101 Exam 3-Nursing
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
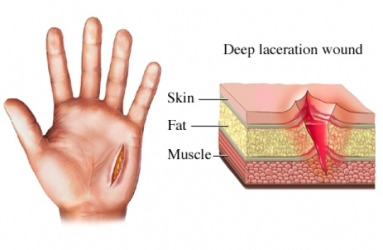
Open Wound
When there is a break in the skin or mucous membrane (Ex. abrasions , lacerations, punctures & incisions)
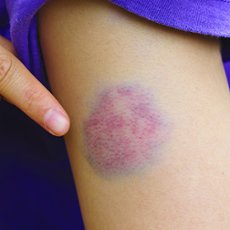
Closed Wound
When there are no breaks in the skin (Ex. contusions or tissue swelling)
Acute Wound
Expected to be of short duration and can heal spontaneously without complication (Ex. surgical incision, abrasions, abscess, contusion, crushing, excoriation, laceration, penetrating, puncture, tunnel)
Chronic Wound
Exceed the expected length of recovery. Natural healing progression has been interrupted. Present for longer than 3 months (Ex. pressure injury, arterial ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers)
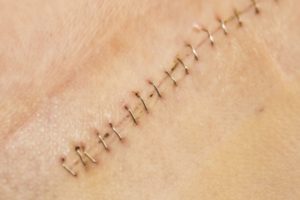
Intentional Wound
Injuries resulting from purposeful human action whether directed at oneself or others.
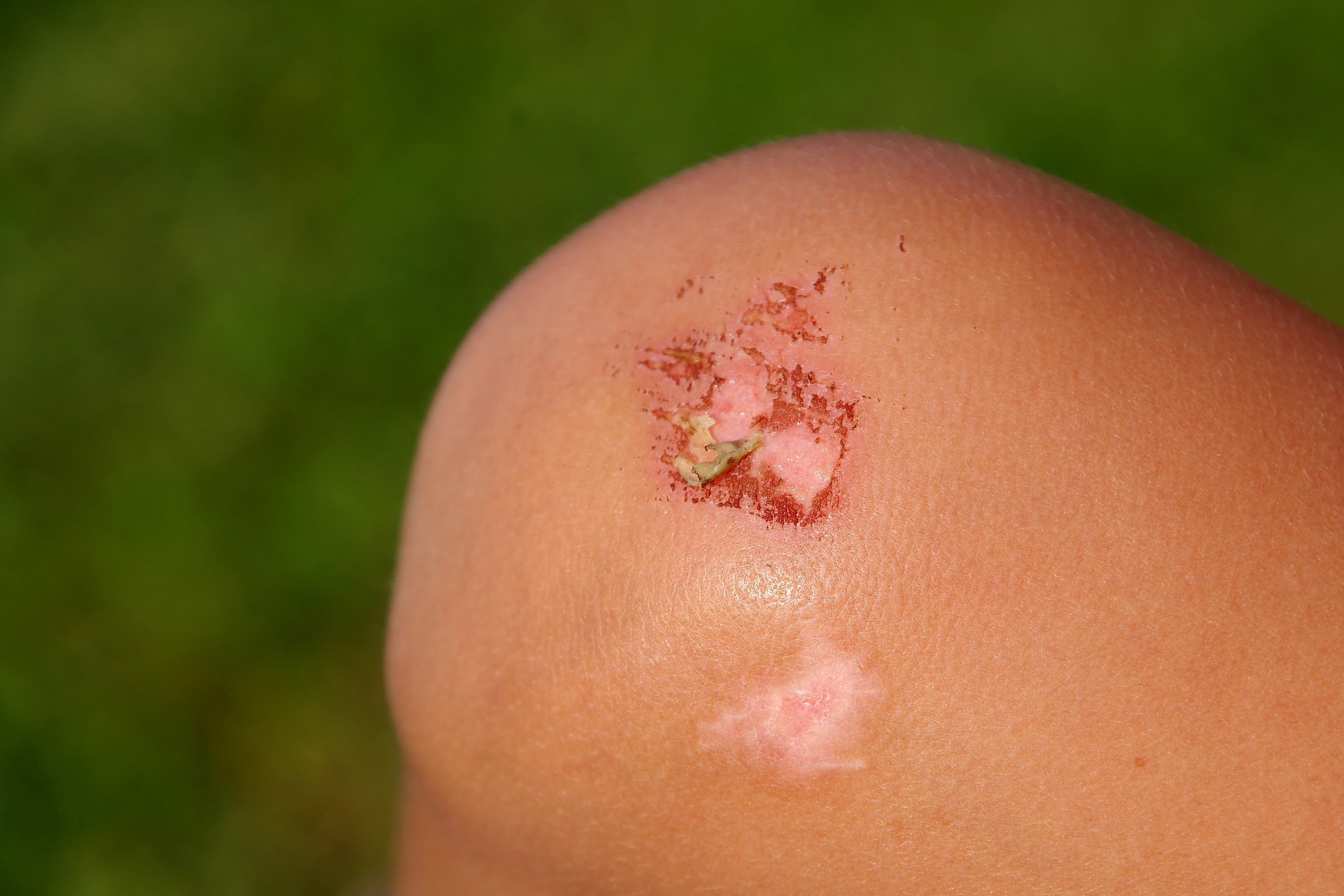
Unintentional Wound
Injuries resulting in an accident (Ex. cuts or falls)
Superficial Wound
Involves only the epidermal layer of the skin.
