CH. 5 | The Integumentary System
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Pictures of Epiderms & Dermis
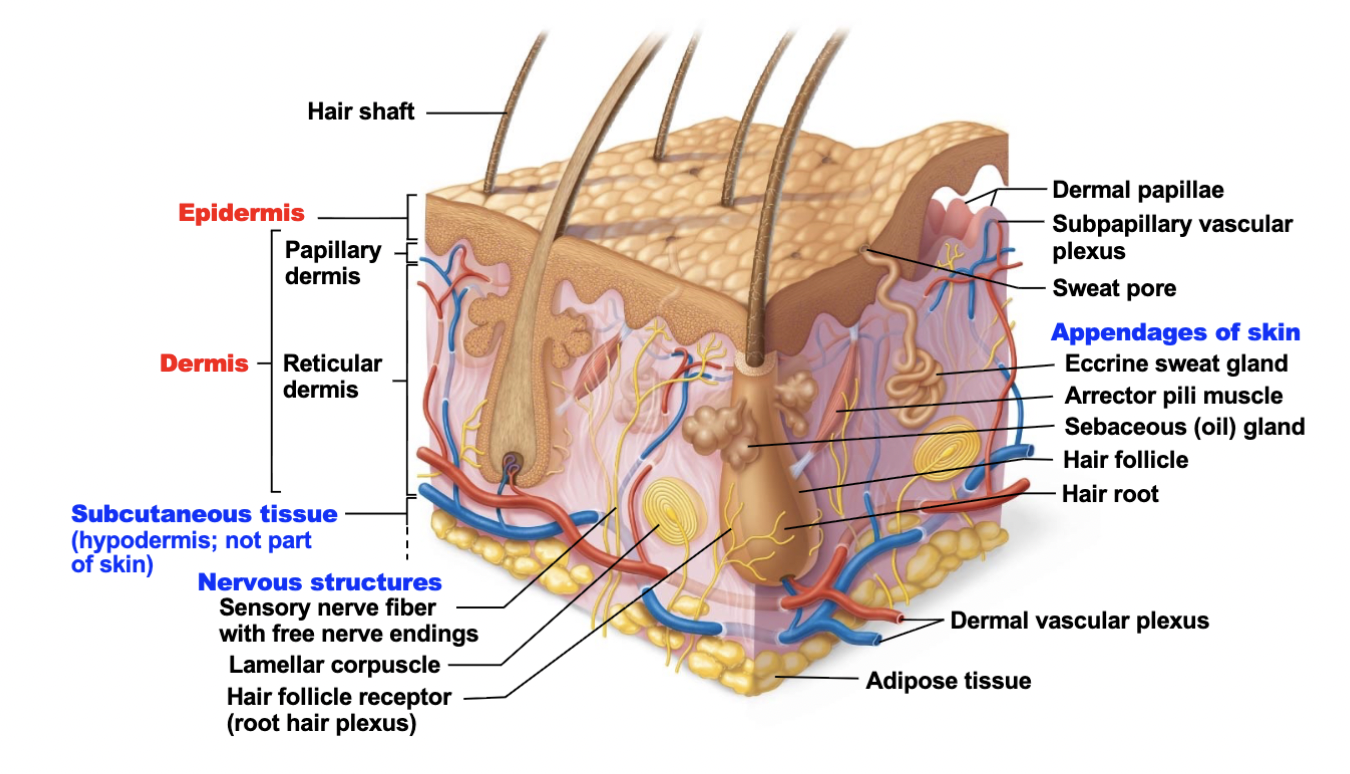
What tissue type is the epidermis (superficial) composed of?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What are the 4 cell types of the of the epidermis?
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Tactile epithelial cells, Dendritic cells
Location of Keratinocytes?
Stratum spinosum and corneum
Description of Keratinocytes
Produces KERATIN
Abundant cell type in epiderms
Arise from deepest layer, dead at skins surface
Location of Melanocytes?
Stratum basale
Description of Melanocytes
Manufactures and secretes pigment (melanin)
Transfers melanin to nearby keratinocytes
Location of Tacticle epithelial cells?
