Syllables and Sequences
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Tutorial 6: Linking Ideas
VOT differentiates “voicing” for stop consonants Stop consonant voicing in English can be differentiated perceptually through: (near-)zero VOT for voiced stops positive VOT for voiceless stops We are perceptually sensitive to small phonetic differences! The three-way distinction for place of articulation is sub-phonemic: they are phonetic characteristics of these different consonants, but these characteristics are not used by themselves to create phonological distinctions Nevertheless, this same pattern is used in perception Takeaway: we are perceptually sensitive to phonetic patterns, even if they are not necessarily phonologically distinctive
What is a syllable?
There is no definition that phoneticians and phonologists can agree upon But there is much evidence that the syllable has a psychological reality: Speakers are able to count the syllables in a word Speakers often agree on syllable boundaries Children can clap syllables before they can read People who have not been exposed to alphabetic writing systems have greater difficulty segmenting phonemic units than syllables Many writing systems are syllabic where each symbol represents a syllable (e.g., Japanese, Chinese) Slips of the tongue occur with whole syllabic constituents: a crushing blow → a blushing crow, *a brushing clow
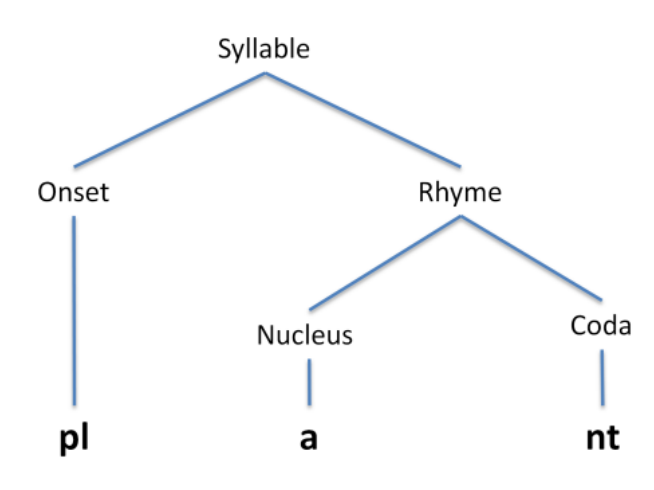
Syllable structure
Onset One or more consonants Rhyme Nucleus Almost always a sonorant, and usually a vowel The only required part of a syllable Coda One or more consonants
Possible syllable types in English
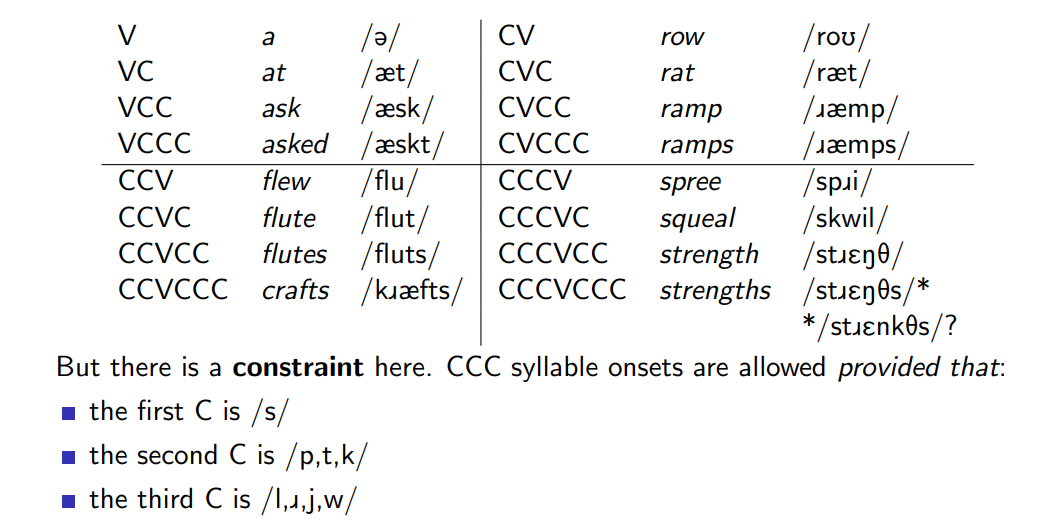
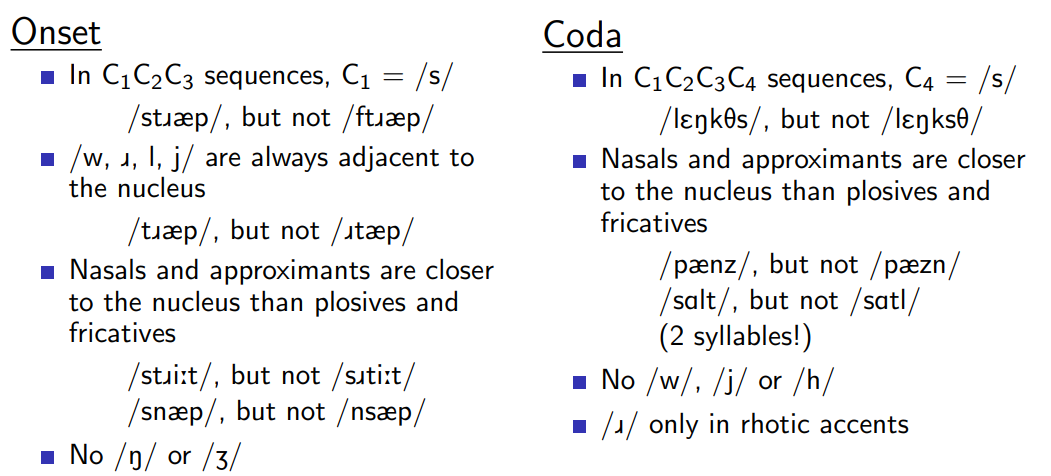
English syllable constraints
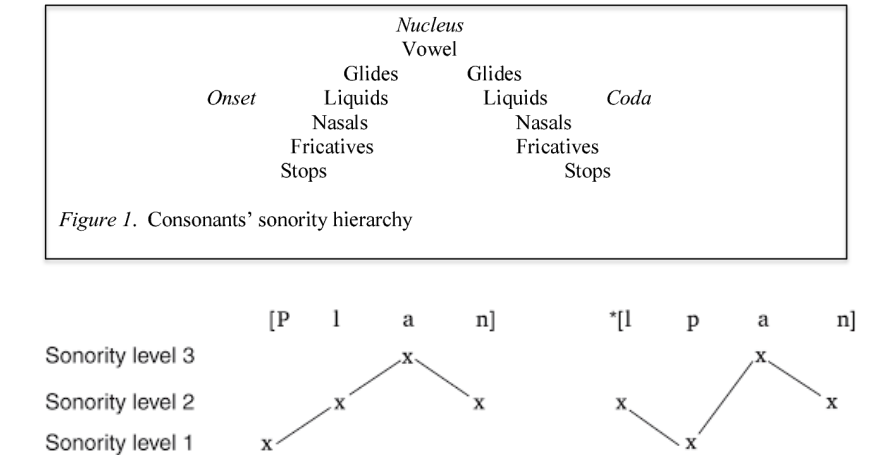
Sonority hierarchy
Stress prominence
Stress on syllables within a word ANswer, SWEAter, BROken aHEAD, reSULT, caREER Stressed syllables tend to be: produced with more modal voice quality spoken more slowly spoken more carefully hence more peripheral vowel quality
Lexical stress in phrases
