspase activity of ced-3 and ced-4.
B) Ced-9 remains inactive until it is signaled by ced-3 and other caspases.
C) Ced-9 cleaves to produce ced-3 and ced-4.
D) Ced-9 prevents blebbing by its action on the cell membrane.
A) Growth factor ligands do not bind as efficiently to receptors.
In research on aging (both cellular aging and organismal aging), it has been found that aged cells do not progress through the cell cycle as they had previously. Which of the following, if found in cells or organisms as they age, would provide evidence that this is related to cell signaling?
A) Growth factor ligands do not bind as efficiently to receptors.
B) Hormone concentrations decrease.
C) cAMP levels change very frequently.
D) Enzymatic activity declines.
C) Signal transduction molecules identified in distantly related organisms are similar.
Which of the following provides the best evidence that cell-signaling pathways evolved early in the history of life?
A) Cell-signaling pathways are seen in "primitive" cells such as bacteria and yeast.
B) Bacteria and yeast cells signal each other in a process called quorum sensing.
C) Signal transduction molecules identified in distantly related organisms are similar.
D) Most signals in all types of cells are received by cell surface receptors.
C) During apoptosis, cellular agents chop up the DNA and fragment the organelles and other cytoplasmic components of a cell.
Cells that are infected, damaged, or have reached the end of their functional life span often undergo "programmed cell death." This controlled cell suicide is called apoptosis. Select the appropriate description of this event on a cell's life cycle.
A) Apoptosis is regulated by cell surface receptors that signal when a cell has reached its density-dependent limits.
B) During apoptosis, dying cells leak out their contents, including digestive enzymes that also destroy healthy cells.
C) During apoptosis, cellular agents chop up the DNA and fragment the organelles and other cytoplasmic components of a cell.
D) Each cell organelle has protein signals that initiate the breakdown of the organelle's components, which leads to cell death.
D) ligand-gated ion channel
Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of substances on opposite sides of the membrane?
A) intracellular receptor
B) G protein-coupled receptor
C) phosphorylated receptor tyrosine kinase dimer
D) ligand-gated ion channel
A) dimerization and phosphorylation.
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is characterized by A) dimerization and phosphorylation.
B) dimerization and IP3 binding.
C) a phosphorylation cascade.
D) GTP hydrolysis.
B) intracellular receptors are present only in target cells.
Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as aldosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because
A) only target cells retain the appropriate DNA segments.
B) intracellular receptors are present only in target cells.
C) only target cells have enzymes that break down aldosterone.
D) only in target cells is aldosterone able to initiate the phosphorylation cascade that turns genes on.
C) lysis of the cell
Apoptosis involves all but which of the following?
A) fragmentation of the DNA
B) cell-signaling pathways
C) lysis of the cell
D) digestion of cellular contents by scavenger cells
C) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells.
Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells?
A) Enzymatic activity was proportional to the amount of calcium added to a cell-free extract.
B) Receptor studies indicated that epinephrine was a ligand.
C) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells.
D) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine and glycogen phosphorylase were mixed.
C) activation of G protein-coupled receptors.
Protein phosphorylation is commonly involved with all of the following except
A) activation of receptor tyrosine kinases.
B) activation of protein kinase molecules.
C) activation of G protein-coupled receptors.
D) regulation of transcription by signaling molecules.
C) DNA and proteins
Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of which of the following macromolecules? A) DNA and RNA
B) DNA only
C) DNA and proteins
D) DNA and phospholipids
D) 64
Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of six cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how many cells?
A) 12
B) 16
C) 32
D) 64
B) 10
In a diploid cell with 5 chromosome pairs (2n = 10), how many centromeres will be found in a nucleus at G2 of the cell division cycle?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
D) in the S phase of the cell cycle
Scientists isolate cells in various phases of the cell cycle. They isolate a group of cells that have 1 1/2 times more DNA than G1 phase cells. What is the most likely part of the cell cycle from which these cells were isolated?
