chem 2 exam 4 chapter 18
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms


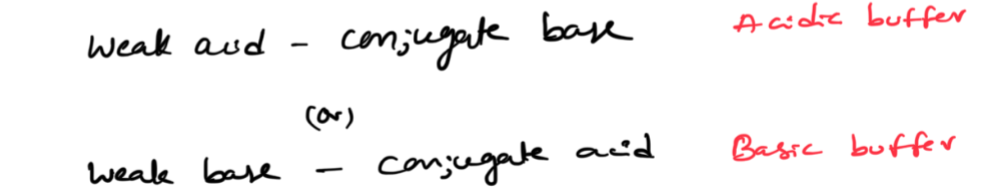

what happend when you add each


weak acids
Acetic acid: CH3COOH (organic) or
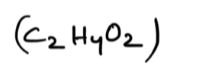
Hydrofluoric acid: HF
Strong Acids

Hydrochloric acid: (HCl)
Hydrobromic acid: (HBr)
Hydroiodic acid: (HI)
Sulfuric acid: (H₂SO₄)
Nitric acid: (HNO₃)
Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
Perchloric acid: (HClO₄)
Chloric acid: (HClO₃)
Strong Bases

Sodium Hydroxide: NaOH
Potassium Hydroxide: KOH
Weak bases

Ammonia: NH3
Amine (organic): R [any organic compound] -NH2
Aniline (organic):C6H5NH2
Pyridine (organic):C5H5N
Sodium Bicarbonate: NaHCO3
Sodium Carbonate: Na2CO3
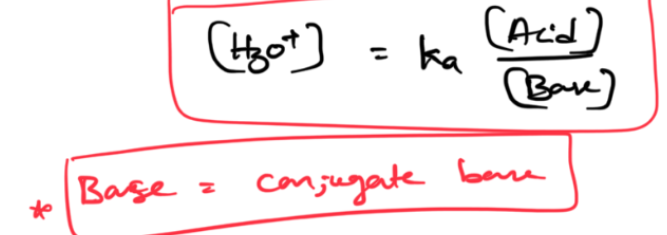
pka
-log(ka)
Henderson Equation —> ONLY FOR BUFFERS
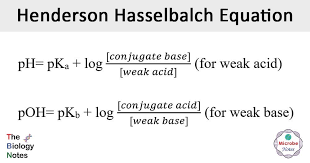
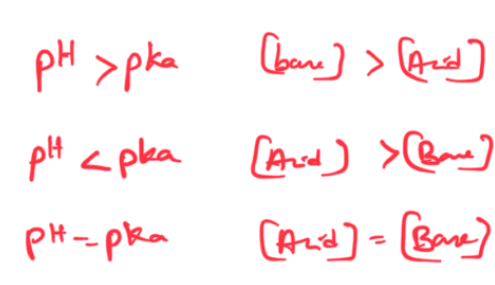
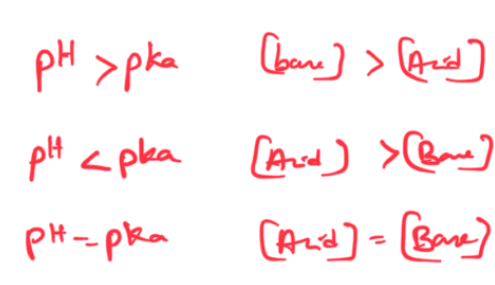
number of moles
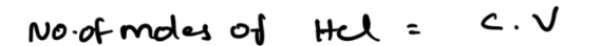
the volume in liters
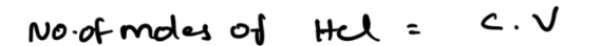
