Final Semester 1 Review - AP Biology
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
catabolism
Which of the following is a statement of the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
Which of the following best describes enthalpy ( H)?
the heat content of a chemical system
Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true?
Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy barrier.
During a laboratory experiment, you discover that an enzyme–catalyzed reaction has a ΔG of –20 kcal/mol. If you double the amount of enzyme in the reaction, what will be the ΔG for the new reaction?
-20 kcal/mol
According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis, which of the following is correct?
The binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site.
Zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is present in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase. The zinc most likely functions as a(n)
cofactor necessary for enzyme activity.
When you have a severe fever, what grave consequence may occur if the fever is not controlled?
change in the tertiary structure of your enzymes
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
by changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
The mechanism in which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway is most precisely described as
feedback inhibition
Protein kinases are enzymes that catalyze phosphorylation of target proteins at specific sites, whereas protein phosphatases catalyze removal of phosphate(s) from phosphorylated proteins. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation can function as an on–off switch for a protein's activity, most likely through
the change in a protein's charge leading to a conformational change
Living organisms increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in a decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the second law of thermodynamics?
As a consequence of growing, organisms cause a greater increase in entropy in their environment than the decrease in entropy associated with their growth.
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
a molecule of glucose
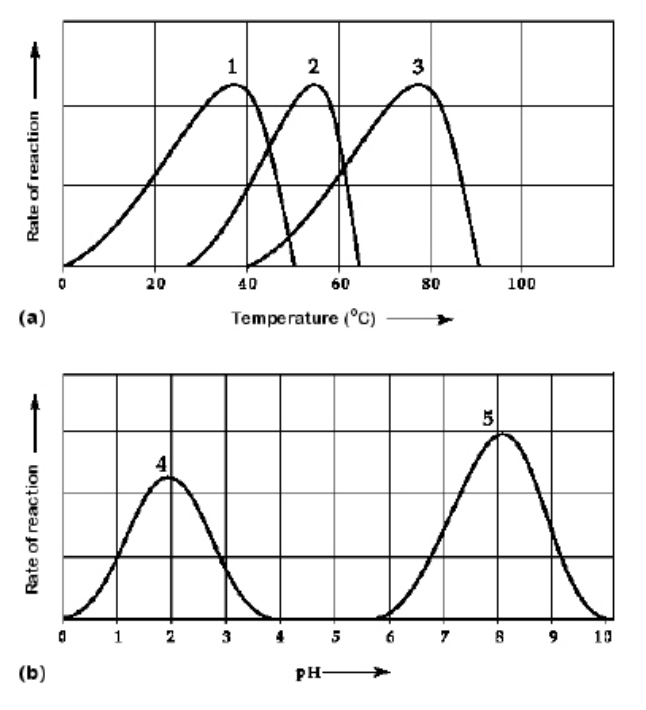
Which curve(s) on the graphs may represent the temperature and pH profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot springs at temperatures of 70°C or higher?
curves 3 and 5
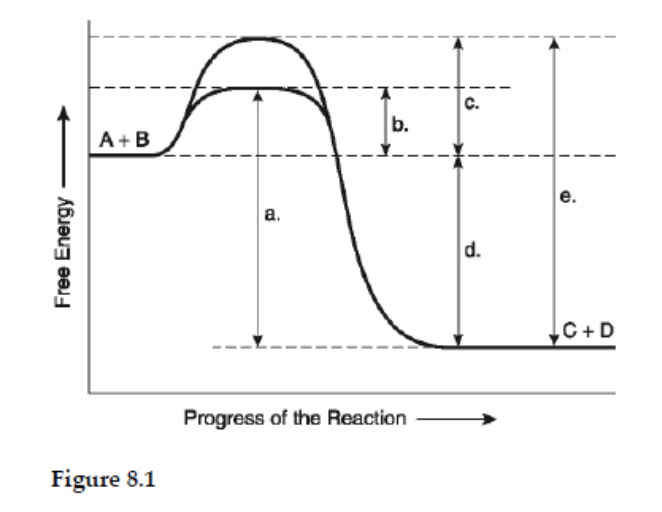
Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in Figure 8.1?
exergonic, ΔG < 0
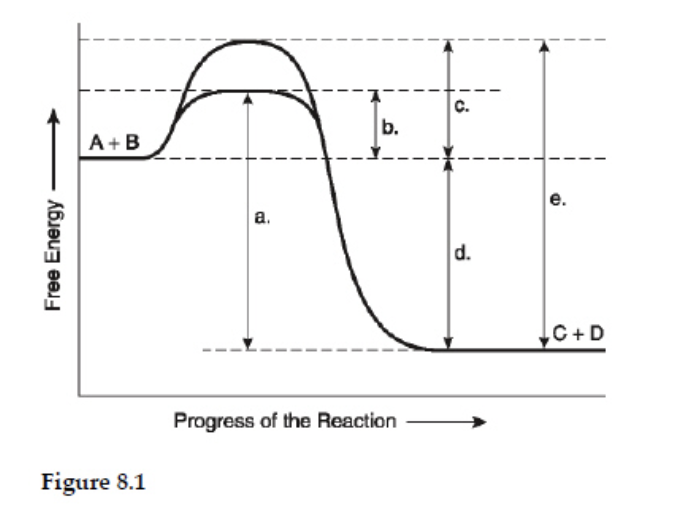
Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the enzyme –catalyzed reaction in Figure 8.1?
