Depressive Disorder & Suicide Meds
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Depressive Disorders Psychopharmacological Therapies (STaMiNa)
General Teaching for All Antidepressants
Do not discontinue suddenly (risk of withdrawal)
Therapeutic effect = delayed, may take weeks
Avoid hazardous activities (sedation risk)
Report suicidal thoughts immediately
Avoid alcohol while on antidepressants
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCA)
Example: Amitriptyline
Change positions slowly (↓ orthostatic hypotension risk)
Reduce anticholinergic effects: chew sugarless gum, eat high-fiber foods, ↑ fluids (2–3 L/day)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI)
Example: Phenelzine
Avoid tyramine foods (risk of hypertensive crisis) → ripe avocados, figs, fermented/smoked meats, liver, aged cheese, some beer/wine, protein supplements
Avoid all other meds (OTC, herbal, etc.) unless cleared by provider (drug interaction risk)
Atypical Antidepressants
Example: Bupropion
Monitor for: headache, dry mouth, GI distress, constipation, ↑ HR, nausea, restlessness, insomnia
Notify provider if adverse effects become intolerable
Monitor food intake/weight (appetite suppression possible)
Contraindicated in clients with seizure risk
SSRIs (Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors): Paroxetine, Sertraline, Fluoxetine, Escitalopram, Fluvoxamine
SNRI (Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor): Venlafaxine
Antidepressants (STaMiNA)
Antidepressants enhance my STAMINA
S
SSRIs (Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors): Paroxetine, Sertraline, Fluoxetine, Escitalopram, Fluvoxamine
SNRI (Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor): Venlafaxine
T
Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline, Imipramine
M
MAOI (Monoamine oxidase inhibitor): Phenelzine
N
NaSSA (Noradrenergic & specific serotonergic antidepressant): Mirtazapine
A
Atypical Antidepressants (Bupropion)
Taper
Takes weeks for full effects
No ETOH or hazards (sedation risk)
Report suicidal thoughts
Nursing Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness (All Antidepressants)
Less anxiety, improved mood, improved memory
Normal sleep pattern
Improved participation in social & occupational activities
Better coping with stressors
Ability to perform ADLs
Increased well-being
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) vs Selective Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Nonselective (indirectly affects more neurotransmitters)
Wider range of side effects
Selective
Newer and preferred 1st/2nd-line
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) (Amitriptyline/Nortriptyline) Action/Use
Inhibit norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake (nonselective)
Improves mood
Relieves depression
Major depression
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) (Amitriptyline/Nortriptyline) Contraindications / Complications (Trilogy - O DO AS SW)
Children under 12
Recent heart attack
Cardiac dysrhythmias
Seizure disorders
Concurrent MAOI use
Overdose risk (life-threatening dysrhythmias)
Drowsiness, sedation
Orthostatic hypotension
Anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision)
Seizure disorders contraindication/increase
Suicide risk increase (especially in children, adolescents)
Withdrawal symptoms (anxiety, headache, nausea)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) Complications: Trilogy - O DO AS SW
Overdose risk (life-threatening dysrhythmias)
Drowsiness, sedation
Orthostatic hypotension
Anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision)
Seizure disorders contraindication/increase
Suicide risk increase (especially in children, adolescents)
Withdrawal symptoms (anxiety, headache, nausea)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) Meds: the IPRA MINES bitcoin and DOXs PINs for AMOXAPINE and TRICYCLES on TRIPLINES
Imipramine
Trimipramine
Doxepin
Amoxapine
Amitriptyline
Nortriptyline
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) (Amitriptyline/Nortriptyline) Interactions / Admin
CNS depressants increase sedation; MAOIs cause hypertensive crisis.
Anticholinergics increase side effects like dry mouth and constipation.
St. John’s wort, kava-kava, and valerian reduce drug efficacy.
Take at bedtime to prevent daytime drowsiness; avoid driving if drowsy.
Move slowly from lying to sitting/standing.