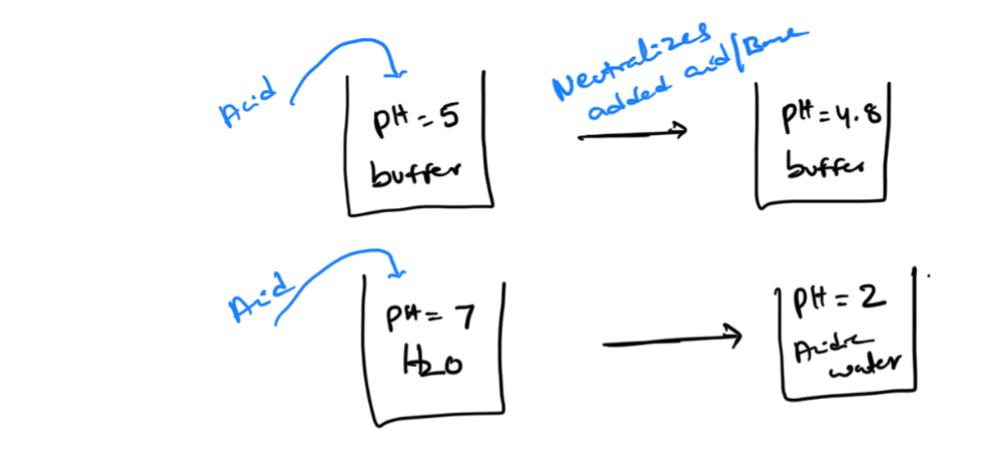
BUFFER EFFECTIVENESS: 1. Buffer capacity
A good buffer can nuetralize higher amounts of external acid/base
The amount of acid and cojugate base—
equal amounts—> higher capacity—> better the buffer—> ph=7
Higher [acid] and [conjugate base] is more effective
higher [acid] is more effective if we are adding external base
higher [base] is more effective if we are adding external acid
BUFFER EFFECTIVENESS: Buffer range
Range 0-10 times [base]/[acid]
OR [base]/[acid]= .1-10
ph= pka-1 and ph= pka+1
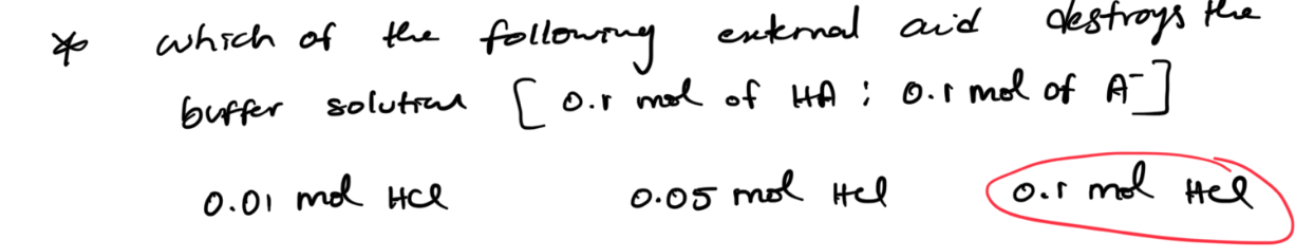
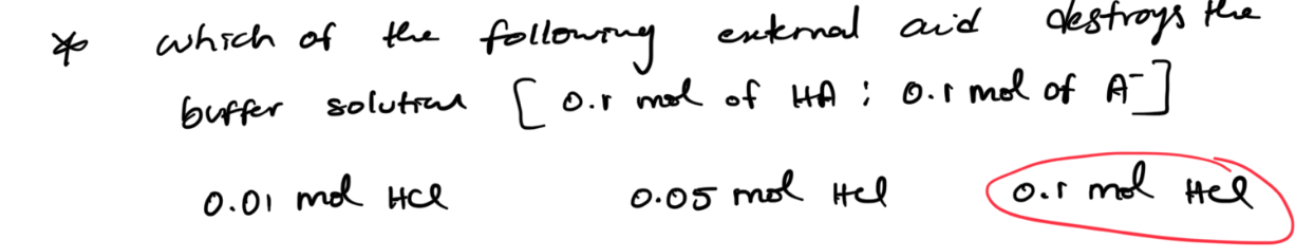
all of the external acid (HCl) is used to destroy the base, so pick the answer with the one that has the same amount of base
will it become acidic/ basic when adding….
Neutral solution (pH ≈ 7): Formed from a strong acid and a strong base (e.g., NaCl, KNO₃).
Acidic solution (pH < 7): Formed from a strong acid and a weak base (e.g., NH₄Cl).
Basic solution (pH > 7): Formed from a weak acid and a strong base (e.g., NaCH₃COO, KCN).
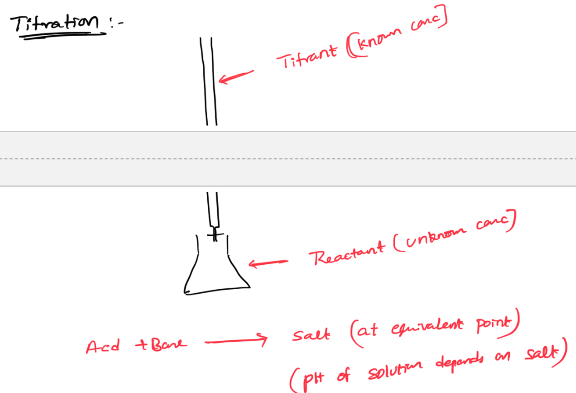

