🫀 Pulmonary Blood Flow
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are the three circulations supplying the lung?
Pulmonary circulation: RV → alveoli → LA; low pressure, low resistance, highly compliant; gas exchange.
Systemic circulation: LV → body → RA; high pressure, nutrient delivery.
Bronchial circulation: from aorta → nourishes conducting airways, pleura, lymph nodes, pulmonary vessels; drains into pulmonary veins → venous admixture.
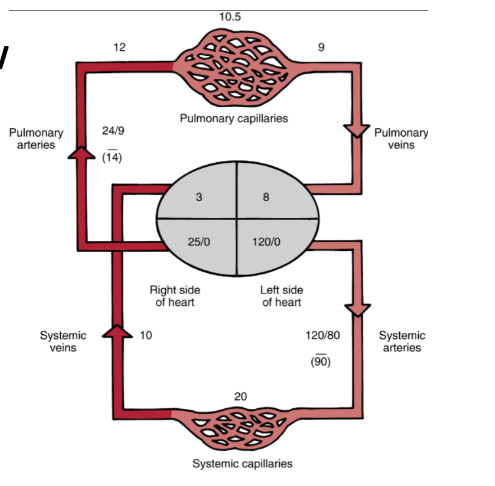
Compare pulmonary vs systemic circulation.
Pulmonary: low pressure/resistance, compliant, gas exchange, filters emboli, regulates pH
Systemic: high pressure, nutrient delivery
Pulmonary pressures: Arteries 24/9 (mean 14), Capillaries ~10.5, Veins ~9
Lower R in plum from higher compliance
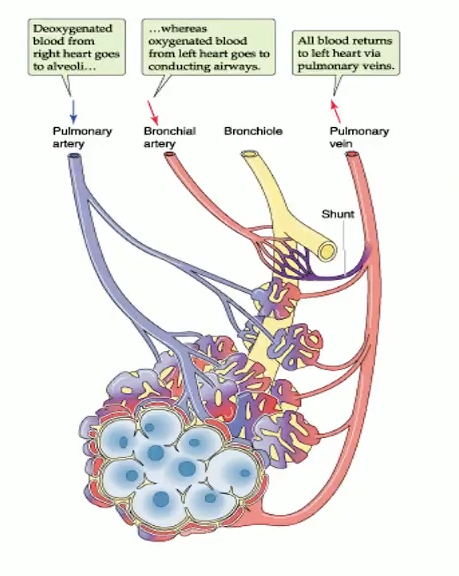
What are features of pulmonary vs bronchial circulation?
Pulmonary arteries: deoxygenated → alveoli
Pulmonary veins: oxygenated → LA
Capillaries: ~1000 per alveolus, low PVR (~10× lower than systemic)
Bronchial arteries: nourish conducting airways, drain into pulmonary veins → venous admixture
Lymphatics: prevent edema