Increase fluids and fiber to prevent constipation.
Report worsening depression or suicidal thoughts.
Taper medication over two weeks when discontinuing.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) (-xetine, -pram) Action / Use
Inhibit serotonin reuptake → more serotonin remains at junction of neurons.
Do not block dopamine or norepinephrine uptake.
Can cause CNS stimulation (e.g., insomnia).
Long half-life → takes up to 4 weeks for therapeutic effect.
General
First-line treatment for panic disorder and trauma-/stressor-related disorders.
Paroxetine
GAD
Panic disorder (reduces frequency/intensity of attacks; prevents anticipatory anxiety)
OCD (reduces serotonin-driven obsessions/compulsions)
Social anxiety disorder
PTSD
Depressive disorders
Adjustment disorders
Associated dissociative disorder manifestations
Sertraline
Panic disorder, OCD, social anxiety disorder, PTSD
Citalopram
Panic disorder, OCD, GAD, PTSD, social anxiety disorder
Escitalopram
GAD, OCD, panic disorder, PTSD, social anxiety disorder
Fluoxetine
Panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, OCD, PTSD
Fluvoxamine
OCD, GAD, social anxiety disorder, PTSD
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Complications: EA TeNDS to LATEly GIB SW (HA)ters BRUtal depreSSion WITHout SALTINESS
Early Adverse
Tremors, Nausea, Diaphoresis, Sleepiness
Late Adverse
GI Bleeding, Sexual Dysfunction, Weight Gain, Headache
Serotonin Syndrome
Withdrawals
Hyponatremia (Without Saltiness)
EA TeNDS to LATEly GIB SW HAters BRUtal depreSSion WITHout SALTINESS
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) (-xetine, -pram) Contraindications / Compllications
Pregnancy: Paroxetine = Category D (others lower risk).
Contraindicated with MAOIs or TCAs.
Avoid alcohol use while on SSRIs.
Use cautiously in clients with:
Liver/renal dysfunction
Seizure disorders
GI bleeding history
Use cautiously in bipolar disorder (risk of mania).
Early Adverse Effects
First few days/weeks: Nausea, diaphoresis, tremor, fatigue, drowsiness.
Client Education:
Report adverse effects.
Take as prescribed.
Usually subside.
Avoid driving if sedation occurs.
Later Adverse Effects
After 5–6 weeks: Sexual dysfunction (impotence, delayed/absent orgasm, decreased libido), weight gain, headache.
Client Education: Report sexual dysfunction (may be managed with dose changes, drug holidays, or switching meds).
Weight Changes
Weight loss early → weight gain with long-term therapy.
Nursing Actions: Monitor weight.
Client Education: Balanced diet, regular exercise.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Risk ↑ with history of GI bleed, ulcers, or anticoagulant use.
Client Education: Report GI bleeding signs (dark stools, coffee-ground emesis).
Hyponatremia
Likely in older adults taking diuretics
Serotonin Syndrome (2–72 hrs after start; can be lethal)
Confusion, agitation, poor concentration, hostility
Disorientation, hallucinations, delirium
Seizures → status epilepticus
Tachycardia → CV shock
Labile BP
Diaphoresis
Fever → hyperpyrexia
Incoordination, hyperreflexia
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
Coma, death (severe cases)
Client Education: Observe for symptoms; withhold medication and notify provider immediately.
Bruxism
Grinding/clenching teeth (usually during sleep).
Nursing Actions:
Report to provider (may change med class).
Treat with buspirone or mouth guard.
Withdrawal Syndrome
Sensory disturbances, anxiety, tremor, malaise, unease.
Client Education:
Taper slowly; avoid abrupt discontinuation.