titration curve
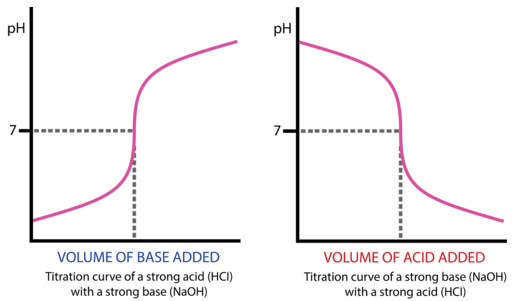

Equivalence point-
N.O of moles of titrant= # moles of reactant
excess
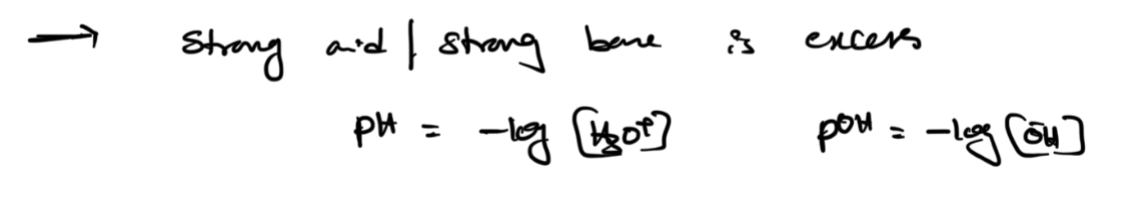