MI HY: Alveoli they do not receive bronchial circulation. So systemic circulation and uh structures of alveoli cellular metabolism for um pulmonary epithelial cells. So they use uh oxygen from um alveolar air instead of um arterialized blood.
How is alveolar fluid balance maintained?
Thin alveolar-capillary membrane (~0.5 µm)
Tight junctions (Type I & II cells)
Surfactant ↓ surface tension
Negative lymphatic pressure + efficient drainage
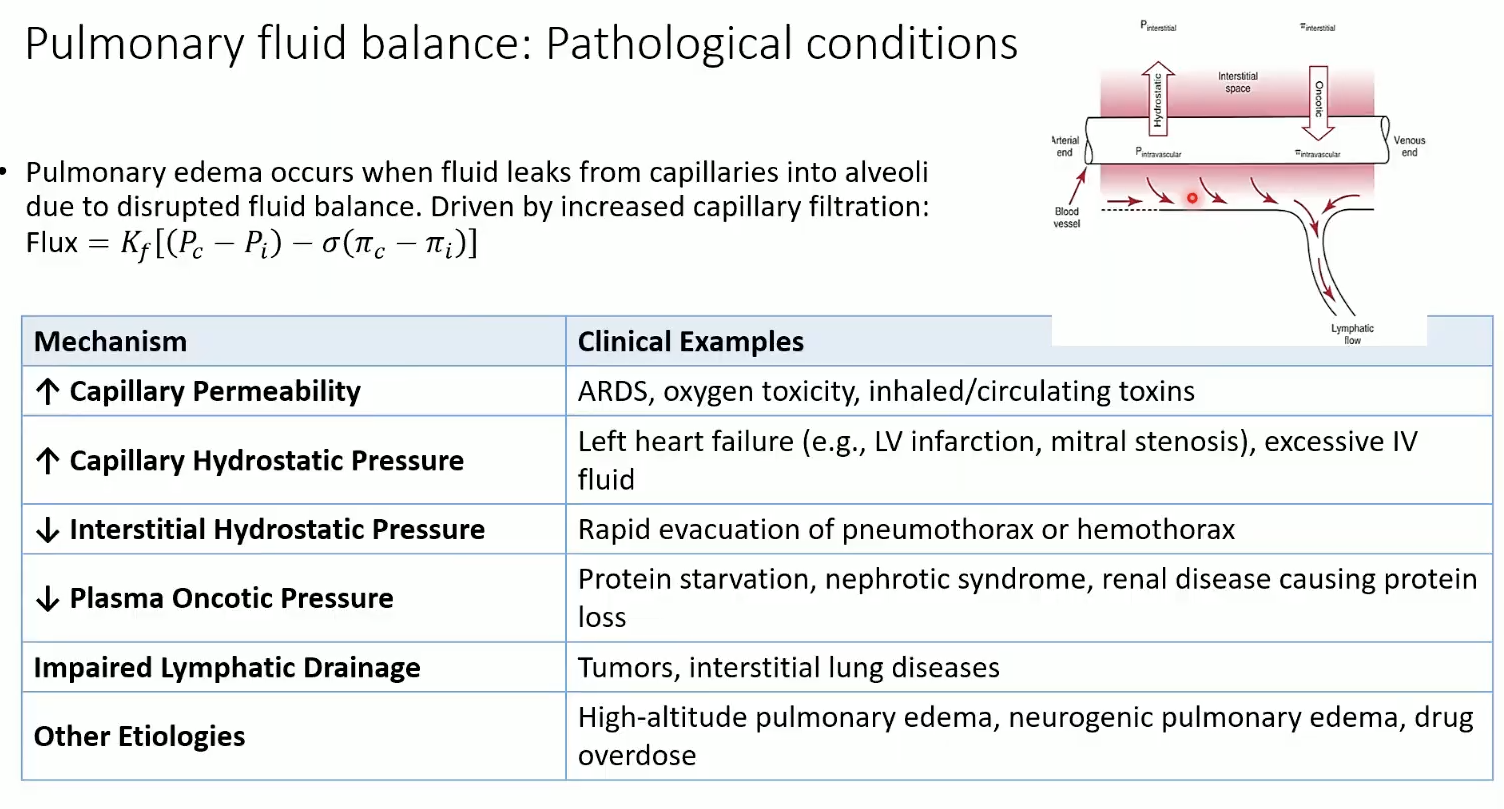
Normal filtration ≈ 30 mL/hr into interstitial, not alveoli. Cap. filtration governed by starling equation
Causes of pulmonary edema?
↑ permeability (ARDS, toxins)
↑ hydrostatic pressure (LV failure, mitral stenosis, IV fluids)
↓ interstitial pressure (rapid evacuation of pneumothorax)
↓ plasma oncotic pressure (protein loss, nephrotic syndrome)
Impaired lymph drainage (tumors, ILD)
Other: high altitude, neurogenic edema, overdose
What are passive vs active mechanisms?
Passive: breathing cycle, lung volumes, pressures, gravity
Active: neurohumoral control of vascular smooth muscle
How does pulmonary circulation adapt to flow changes?