Partial-Thickness Wound
Extends through the epidermis but not through the dermis.
Full-Thickness Wound
Extend into the subcutaneous tissue and beyond (potentially to the bone)
Clean
Uninfected wounds with minimal inflammation.
Clean-Contaminated
Surgical incisions that enter the gastrointestinal, respiratory, or genitourinary tracts.
Contaminated
Open traumatic wounds or surgical incisions in which a major break in asepsis occurs.
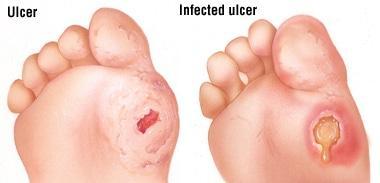
Infected
Bacteria in the wound tissues are above 100,000 organisms per gram tissue.
Abrasion
Scrape off the superficial layers of the skin. Intentional or Unintentional.
Abscess
Localized collection of pus resulting from a pathogen. Requires drainage to heal.
Contusion
Closed wound caused by blunt trauma.
Excoriation
Superficial wound, usually self-inflicted (Ex. scratches)
Crushing
Wound caused by force leading to compression or disruption of tissues.
Incision
Open, intentional wound caused by a sharp instrument.
Laceration
Skin or mucous membraned are torn open (Ex. jagged edges)
Penetrating
Open wound in which the agent causing the wound lodges in the body tissue.
Puncture
Open wound caused by a sharp object.
Tunnel
Wound with an entrance and exit site.
Arterial Ulcer
Caused by inadequate circulation of oxygenated blood to the tissue. Leads to ischemia and damage.
Venous Stasis Ulcers
Caused by incompetent venous valves, deep vein obstruction, or inadequate calf muscle function. (Ex. Venous pooling, edema, & impaired microcirculation of the skin)
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Narrowing of the arteries leads to reduced oxygenation to the feet (Delayed wound healing and tissue necrosis)
Exudate
Drainage that oozes from a wound or cavity.
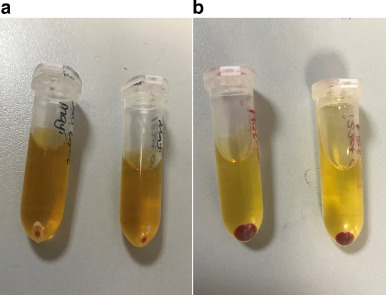
Serous Exudate
Watery consistency
Clean wounds typically have this
Straw-colored fluid that separates out of blood.

Sanguineous Exudate
Bloody drainage
Indicated damage to capillaries
Deep wounds or in highly vascular areas
Serosanguineous Exudate
A combination of bloody and serous drainage
New wounds
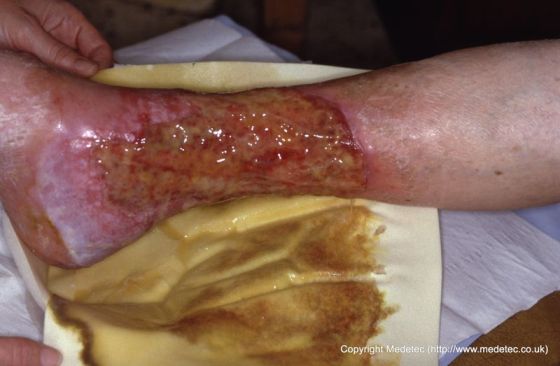
Purulent Exudate
Thick, & smelly drainage
Infected Wounds
Pus, bacteria, and cellular debris
Yellow but can be blue/ green with bacteria
Purosanguineous Exudate
Red-tinged pus
Small vessels in wound have ruptured
Regeneration
No scar forms
New regenerated epithelial and dermal cells form new skin
Only effects the epidermis and dermis
Primary Intention
Minimal or no tissue loss
Wound edges are are well approximated
Little scarring expected
Surgical incisions
Secondary Intention
Extensive tissue loss, which prevents wound edges from approximating
Should not be closed if there is an infection
Will likely scar
Does not have to be an open wound
Pressure sore, stitches broke open?