A) between the G1 and S phases in the cell cycle
B) in the G2 phase of the cell cycle
C) in the M phase of the cell cycle
D) in the S phase of the cell cycle
A) normal growth and cell function
G1 is associated with which of the following cellular events?
A) normal growth and cell function
B) DNA replication
C) the beginning of mitosis
D) break down of the nuclear membrane
B) centrosome
What is the name of the microtubule-organizing center found in animal cells as an identifiable structure present during all phases of the cell cycle?A) centriole
B) centrosome
C) centromere
D) kinetochore
B) attachment of microtubules to kinetochores
In the cells of many eukaryotic species, the nuclear envelope has to disappear to permit which of the following events in the cell cycle?
A) DNA synthesis
B) attachment of microtubules to kinetochores
C) separation of the centrosomes
D) condensation of the chromosomes
D) separation of sister chromatids
The mitotic spindle plays a critical role in which of the following processes?
A) splitting of the cell (cytokinesis) following mitosis
B) triggering the compaction and condensation of chromosomes
C) dissolving the nuclear membrane
D) separation of sister chromatids
A) alignment of chromosomes on the equator of the cell
Metaphase is characterized by ________.
A) alignment of chromosomes on the equator of the cell
B) separation of the centromeres
C) cytokinesis
D) separation of sister chromatids
B) They create tension by pulling toward opposite poles.
In what way do kinetochore microtubules facilitate the process of splitting the centromeres?
A) They use motor proteins to hydrolyze the centromere at specific arginine residues.
B) They create tension by pulling toward opposite poles.
C) They slide past each other like actin microfilaments.
D) They phosphorylate the centromere, thereby changing its conformation.
C) The cell underwent repeated mitosis, but cytokinesis did not occur.
Certain cell types normally have several nuclei per cell. How could such multinucleated cells be explained?
A) The cell underwent repeated cytokinesis but no mitosis.
B) The cell underwent repeated mitosis with simultaneous cytokinesis.
C) The cell underwent repeated mitosis, but cytokinesis did not occur.
D) The cell had multiple S phases before it entered mitosis.
B) Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell wall building blocks on the metaphase plate; animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
How is plant cell cytokinesis different from animal cell cytokinesis?
A) The contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates; the cleavage furrow in animal cells is composed of contractile proteins.
B) Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell wall building blocks on the metaphase plate; animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
C) The structural proteins of plant cells separate the two cells; in animal cells, a cell membrane separates the two daughter cells.
D) Plant cells divide after metaphase but before anaphase; animal cells divide after anaphase.
A) the cleavage furrow of eukaryotic animal cells
FtsZ is a bacterial cytoskeletal protein that forms a contractile ring involved in binary fission. Its function is analogous to ________.
A) the cleavage furrow of eukaryotic animal cells
B) the cell plate of eukaryotic plant cells
C) the mitotic spindle of eukaryotic cells
D) the microtubule-organizing center of eukaryotic cells
D) prophase
At which phase of the cell cycle do centrioles begin to move apart in animal cells?
A) anaphase
B) telophase
C) metaphase
D) prophase
C) 20
In a diploid cell with 5 chromosome pairs (2n = 10), how many sister chromatids will be found in a nucleus at prophase of mitosis?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
B) 20
If there are 40 centromeres in a cell at anaphase of mitosis, how many chromosomes will be found in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 80
A) the mitotic spindle
Taxol is an anticancer drug extracted from the Pacific yew tree. In animal cells, Taxol prevents microtubule depolymerization. Thus, Taxol stops mitosis by interfering with which of the following structures or processes?
A) the mitotic spindle
B) cytokinesis
C) centriole duplication
D) chromosome condensation
C) shortening of microtubules
Movement of the chromosomes during anaphase would be most affected by a drug that prevents which of the following events in mitosis and cell division?A) nuclear envelope breakdown
B) elongation of microtubules
C) shortening of microtubules
D) formation of a cleavage furrow
C) G2
Measurements of the amount of DNA per nucleus were taken on a large number of cells from a growing fungus. The measured DNA levels ranged from 3 to 6 picograms per nucleus. In which stage of the cell cycle did the nucleus contain 6 picograms of DNA?
