Genetics and Biotechnology Unit 8 IB Bio SL
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the difference between two alleles of the same gene?
The order of bases in the DNA
What was the goal of the Human Genome Project?
Determine the base sequence of the human genome
Why would Bt corn impact the insects that eat corn?
Bt toxin is in the corn and pollen which is eaten by various insects which kill the insects. This is typically good unless it’s an insect needed for pollination or is close to extinction
Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic chromosomes
Eukaryote: linear, has histone proteins, no plasmids, organized into pairs
Prokaryote: Circular, no histone proteins, sometimes has plasmids, not organized into pairs
How are plasmids used in biotechnology?
Transfer genetic information (DNA fragments)
Can be used to produce insulin or another important protein
Outline the base substitution mutation of sickle cell anemia and the implications it has on the individual
mRNA is altered by one base (GAG → GUG) due to the one base substituted for another in DNA (GAG → GTG)
One codon is changed due to the change in DNA
The change in mRNA causes tRNA to change
Different amino acid is used to build the polypeptide (glutamic acid → valine)
The polypeptide is changed resulting in altered hemoglobin
Change in hemoglobin can cause the red blood cells to be sickle shaped
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia: fatigue, shortness of breath
What determines the difference between different types of cell?
Some genes are expressed, some aren’t
If the diploid number is 18, what is the haploid number?
9