Goal: maintain low pressure despite ↑ flow
Mechanisms: recruitment, distension, compliance
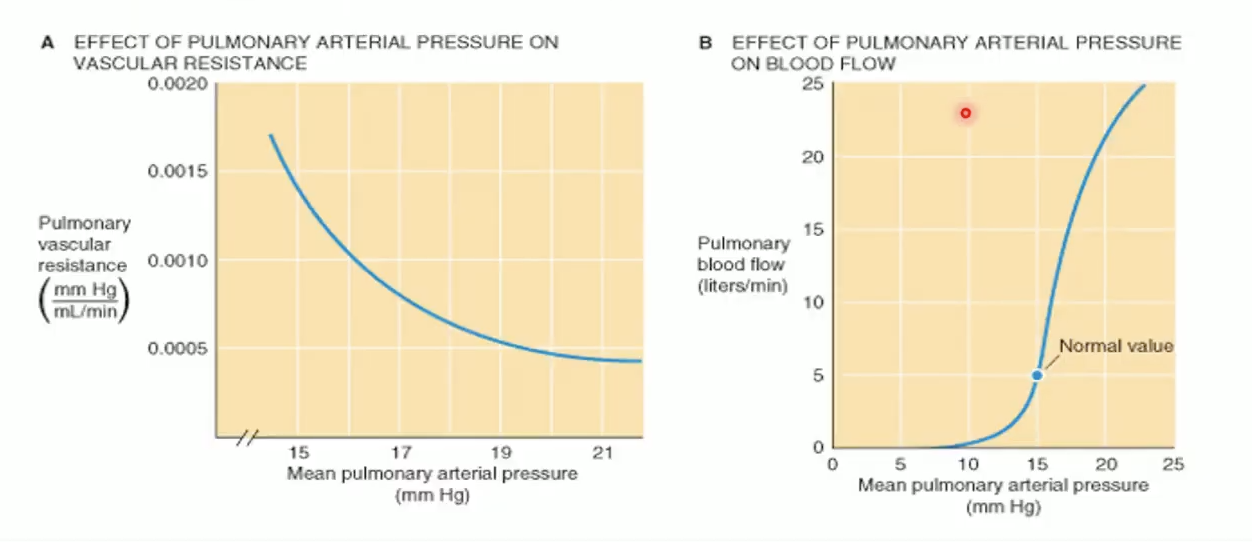
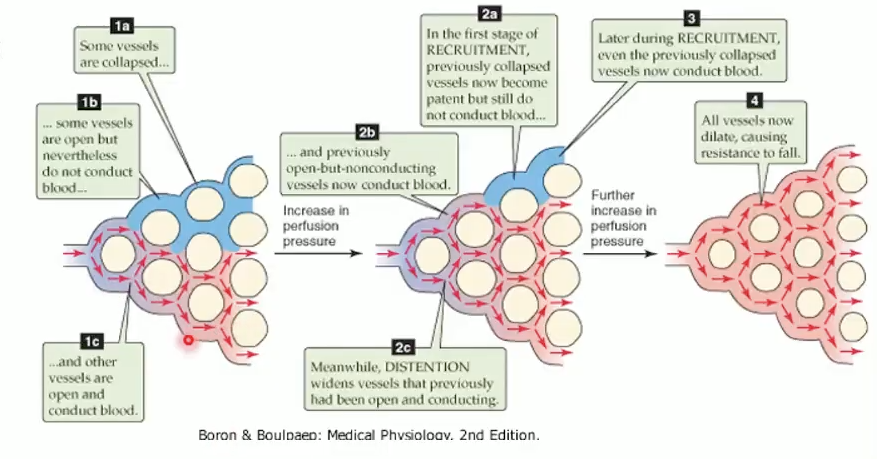
What are passive adaptive mechanisms of pulmonary circulation?
Recruitment: open previously unperfused capillaries (exercise).
Distension: dilate existing vessels.
Compliance: thin, elastic vessels buffer pressure changes.
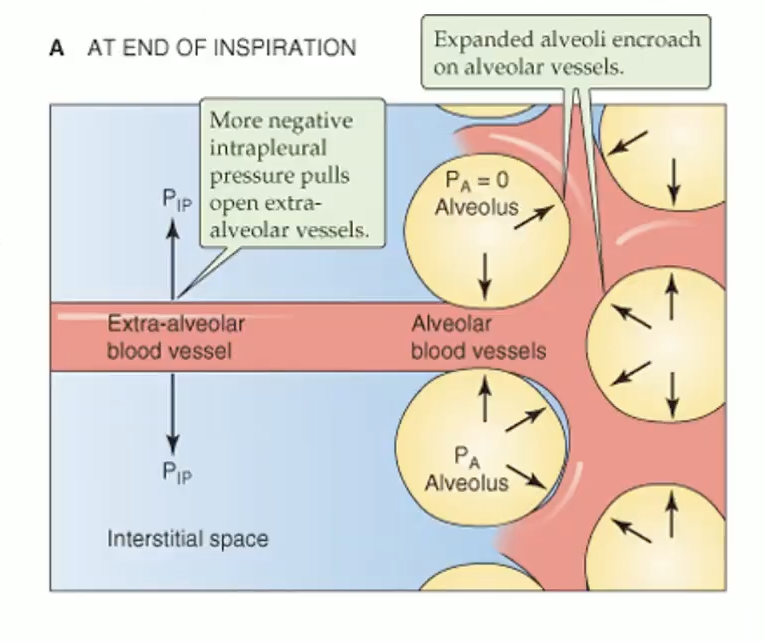
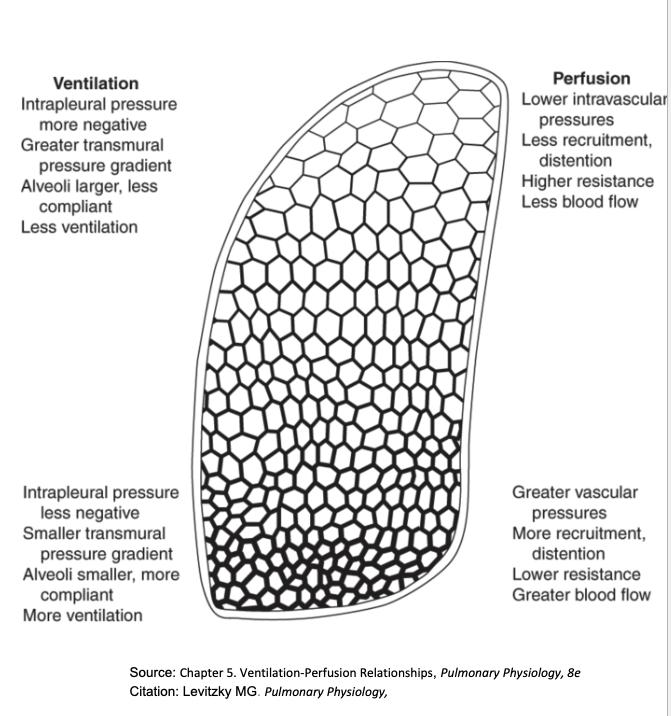
How does inhalation affect alveolar vs extra-alveolar vessels?
Alveolar capillaries: compressed by ↑ PA → ↑ resistance