When words are combined into phrases, lexical stress pattern can alter afterNOON AFternoon NAP Causes include: when words form compounds “black board” vs. “blackboard” “long island” vs. “Long Island” preserving rhythm, avoiding sequence of stressed syllables (“stress clash”) “thirteen”... but “thirteen companies” “Japanese”... but “Japanese institute” Hard to predict!
EMA signal word identification
Electromagnetic articulography/articulometry (EMA)
Effect of damping on mechanical dynamics
Under-damped Target overshoot Over-damped Target reached very slowly Critically damped Target reached as quickly as possible without overshoot
Gesture undershoot
Articulatory undershoot will have an effect on speech sounds e.g. if the tongue fails to reach the articulatory position for a peripheral vowel, then it may appear to sound centralized If the articulators fail to close for a plosive, or fail to create a narrow-enough channel for a fricative then the whole sound may be weakened (this is called lenition) A plosive might turn into a fricative e.g. “recognition” as [ôEX@KnIS@n] A fricative into an approximant e.g. “saving” as ["seIVIN]
Gesture timing requires planning
Different articulators have different critically-damped trajectories If different gestures start at the same time, they won’t reach the target at the same time So: different articulatory gestures start at different times
Different starts = different gestural anticipation
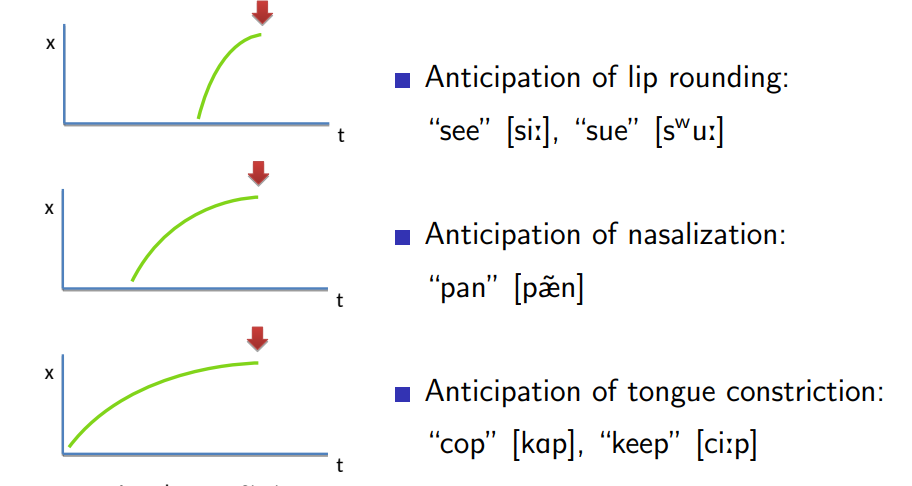
Consequences
Speaking sequences of speech sounds — involving multiple articulators each with different dynamical properties — is going to take a lot of planning. We need to allow sufficient time for each articulator to reach its target location and we need to ensure that the slower moving articulators are in position for when they are needed to synchronise with the faster moving articulators. Articulatory planning to allow rapid articulation causes contextual effects, these are changes to the articulation of phonological segments depending on the context
Contextual effects
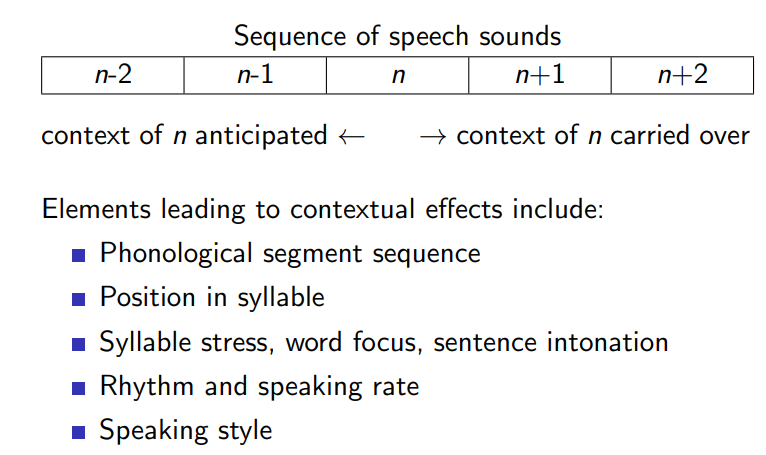
Contextual effect: coarticulation