Explain how red-green color blindness is inherited.
Sex linked (on the X chromosome)
The r-g color blindness allele is recessive
Heterozygous (carrier) females are not affected
X^N = normal female
X^n = color blindness allele
More common in males than females because males only have one X chromosome
If the mother is heterozygous, 50% chance son is r-g colorblind
If the mother is homozygous recessive, 100% chance son is r-g colorblind
Distinguish between genome and proteome
The genome (DNA) is the same in every cell within the human body (or other living organism)
Proteome is different in each cell depending on what type of cell it is.
For example: liver cells have different proteins than brains cells but the same DNA is found in both types of cells
Identify some methods of natural cloning
Clones are genetically identical to the parent organism
Type of asexual reproduction
Found in non-vertebrates such as hydra and yeast → budding
Another example: identical twins in humans
How is DNA from one species able to be used by a different species?
The DNA code is universal (same bases and structure in all living organisms)
Define homologous chromosomes
Two chromosomes of the same size and shape with the same genes but could have different alleles
Define PCR
Makes copies of very small samples of DNA
List benefits and risks of genetically modified crops
Benefits:
Increase crop growth
Less water typically needed
Crops more hardy
Requires less land for crop growth due to large yeild
Risks:
GMOs may outcompete natural species of crops
GMO crops can affect natural food chains and ecosystems
Modified genes can pass on to other organisms
May impact human health