Extra-alveolar capillaries: pulled open by ↓ PPL → ↓ resistance
Net effect: balance of pressures
MI HY: Inhalation blood flow is increased through extra alveolar vessels but decreased uh in alveolar blood vessels.
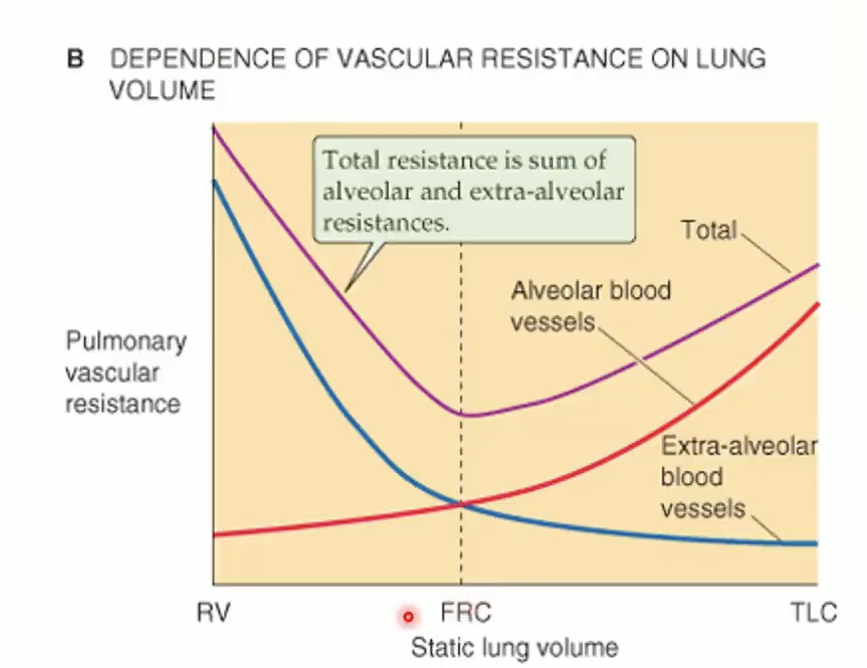
How does lung volume affect total PVR?
Alveolar resistance ↑ with inflation
Extra-alveolar resistance ↓ with inflation
Total PVR lowest at FRC
MI HY:
the lowest resistance to blood flow in pulmonary system and the functional residual capacity. Total uh resistance will increase if we inhale up total lung capacity and resistance will also increase if we exhale everything down to the residual volume.