Until I reached a point in my life where like oh you and I are nurse want to help you OK this is something that I can cause the girl was talking the same hobbies same hobbies and same upbringing is not no it’s work all
SNRI vs SSRI Complications
Anxiety
Anorexia / Weight loss
Sexual dysfunction
Headache, nausea, agitation, dry mouth, sleep disturbances
Hypertension
Hyponatremia (esp. older adults on diuretics)
AN ANOREXIC SEXUAL HANDSy SNaps depression and HYPERTENSION like a DIURETIC
Early Adverse
Tremors, Nausea, Diaphoresis, Sleepiness
Late Adverse
GI Bleeding, Sexual Dysfunction, Weight Gain, Headache
Bruxism (teeth grinding/clenching)
Serotonin Syndrome
Withdrawals
Hyponatremia (Without Saltiness)
EA TeNDS to LATEly GIB SW HAters BRUtal depreSSion WITHout SALTINESS
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) (-xetine, -pram) Interactions / Admin
TCAs, MAOIs, St. John’s Wort → ↑ risk of serotonin syndrome.
Discontinue MAOIs 14 days before starting SSRI.
Discontinue fluoxetine 5 weeks before starting MAOI.
Avoid concurrent TCA/St. John’s Wort use.
Warfarin → displacement → ↑ bleeding risk.
Nursing Actions: Monitor PT/INR, assess for bleeding, dosage adjustment may be needed.
TCAs + Lithium → ↑ levels of both.
Client Education: Avoid concurrent use.
NSAIDs + Anticoagulants → ↑ bleeding risk (platelet suppression).
Client Education: Monitor for bleeding (bruising, hematuria), notify provider.
Take with food to minimize GI upset.
Take in morning to reduce sleep disturbances.
Daily dosing required to establish plasma levels.
May take up to 4 weeks to achieve therapeutic effects.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Meds: DepreSSed moms need a SERT (special emergency reaction team) and PRAMS (pregnancy risk assessment monitoring system) for PAROXysmal FLU symptoms
Prototype Medication
Paroxetine
Other Medications
Sertraline
Citalopram
Escitalopram
Fluoxetine
Fluvoxamine
Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) (-loxetine, -faxine) Action / Use
Inhibit reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine (minimal dopamine inhibition).
Major depression
Panic disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors Complications: AN ANOREXIC SEXUAL HANDSy SNaps depression and HYPERTENSION like a DIURETIC
Anxiety
Anorexia / Weight loss
Sexual dysfunction
Headache, nausea, agitation, dry mouth, sleep disturbances
Hypertension
Hyponatremia (esp. older adults on diuretics)
Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) (-loxetine, -faxine) Contraindications / Complications
Pregnancy Risk: Category C.
Contraindicated with MAOIs.
Duloxetine contraindicated in hepatic disease or heavy alcohol use.
Client Education
Avoid abrupt discontinuation.
Avoid alcohol.
Headache, nausea, agitation, anxiety, dry mouth, sleep disturbances
Hyponatremia (esp. older adults on diuretics)
Nursing Action: Monitor sodium levels.
Anorexia / Weight loss
Nursing Action: Monitor weight.
Client Education: Maintain balanced diet, exercise.
Hypertension
Nursing Action: Monitor blood pressure.
Sexual dysfunction
Nursing Action: Report issues (can manage with dose change, med holiday, or switching meds).
Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) (-loxetine, -faxine) Interactions / Admin
MAOIs & St. John’s Wort → risk of serotonin syndrome.
Nursing Action: Discontinue MAOIs 14 days before starting SNRI.
Client Education: Avoid St. John’s Wort.
CNS Depressants (alcohol, opioids, antihistamines, sedatives/hypnotics) → ↑ CNS depression.
Nursing Action: Avoid concurrent use.
NSAIDs & Anticoagulants → ↑ risk of bleeding.
Client Education: Monitor for bleeding (bruising, hematuria), notify provider.
Duloxetine contraindicated in hepatic disease or heavy alcohol use.
Client Education:
Avoid abrupt cessation.
May take with food.
Take daily to maintain therapeutic plasma levels.
Takes up to 4 weeks for therapeutic effect.
Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) Meds: SportsNet (SN)’s DULO smart wear sponsored BJJ champ VENLA luukkonen.
