Anxiety, Stress, and Addiction Behaviors Overview
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is anxiety?
A feeling of discomfort, apprehension, or dread related to anticipation of danger, the source of which is nonspecific or unknown.
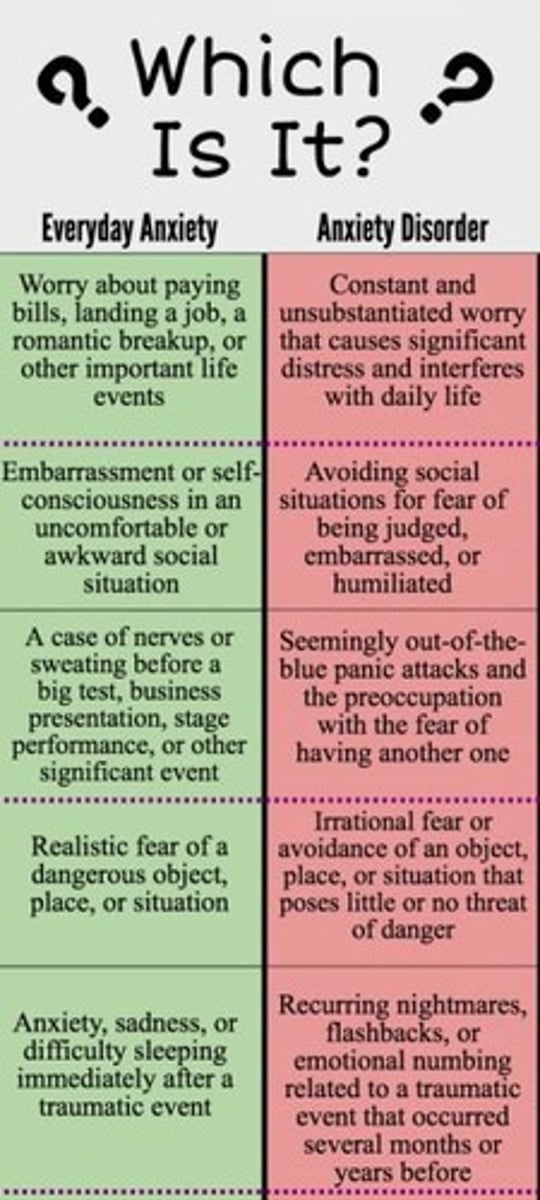
What are the types of anxiety disorders listed in DSM-5?
Separation Anxiety Disorder, Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Selective Mutism, Substance/Medication-Induced Anxiety Disorder, Specific Phobia, Social Anxiety Disorder, Panic Disorder, Agoraphobia, and others.
What is Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)?
Persistent, unrealistic, and excessive anxiety and worry occurring more days than not for at least 6 months, associated with somatic symptoms and causing clinically significant distress or impairment.
What are some causes of Generalized Anxiety Disorder according to different theories?
Psychodynamic Theory: Defects in ego function; Cognitive Theory: Faulty thinking patterns; Biological Aspects: Genetic vulnerability, limbic system dysfunction, elevated blood lactate and norepinephrine, low serotonin.
What nursing interventions are recommended for patients with GAD?
Educate about the illness, provide support services, teach stress management techniques, and ensure safety by not leaving clients with severe anxiety alone.
What are some treatment modalities for managing anxiety?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, individual psychotherapy, behavior therapy, and psychopharmacology including benzodiazepines, anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antihypertensive agents.
What are the expected nursing outcomes for a patient with anxiety?
The patient will recognize unrealistic thoughts, identify signs of escalating anxiety, and maintain anxiety at a manageable level.
What is the new chapter in DSM-5 related to trauma and stressor-related disorders?
It includes Acute Stress Disorder, Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), and Adjustment Disorder.
What is Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
A reaction to extreme trauma characterized by symptoms lasting more than 1 month, including re-experiencing the event, psychological distress, high anxiety, and avoidance of trauma-related stimuli.

What are the characteristic symptoms of PTSD?
Re-experiencing the event, psychological distress, high anxiety or arousal, numbing of responses, avoidance of stimuli, intrusive recollections, and negative alterations in mood.
What is the duration of symptoms for Acute Stress Disorder?
Symptoms last from 2 days up to 4 weeks.
What is the duration of symptoms for Adjustment Disorder?
Symptoms occur within 3 months of the stressor and subside within 6 months after the stressor is removed.
What influences the development of PTSD?
The notes do not specify, but generally, factors may include the severity of the trauma, personal history, and support systems.
What are some somatic symptoms associated with Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
Muscle tension, restlessness, and feeling keyed up.

What role does cognitive behavioral therapy play in managing anxiety?
It helps patients recognize and change faulty thinking patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety.
What types of medications are used for anxiety management?
Benzodiazepines for short-term relief, anxiolytics like Buspar, SSRIs, SNRIs, and antihypertensive agents.
What is the significance of recognizing signs of escalating anxiety?
It allows for timely intervention before reaching panic levels.
What is the expected outcome regarding decision-making for patients with anxiety?
Patients should be able to make independent decisions about their life situations.
What is the impact of trauma on psychological responses?
Trauma can lead to pervasive distress and symptoms such as anxiety, avoidance, and re-experiencing the event.
How does the DSM-5 categorize anxiety disorders?
It categorizes them into various types, including those induced by substances or other medical conditions.
What is the relationship between anxiety and social functioning?
Anxiety can cause significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
What is the role of support services in managing anxiety?
Support services like crisis hotlines, therapy groups, and individual therapy provide essential help for managing anxiety.
What factors influence the severity and duration of a stressor?
Severity and duration of the stressor, extent of anticipatory preparation, exposure to death, numbers affected by life threat, amount of control over reoccurrence, location of trauma, effectiveness of coping resources, presence of pre-existing psychopathology, behavioral tendencies, availability of social supports, cohesiveness of family and friends, and societal attitudes.
What is a key nursing intervention when working with trauma patients?
Use a non-threatening, matter-of-fact, friendly approach and respect patients' wishes regarding interaction with individuals of the opposite sex.
How can a nurse help develop trust with a trauma patient?
Stay with the patient during flashbacks and nightmares, offer reassurances of safety and support.
What should a nurse encourage a trauma patient to do regarding their trauma?
Encourage the patient to talk about the trauma at their own pace and discuss coping strategies used in response to trauma.
What feelings should a nurse acknowledge in trauma patients?
Feelings of guilt or self-blame.
What are some treatment modalities for PTSD?
Cognitive therapy, prolonged exposure therapy, group and family therapy, Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and psychopharmacology.
What are the first-line medications for treating PTSD?
SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors).
What is the definition of addiction?
A compulsive or chronic requirement for a substance, where tolerance develops and the need generates distress if unfulfilled.
What is intoxication?
A physical and mental state characterized by exhilaration and emotional frenzy or lethargy and stupor.
What is withdrawal in the context of substance use?
The physiological and mental readjustment that occurs with the discontinuation of an addictive substance.
What are the patient outcomes expected after trauma treatment?
Patients will acknowledge the traumatic event, experience fewer flashbacks, demonstrate adaptive coping strategies, concentrate on realistic goals, include others in recovery, work through survivor's guilt, verbalize community resources, attend support groups, and express a desire to move past the trauma.
What is trauma-informed care?
An approach that realizes the widespread impact of trauma, recognizes signs and symptoms in patients, and responds by integrating trauma knowledge into policies and practices.
What are the consequences of past trauma on health?
Past trauma can lead to various mental and physical health issues.
What is the significance of social supports in trauma recovery?
Availability of social supports and the cohesiveness of family and friends can significantly affect recovery outcomes.
What should a nurse assess regarding a trauma patient's mental state?
Assess for self-destructive ideas or behaviors and the stage of grief the patient is experiencing.
What role does community resource identification play in trauma care?
Identifying and sharing valuable community resources can aid in the recovery process for trauma patients.
What types of therapy can be encouraged for trauma patients?
Encourage participation in behavior therapy, individual psychotherapy, self-help groups, or crisis intervention as needed.
What is the impact of societal attitudes on trauma experiences?
The attitude of society regarding the experience can influence the recovery process and the patient's perception of their trauma.
What is the importance of consistency in nursing interventions for trauma patients?
Being consistent, keeping promises, and conveying acceptance helps build trust and support for the patient.