b
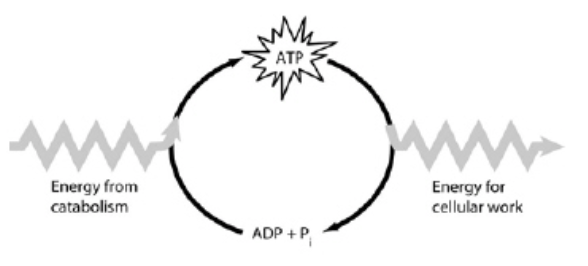
Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of the figure?
ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work.
Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid.
What is malonic acid's role with respect to succinate dehydrogenase?
It is a competitive inhibitor.
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as _____ is to _____.
exergonic; endergonic
Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because
their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells?
cytosol
The ATP made during glycolysis is generated by
substrate–level phosphorylation.
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent?
glycolysis
Starting with one molecule of glucose, the energy–containing products of glycolysis are
2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
Which of the following intermediary metabolites enters the citric acid cycle and is formed, in part, by the removal of a carbon (CO2) from one molecule of pyruvate?
acetyl coA
During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence?
food → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
In cellular respiration, the energy for most ATP synthesis is supplied by
a proton gradient across a membrane.
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
FADH2
Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follow which pathway?
citric acid cycle → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
In chemiosmotic phosphorylation, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + Pi to ATP?
energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down the electrochemical gradient
Which of the following produces the most ATP when glucose (C6H12O6) is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water?
oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
The synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, using the energy released by movement of protons across the membrane down their electrochemical gradient, is an example of
an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction.
Which metabolic pathway is common to both cellular respiration and fermentation?
glycolysis
The ATP made during fermentation is generated by which of the following?
substrate–level phosphorylation
Why is glycolysis considered to be one of the first metabolic pathways to have evolved?
It does not involve organelles or specialized structures, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms.
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is
oxygen
Most CO2 from catabolism is released during
the citric acid cycle
In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules?
harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction–center chlorophyll
Which of the following are directly associated with photosystem I?
receiving electrons from the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
Some photosynthetic organisms contain chloroplasts that lack photosystem II, yet are able to survive. The best way to detect the lack of photosystem II in these organisms would be
to test for liberation of O2 in the light
What does the chemiosmotic process in chloroplasts involve?
establishment of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane
P680+ is said to be the strongest biological oxidizing agent. Why?
This molecule has a stronger attraction for electrons than oxygen, to obtain electrons from water.
The reactions that produce molecular oxygen (O2) take place in
the light reactions alone
What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle?
synthesize simple sugars from carbon dioxide
The NADPH required for the Calvin cycle comes from
reactions initiated in photosystem I.
Reactions that require CO2 take place in
the Calvin cycle alone.
Photorespiration occurs when rubisco reacts RuBP with
O2
Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2
The alternative pathways of photosynthesis using the C4 or CAM systems are said to be compromises. Why?
Both minimize photorespiration but expend more ATP during carbon fixation.
Compared to C3 plants, C4 plants
can continue to fix CO2 even at relatively low CO2 concentrations and high oxygen concentrations.
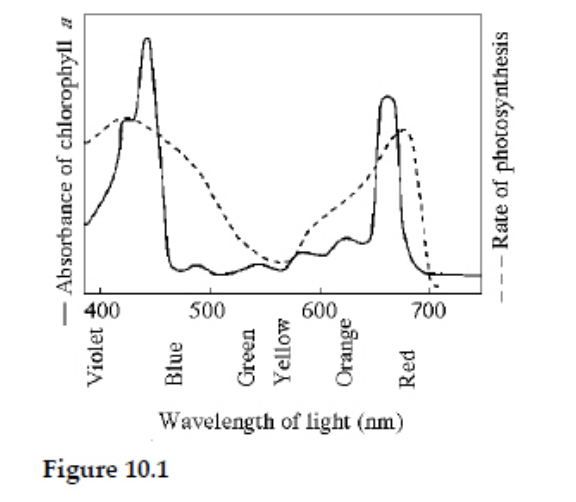
Figure 10.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Why are they different?
Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a.
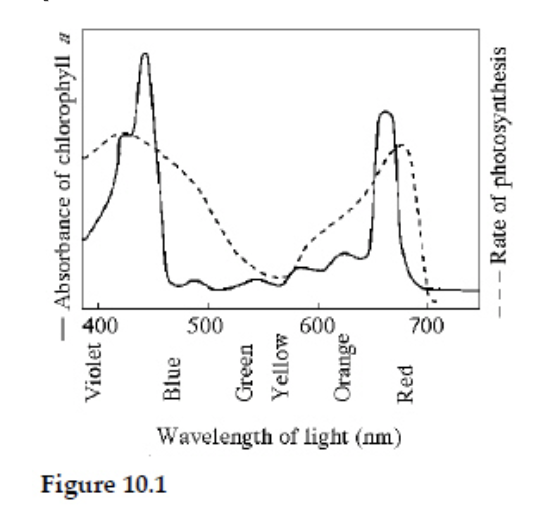
What wavelength of light in the figure is most effective in driving photosynthesis?