Stratum basale
Description of Tactile epithelial cells
Attached to sensory nerve endings to function as a touch receptor
Location of Dendritic cells?
Stratum spinosum
Description of Dendritic cells
Act as the sentinels of the immune system
Presents antigens to T-Cells
What tissue type is the dermis (deep) composed of?
Dense irregular connective tissue
Name and describe the 5 primary functions of the skin.
Protection (protection of bumps, chemicals, water loss, UV, abrasion, etc)
Body temperature regulation (maintaining body temp. and regulating heat loss through capillary networks and sweat glands)
Excretion (removal and waste of bodily fluid through sweat)
Production of Vitamin D (epidermal cells use UV radiation to synthesize Vitamin D)
Sensory Reception (contains sense organs associated with nerve endings)
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis? (Deep to Superficial)
Stratum basale
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum corneum
Describe the structure and function of each layer.
1) Stratum basale
Deepest layer and is attached to underlying dermis
Cells are activiely dividing
Contains tactile epithelial cells and melanocytes
2) Stratum spinosum
Spiny layer
Contains keratinocytes (with thick bundles of intermediate filaments
- among them are dendritic cells
3) Stratum granulosum
Consists 8-10 layers of keratinocytes
Contains Keratohyaline granules and Lamellar granules
Cells are flattened with deteriorating organelles
4) Stratum lucidum
Occurs only in thick skin
Located in the palms of hands and soles of feet
Composed of a few, flat dead keratinocytes
5) Stratum corneum (horny layer)
Superficial and external layer
Layers thick of dead keratinocytes
Protects skin against abrasion and penetration
Cells are shed regularly
What are the 2 layers of the dermis?
Papillary dermis
Reticular dermis
Describe the structure and function of each layer.
1) Papillary dermis
Superficial, and makes up 20% of the dermis
Aerolar C.T containing thin collagen and elastic fibers
Includes dermal papillae
Increases surface area for exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes
2) Reticular Dermis
Deeper, and makes up 80% of the dermis
Dense irregular C.T
Has cleavage and flexure lines
Rich nerve supply
2 massive vascular plexuses
- dermal plexus
- subpapillary plexus
Describe the structure and function of the hypodermis.
Deep to the skin (Also known as the superficial fascia)
Contains aerolar and adipose C.T
Anchors skin
Insulates the body
Describe the factors that contribute to skin color
3 Pigments:
1) Melanin
Most important pigment
Passes from melanocytes to keratinocytes in the stratum basale of the epidermis
Difference in skin color results from the amount and type of melanin produced
2) Carotene
Yellow-orange pigment from carrots and tomatoes
3) Hemoglobin
Crimson color of oxygenated blood is due to this
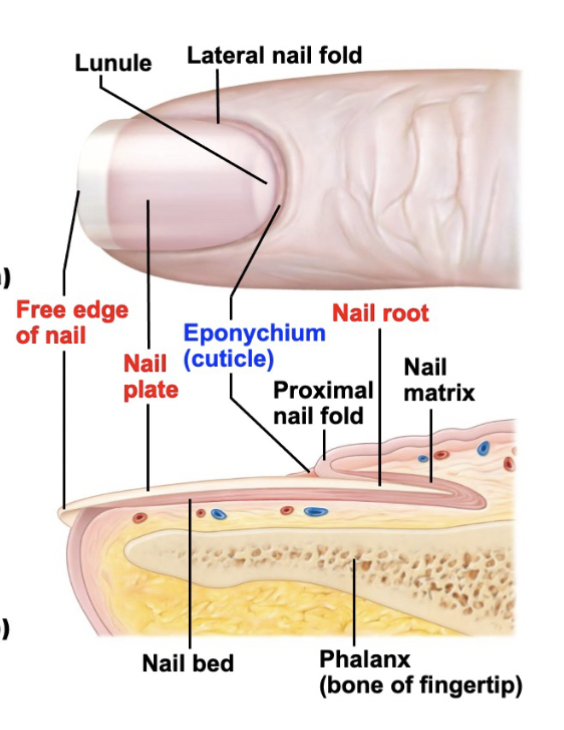
Describe the structure of nails.