What are the behavioral tendencies that can affect trauma response?
Behavioral tendencies can influence how an individual copes with and responds to trauma.
What is the role of anticipatory preparation in trauma response?
Extent of anticipatory preparation can affect how an individual experiences and copes with a stressor.
What is the significance of location in trauma experiences?
The location where trauma was experienced can impact the severity and recovery process.
What are the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for alcohol use disorder?
1. Recurrent drinking resulting in failure to fulfill role obligations. 2. Recurrent drinking in hazardous situations. 3. Continued drinking despite alcohol-related social or interpersonal problems. 4. Evidence of tolerance. 5. Evidence of alcohol withdrawal or use of alcohol for relief or avoidance of withdrawal. 6. Drinking in larger amounts or over longer periods than intended. 7. Persistent desire or unsuccessful attempts to stop or reduce drinking. 8. Great deal of time spent obtaining, using, or recovering from alcohol. 9. Important activities given up or reduced because of drinking. 10. Continued drinking despite knowledge of physical or psychological problems caused by alcohol. 11. Alcohol craving.
What are some complications associated with chronic alcohol use?
1. Vitamin B deficiency causing peripheral neuropathy. 2. Thiamine (B1) deficiency leading to Wernicke's encephalopathy and Korsakoff Psychosis. 3. Hepatitis leading to cirrhosis of the liver, portal hypertension, ascites, esophageal varices, and hepatic encephalopathy. 4. Esophagitis, gastritis, and pancreatitis. 5. Anemias. 6. Immune system dysfunction. 7. Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. 8. Sexual dysfunction.
What is Delirium Tremens (DT's) and its symptoms?
