BS101: Lecture 5 - The Endomembrane System
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
How do cells increase the chance of Biochemical Reactions?
Concentrate and compertmentalise chemistry
What is Concentration?
Number of molecules in a given time
What is the effect of a decrease in Volume on a reaction?
Increases probability a chemical reaction happens
What is Cytosol?
Intracellular fluid present inside cells
What is Cytosol comprised of? (W, I, SM, P)
Water, ions, small molecules, proteins
What is the role of Cytosol?
Site of all metabolic chemical reactions of prokaryotes
Where is the Cytoplasm?
Contained w/in cell membrane
What is the Cytoplasm compromised of?
Water, nucleic acids, enzymes, lipids, amino acids, carbs
What is the role of the Cytoplasm?
Site of large scale cellular activities including glycolysis & cell division
Describe Cytoplasm
Jelly-llike substance w/ organelles
What is the Plasma Membrane?
Selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients and waste to service the volume of cells
What is the general structure of a Biological Membrane?
Double layer of phospholipids
What is the effect of the logistics of carrying out cellular metabolism?
Sets limits on the size of cells
What do Cell’s compartments provide?
DIfferent local environments that facilitate specific membrane functions, so processes can continue in the cell @ same time
Describe the Phospholipid Bilayer?
Tails
Head
Hydrophobic Tails - Face inward
Hydrophilic Head - Face outward
Describe the components of the Endomembrane System
Continuous or connected via transfer by alleles
What are the main functions of the Endomembrane System?
Protein
Lipids
Poison
Protein synthesis/transport, metabolism and movement of lipids, detoxification of poisons
What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Extensive network of membranes
What is cisternae?
Network of membranous tubules and sacs
What is the internal component of the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
ER lumen, where proteins/lipids are found
What are proteins made by?
Ribosomes on ER’s surface
How are proteins threaded into ER cavity?
Through a pore in ER membrane
What are most secretory proteins?
Glycoproteins
What are Glycoproteins?
Proteins w/ carbs covalently attached, done w/in ER cavity
How do secretory proteins depart from the ER?
In membrane-bound vesicles (transport vesicles)
What is the role of the rER?
Makes enzymes for membrane production and adds membrane proteins/phospholipids to its membrane
What does the Endoplasmic Reticulum account for?
> Half of total membrane in many eukaryotes
How can we identify rER vs sER?
rER - ribosomes studding its surface
sER - w/o ribosomes
What does the rER contain?
Bound ribosomes which make glycoproteins
What is the function of the rER?
Distributes transport vesicles - proteins surrounded by membranes
What are Ribosomes?
Complexes made of ribosomal RNA and protein
What do Ribosomes do?
Carry out protein synthesis in cytoplasm and on outside of rER/nuclear envelope
Where are free ribosomes?
Cytoplasm
Where are bound ribosomes?
Outside of rER or nuclear envelope
What happens to proteins made by free ribosomes?
Used in the cell
What happens to proteins made by bound ribosomes?
Often secreted
What is a role of the sER relating to lipids?
Synthesis of lipids by its enzymes
What is a role of the sER relating to carbs?
Metabolises carbs
What is a role of the sER relating to poison?
Detoxification
What is a role of the sER relating to Calcium?
Stores Calcium
What is the relationship between Reproductive Cells and the sER?
Reproductive cells contain sER that produce steroid hormones
What are the roles of the sER in Liver Cells?
Have enzymes to detoxify drugs & neutralise toxic compounds by making them soluble and easily removeable
What is the relationship between the sER and Calcium?
Stores Calcium ions, essential for muscle contraction
What is a role of the Golgi relating to the ER?
Modifies products of the ER
What is a role of the Golgi relating to macromolecules?
Manufactures macromolecules
What is a role of the Golgi relating to transport?
Sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
How do the transport vesicles work?
Comes from where?
Passes through where?
Sent off to where?
Come from ER into cis side
Pass through cisternae to trans side
Sent off to various destinations
Where are products of the ER modified?
During transport from the cis face of the Golgi to the trans face
What are Pi Groups?
Molecular identification tags that target protein products to correct part of cell
Where are Molecular Identification Tags added?
Golgi
What is the change in DNA Replication?
DNA to DNA
What is the change in Transcription?
DNA to RNA
What is the change in Translation?
RNA to Protein
What are Lysosomes?
Membrane sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
Process of making Lysosome Enzymes
Made by
Transfer
Lysosome
rER
Transferred to Golgi (cis side)
Lysosome buds off from trans face as a vesicle
What are the roles of Lysosomal Enzymes?
Hydrolyse proteins, fats, polysaccharides, nucleic acids
What is a function of the Lysosome relating to engulfment?
Engulf potentially harmful bacteria/viruses
What is a function of the Lysosome relating to Recycling?
