AQA CHEM - aldehydes and ketones
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
aldehydes are produced from the oxidation of which alcohols
ketones are produced from the oxidation of which alcohols?
aldehydes - primary alcohols
ketones - secondary alcohols
will aldehydes oxidise further?
will ketones oxidise further?
aldehydes - yes
ketones - no
what will aldehydes further oxidise into?
what is the oxidising agent used in this?
what is the visible colour change of this?
oxidise further into carboxylic acids
this is done by acidified potassium dichromate
goes from orange to green (orange → green)
for both of the tests for aldehydes and ketones, which one gives the positive result
aldehyde gives the positive result for both
are Fehling’s solution and tollens reagent oxidising agents or reducing agents
they are both oxidising agents
what are all the acronyms that I use for the mechanism for aldehydes and ketones, and what do they mean
the only one is ANAR (like pomegranate in urdu)
A = aldehyde
NA = nucleophilic addition
R = reaction
what reduces aldehydes and ketones (is the reducing agent)
I want symbol and name
NaBH4
is sodium tetrahydridoborate
(if broken down: sodium tetra hydrido borate)
what is the condition for the nucleophilic addition of aldehydes and ketones (what is it)
must be in aqueous conditions
which reagent is often used as the reagent for N.A to form hydroxy nitriles (full formula, not just nitrile group)
i want symbol of reagent, and I want its written name as well
KCN (potassium cyanide)
why is KCN used as the reagent instead of HCN (2 reasons)
because:
HCN is hard to store as a gas
HCN reacts to produce dangerous byproducts
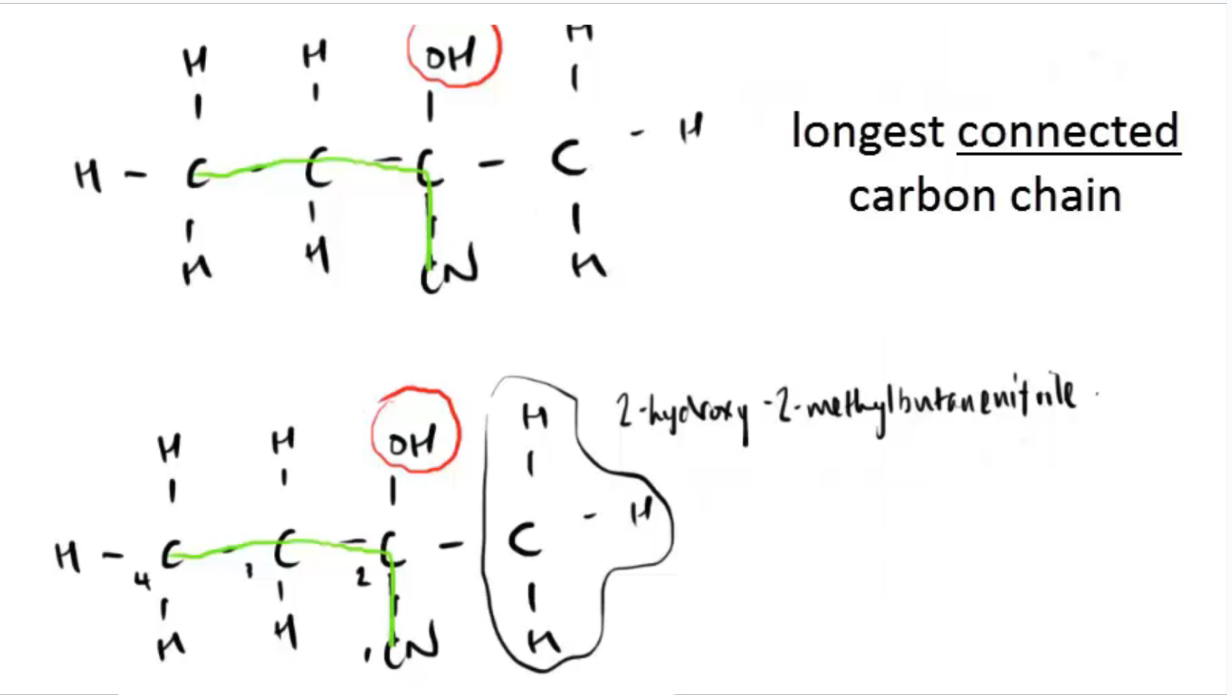
when naming hydroxy nitriles, what is the rule
the nitrile (CN) is part of the longest chain, and then u use the IUPAC order to name)
if the carbonyl group is where O is at top, what direction do the arrows for the N.A mechanism always point, for every step
up
when doing the N.A mechanism, and it says “followed by a dilute acid”, is there anything to worry about? is it the same? what doe sit mean
it just means the H+ in the final step of mechanism is form an acid
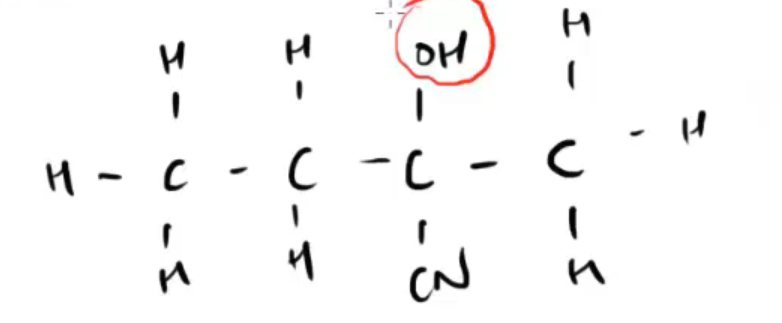
what is the (IUPAC) name for this molecule, what where/what is the longest carbon chain
2-hydroxy-2methylbutanenitrile