Fashion Fabrics Exam 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Woven types
plain, twill, satin, jacquard, extra yarn, dobby, pile, slack tension
Knit types
weft-single, double
warp-tricot, raschel
pile
Woven thread count
Balanced: similar # of yarns/inch in both directions
Unbalanced: more yarns/inch in both directions
Knit gauge
Stitches per inch across the fabric
Higher gauge= finer loops
Lower gauge= courser loops
Higher thread count/gauge
-finer yarns
-smoother hand
-better flexibility/softer drape
-better abrasion resistance
-better dimensional stability
-better cover
Lower thread count/gauge
-bulkier yarns
-coarser hand
-more structured drape
-poorer abrasion resistance
-can be less opaque
-less durable
Extremely light or sheer weight clothes
sheer or gauzy fabrics
Light or top weight clothes
blouses, shirting, light dresses
Medium weight clothes
heavier shirting or lighter bottoms
Bottom weight clothing
slacks, suiting, lighter jackets
Heavy weight clothing
work clothes, heavier coats, traditional denim
Heavy weight properties
-more fiber
-more structured drape
-better durability
-potential thicker cover
Light weight properties
-less fiber
-softer drape
-softer hand
-potential thin cover
Woven fabric definition
2 sets of yarns interlacing at right angles to one another
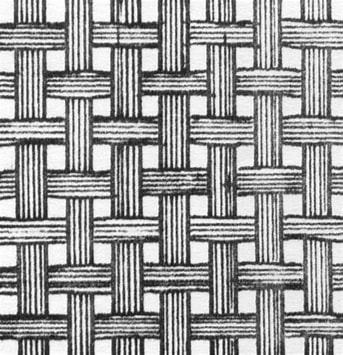
Plain weave
-grid-like appearance (1×1)
-half basket (2×1)
-most common, least expensive
-can improve resiliency and flexibility

Twill weave
-diagonal ridges of face
-floats
-2/1 or 3/1
-better flexibility and resiliency
-allows for higher thread counts

Broken twill
-herringbone
-houndstooth

Satin weave
-smooth face with long floating yarns
-at least 4/1
-better resiliency and higher thread count
-more flexible and fluid drape
snags
-good to excellent luster
-can unravel
Satin vs. sateen
satin: filament yarns, typically silk or polyester, lustrous, more fluid
sateen: spun yarns, cotton blend, subdued luster, more structured

Jacquard weave(complex)
-larger, complex designs woven in
-floats that snag
-created on jacquard loom
-heavy weight
ex: coats and accessories
Jacquard damask vs. brocade
damask: 1 or 2 colors, reversible, flat and curvilinear design, either filaments or spun
brocade: richly colored, woven curvilinear design, metallics, filaments

Dobby(complex)
-small, geometric woven in with floating yarns.
-flat: dobby shirting or lining
-textured: pique and waffle cloth

Pile(complex)
-extra sets of yarns on the surface-looped or cut
-bottom to heavy weight
-warmer
-softer hand
-good resilience
Cut vs uncut pile
cut: fuzzy ends on surface, velvet, corduroy
uncut: loops on surface, terrycloth
Velvet vs. velveteen
velvet:
-cut warp, longer pile
-filament
-better drape and luster
-distinct face and back
-formal
velveteen:
-cut weft, shorter pile
-spun
-more structured
-distinct face and back

Extra yarn weave
-extra yarn floats
-floating or clipped yarns
Ex: dotted swiss and shirtings
Why are extra yarn fabrics used?
texture, durability, unique designs, functional properties-insulation and moisture-wicking

Slack-tension(complex)
-puckering along alternating warp yarn tension
-expensive because of slow process
-no ironing
-crinkle look
Knit fabric
yarn creates interconnected loops, better elasticity than weaves, susceptible to snags and distortion
Knit stitches
knit: V’s, purl: waves, tuck: openwork, ex-pointelle or miss floats
Courses
across in knits
Wales
length in knits
Warp
yarns running parallel to selvage (stronger), no stretch
Weft
yarns running perpendicular to the selvage (crosswise grain), little stretch
Woven stretch
most is in the bias of the fabric
Balanced weave
similar number yarns/inch in each direction
Unbalanced weave
more yarns/inch in either warp or weft direction and create ribs and less drape
Which kinds of weaves are more likely to have a higher thread count?
sateen, twill, jaquard, damask
How does yarn type affect thread count?
-finer yarns allow for more thread
-thicker yarns have fewer thread count
-single-ply have a higher thread count
-finish and treatment can support higher thread count
Balanced weave properties
-better abrasion resistance
-lower resiliency
-more structure
-poor luster
Unbalanced weave properties
-ribbed surface
-less fluid
-less resilient
-lower abrasion resistance
Knit good properties
-faster to produce
-increased elasticity
-fluid drape
-better wrinkle recovery
-can insulate well
Knit bad properties
-distortion
-snag and pull
-run or ladder
Weft knits
-one yarn feeds across fabric
-single or double
-better elasticity
-snags and runs

Single weft (jersey)
knit stitches on face, purl on reverse
-top weight
-fluid drape
-bulkier yarn, lower gauge=sweater knit
drawbacks:
-edges curl
-shape is distorted
Double knit
made with two sets of of needles
-less distortion
-more stability
-wide range of yarns, end uses
ex: rib, interlock, some sweater knits

Rib knit
Alternating rib and purl stitches
-increased elasticity
-cuffs and collars
-thicker yarns=sweater knits

Jacquard knit
-pattern knitted in with different color yarns
-can be single or double

Pointelle
-open work patterns made with tuck stitches
-typically lighter weight

Waffle knit
adds more bulk through texture and extra yarn layers
Warp knits
-one yarn or set of yarns fed in across the fabric, in courses
-loops fed in wales, zigzagging the length of fabric
-less susceptible to running or laddering
-less elasticity
-made on flat knitting machines
Tricot
fastest knit production
-finer/higher gauge and more tightly
-filament
-uniform filament
-knit stitches on face
-horizontal floats and reverse underlaps
Tricot end uses
lingerie, sleepwear, swimwear, and activewear

Raschel
knitted in patterns and openwork
-filament or spun
common uses: laces, crochets, nets, sweater knits, and power mesh
Filament
long, continuous strands
Spun/staple
short, fuzzy and need to be spun
Knits apparel use
sweaters, outerwear, comfy clothing
Knits vs. woven
knits are more elastic, soft, wrinkle resistant, and less durable and wovens are durable, wrinkle, and have more structure