A) G1
B) S
C) G2
D) G0
C) 16
A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms of DNA would be found in a nucleus at prophase of mitosis?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 24
C) Enzymatic cleavage of cohesin.
The beginning of anaphase is indicated by which of the following processes?
A) Loss of kinetochores from the chromatids.
B) Attachment of sister chromatids to each other by cohesin.
C) Enzymatic cleavage of cohesin.
D) Disappearance of the nuclear membrane.
B) anaphase
During which phase of mitosis do the chromatids become chromosomes?
A) telophase
B) anaphase
C) prophase
D) metaphase
C) a groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei
A cleavage furrow is ________.
A) a ring of vesicles forming a cell plate
B) the separation of divided prokaryotes
C) a groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei
D) the space that is created between two chromatids during anaphase
A) B
Use the figure to answer the question below.
The unlettered circle at the top of the figure shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes that have not yet replicated. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is black, and the other is gray. The circles labeled A to E show various combinations of these chromosomes.
What is the correct chromosomal condition at prometaphase of mitosis?
A) B
B) C
C) D
D) E
D) E
Use the figure to answer the question below.
The unlettered circle at the top of the figure shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes that have not yet replicated. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is black, and the other is gray. The circles labeled A to E show various combinations of these chromosomes.
What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at telophase of mitosis?
A) B
B) C
C) D
D) E
C) formation of telophase nuclei
Use the figure to answer the question below.
If the cell whose nuclear material is shown in the figure continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next?
A) spindle fiber formation
B) nuclear envelope breakdown
C) formation of telophase nuclei
D) synthesis of chromatids
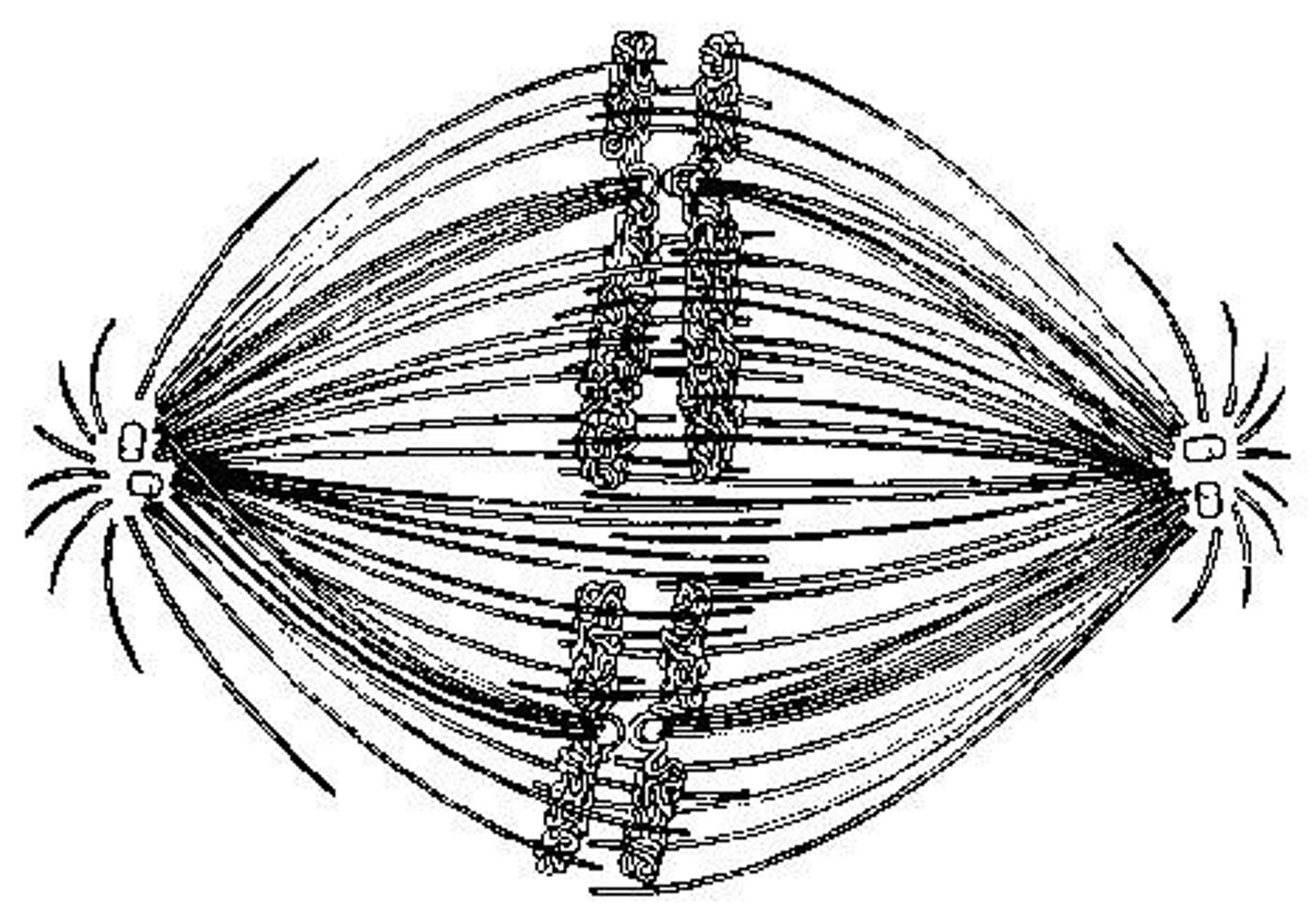
A) I and V
Use the figure to answer the question below.
In the figure, G1 is represented by which numbered part(s) of the cycle?
A) I and V
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
Use the figure to answer the question below.
In the figure, which number represents DNA synthesis?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C) III only
Use the figure to answer the question below.
In the figure, at which of the numbered regions would you expect to find cells at metaphase?
A) II and IV
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
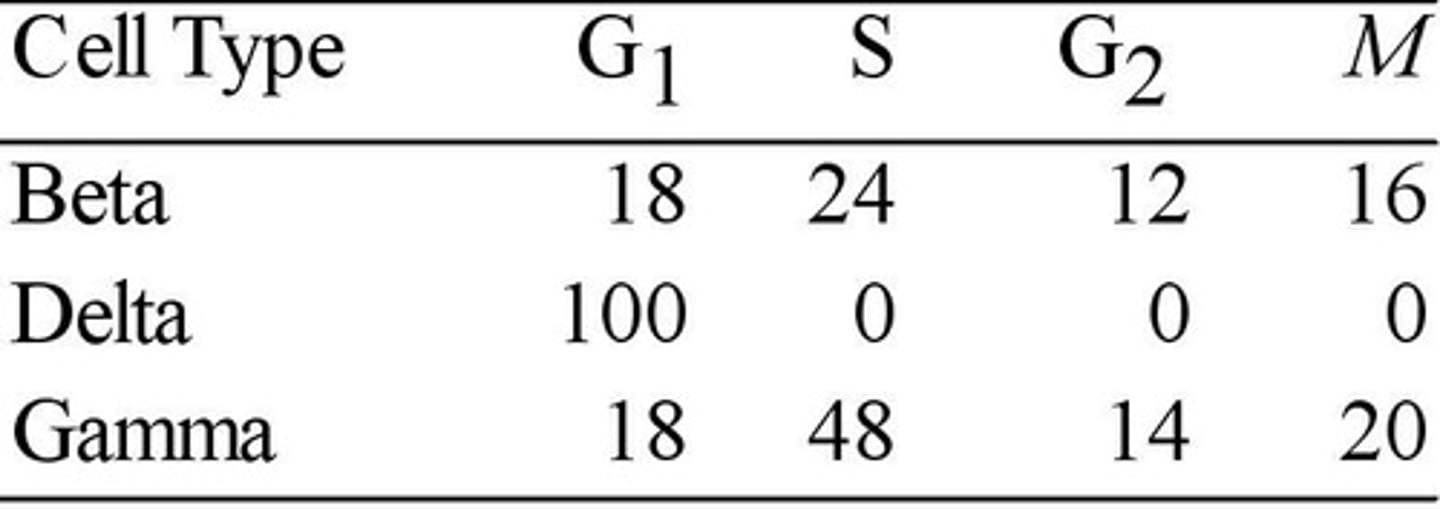
A) Gamma contains more DNA than beta.