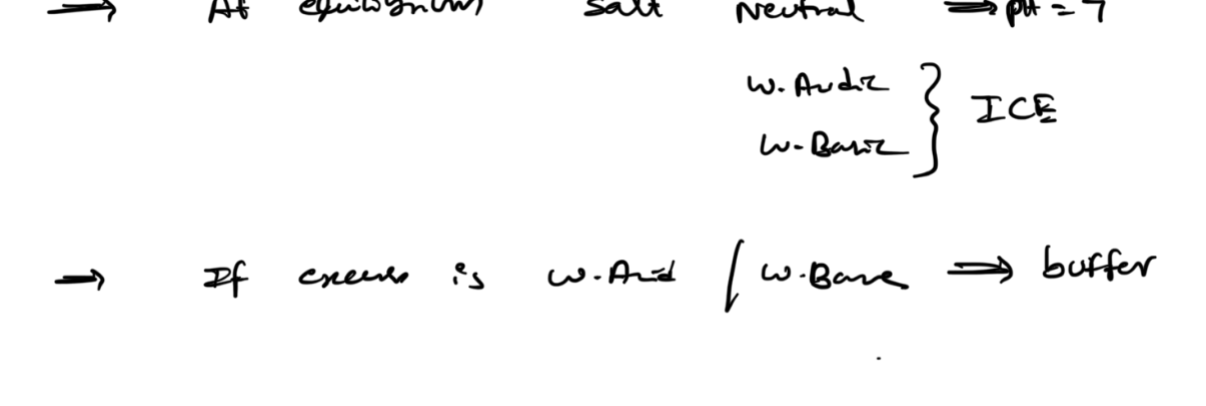
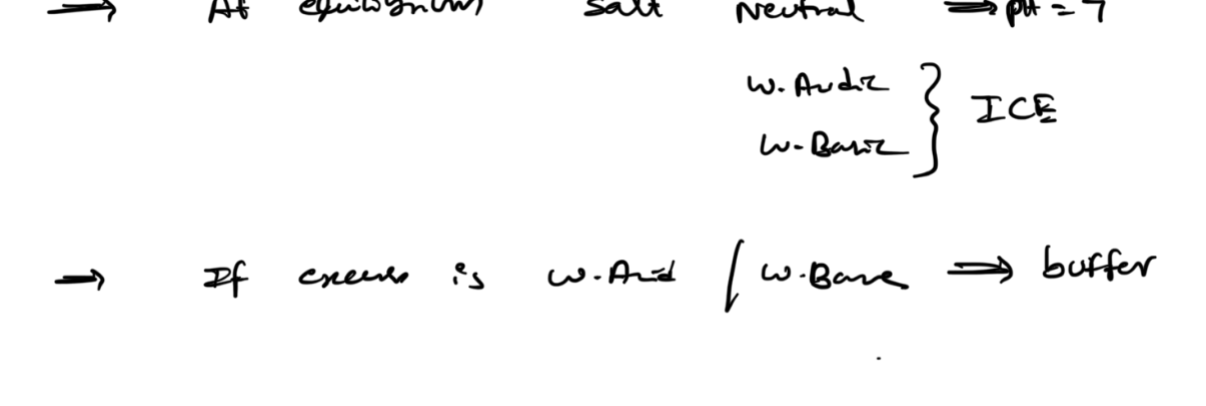
molar solubility
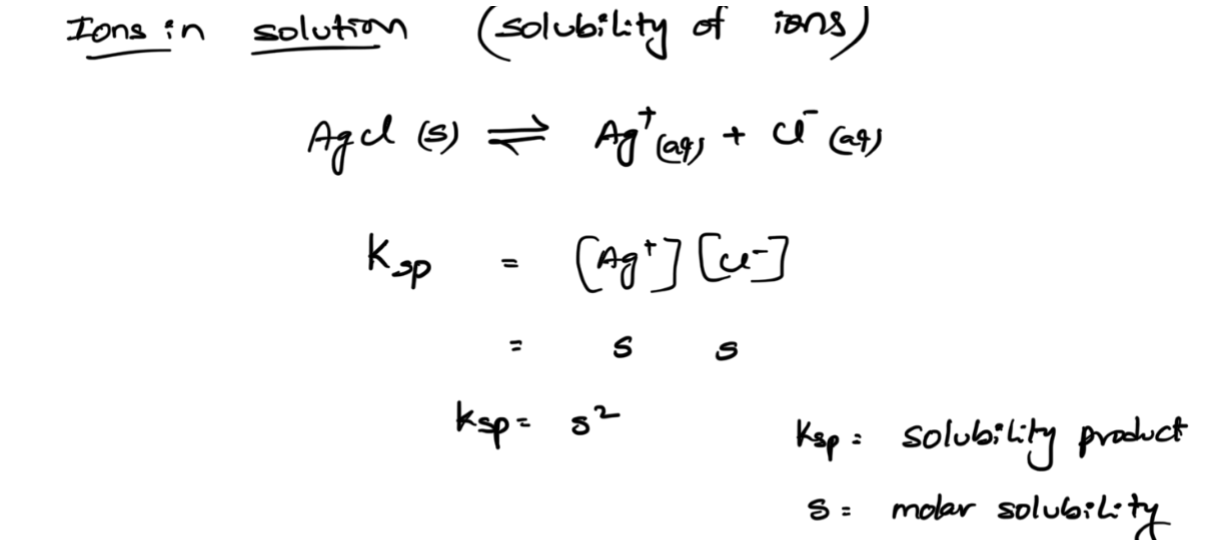
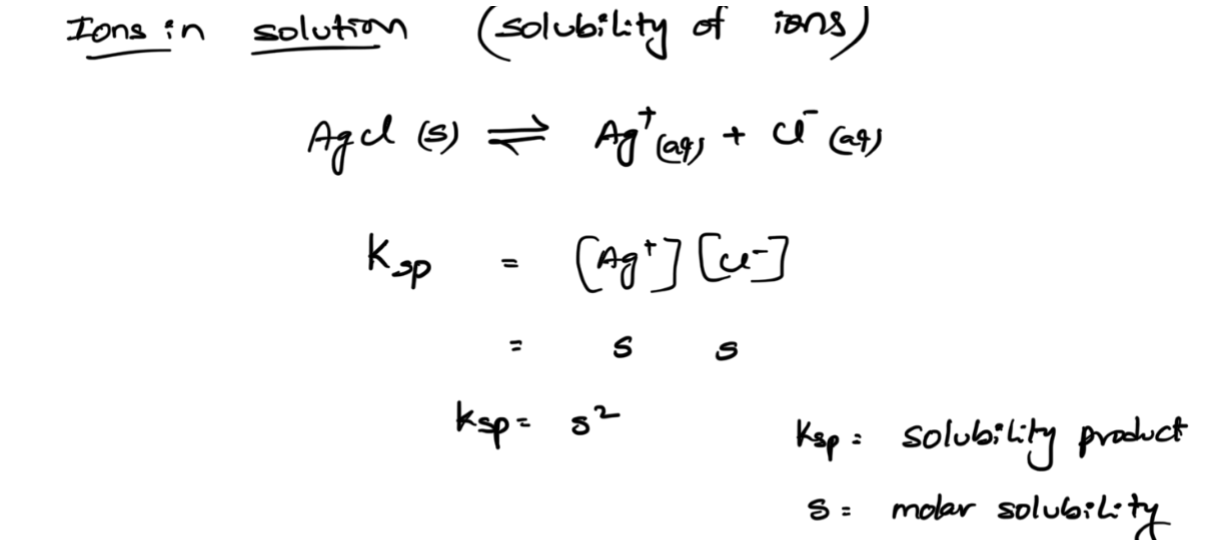
common ion effect