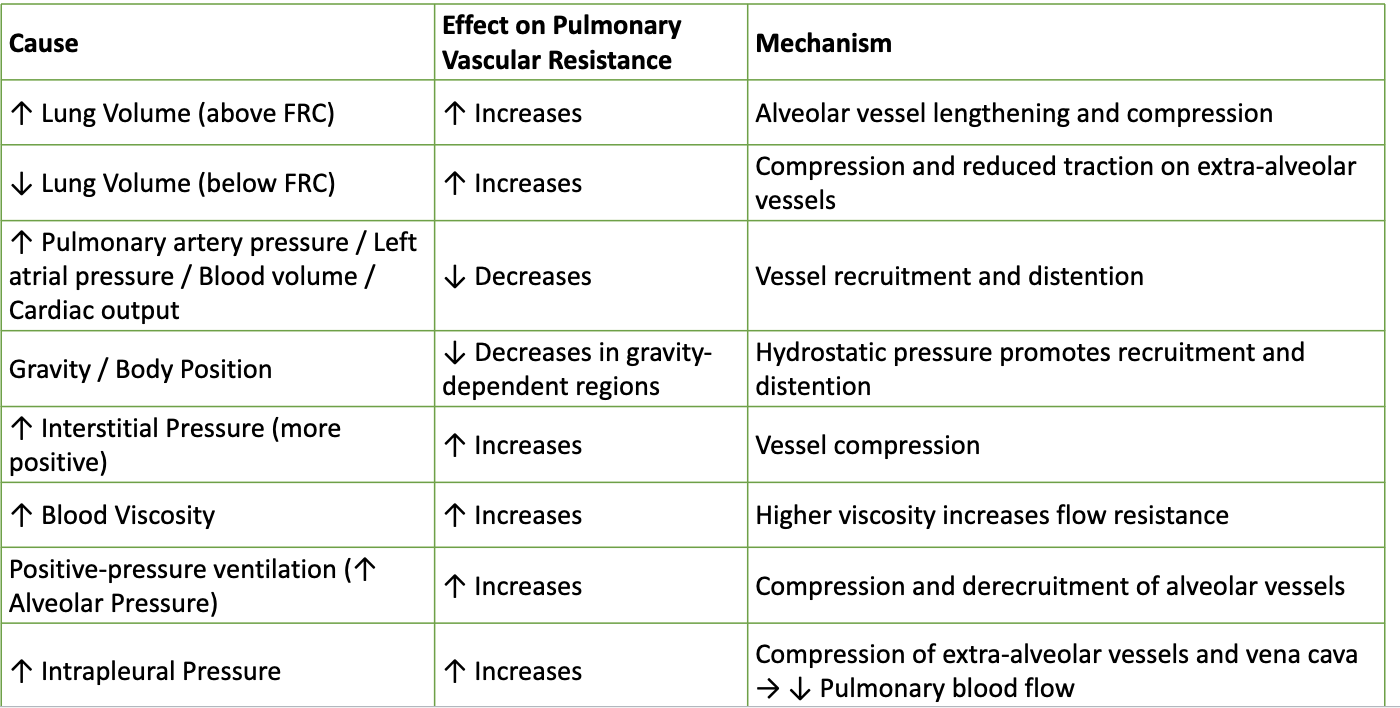
What factors ↑ or ↓ PVR?
↑ Lung volume above FRC → ↑ PVR
↓ Lung volume below FRC → ↑ PVR
↑ PA pressure/LA pressure/CO → ↓ PVR (recruitment/distension)
Gravity → ↓ PVR at base
↑ Interstitial pressure, ↑ viscosity, positive pressure ventilation, ↑ intrapleural pressure → ↑ PVR
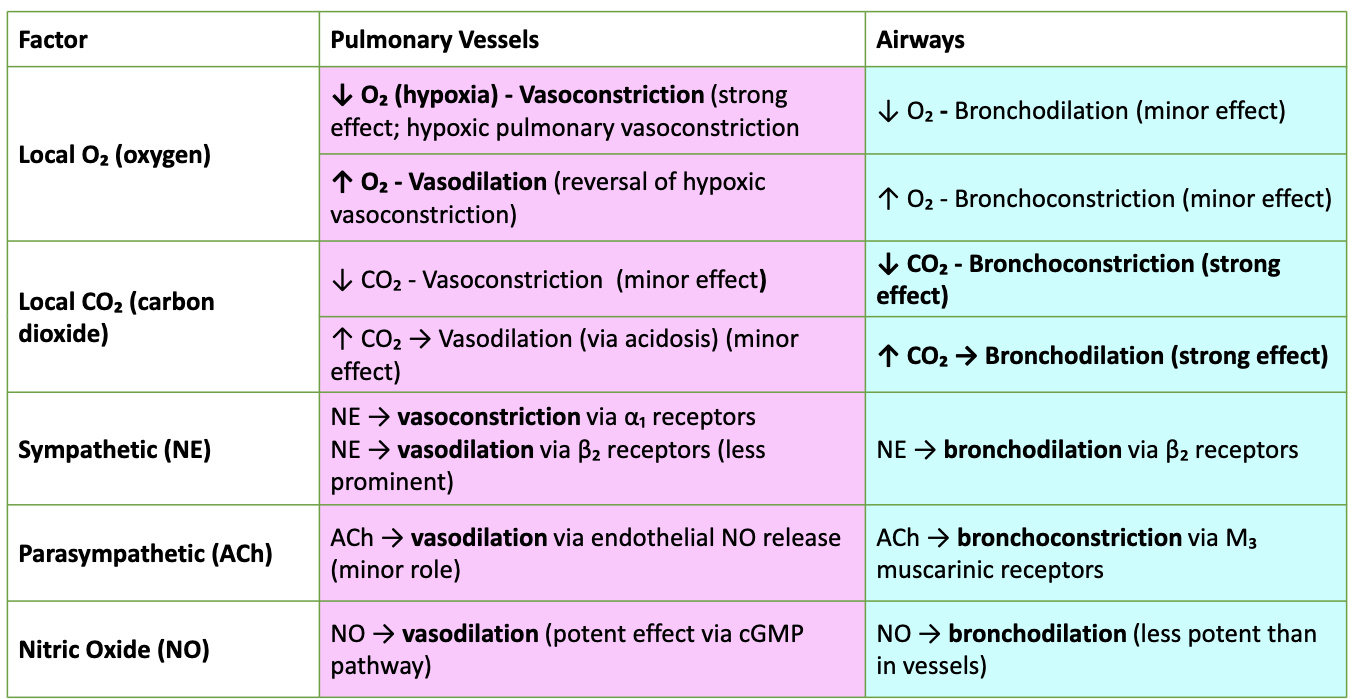
How do O₂ and CO₂ affect pulmonary vessels vs airways?