Recycle old/worn-out organelles
How does Phagocytosis relate to Vacuoles?
Phagocytosis forms a food vacuole (Phagosome)
How do Lysosomes relate to Phagosomes?
Lysosome fuses w/ phagosome & digests molecules inside
What is Autophagy?
Lysosomes use enzymes to recycle cell’s own organelles/macromolecules
What are Peroxisomes?
Specialised metabolic compartments
What is important about Peroxisome’s Enzymes?
Remove H atoms from various substances & transfer them to oxygen to form H2O2
How do Peroxisomes relate to Fatty Acids?
Some peroxisomes break down FAs to be used in cellular respiration
How are Peroxisomes involved in detoxification?
Some break down FAs to detoxify alcohol & harmful compounds by transferring H atoms to oxygen
Why is the toxicity of Hydrogen Peroxide not an issue?
Peroxisomes contain an enzyme to convert it to water
What are Vacuoles?
Large vesicles derived from ER and Golgi apparatus
How are Vacuoles formed?
By fusion of multiple, smaller vesicles
How is the Vacuole Membrane selective?
Selective for transporting solutes so solution inside vacuole is different in composition to cytosol
What are food vacuoles used for?
Phagocytosis
What are contractile vacuoles used for?
Freshwater organisms use this to pump excess water out cell, maintaining correct ion concentration
How is the Central Vacuole formed (Plant’s only)?
Joining up many smaller vacuoles
What is the purpose of cell sap in the Central Vacuole?
Cell’s main store of ions (Eg K+, Cl-)
What is the role of the Central Vacuole?
Helps maintain turgor pressure in plants
Why is the Vacuole important in plants?
Contains water, allows structural support due to increased pressures, pushes chloroplasts closer to light
Why is the Vacuole important in animals?
Important in phagocytosis, contractile vacuole pumps water out cells
What is Potential Energy?
Energy possessed by matter due to its location or structure.
How is cell-cell recognition important in tissue formation during embryogenesis?
Membrane proteins w/ short sugar chains form identification tags that are recognized by other cells
Consider the currently accepted fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane. Where in the membrane would carbohydrates most likely be found?
On the outside (external) surface of the membrane
plasmolysis
the process in which a plant cell loses water and shrinks in a hypertonic solution, causing the cytoplasm and plasma membrane to pull away from the rigid cell wall
The diameter of a typical eukaryotic cell is approximately ten times the diameter of a typical prokaryote. What is the ratio of the volume of typical eukaryotic:prokaryotic cells?
1000:1
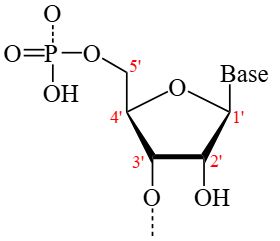
In a nucleotide, the nitrogenous base is attached to the sugar's _____ carbon and the phosphate group is attached to the sugar's _____ carbon.
1’, 5’
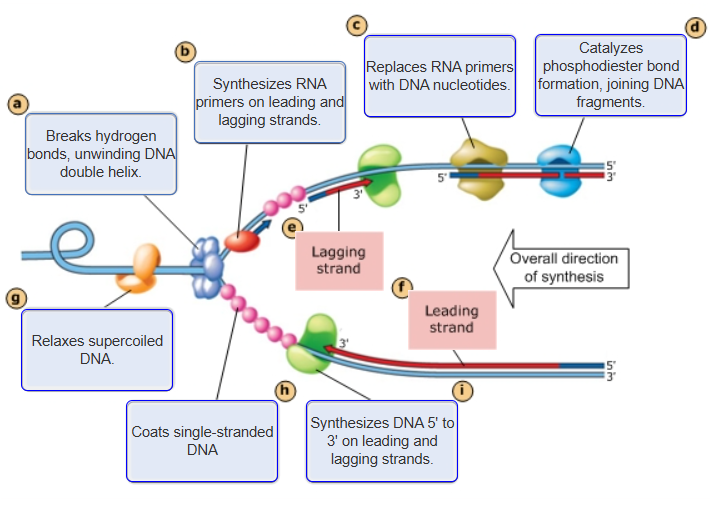
Bacterial Replication Fork
a - Breaks H bonds, unwinding DNA Double Helix
b - Synthesizes RNA Primers on leading and lagging strands
c - Replaces RNA primers w/ DNA nucleotides
d - Catalyzes Pi bond formation, joining DNA fragments
e - Lagging Strand
f - Leading Strand
i - Synthesizes DNA 5' to 3' on leading and lagging strands
g - Relaxes supercoiled DNA
What is the function of a bacterium's capsule?
protection
Where is a bacterial cell's DNA found?
Nucleoid
Beginning within the nucleus, the first step leading to the synthesis of a polypeptide is _____.
Transcription - transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA