6.1 Stimuli, both internal and external, are detected and lead to a response (DONE
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
need to add parcinian curpuscal and receptor + control of heart rate
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
How do organisms respond? List the order and role of each component.
Stimulus - a change in the internal and/or external environment
Receptor - detects the stimulus
Coordinator - formulates a suitable response
Effector - produces the response, which increases the chance of survival
List the three types of simple response.
Taxis, Kinesis, Trophism
Define a taxis
Directional movement of a mobile organism towards or away from a stimulus.
Define kinesis
Non-directional movement of a mobile organism.
The stronger the stimulus, the faster the rate of movement and turns until a favourable environment is reached.
Define a trophism
Directional growth of a part of a plant towards or away from a stimulus.
Describe how positive phototropism occurs.
Indoleacetic acid is an auxin that is produced in the shoot tip and is initially evenly distributed.
Light causes IAA to diffuse to the shaded shide of the shoot.
IAA causes cells to elongate in the shoot.
Cells of the shaded side grow faster than the illuminated side.
The shoot now bends towards the light to increase the rate of photosynthesis.
Describe the process of postive gravitrophism.
IAA is produced in the root tip and is initially evenly distributed.
Gravity causes IAA to diffuse to the lower side of the root.
IAA inhibits cell elongation in the roots.
Cells on the upper side grow faster than the lower side.
Root bends towards gravity for anchorage and to increase the rate of water, nitrate and phosphate uptake.
List the features of reflexs.
Rapid as the consist of three neurons.
Effective from birth so you don’t need to learn them.
Automatic so no decision making is needed.
How are reflexes inportant for survival?
Allow escape from predators.
Protect against tissue damage.
Allow homestatic control eg. control of body temp.
Allow control of balance and posture.
What are receptors?
Specealised cells that detect 1 specific stimulus
Each receptor is linked to a sensory neuron
They are transdeucers because they convert one energy form into another (electrical energy
What is a generator potential?
A generator potential is the initial depolarisation of a sensory neuron caused by Na+ diffusing in
If the generator potntial is large enough to rreach the threshold of depolarisation action potentials are made.
What is the paciniam corpuscle?
A receptor that detects changes in pressure
They are found in the skin, joints and genetalia
Describe the structure of the parcian curpuscle.
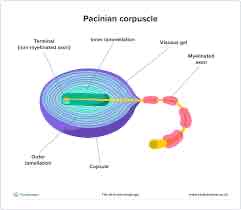
How does the pacinian curpuscle work?
When a pressure is applied to a parcinian corpuscle, the lamellae and gel are distorted, producing a ripple effect.
This deforms stretch mediated Na+ channels in the sensory neuron membrane, which forces them open.
Na+ diffuse into the sensory neuron, causing depolarisation which forms the generator potential.
If the generator potential is big enough to reach the depolarisation threshold, action potentials in the sensory neuron are produced.
Name the two photoreceptors in the eye.
Rods and Cones
Describe what happens when light hits a rod or cone.
A pigment is broken down and produces a generator potential. If it is big enough to reach the threshold, action potentials are produced and sent along a bipolar neuron in the optic nerve to the brain.
What is Rhodospin?
The pigment in rods
It cant distinguish between different wavelengths of light, so images are percieved in black and white.
What is Iodospin?
The pigment in cones
There are three different types that can detect red, blue and green wavelengths, so images are percieved in colour
Rods ahve retinal convergence where 2 or 3 rods connect with 1 bipolar neuron. What is the advantage and disadvantage?
Rods have a high sensitivity to light as neurotransmitters can be combined to reach the threshold even in low light intensitys
Rods have low visual accuity because light spots close together only produce 1 action potential
Cones do not have retinal convergence so 1 cone always conects to 1 bipolar neuron. What is the advantage and disadvantage?
It gives low sensitivity to light as more neurotransmitters are needed from each cone to reach the threshold, needing high light intensities
Cones have high visual accuity because light spots close together produce separate action potentials
How are rods and cones distributed on the retina?
Cone cells have the highest density on the fovea
Rod cells have the highest density on the periphery of the retina
Cardiac muscle is myogenic…
…this means it produces its own action potentials which can cause its own contraction
Desbribe how the cardiac muscl produces its own action potentials.
The SAN emitts a wave of impulses across the atrial muscle, causing its contraction.
A layer of non-conducting tissue prevents the impulses from causing immediate ventricular contraction.
The AVN recieves the impulses from the SAN. After a delay to allow the ventricles to fill with blood, the AVN emits its own impulses.
These are then transmitted through the purkinje fibre in the bundle of His, which causes ventricle contraction from the bottom upwards.
What is the purpose of the automatic nervous system?
Controls the automatic process in the body
Its control centre is in the medulla oblongata in the brainstem
The sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerves transmit nerve impulses from the medulla to the organs
How is heart rate increased during excercise?
chemoreceptors in the walls of the aorta and carotoid arteries detect an increase in blood pH due to a higher concentration of CO2
Chemoreceptors send more nerve impulses to the cardiac centre in the medulla oblongata
The medulla sends more impulses down the sympathetic nerve which synapses with the sinoatrial node using noradrenaline as the neurotransmitter
The sinoatrial node emitts more impulses which increses the heart rate
How does heart rate decrease when blood pressure is high?
Baroreceptors in the wall of the aorta and carotoid arteries detect an increase in blood pressure due to increased strotching of the elastic layer.
Baroreceptors send more nerve impulss to the cardiac centre in the medulla oblongata
The medulla sends more impulses down the parasympathetic nerve, which synapses with the sinoatrial node using acetylcohline as the neurotransmitter
The sinoatrial node emits fewer impulses, which decreases the heart rate.