420 mm
Theodor W. Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism, thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light. He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated. He noted that the largest groups were found in the areas illuminated by the red and blue light.
An outcome of this experiment was to help determine
the relationship between wavelengths of light and the rate of photosynthesis.
The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the Calvin cycle with
ATP and NADPH.
Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle
How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants and CAM plants?
In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially.
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation–reduction reaction
loses electrons and loses potential energy.
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
Halobacterium has a photosynthetic membrane that is colored purple. Its photosynthetic action spectrum is exactly complementary (opposite to) the action spectrum for green plants. What wavelengths of light do the Halobacterium photosynthetic pigments absorb?
blue and red
Which of the following is characterized by a cell releasing a signal molecule into the environment, followed by a number of cells in the immediate vicinity responding?
paracrine signaling
In the formation of biofilms, such as those forming on unbrushed teeth, cell signaling serves which function?
aggregation of bacteria that can cause cavities
When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway?
signal molecule
Of the following, a receptor protein in a membrane that recognizes a chemical signal is most similar to
the active site of an allosteric enzyme that binds to a specific substrate.
Which of the following is true for the signaling system in an animal cell that lacks the ability to produce GTP?
It would not be able to activate and inactivate the G protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
Testosterone functions inside a cell by
binding with a receptor protein that enters the nucleus and activates specific genes.
Which of the following is true of transcription factors?
They regulate the synthesis of DNA in response to a signal.
Because most receptors are membrane proteins, which of the following is usually true?
They change their conformation after binding with signal polypeptides.
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are found at high levels on various cancer cells. A protein, Herceptin, has been found to bind to an RTK known as HER2. This information can now be utilized in breast cancer treatment if which of the following is true?
If the patient's cancer cells have detectable HER2
In general, a signal transmitted via phosphorylation of a series of proteins
brings a conformational change to each protein
Which of the following would be inhibited by a drug that specifically blocks the addition of phosphate groups to proteins?
receptor tyrosine kinase activity
Which of the following most likely would be an immediate result of growth factor binding to its receptor?
protein kinase activity
If a pharmaceutical company wished to design a drug to maintain low blood sugar levels, one approach might be to design a compound
to block G protein activity in liver cells.
An inhibitor of which of the following could be used to block the release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum?
phospholipase C
Which of the following is the best explanation for the fact that most transduction pathways have multiple steps?
Multiple steps provide for greater possible amplification of a signal.
In which of the following ways could signal transduction most probably be explored in research to treat cancer?
alteration of protein kinases in cell cycle regulation in order to slow cancer growth
A drug designed to inhibit the response of cells to testosterone would almost certainly result in which of the following?
a decrease in transcriptional activity of certain genes
At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects?
Estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each of which have different responses to its binding.
What are scaffolding proteins?
large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facilitate cascade effect
Which of the following describes the events of apoptosis?
Its DNA and organelles are fragmented, the cell shrinks and forms blebs, and the cell self–digests
Why is apoptosis potentially threatening to the healthy "neighbors" of a dying cell?
Lysosomal enzymes exiting the dying cell would damage surrounding cells.
In C. elegans, ced–9 prevents apoptosis in a normal cell in which of the following ways?
It prevents the caspase activity of ced–3 and ced–4.
In research on aging (both cellular aging and organismal aging), it has been found that aged cells do not progress through the cell cycle as they had previously. Which of the following would provide evidence that this is related to cell signaling?
Growth factor ligands do not bind as efficiently to receptors.
Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because
they amplify the original signal manyfold
Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane?
ligand–gated ion channel
Lipid–soluble signaling molecules, such as testosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because
intracellular receptors are present only in target cells
Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein–coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP. Identify the second messenger.
cAMP
Apoptosis involves all but which of the following?
lysis of a cell
Besides the ability of some cancer cells to overproliferate, what else could logically result in a tumor?
lack of appropriate cell death |
A student is looking through his light microscope (~450 X) at a squashed and stained onion root tip. Some, but not all, of the cells have clearly visible chromosome strands.
When a cell is in anaphase of mitosis, which of the following will he see?
a clear area in the center of the cell |
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B?
cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis
At which phase are centrioles beginning to move apart in animal cells?
prophase
If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested?
metaphase
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer cells
continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together. |
Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells?
They do not exhibit density–dependent inhibition when growing in culture. |
Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active?
CDK
All cell cycle checkpoints are similar in which way?
They give the go–ahead signal to progress to the next checkpoint |
For a chemotherapeutic drug to be useful for treating cancer cells, which of the following is most desirable?
It interferes with rapidly dividing cells. |
Through a microscope, you can see a cell plate beginning to develop across the middle of a cell and nuclei forming on either side of the cell plate. This cell is most likely
a plant cell in the process of cytokinesis. |
Which of the following does not occur during mitosis?
replication of the DNA |