Made up of dead, keratinized cells filled with hard keratin
Rests on nail bed of epidermis
At the root, the nail bed thickens into nail matrix (actively growing part of the nail)
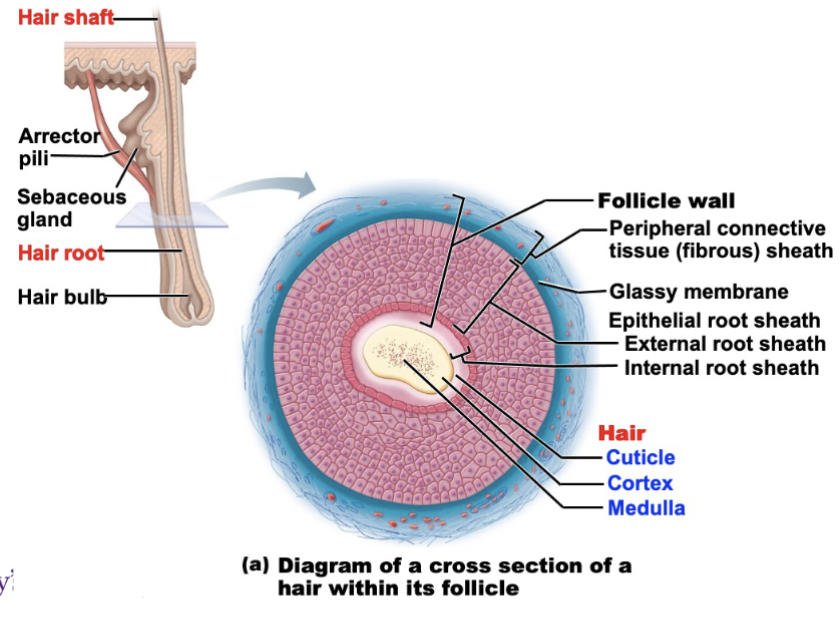
What are the parts of a hair? Explain the function of each part
Root
Embedded in the skin
Shaft
Projects above the skin’s surface
Medulla - central core; contains large cells and air spaces
Cortex - surrounds the medulla; layers of flattened cells; most heavily keratinized (provides strength)
Cuticle - outermost layer; single layer of overlapping cells (provides protection)
What are the parts of a hair follicle? Explain the function of each part.
Hair follicle - extends from epidermal surface into dermis; structure that surrounds and produces the hair
Hair bulb - deep, expanded end of the follicle; site of active cell division that produces/grows the hair
Dermal papilla - projection at the base of the hair bulb; contains blood vessels that nourish the growing hair
Hair follicle receptor (root plexus) - knot of sensory nerves wrapped around the hair bulb; detects hair movement and touch
Arrector pili muscle - bundle of smooth muscle attached to the follicle; contracts to make hair stand erect (causes goosebumps)
Sebaceous (oil) gland - attached to the hair follicle; produces sebum (oil) to lubricate the hair and skin
Describe the structure and function of oil glands
Oil glands (sebaceous glands)
Occurs everywhere around the body except palm and soles
Secretes sebum (oily substance)
Functions of sebum
Collects dirt
Helps slow water loss across skin
Helps kill bacteria
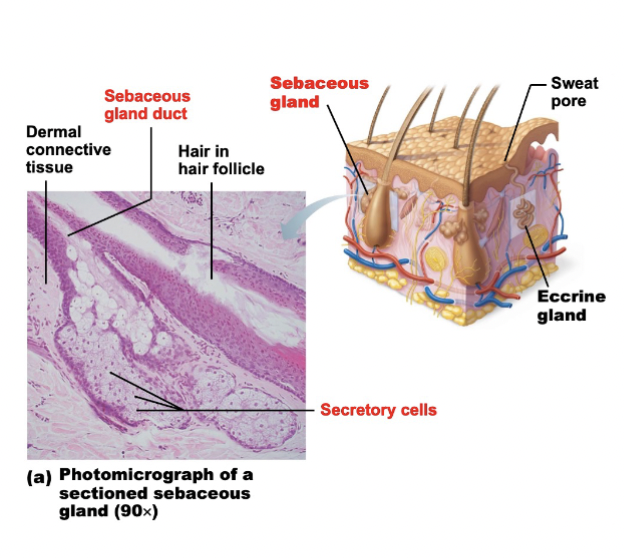
What are the 2 type of sweat glands?