Joint articulation A single articulator for multiple segments The articulator is “shared” between segments Anticipatory (“regressive”) cop [k ¯ Ap] vs. keep [k ff ip] heat [i ˚ it] vs. hot [A ˚ At] bad [bæd] vs. ban [b˜æn] Carry-over (“perseverative”) please [pl ˚ iz]
Contextual effect: assimilation
A type of coarticulation Contextual effects in planning that causes a phoneme to become more similar to an adjacent phoneme, often resulting in it appearing as a new phoneme good [gUd] → good boy [gUbbOI] vs. good girl [gUggE~l] have [hæv] → have to [hæftU] happen [hæpm " ] May make underlying phonological sequence ambiguous
Contextual effect: elision (a.k.a. deletion)
Contextual effect in planning appears to lose phonological elements next week [nEkswi:k], don’t ask [doUnæsk] library [laIbôI], February [fEbôI] But they may not be completely deleted... bookcase [bUk:eIs]: gemination preserves timing support [s:ph Oôt]: preserved syllable context perfect memory: tongue tip gesture preserved
Contextual Effects Summary
Coarticulation Effect of multiple phonological segments on single articulator (sound segments are modified but identifiable) Assimilation Blurring of phonological segments (sound segments are ambiguous) Elision Loss of phonological material in phonetic form (sound segments are acoustically absent)
Connected speech: speech is not like “beads on a string”
Rapid, smooth, continuous movements of the articulators No explicit breaks in articulation between segments, syllables, or words No explicit breaks in the spectrographic pattern between segments, syllables, or words Pauses that do occur tend to be at phrase boundaries
Lecture 7: Big Ideas
Syllables are intuitive units of speech planning Languages place constraints on syllable structure The dynamics of articulation mean that speech must be planned to ensure appropriate sounds are produced at normal speaking rates Planning creates anticipatory and carry-over contextual effects: coarticulation, assimilation, and elision Thus, the articulatory and acoustic form of speech segments depends on context There are not necessarily precise acoustic cues to segment, syllable, or word boundaries in the signal