Tertiary intention
Occurs when two surfaces of granulation tissue are brought together
Initially uses secondary intention
When there is no evidence of edema, infection, or foreign matter, the wound edges are closed by bringing granulating tissue and suturing the surface
Inflammatory Phase
Cleansing
Hemostasis
Vessels constrict to limit blood loss and platelet clump together to slow the bleeding
Inflammatory phase
Inflammation
Phagocytosis
Migration of white blood cells into the wound tissue
Edema, erythema, pain, temperature elevation
A formed scab
In the inflammatory phase
Proliferative Phase
Granulation
Cells develop to fill the wound defect and resurface the skin
Collagen is formed-adds strength to the healing wound
New blood and lymph vessels sprout from capillaries around the wound
Maturation Phase
Epithelialization
Collagen fibers that were laid in the wound bed during proliferative phase are broken down & remodeled into an organized structure
Scar tissue
Hemorrhage
Profuse or rapid blood loss
Internal or external
Infection
Microorganisms are introduced to a wound
Smoking
Causes vasoconstriction
Dehiscence
Rupture (Separation) of one or more layers of a wound
Usually associated with abdominal wounds
“pop” or “tear” often felt by patient
Evisceration
Total separation of the layers of the wound with internal viscera
Medical emergency
Pressure Injury
Localized injury to the skin and underlying tissue usually over a bony prominence
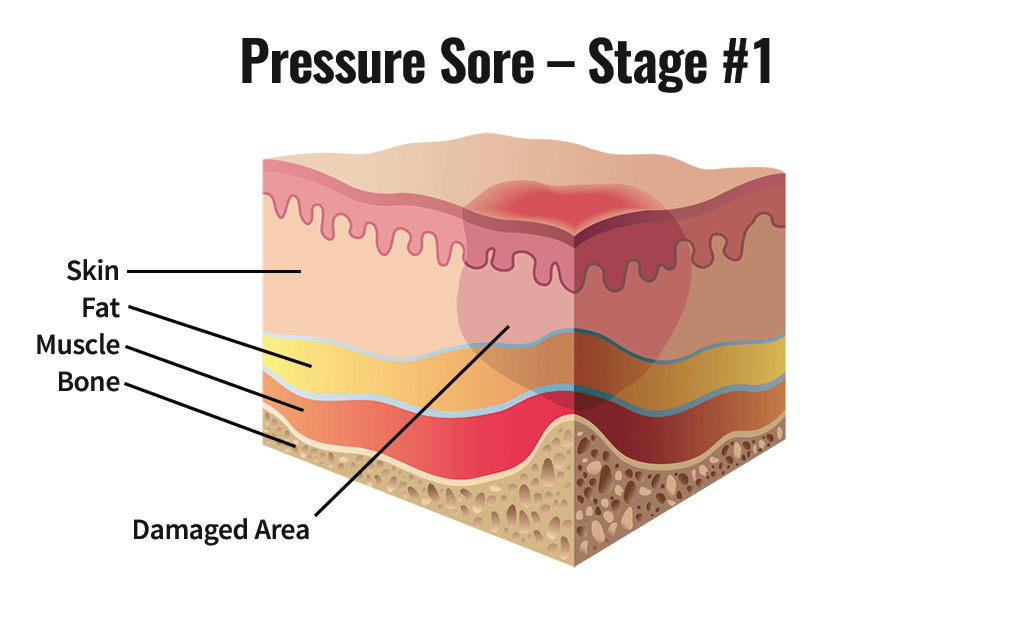
Stage 1 Pressure Injury
Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin that lasts for greater than 30 minutes after pressure is relieved
May be painful
May be firm, soft, warmer, or cooler compared to adjacent tissue
Dark skin may seem discolored instead of red
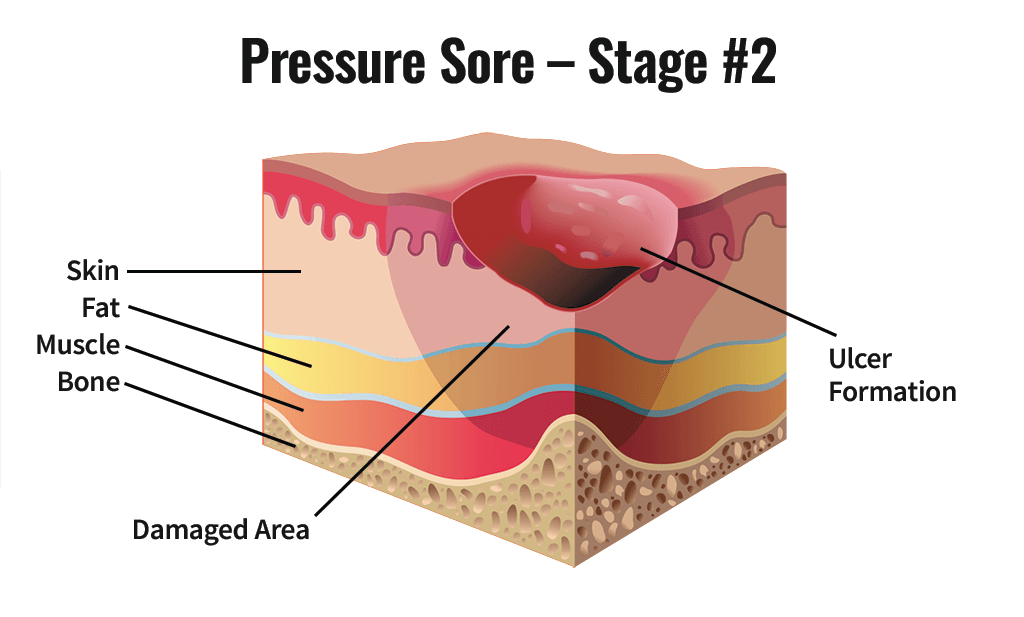
Stage 2 Pressure Injury
Partial-thickness loss of dermis
Open but shallow & with a red/pink wound bed
No slough (tan, yellow, gray, green, or brown necrotic tissue)
May also be intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister
Might look like a scrape, blister, “zit” or crater
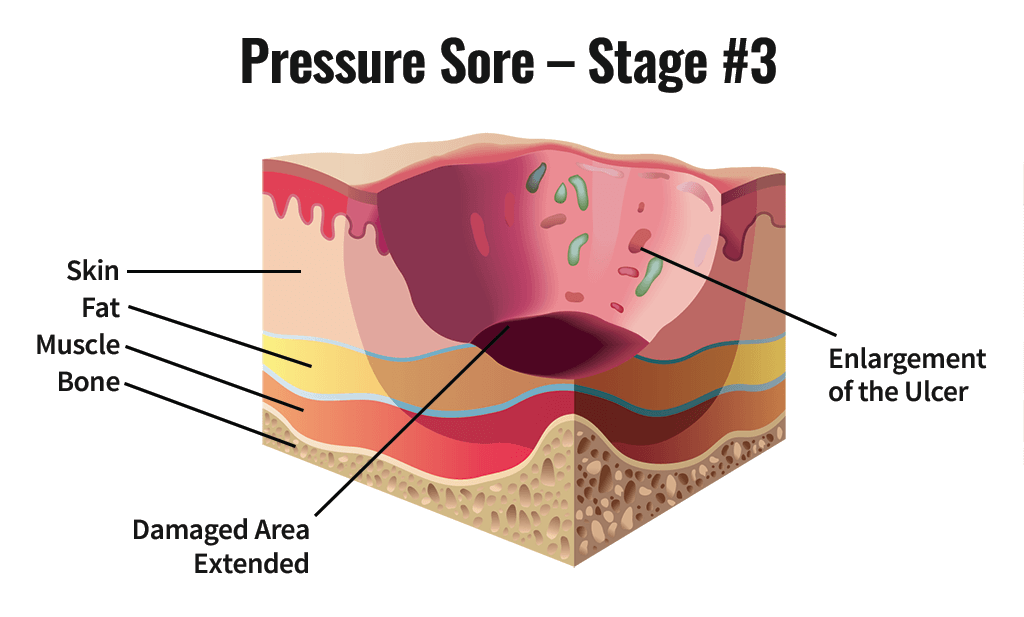
Stage 3 Pressure Injury
A deep crater characterized by full-thickness skin loss
Image or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue
Adipose tissue is visible
Damage all the way down to fascia(connective tissue of body)
Does not extend through the fascia
Bone/tendon is not visible or directly palpable
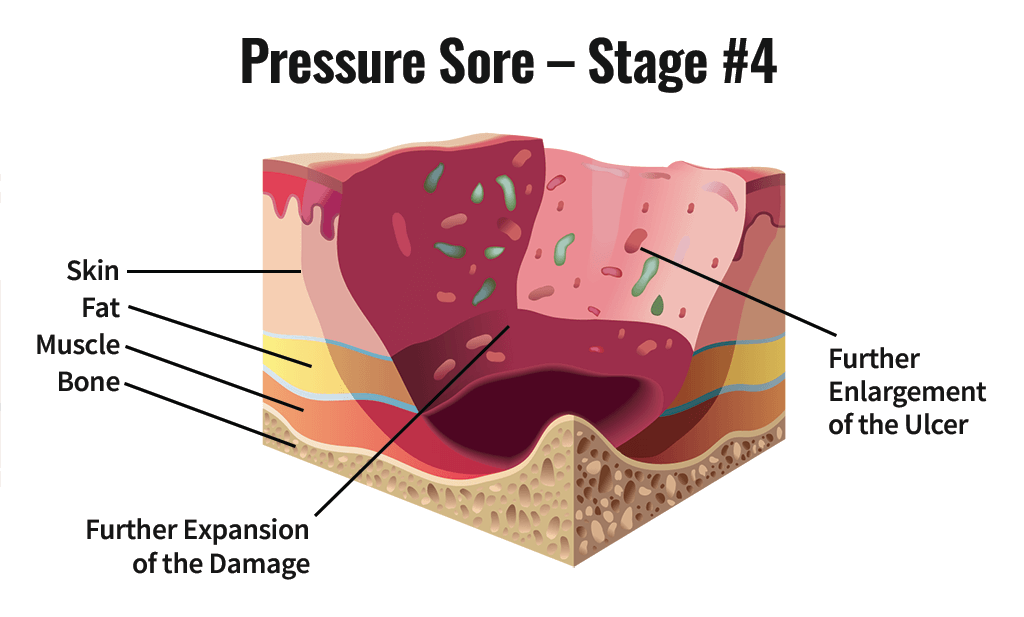
Stage 4 Pressure Injury
Full-thickness skin loss with extensive destruction, tissue necrosis, or damage to muscle, bone, or support structures
Exposed bone, tendon, or cartilage is visible or directly palpable
Slough or eschar may be present
Depth varies by location
Can extend to muscle and supporting structures
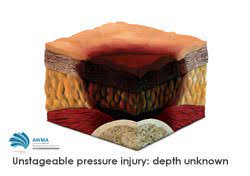
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Involves full-thickness skin loss
The base of the wound is obscured by slough or eschar
Braden scale
Rates sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, friction, & sheer
The lower the score, the more likely the patient will develop a pressure injury
Norton Scale
Based on the patient’s physical condition, mental state, activity, mobility, & incontinence
A low score indicates risk for pressure injury
PUSH (Pressure Ulcer Surface of Healing)
Reports the progression of a pressure injury
Surface area, exudate, &type of wound tissue are scored and totaled
As the injured area heals, the total score decreases
Pressure
Compresses small blood vessels, hindering blood flow and nutrient supply
Tissues become ischemic, damaged, or die
Shear
Occurs when one layer of tissue slides horizontally over another
Commonly occurs when a patient slides down in bed
Friction
When skin is moist, fragile, or dragged across a surface
Moisture
Urine, feces, & diaphoresis macerate the skin
Patient Health Status
Immobility, poor nutrition, fever, infection, dehydration, edema, impaired sensation
Manage Moisture
Incontinence care-clean after every episode
Keep skin clean & dry
Apply barrier cream
Moisturize dry skin
Massage to help with circulation