Prototype Medication
Venlafaxine
Other Medication
Duloxetine
Contraindiction: MAOIs
(Almost Everything)
Atypical Antidepressants (Bupropion hydrochloride)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Serotonin Agonists (-triptans)
Centrally Acting Muscle Relaxants
Carbamazepine
Opioids (w/in 2 weeks)
Amphetamines (w/in 2 weeks)
Methylphenidate (w/in 2 weeks)
Dopamine-Replacements (-dopa)
Monoamine Oxidase Type B Inhibitors (-gilines)
Avoid most cheeses, fish (cured/dried), pepperoni, salami, because BOUGIE Foods = High Tyramine = Hypertensive Crisis
Inhibiting this enzyme prevents tyramine breakdown
Beef and other fresh meats do not interact
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) (Phenelzine)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) (Phenelzine) Action/Use
Blocks the enzyme that breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Increases serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine
Improves mood and alleviates depression.
Depression unresponsive to other treatments
Depression in bipolar disorder
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) (Phenelzine) Complications (GIorgio armani MONOcles and ORTHOtics use A.I. SIgnals for HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS)/ Contraindications
Orthostatic hypotension
Anxiety, insomnia, agitation
Hypertensive crisis (with tyramine-containing foods)
GI disturbances (constipation, nausea, vomiting)
Increased suicidal ideation (children, young adults)
Inability to follow a tyramine-free diet, renal failure, liver disorders
Suicidal ideation, cardiac disease, concurrent SSRI use, glaucoma
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) (Phenelzine) Complications: GIorgio armani MONOcles and ORTHOtics use A.I. SIgnals for HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS
GI disturbances (constipation, nausea, vomiting)
Orthostatic hypotension
Anxiety, insomnia, agitation
Increased suicidal ideation (children, young adults)
Hypertensive crisis (with tyramine-containing foods)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) (Phenelzine) Meds: TRANYa earbuds made of SELEnium produce MONOphonic and ISOChronic tones
Tranylcypromine
Selegiline transdermal
Isocarboxid
Atypical Antidepressants Action/Use
Inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine (Bupropion hydrochloride) - NDRI
Inhibits the presynapse receptors of serotonin and norepinephrine (Mirtazapine) - NaSSA
Inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine (Reboxetine) - SNRI
Treats depression
Prevents seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
Smoking cessation adjunct
Inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine (NDRI)
Bupropion hydrochloride
Inhibits the presynapse receptors of serotonin and norepinephrine (NaSSA)
Mirtazapine
Inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine (SNRI)
Reboxetine
Atypical Antidepressants Complications: ATYPICAL ANOREXIC psychics SEIZE IDEATION but DEPRESS their GI, MIND, and CNS / Contraindications
GI effects: Nausea, vomiting, weight loss
Increased risk for seizures
CNS effects: insomnia, agitation, tremor, headache
Psychosis, hallucinations, delusions
Increased risk for suicidal ideation (children, young adults)
History of eating disorder, seizure disorder, suicidal ideation
Concurrent MAOI use
Head trauma or CNS tumors
Atypical Antidepressants (Bupropion hydrochloride) Complications ATYPICAL ANOREXIC psychics SEIZE IDEATION but DEPRESS their GI, MIND, and CNS
Increased risk for seizures
Increased risk for suicidal ideation (children, young adults)
GI effects: Nausea, vomiting, weight loss
Psychosis, hallucinations, delusions
CNS effects: insomnia, agitation, tremor, headache
Atypical Antidepressants Meds MIRTA sells ATYPICAL ANTIDEPRESSANTS like REBOXEd
BUPROPRION illegally
Mirtazapine
Reboxetine
Bupropion hydrochloride
Antidepressants – SSRIs (Citalopram, Fluoxetine, Sertraline)
Nursing Actions
Lower lethality risk compared to other antidepressants
Do not stop medication suddenly (risk of withdrawal)
Onset: 1–3 weeks for initial effects, up to 2 months for full response
Avoid hazardous activities until side effects known (driving, machinery)
Common adverse effects: nausea, headache, CNS stimulation (agitation, insomnia, anxiety)
Possible sexual dysfunction → notify provider if intolerable
Encourage healthy diet (risk of weight gain with long-term use)
Monitor for worsening depression or suicidal intent
Sedative Hypnotic Anxiolytics (Benzodiazepines: Diazepam, Lorazepam)
Client Education
Watch for CNS depression: sedation, lightheadedness, ataxia, ↓ cognition
Avoid other CNS depressants (alcohol)
Avoid hazardous activities (driving, machinery)
Avoid caffeine (interferes with medication effectiveness)
Taper gradually under provider supervision (risk of withdrawal seizures if stopped abruptly)
Mood Stabilizers (Lithium carbonate)
Nursing Actions
Encourage healthy diet and regular exercise (minimize weight gain).