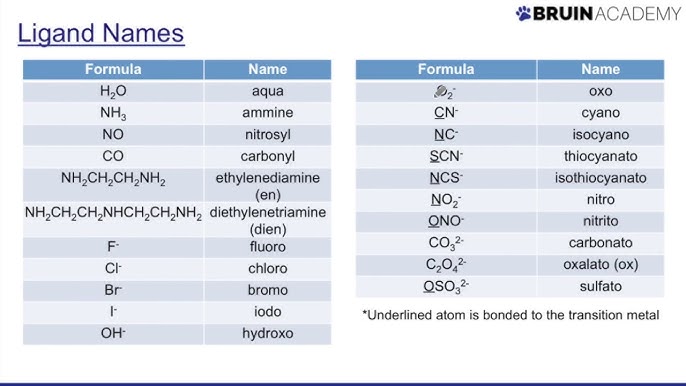
ligands
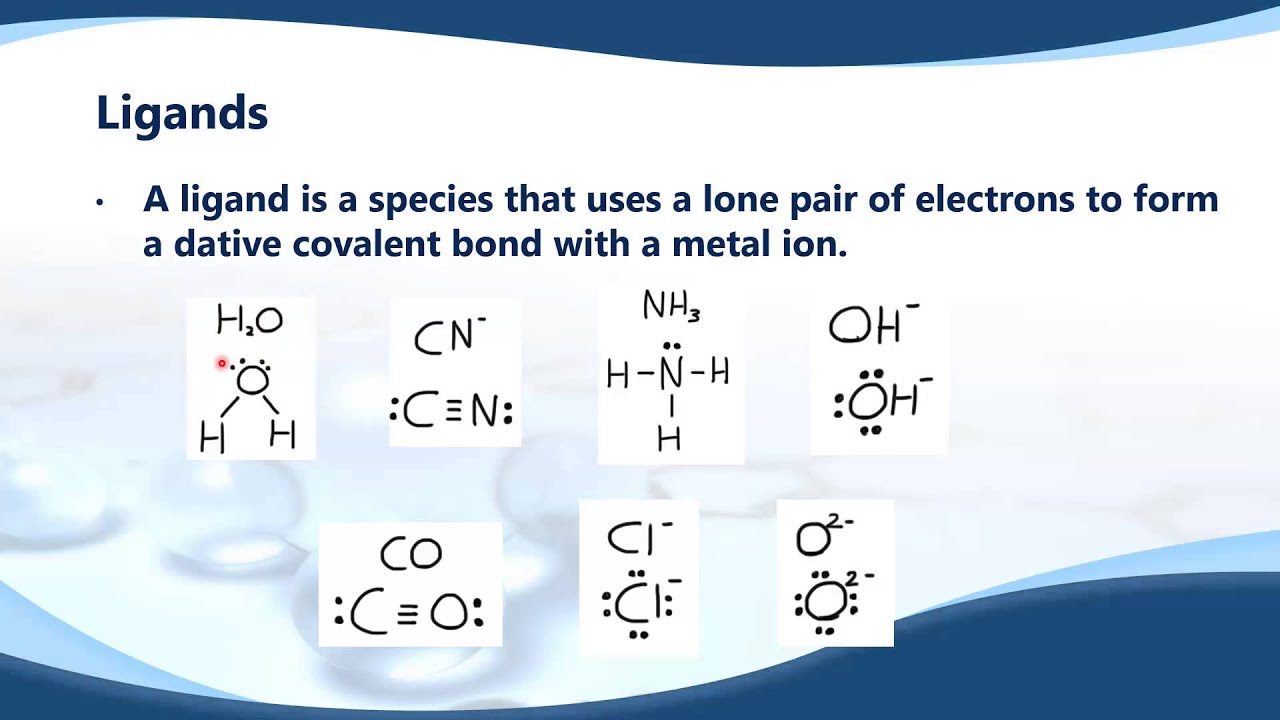
they increase solubility and maek it more favorable
complex compound
chemical structures with a central metal atom or ion bonded to surrounding ligands
Summary of Q vs. Ksp
Comparison Meaning Result
Q < Ksp Unsaturated More solid dissolves
Q = Ksp Saturated System at equilibrium
Q > Ksp Supersaturated Precipitation occurs