↓ O₂: pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV); bronchodilation (minor).
↑ O₂: pulmonary vasodilation; bronchoconstriction (minor).
↓ CO₂: pulmonary vasoconstriction (minor); bronchoconstriction (strong).
↑ CO₂: pulmonary vasodilation (minor, via acidosis); bronchodilation (strong).
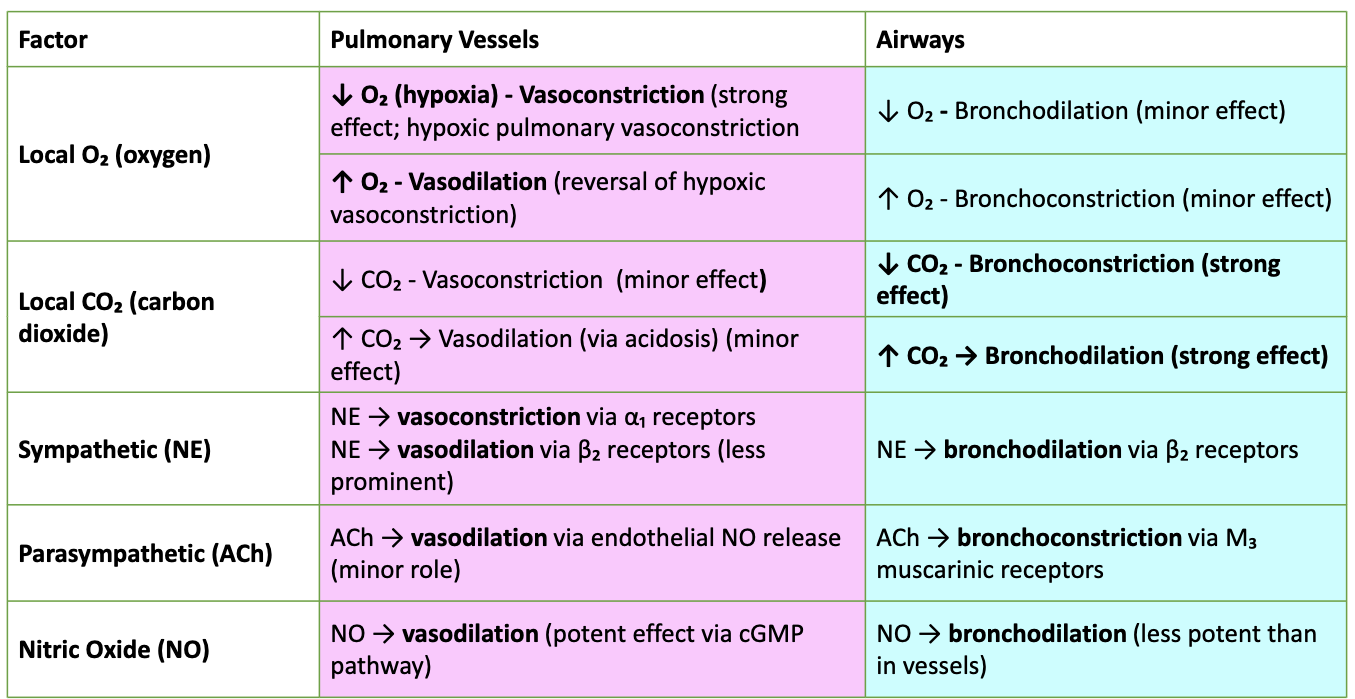
Neurohumoral regulation?