A medical emergency that usually begins 48-96 hours after the last drink and lasts 1-5 days. Symptoms include hallucinations, disorientation, tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, agitation, and diaphoresis.
What is dual diagnosis in substance use disorders?
When clients have a co-existing substance disorder and mental illness, each diagnosis has its own treatment plan.
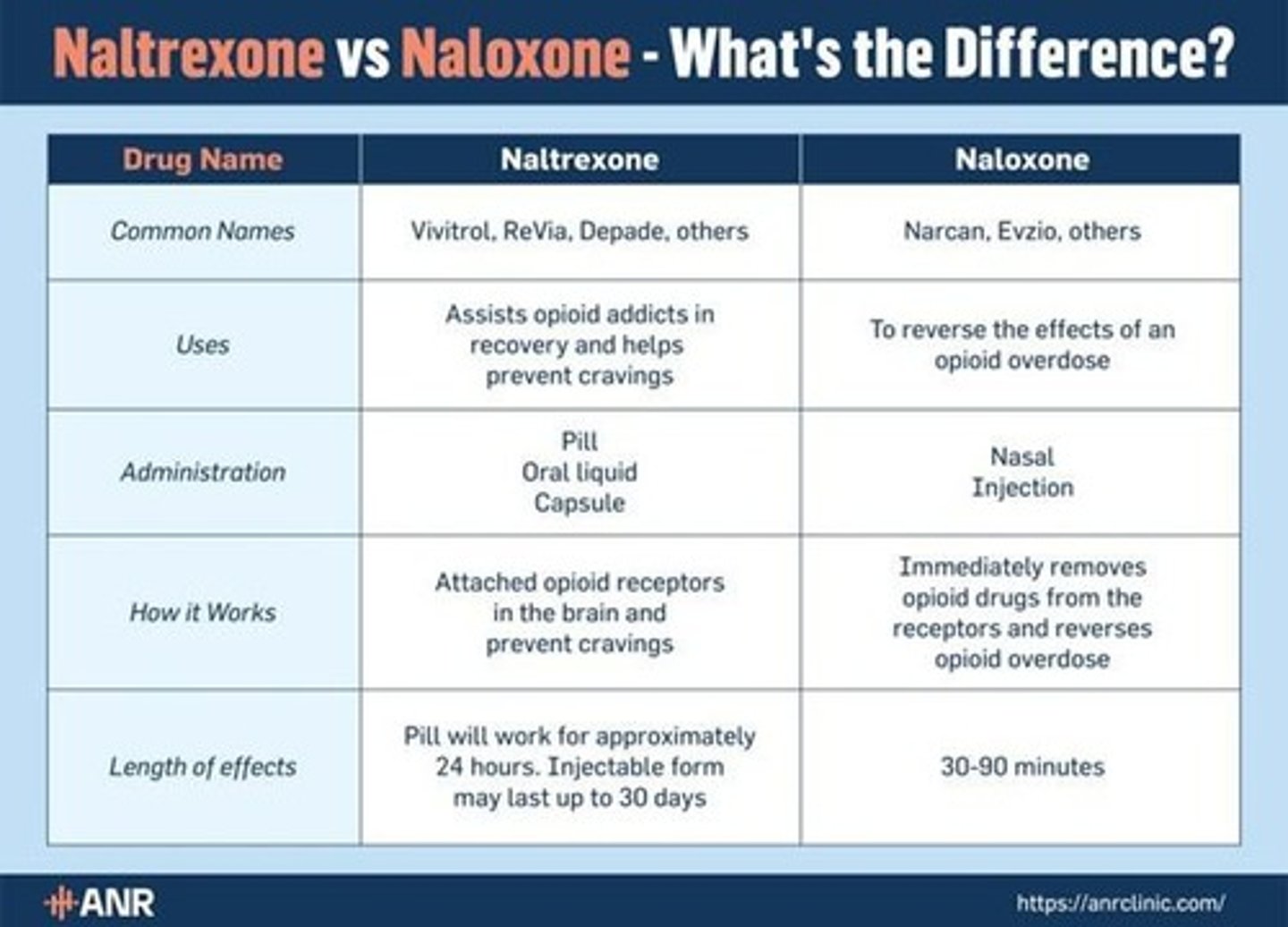
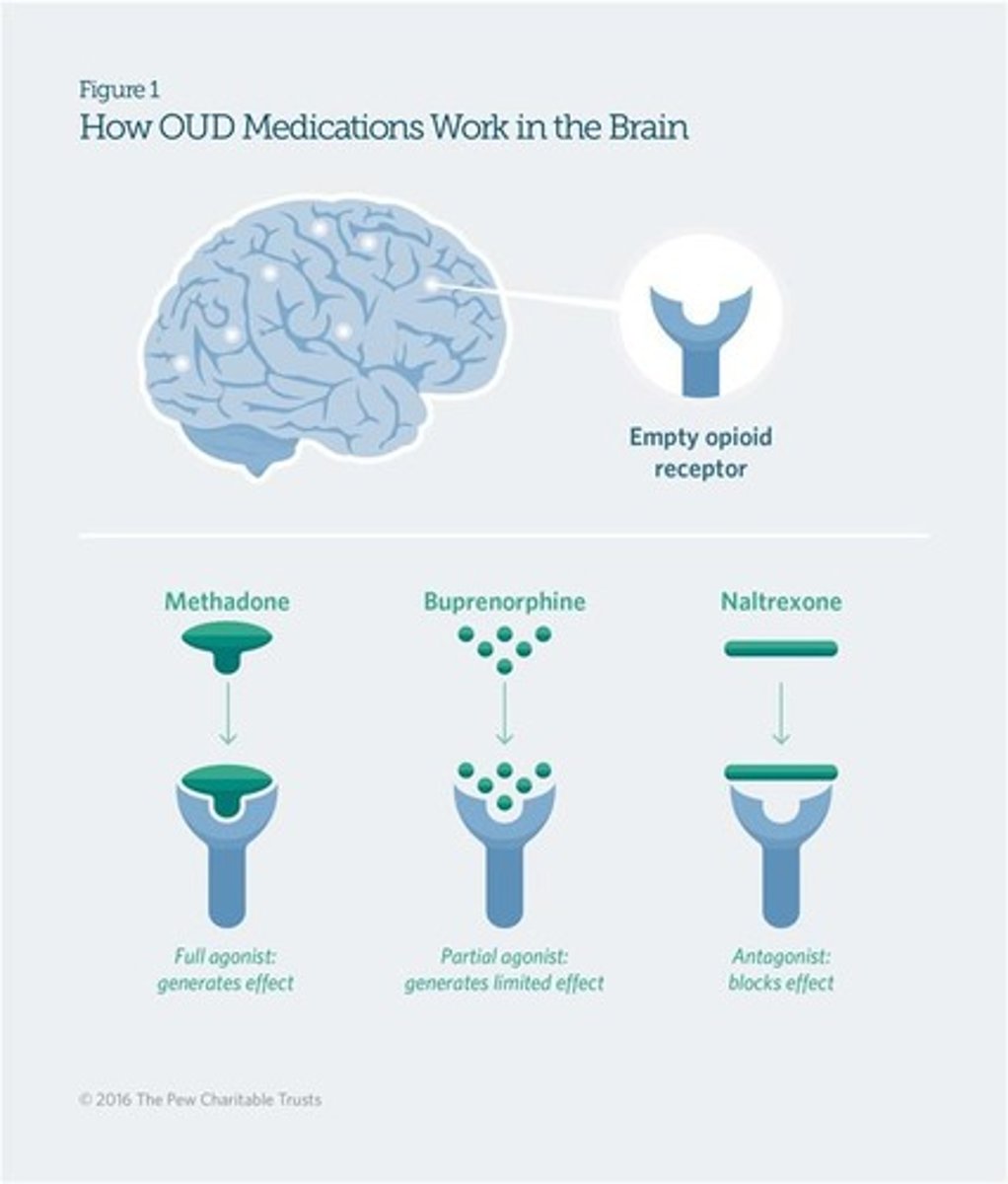
What are the three medications commonly used in Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder?
1. Methadone - Opioid agonist that reduces opioid craving, dispensed in regulated clinics. 2. Buprenorphine - Partial agonist that blocks other narcotics while reducing withdrawal risk, available as a dissolving tablet, cheek film, or implant. 3. Naltrexone - Non-addictive opioid antagonist that blocks effects of other narcotics, available as a daily pill or monthly injection.
What is Narcan/Naloxone used for?
It is an opioid reversal agent given as a nasal spray or shot to reverse opioid action during an overdose.
What are the treatment modalities for substance-related disorders?
1. 12 Step Programs. 2. Detoxification. 3. Rehabilitation. 4. Psychotherapy. 5. Pharmacotherapy.
What nursing care should be provided for patients with substance use disorders?
1. Prevent physical injury or harm to self or others. 2. Treat all patients without bias or judgment. 3. Conduct drug history and assessments (e.g., CIWA, CAGE). 4. Assess for psychological and physical symptoms. 5. Refer to therapy and support groups. 6. Administer medications as ordered. 7. Educate patient and family.
What are the predisposing factors to substance-related disorders?
1. Genetics. 2. Biochemical factors. 3. Developmental influences. 4. Personality traits. 5. Cognitive factors. 6. Social learning. 7. Conditioning. 8. Cultural and ethnic influences.
What is the role of therapy in treating Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD)?
