Anticonvulsants and Anti-Parkinsonians
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Okay WARNING of course our professor for this section was older than dirt so he's so out of date it's crazy. So this is not the PANCE deck, this is the test deck!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Seizures
The clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation of a population of neurons
Epilepsy
A tendency towards recurrent seizures unprovoked by systemic or neurologic insults
Tonic-clonic, absence, status epilepticus, atypical (myoclonic, atonic)
Types of generalized seizures
simple, complex, partial evolving to generalized
Types of partial seizures
Tonic-clonic (grand mal)
Which type of seizure is characterized by an aura, epileptic cry, LOC and loss of postural tone, tonic spasm of the entire body, synchronous clonic movements that are followed by confusion and sleep
synchronous, bilateral, high voltage polyspike
EEG changes for Grand Mal
Absence (petit mal)
Which type of seizure characteristically occur in childhood and includes a 5-10 sec LOC that looks like day dreaming and may have local/widespread clonic movements
with epilepsy, with acute disorders affecting the brain, after rapid withdrawal of anticonvulsants
Status epilepticus may develop in patients…
local, unilateral discharge
EEG change for simple partial Seizures
Simple partial
Which type of seizure is characterized by consciousness and is often limited to certain muscles, specific sensory changes, or autonomic activity (may spread causing progressive symptoms - jacksonian march)
Complex partial
Which type of seizure is characterized by impaired consciousness, stereotype movements, and flashbacks that usually originate in the temporal or frontal lobes
bilateral or unilateral changes
EEG changes in complex partial
Drugs, EtOH, DM, fever, anoxia, brain tumor, head trauma, photosensitivity (television, raves, etc), hormone; vascular (SAH, ischemic strokes), infectious (meningitis, etc), trauma (epidural hematoma), autoimmune (SLE), metabolic (hyponatremia, glucose), Ecclampsia
For seizure with a KNOWN etiology (28%) what are some triggers?
Ion conductance of neuronal membranes, Defects in GABA neuronal circuitry (Decreased GABA), overactivity of glutamatergic transmission
What is happening at the neuronal level for seizures?
phenobarb, primidone, ethosuximide
Which AEDs decrease the excitability of the focus?
phenytoin, phenobarb, carbamazepine, valproate
Which AEDs prevent the spread of nervous activity?
valproate, Benzos, phenobarb, primidone
Which AEDs enhance inhibitory mechanisms?
Sedation at therapeutic doses (NOT phenytoin), blood dyscrasias (NOT benzos), teratogenic potential, may induce CYP450s,
Common Characteristics of AEDs
antacids and antihistamines (decrease absorption)
DDIs for AEDs
Phenytoin
The 1st drug for seizures that is the drug of choice for grand mal seizures (also used for partial, status epilepticus, trigeminal neuralgia)
Inhibits sodium channels reactivation (potassium potentiates this)
MOA for phenytoin
Highly bound, slow oral absorption, Zero order kinetics
PK rules for Phenytoin
10-20 (therapeutic), 20+ (Nystagmus, thought disorders, sedation, diplopia), 30+ (Loss of coordination, confusion, hyperactivity), 40+ (lethargy, stupor, coma)
Describe the ranges for Phenytoin
hirsutism, blood dyscrasias, teratogenic, gingival hyperplasia, osteomalacia
ADRs for phenytoin
Grand mal, partial, trigeminal neuralgia (#1 draft pick)
Uses for carbamazepine
inhibits Na+ reactivation, inhibits Ca2+ influx
MOA for carbamazepine
Slowly absorbed, 70% bound, 10-20 hr t1/2, liver microsomal enzyme activity
PK for Carbamazepine
teratogenic, Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, involuntary motor activity (elderly), temporary taste disorder, OD symptoms (dizziness, diplopia, drowsiness, ataxia, slurred speech)
ADRS for Carbamazepine
tonic-clonic, partial seizure, #1 choice for seizures in infants
Uses for Phenobarb
Enhances the binding of GABA (inhibits voltage-gated Ca2+ currents to prevent NT release)
MOA for phenobarb
Slowly absorbed, 50% bound, 50-140 hr T1/2, liver metabolism, induces p450s for tetracycline and other antibiotics
PK of phenobarb
sedation, depression of Cardio and respiration, hepatotoxicity, megaloblastic anemia, osteomalacia, NOT teratogenic but enhances phenytoin
ADRs for phenobarb
saliva
How do you test AED levels
Tonic-clonic, complex partials
Uses of primidone
Rapidly and completely absorbed after oral, 5-15 t/12, 2 active metabolites (phenobarb and PEMA)
PK for primidone
SAME as phenobarb + maybe some action at Na+ channels
MOA for primidone
sedation, depression of Cardio and respiration, hepatotoxicity, megaloblastic anemia, osteomalacia, NOT teratogenic but enhances phenytoin, acute intox, acute psychotic reactions (rare)
ADRS for primidone
absence seizures, PREFERRED IN PREGNANCY
Uses for ethosuximide
Inhibits activity T-type calcium channels
MOA for ethosuxmide
rapidly absorbed by GI tract, metabolized by liver,
PKs for Ethosuximide
GI distress, transient CNS depression, blood dyscrasia (rare), bone marrow depression,
ADRs for ethosuximide
absence, tonic clonic, myoclonic, partial, chronic neuropathic pain
Uses for Valproic acid
prolonged inactivation of Na+ channel, inhibits T-type Ca2+ channels, increases GABA levels
MOA for valproic acid
completely absorbed from GI tract, highly bound, 10-15 hr T1/2, excreted in the urine after conjugation and oxidation
PK for valproic acids
GI distress, sedation, severe hepatotoxicity, teratogenic (neural tube defects), increases phenobarb
ADRs for valproic acid
Absence (clonazepam), partial (clorazepate), myoclonic (clonazepam), status epilepticus (diazepam, lorazepam)
Uses for Benzos (lorazepam, diazepam, clonazepam, clorazepate)
enhances the binding of GABA (desmethyldiazepam is the anti-convuslant metabolite)
MOA for Benzos
Well absorbed, tolerance develops in 1-6 months
PKs of Benzos
hyperactivity (children)
ADRs for benzos
partial seizures adjunct, trigeminal neuralgia, neuropathic pain (DM)
Uses for Gabapentin
binds voltage gated Ca2+ channels, does not interact with GABA receptors
MOA for gabapentin
excreted unchanged, does not affect other AEDs
PKs for gabapentin
partial seizures adjunct, bipolar depressive
Uses of Lamotrigine
Action on Na+ channels
MOA of lamotrigine
SJS, flu-like symptoms
ADRs for lamotrigine
partial seizures
Felbamate uses
aplastic anemia (may require bone marrow transplant)
ADRs for felbamate
Dopaminergic agents (levodopa/carbidopa and dopamine agonist) COMT inhibitors, MOAB inhibitors, anticholinergics, amantadine
Drugs for Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Levodopa
What is the most effective drug for parkinsonian symptoms but requires active transport since its a large neutral amino acid
Nausea, postural hypotension, dyskinesias, motor fluctuations
ADRs of levodopa
Increases levodopa in the brain, decreases peripheral conversion
Why do we add carbidopa to levodopa?