Define natural cloning
Clones typically identical to parent organism
Asexual
Found in non-vertebrates with yeast and hydra budding
Identical twins in humans
How are karyograms used in pregnancy?
Karyograms are photographs homologous pairs of chromosomes that can be analyzed to determine if abnormalities are present and possible birth defects
Trisomy conditions (such as Down syndrome) can be seen if there are three copies of a chromosome
Missing or extra pieces of chromosomes can be detected
Gender can be determined by presence of XX or XY
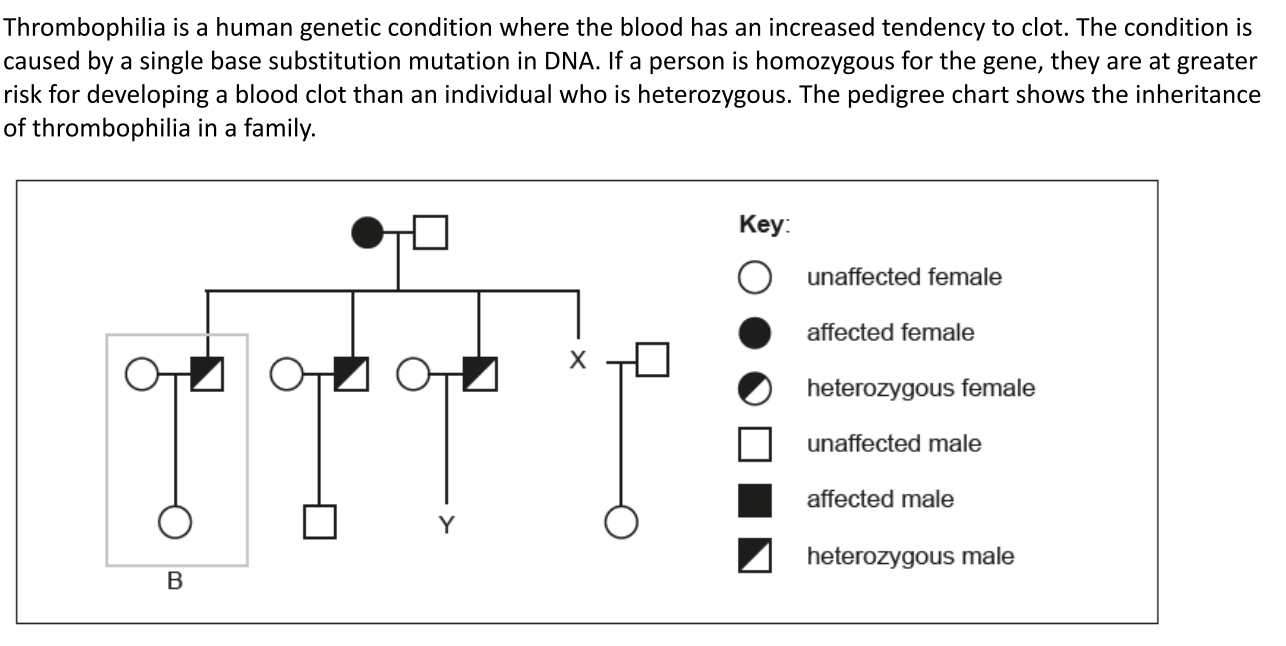
Draw the symbol for individual X on the diagram
Half colored circle
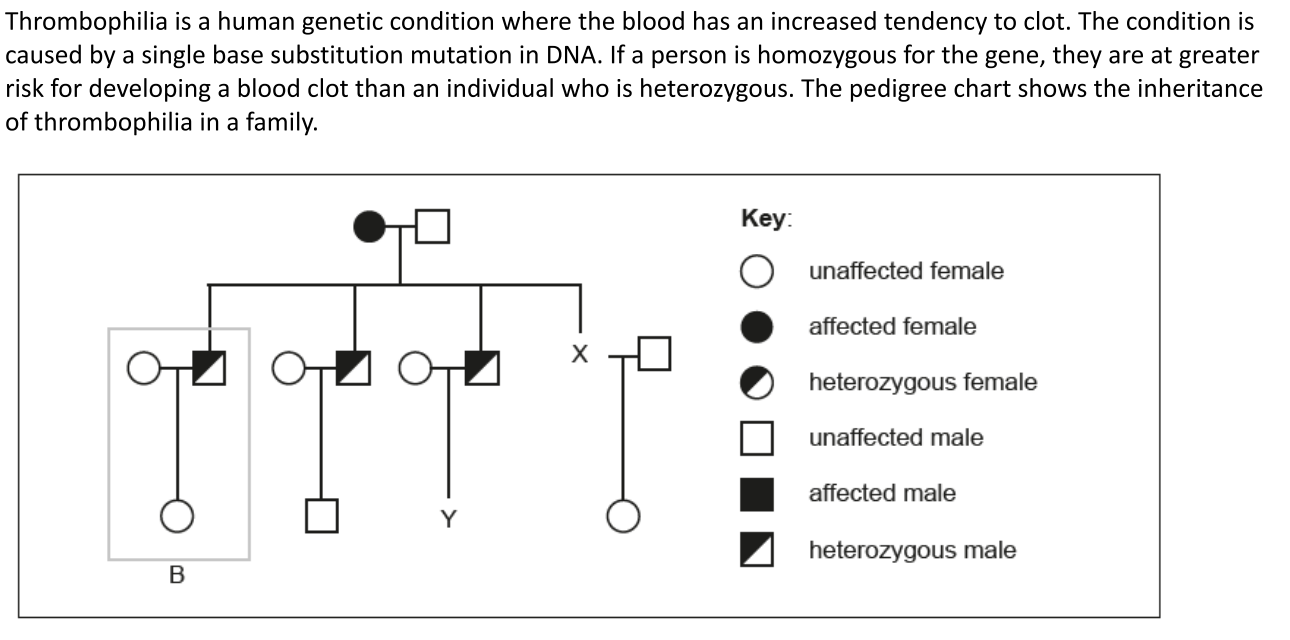
Calculate the probability of male Y having an allele for the disorder
50%
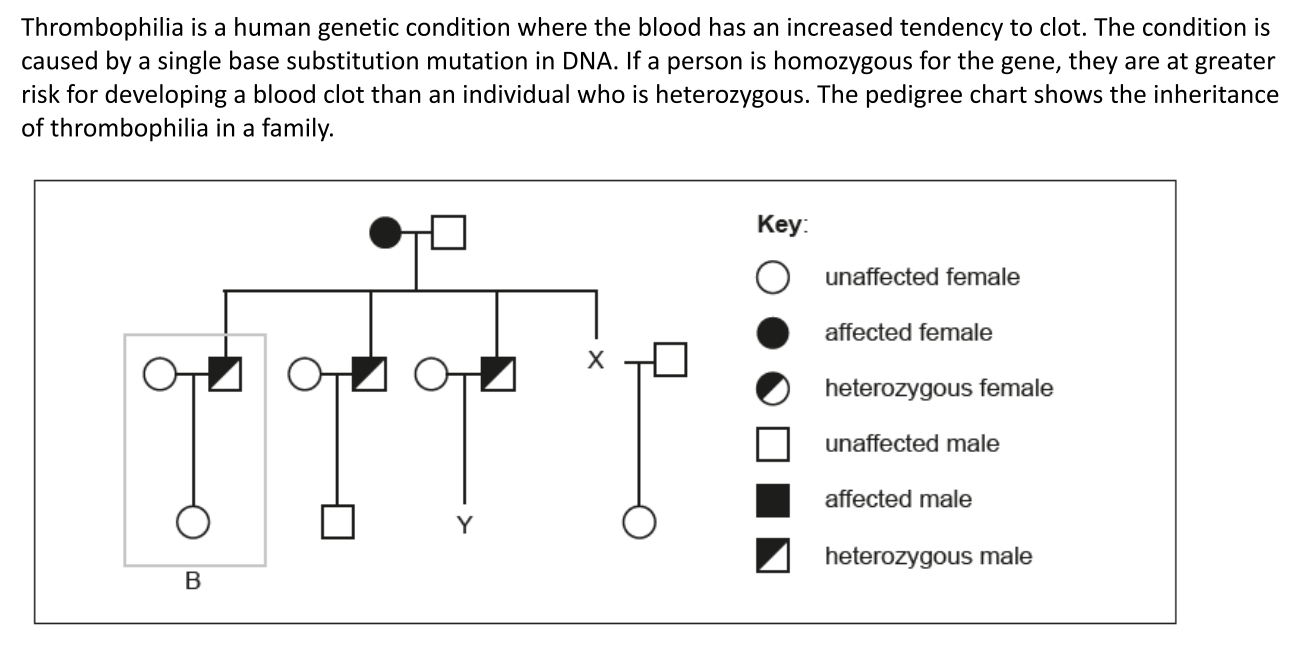
Explain how the information in the box labelled B indicates that the gene is not sex-linked
If it was sex-linked it would be on the x chromosome
There cannot be a heterozygous male if the trait is sex linked
Males would pass the allele to their daughter
Daughter is not shown as heterozygous so it is not sex linked
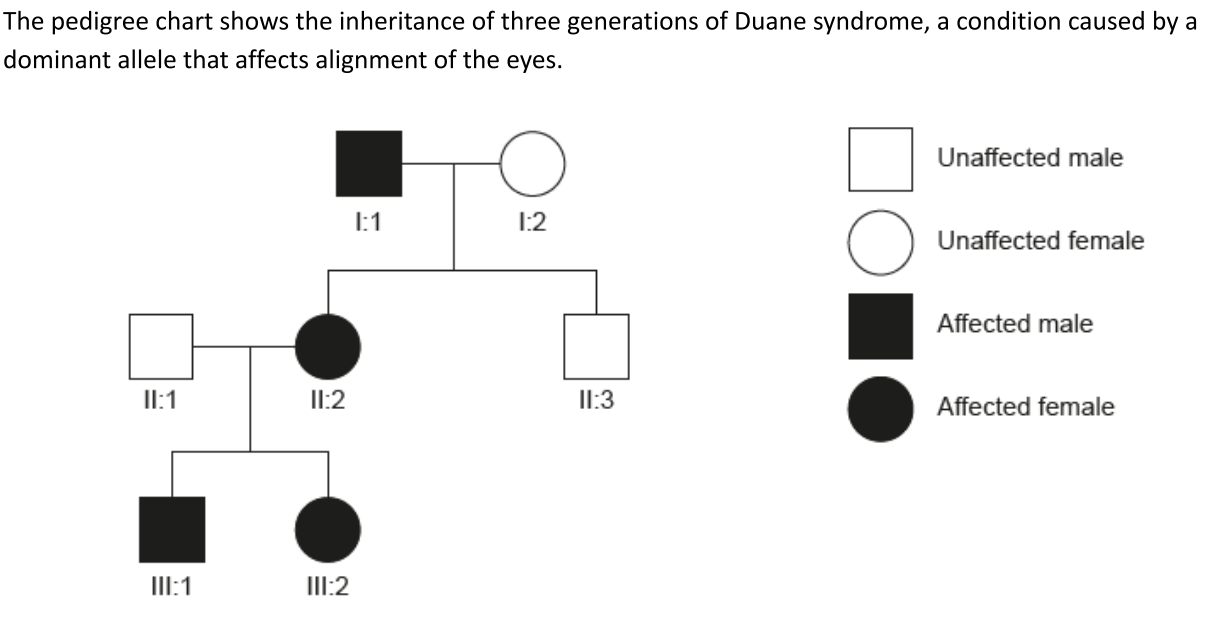
If individuals II:1 and II:2 had a third child, what is the probability that the child would have Duane syndrome?
50%
A couple have four children whose blood groups are A, B, and AB. What is the likely combination of the parent’s genotypes?
I^Ai and I^Bi
What technique was used by John Cairns to measure the length of the DNA molecule in escherichia coli?
Autoradiography
What determines the genomic size of a species?
Total amount of DNA
Which genotype would be seen in those with Huntington’s disease?
Hh