Maintain fluid intake 2–3 L/day (food + beverages).
Maintain adequate sodium intake (prevents lithium toxicity).
Client Education
Take with food/milk to reduce GI upset.
Keep lab appointments (monitor lithium levels and adverse effects).
Second-Generation Antipsychotics (Risperidone, Olanzapine)
Nursing Actions
Preferred over first-generation antipsychotics → fewer adverse effects.
Client Education
Maintain healthy diet + regular exercise (prevents weight gain).
Report adverse effects: agitation, dizziness, sedation, sleep disruption (medication adjustment may be required).
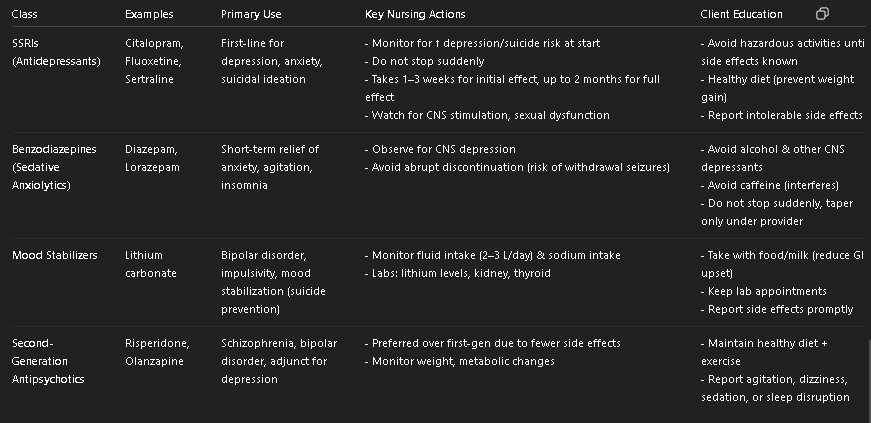
SSRIs vs Benzos vs Mood Stabilizers vs 2nd Gen Antipsychotics (Table)
Class | Examples | Primary Use | Key Nursing Actions | Client Education | Major Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SSRIs (Antidepressants) | Citalopram, Fluoxetine, Sertraline | First-line for depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation | - Monitor for ↑ depression/suicide risk at start - Do not stop suddenly - Takes 1–3 weeks for initial effect, up to 2 months for full effect - Watch for CNS stimulation, sexual dysfunction | - Avoid hazardous activities until side effects known - Healthy diet (prevent weight gain) - Report intolerable side effects | - Risk of serotonin syndrome - Sexual dysfunction - Weight gain |
Benzodiazepines (Sedative Anxiolytics) | Diazepam, Lorazepam | Short-term relief of anxiety, agitation, insomnia | - Observe for CNS depression - Avoid abrupt discontinuation (risk of withdrawal seizures) | - Avoid alcohol & other CNS depressants - Avoid caffeine (interferes) - Do not stop suddenly, taper only under provider | - Sedation, dependence, withdrawal risk - Cognitive impairment |
Mood Stabilizers | Lithium carbonate | Bipolar disorder, impulsivity, mood stabilization (suicide prevention) | - Monitor fluid intake (2–3 L/day) & sodium intake - Labs: lithium levels, kidney, thyroid | - Take with food/milk (reduce GI upset) - Keep lab appointments - Report side effects promptly | - Lithium toxicity (GI upset, tremor, confusion, seizures) - Weight gain |
Second-Generation Antipsychotics | Risperidone, Olanzapine | Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, adjunct for depression | - Preferred over first-gen due to fewer side effects - Monitor weight, metabolic changes | - Maintain healthy diet + exercise - Report agitation, dizziness, sedation, or sleep disruption | - Metabolic syndrome (weight gain, diabetes, dyslipidemia) - Sedation |
Suicide Meds: Suicide Boys touring from Los Angeles to San Bernadino (Suicide = LA2SB)
Lithium (Mood Stabilizer)
Encourage healthy diet and regular exercise (minimize weight gain).