Does not cross BBB, blocks levodopa metabolism in the periphery
Tell me about Entacapone (COMT)
Cross BBB, longer t1/2 than entacapone, hepatotoxic
Tell me about Tolcapone
N/V, orthostatic hypotension, arrhythmias
Acute ADRs of levodopa that can be controlled by lowering the dose
Dyskinesias, psychiatric disturbances (psychosis)
Chronic ADRs of levodopa that can be controlled by lowering the dose
wearing-off effect (end of dose akinesia), on-off phenomenon
irreversible levodopa ADRs
Smaller doses more frequently, drug holidays, dopamine agonists, MAOBs, sustained release formulation
Treatment for off-on phenomenon
phenothiazines (blocks benefits), Epi (potentiates ADRS, arrythmias)
DDIs for levadopa
pergolide, bromocriptine, pramipexole
Dopamine receptor agonist examples
directly stimulate dopamine receptors, no metabolic conversion, no absorption delay, longer t1/2, mono or adjunct, may delay motor fluctuations and dyskinesia
Quirks of dopamine agonists
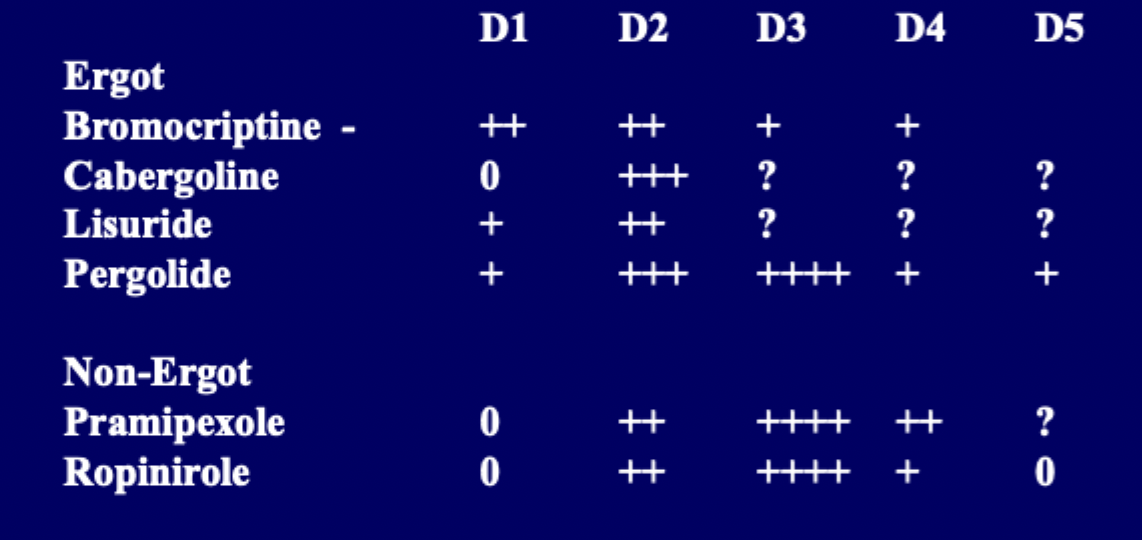
N/V, dizziness, postural hypotension, HA, drowsiness, somnolence, dyskinesia, confusion, hallucinations, paranoia
ADRs for dopamine agonists
Irreversible MAO-B inhibition (inhibits dopamine metabolism in the brain - lessens on-off effects)
MOA for selegiline
insomnia, hallucination, nausea, DDI with TCAs and SSRI
ADRs for selegiline
tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, dyskinesia
Which symptoms of of parkinson’s disease does amantadine treat?
enhancing release of dopamine, inhibits presynaptic uptake of catecholamines, dopamine receptor agonist, NMDA receptor blockage
MOA for amantadine (theoretically)
autonomic, psychiatric
ADRs of amantidine
Dopaminergic depletions → cholinergic overactivity
Why do anticholingergics help with parkinson’s (especially with initial therapy OR as an adjunct)
trihexyphenidyl, benztropine, ethopropazine
Common anticholinergic agents
dry mouth, sedation, delirium, confusion, hallucination, constipation, urinary retention
ADRs of anticholinergics