Therapy options include Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), group therapy, and individual therapy.
What are the symptoms of Wernicke's encephalopathy?
Acute syndrome characterized by nystagmus, ataxia, and confusion.
What is Korsakoff Psychosis?
A syndrome resulting in memory loss and confabulation, often leading to permanent brain damage.
What is the purpose of multivitamin therapy in treating AUD?
To address deficiencies, particularly Thiamine (B1), which is crucial for preventing complications.
What is the significance of assessing for psychological symptoms in substance use disorder patients?
To identify co-occurring mental health issues that may require integrated treatment.
What is the importance of drug history and assessment tools in nursing care for substance use disorders?
They help to evaluate the extent of substance use and guide treatment planning.
What is the expected time frame for symptoms of Delirium Tremens to begin after the last drink?
Symptoms typically begin between 48-96 hours after the last drink.
What are the potential consequences of continued alcohol use despite knowledge of physical or psychological problems?
Continued drinking can lead to worsening health issues and complications.
What is the significance of monitoring for DT's in patients with alcohol use disorder?
To ensure timely intervention and management of this potentially life-threatening condition.
What are some common psychological symptoms assessed in substance use disorder patients?
Anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
What is the role of the SAMHSA Center for Substance Abuse Treatment?
To provide information and support for treatment options, including buprenorphine therapy.
What is the significance of cultural and ethnic influences in substance-related disorders?
They can affect substance use patterns, perceptions, and treatment responses.