Sympathetic NE: α₁ → vasoconstriction; β₂ → vasodilation (less); β₂ → bronchodilation.
Parasympathetic ACh: vasodilation via NO (minor); bronchoconstriction via M₃.
Nitric Oxide: potent vasodilation (cGMP); mild bronchodilation.
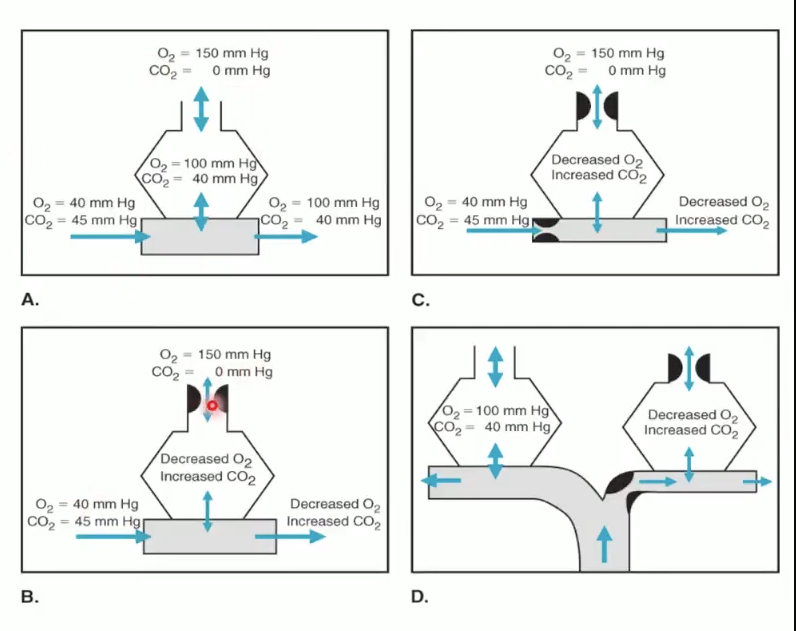
What is HPV and why is it important?
Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction (HPV)
Local hypoxia → pulmonary vasoconstriction (via K⁺ channel inhibition → depolarization → Ca²⁺ influx).
Redirects blood away from poorly ventilated alveoli → improves V/Q matching.
Pathology: chronic hypoxia → pulmonary hypertension, vascular remodeling.
Contrast: systemic vessels dilate in hypoxia (opposite).
What does HPV accomplish?
Normal: matched ventilation/perfusion
Hypoventilation: low O₂, high CO₂
HPV: constricts vessels near hypoxic alveoli → diverts blood to better ventilated regions
Maintains efficient gas exchange
What are the lung perfusion zones (upright)
Upright: base > apex perfusion due to hydrostatic pressure gradient
Creates Zones 1–3 based on PA, Pa, Pv relationships
Zone 1 (apex): PA > Pa > Pv → no flow
Zone 2 (mid): Pa > PA > Pv → intermittent flow
Zone 3 (base): Pa > Pv > PA → continuous flow
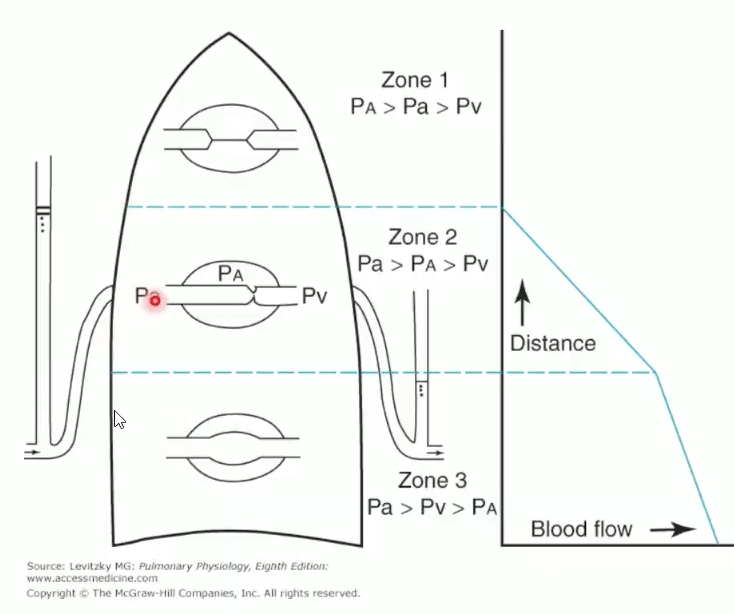
Factors shifting zones?
