Containment - lecture 7 - infectious disease and human rights
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
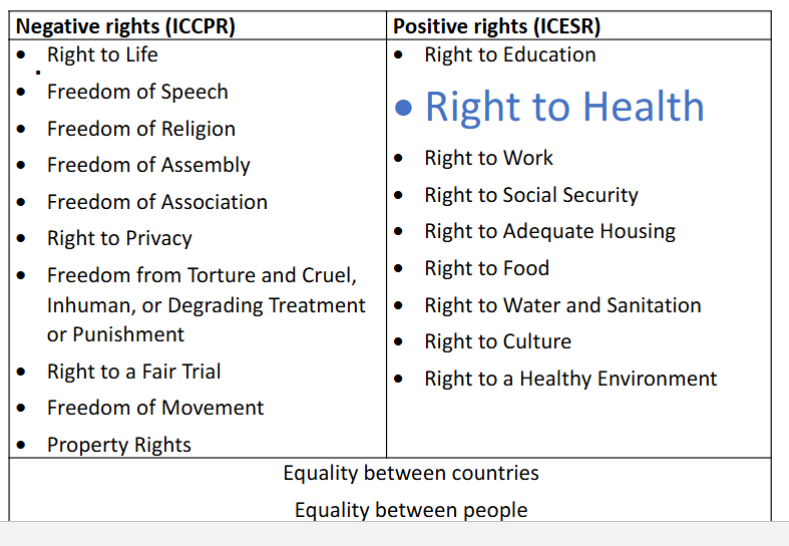
what are the 3 important articles that state the need to take steps to control epidemics
UDHR → universal declaration of human rights
ICESCR → international covenant on economic, social and cultural rights
ICCPR → the right to life
UDHR
Article 25 → standard of living/health/wellbeing
everyone has the right to a standard of living adequate for their health and wellbeing (food, clothing, housing, medical care)
ICESCR
article 12 → the right to health
epidemic prevention and response are core elements of the right to health
requires to set up a health system
the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health
used to be the more russian approach
ICCPR
article 6 → the right to life
American approach
freedom of speech, right of assembly
difference between positive and negative rights
negative rights → governments should not harm your rights (of speech/assembly)
positive rights → organize a lot
4 important rights / terms to know (equality, dignity, liberty, security)
equality → don’t discriminate, treat everybody equal
dignity → treat people with dignity and respect. don’t humiliate
liberty → freedom, autonomy. informed consent. free to make your own decisions.
security → individual safety (no unsafe medicine / treatment). also includes security against diseases (prevention).
human rights based on these 4 principles
important terms about human rights (proportional, universal, subsidiarity, duration)
proportional → if we deviate from human rights it should be proportional (e.g. someone has Ebola, needs to be in isolation, do it for the
universal → for everyone around the world.
subsidiarity → there should not be an alternative that is better (we do not want to violate human rights)
duration → if we violate human rights it should be as short as possible.
timeline of human rights
important;
1978 declaration of Alma Ata
health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well being not just the absence of disease
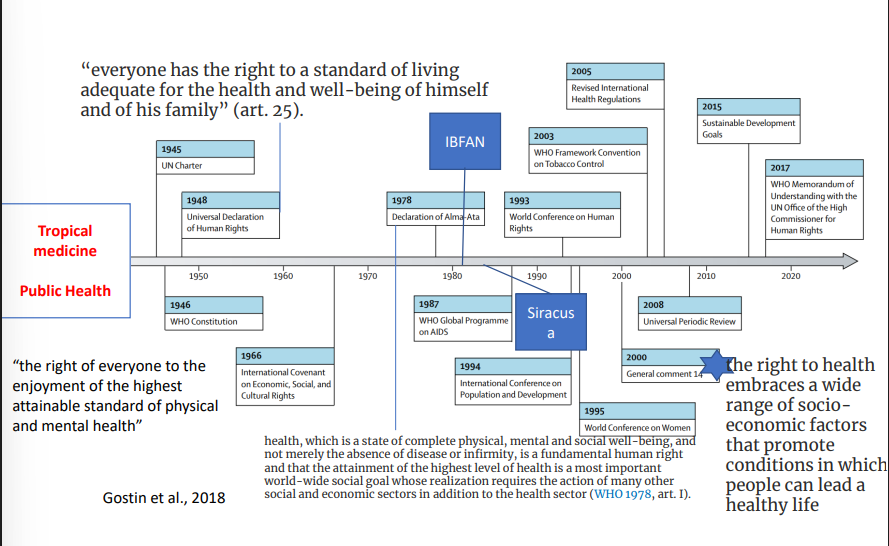
siracusa principle
guidelines adopted by the UN to limit human rights restrictions during public emergencies.
public health may invoke derogations
derogation → is an exemption from or relaxation of a rule or law
They provide guidelines on how and when governments may lawfully restrict certain human rights under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR)
important points → proportional, no alternative, temporal
explain what increases stigma
Discrimination and coercive tools such as compulsory testing, named reporting, travel restrictions, and isolation or quarantine were counterproductive
this violates especially freedom and dignity
HIV AIDS and human rights in Africa
treatment actions group (TAG) → went to court in south Africa
sued pharmaceutical companies that anti retro viral medication should be available
when they sued this pharmaceutical company they used human rights as an argument
PHEIC
public health emergency of international concern
formal declaration by the WHO of "an
extraordinary event which is determined
to constitute a public health risk to other
States through the international spread
of disease and to potentially require a
coordinated international response"formulated when a situation arises that
is "serious, sudden, unusual, or
unexpected", which "carries implications
for public health beyond the affected
state's national border" and "may
require immediate international action"
EXAM 7 moments of public health concern after SARS
swine flu / mexican flu
ebola (west africa)
zika
ebola (democratic republic of congo)
covid
mpox
polio
adverse effects of Covid treatment
47000 additional malaria deaths in 2020
100000 additional tuberculosis deaths.
Severe disruption of vaccination programs
121 (93%) of 130 countries reported mental health
service disruptions, as depression and anxiety
levels greatly increasedCOVID-19 prevalence during Brazil’s first wave was
four-times higher for Indigenous populations than
White Brazilian peoplemore than 200 million additional people faced acute
hungernearly 90 million people into extreme poverty.
Policy was discriminatory and inequitable (migrants)
463 million (1/3) of children could not access (online)
educationViolence against women increased
Leaders ignored evidence; Religious festivals, divine
interventions, not closing businessesCritics / health workers were detained
importance when answering exam question
when something is asked about human rights argue it through the terms talked about (equality, dignity, liberty, security, proportional, universal, subsidiarity, duration)
some topics to think about that could be on the exam → argue via the important terms, equality, dignity, liberty, security
Ebola outbreak 2014-2016 – forced quarantine of individuals and communities
Lack of access to TB services in Nigeria (now)
Stop PCR screening for HIV, HBV, and HCV PCR testing (€5,199,220 per QALY)