Monitor the Injury
Reassess patients often every 8-12 hours for at risk patients
Minimize Pressure
Turn & reposition
Elevate the head of bed 30 degrees or less
When side-lying, position at 30 degrees to avoid direct pressure on the trochanter
Limit time in 30 degrees or greater to prevent pressure and shear
Support Surfaces
Specialty mattresses and chair cushions they redistribute pressure
Proper Nutrition
Monitor hydration and offer water
Provide adequate calories and protein
Offer supplemental nutrition if needed
Dietary referral if needed
Patient/family teaching
Ongoing assessments
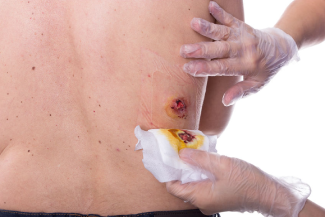
Staples & Sutures
Remove every other
Count & lay on gauze & make sure you get the same number
Approximate (bring together)
Sutures & Staples
Remove when ordered by physician
NEVER pull contaminated portion of suture through underlying tissue because of bacteria
Always clean incision before removal
Bandage
Cloth, gauze, or elastic coverings wrapped in place
Abdominal Binders
Provides support to abdomen after surgery
Decreases risk for dehiscence
T-Binder
Secures dressing or pads in perineal area
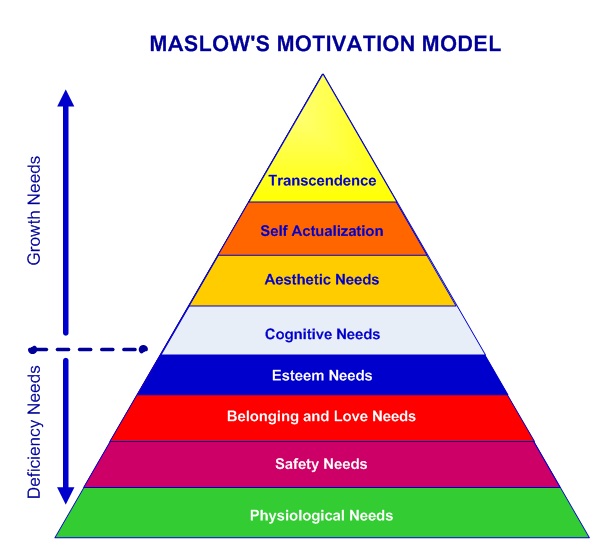
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Self-Concept
Is the frame of reference that influences how one handles life situations and relationships
Overall view of what person thinks or feels about self
Self-Perception
A filtering process that evaluates events and enters them into the subconscious
Filtering prevents feeling of guilt, anxiety, and unworthiness from surfacing
Perceives physical self & personal self-worth
Body Image
Your mental image of your physical self
Characteristics & abilities
Physical appearance & function
Gradual vs sudden body changes
Influence of body image on health
Ideal Body Image
How we would like to look
Perceived Body Image
How others objectively see your body
Actual Body Image
How the body actually looks
Role Performance
The actions a person takes and the behaviors they demonstrate in fulfilling a role
May be ascribed or assumed