Use the data in the accompanying table to answer the question.
Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
The data in the table were obtained from a study of the length of time spent in each phase of the cell cycle by cells of three eukaryotic organisms designated beta, delta, and gamma.
Which of the statements is the best explanation for the difference between time spent in S phase by beta and gamma?
A) Gamma contains more DNA than beta.
B) Beta and gamma contain the same amount of DNA.
C) Beta cells reproduce by binary fission and gamma cells reproduce by mitosis and cytokinesis.
D) Beta is a plant cell and gamma is an animal cell.
C) Chromosomes are segregated by a mitotic spindle, but the nuclear envelope remains intact during division.
Certain unicellular eukaryotes, including diatoms and some yeasts, have mechanisms of nuclear division that may resemble intermediate steps in the evolution of mitosis. Which of the following is a characteristic feature of nuclear division in these organisms?
A) They reproduce by binary fission in their early stages of development and by mitosis when they are mature.
B) They have circular chromosomes that are segregated by a mitotic spindle.
C) Chromosomes are segregated by a mitotic spindle, but the nuclear envelope remains intact during division.
D) Chromosomes are segregated by attachment to the plasma membrane.
D) They show some but not all of the evolutionary steps toward complete mitosis.
Several organisms, primarily protists, have what are called intermediate mitotic organization. What is the most probable hypothesis about these intermediate forms of cell division?
A) They represent a form of cell reproduction that must have evolved completely separately from those of other organisms.
B) They rely on totally different proteins for the processes they undergo.
C) They may be more closely related to plant forms that also have unusual mitosis.
D) They show some but not all of the evolutionary steps toward complete mitosis.
B) What is the length of the S phase of the cell cycle?
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly synthesized DNA and, therefore, can be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student- faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into a culture of dividing human cells at specific times. Which of the following questions might be answered by using the method described?
A) How many cells are produced by the culture per hour? B) What is the length of the S phase of the cell cycle?
C) How many picograms of DNA are made per cell cycle?
D) When do spindle fibers attach to chromosomes?
B) Infection causes lymphocytes to divide more rapidly.
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and, therefore, can be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides to study the incorporation of labeled nucleotides into a culture of lymphocytes. They found that the lymphocytes incorporated the labeled nucleotide at a significantly higher level after a pathogen was introduced into the culture. What might they conclude from this observation?
A) The pathogen consumed radiolabeled nucleotides.
B) Infection causes lymphocytes to divide more rapidly.
C) Infection causes lymphocytes to increase in size.
D) Infection causes lymphocyte cultures to skip some parts of the cell cycle.
C) a plant cell in the process of cytokinesis
Through a microscope, you can see a cell plate beginning to develop across the middle of a cell and nuclei forming on either side of the cell plate. This cell is most likely ________.
A) an animal cell in the process of cytokinesis
B) an animal cell in anaphase of mitosis
C) a plant cell in the process of cytokinesis
D) a plant cell in metaphase of mitosis
D) replication of the DNA
Which of the following events occurs during interphase of the cell cycle?
A) condensation of the chromosomes
B) separation of the spindle poles
C) spindle formation
D) replication of the DNA
D) cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the animal cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B?
A) spindle formation
B) spindle attachment to kinetochores
C) movement of chromosomes to the poles during anaphase
D) cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis