Introduction to Cell Biology and Genetics - Ch. 7
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Fermentation
Partially breaks down organic molecules without using O2.
Comes in two types:
-Alcohol
-Lactic Acid
Most of the ATP produced during cellular respiration is due to oxidative phosphorylation.
Without O2, the electron transport chain will stop operating and oxidative phosphorylation will cease.
(Does NOT use an electron transport chain)
Aerobic Respiration
The most efficient catabolic pathway consumes O2 and other organic molecules.
Anaerobic Respiration
Similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2.
Cellular Respiration
Includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to the former.
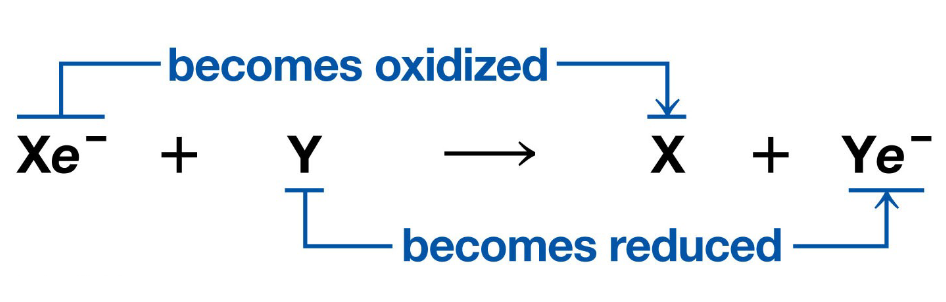
Redox Reactions
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants are called oxidation-reduction reactions.
Oxidation and Reduction always go hand-in-hand.
Oxidation
A substance loses electrons and becomes oxidized.
Reduction
A substance gains electrons and becomes reduced (The amount of positive charge is reduced).
Reducing Agent
A.K.A. the electron donor
Reduces the electron acceptor
Oxidizing Agent
A.K.A. the electron receptor
Oxidizes the electron donor
First Stages of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Breaks down glucose, a 6-carbon sugar, into two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon sugar).
Occurs in the cytosol of eukaryote and prokaryote cells.
(The breakdown of a glucose molecule happens in two phases; the initial ATP investment and the payoff which produces more ATP and NADH)
Occurs in the presence or absence of O2
If O2 is present, pyruvate is oxidized and enters the Citric Acid cycle.
Second Stages of Cellular Respiration
Pyruvate is oxidized to produce Acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA enter the Citric Acid cycle where glucose breakdown is completed.
Citric Acid Cycle
A.K.A. the Krebs cycle
Where glucose breakdown is completed.
In Eukaryotes, takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. In Prokaryotes, they take place in the cytosol.
Pyruvate Oxidation
With O2 present, _____________________ will continue in the cytosol (prokaryotes) or move into the mitochondrial matrix (eukaryotes).
Pyruvate release CO2 and the remaining 2-carbon fragment is oxidized by NAD+ producing NADH and H+
The 2-carbon fragments bond with Coenzyme A (CoA) to form Acetyl CoA
1 NADH released per pyruvate molecule (2 per glucose).
Electron Transport Chain
Electron carriers alternate between reduced and oxidized states as they develop and donate electrons.
Electrons drop in free energy with each transfer between carriers down the chain to O2
O2 is the final electron acceptor in the chain because oxygen atoms are very electronegative.
Each reduced oxygen atom picks up a pair of hydrogen atoms from solution producing H2O as a by-product.
PRODUCES NO ATP — Energy is harnessed and released in manageable amounts to power chemiosmosis.
Chemiosmosis
The energy released by electron transfer chain is used to pump H+ into the intermembrane space.
This establishes an H+ gradient cross the inner mitochondrial membrane.
H+ diffuses down its concentration gradient into the mitochondrial matrix.
H+ can only cross the inner membrane through protein complexes called ATP Synthase
ATP Synthase
Uses the exergonic flow of H+ ions down their concentration gradient to drive phosphorylation of ATP.
The use of an H+ ion gradient drives cellular work is called chemiosmosis.
How much energy is made from glucose?
About 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP, making ~32 ATP.
The remaining energy from glucose is lost as heat.
Alcohol Fermentation
Pyruvate is converted to ethanol (ethyl alcohol) in two steps:
CO2 is released from pyruvate, forming acetaldehyde
-Acetaldehyde is reduced to NADH to ethanol
NADH is oxidized, regenerating NAD+
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Pyruvate is converted directly to lactate (an ionized form of lactic acid) without producing.
NADH is oxidized, regenerating NAD+