Eccrine glands
Apocrine glands
Compare eccrine and apocrine glands.
Eccrine glands
Produces true sweat
99% water with some salt
Contrains traces of metabolic waste
Apocrine glands
Confined to axillary, anal, and geniteal areas
Produces sweat + fatty substances + proteins
Involved with sexual signaling, attractiveness, mate selection
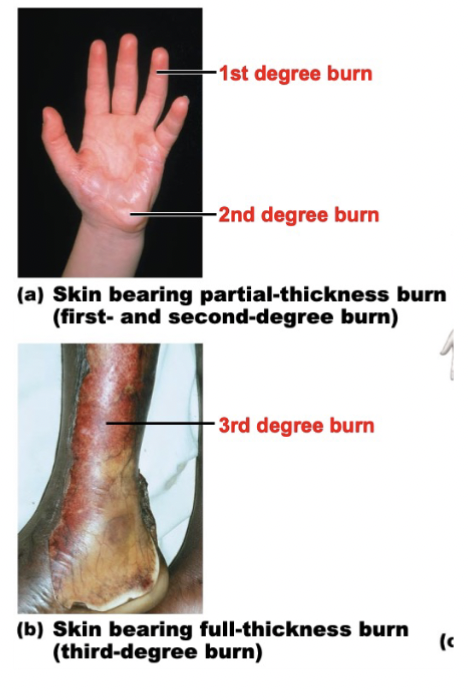
Describe the layers involved in first-, second-, and third-degree burns, along with the symptoms, and explain why serious burns are life-threatening.
1st Degree Burn
Upper epidermis is damaged
2nd Degree Burn
Epidermis and superficial region of dermis is also damaged
- Blisters appear
- Skin heals with little scarring
3rd Degree Burn
Consumes entire thickness of the skin (Both epidermis and dermis are affected)
- Burned area appears white, red, or blackened
- Graft is needed
Serious burns are life-threatening because it can lead to a catastrophic loss of body fluids
Can lead to fatal circulatory shock
After the initial crisis, infection becomes the main threat
- Pathogens can easily pass through the skin
Rule of Nines help estimate the extent of the burn
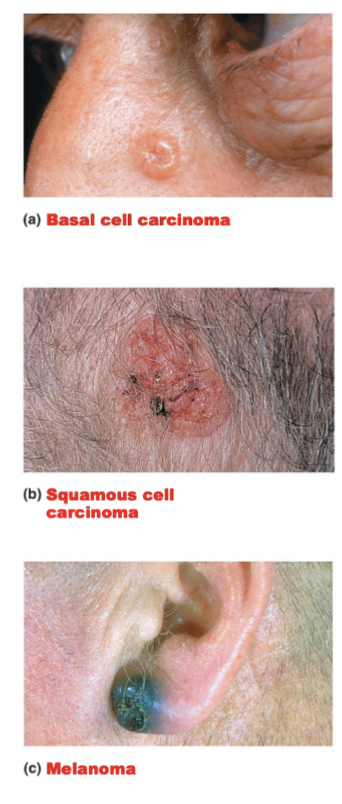
Identify the cell type involved and the degree of malignancy in the three types of skin cancer.
3 types of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma
- Stratum basal cells proliferate, invading the dermis and subcutaneous tissue
- Least Malignant and most common
- Full cure after removal
Squamous cell carcinoma
- Arises from keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
- Grows rapidly and metastasizes if not removed
Melanoma
- A cancer of melanocytes
- MOST DANGEROUS due to it being very invasive in nature