Zone 1 disappears: normal tidal breathing, exercise (↑ CO).
Zone 1 expands: positive-pressure ventilation (PEEP), hypovolemia, high lung volumes.
Supine position: perfusion more uniform.
Lung volume: perfusion highest at TLC base, moderate at FRC, lowest at RV
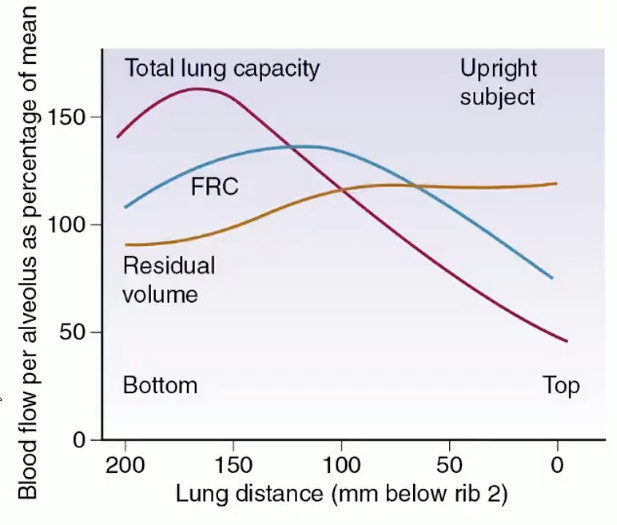
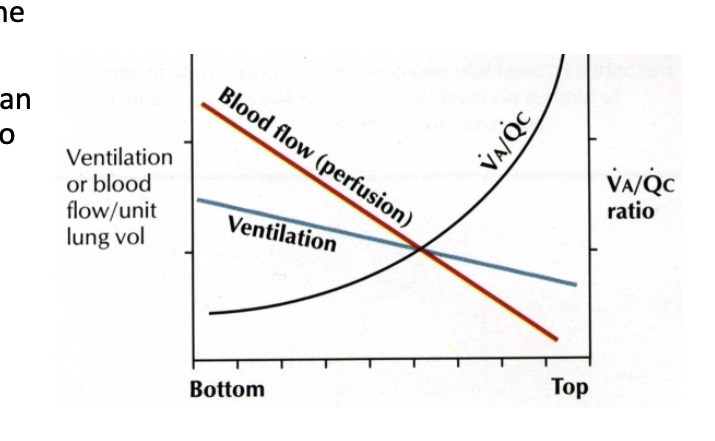
How does gravity affect ventilation?
Pleural pressure more positive at base →Transpulmonary pressure is lower —>alveoli smaller, more compliant.
Base alveoli expand more during inspiration → ↑ ventilation.
Perfusion ↓ more steeply than ventilation → V/Q ratio ↑ from base → apex.
Base: low V/Q, efficient gas exchange.
Apex: high V/Q, less efficient.
Normal ABG values: PaCO₂ 35–45 mmHg, PaO₂ 75–100 mmHg.
What happens in healthy individuals during exercise?
↑ pulmonary blood flow (not ↑ resistance).
What occurs during tidal exhalation?
Total pulmonary vascular resistance ↑ (alveolar compression + ↓ traction on extra-alveolar vessels).
Effect of ACh?
Pulmonary vasodilation (via NO); bronchoconstriction (via M₃).
At TLC upright, which is true?
No Zone 1 (Pa > PA).
Effect of lung volume on resistance?
↑ Lung volume (above FRC): alveolar vessel compression → ↑ resistance.
↓ Lung volume (below FRC): extra-alveolar compression → ↑ resistance.
Minimum resistance at FRC.