Maintain fluid intake 2–3 L/day (food + beverages).
Maintain adequate sodium intake (prevents lithium toxicity).
Antipsychotics (2nd gen, -idone, -apine)
Maintain healthy diet + regular exercise (prevents weight gain).
Report adverse effects: agitation, dizziness, sedation, sleep disruption (medication adjustment may be required).
SSRIs (Antidepressant)
Lower lethality risk compared to other antidepressants
Do not stop medication suddenly (risk of withdrawal)
Onset: 1–3 weeks for initial effects, up to 2 months for full response
Benzodiazepines (Sedative-Hypnotics)
Watch for CNS depression: sedation, lightheadedness, ataxia, ↓ cognition
Avoid other CNS depressants (alcohol)
Avoid hazardous activities (driving, machinery)
Avoid caffeine (interferes with medication effectiveness)
Taper gradually under provider supervision (risk of withdrawal seizures if stopped abruptly)
Complication: Increased Suicide Ideation
SSRIs (more so Paroxetine)
SNRIs (more so Venlafaxine)
TCAs
MAOIs
Bupropion (Atypical NDRI - low risk)
Complication: Weight Loss / Anorexia (Avoid with eating disorders)
Bupropion (Atypical NDRI)
SNRIs
ANOREXIC BUtts need SNacks
Complication: Weight Gain (1)
SSRIs
SS Cruises Fatten people
Use: Smoking cessation
Bupropion (Atypical NDRI)
Cigarette BUtts
Complication: Anticholinergic Effects
TCAs
SNRIs
TRICYCLE hikes with DRY SNacks
Complication: Hypertension (2)
SNRIs
MAOIs (w/ tyramine)
MONOsaturated fat, low salt SNacks prevent HYPERTENSION
Complication: Increased Seizure risk (or contraindication) (2)
Bupropion (Atypical NDRI)
TCAs
SEIZE BUtts on TRIcycles
St. John’s Wort Complications: JOHN gets GAS from PT
GI issues
Abdominal Pain
Skin Rash
Photosensitivity
Tachycardia
Serotonin Syndrome S/S
Onset: Immediate (2 hours to 3 days)
Tachycardia → CV shock
BP fluctuations (labile BP)
Diaphoresis
Fever → hyperpyrexia
Seizures → status epilepticus
Hyperreflexia (Incoordination)
GI upset: n/v/d, abdominal pain
↓ LOC / Coma / death (severe cases)
Confusion, agitation, poor concentration, hostility
Disorientation, hallucinations, delirium
What are the 8 progressive symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome?
Diarrhea (n/v) -> Fever -> Diaphoresis -> Shivering -> Hyperreflexia -> Seizure -> Coma -> Death
Complication: Hyponatremia, Sexual dysfunction (2)
SSRIs
SNRIs
Selective Sexual Salt Suckers
Maintain fluid intake 2–3 L/day (food + beverages).
Maintain adequate sodium intake (prevents toxicity).
Lithium (Mood Stabilizer)