Involve expectations or standards of behavior that have been accepted by society or the social group
Role strain, conflict (intrapersonal/interrole), ambiguity
Personal Identity
Your view of yourself as a unique human being different and separate from all others
Values, beliefs, personality, character, age, weight, height, sex, ethnicity
Self Esteem
How well a person likes themselves
The difference between “ideal self” & “actual self”
Sympathetic System
Responses & energy “fight or flight”
Parasympathetic System
Restoration of energy
Adrenal Glands
The inner portion (medulla) secretes
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
Stimulus-Based Model
Life events scale (also known as the Holmes & Rahe Social Readjustment Rating Scale)
Response-Based Model
Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
Local Adaptation Syndrome (LAS)
Maladaptive Disorders
Stress induced psychological response: CRISIS & BURNOUT
Family
Social group whose members share values, occupy specific positions & interact with each other
Basic unit of society
Role: protect & socialize it’s members
Family Structure
Who the members of the family are and what their relationships are to one another
Family Function
What the family does
Types of Families
Traditional (nuclear) families, grandparent families, dual-earner families, military families, etc.
Challenges in Family Health
Poverty & unemployment
Infectious diseases
Chronic illness/disability
Homelessness
Violence/neglect within families
Parental Styles
Authoritarian
Permissive
Authoritative
Beliefs
Mental acceptance or conviction in truth of something
Attitudes
State of mind or feeling with regard to something
Morals
Principles of what is right and wrong
Ethics
Standards that govern proper conduct
Value
The worth of something: serves as principle or standard that influences decision making
Terminal Value
Desired goals such as happiness or career success
Instrumental Value
Desirable modes of conduct such as honesty or maintaining
Modeling
Children model their parents’ behavior along with peers & celebrities