CH. 21: The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What are the primary structures (organs) of the immune system?
Red bone marrow & thymus
What is another name for primary structure of the immune system?
Central
What occurs in primary immune structure?
Lymphocyte production
What are the secondary structures (organs) of the immune system?
Lymph nodes, spleen, & tonsils
What occurs in secondary immune structure?
Activation of lymphocytes (they begin to work)
What is another name for secondary structure of the immune system?
Peripheral
What is a pathogen?
A potential disease-causing microorganism
What is the focus of the innate immune system?
Pathogens
What are examples of pathogens?
Bacterium, parasites, & viruses
What is an antigen?
Something that elicits an adaptive immune response (immunogenicity)
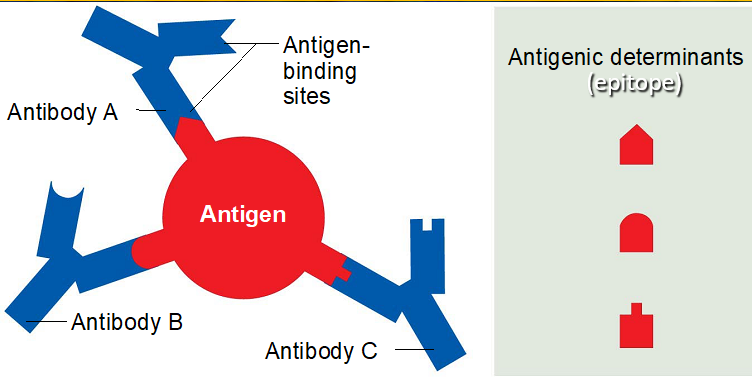
What does an antigen react to?
It reacts specifically to the antibodies and cells it provoked (reactivity)
How are antigens built?
Either complete (cancer cell, bacteria, virus, parasite) or just a small part (hapten)
What is an epitope?
The part of the antigen that is bound by an antibody or lymphocyte receptor
What is an allergen?
Antigen causing the allergic reaction
What type of white blood cells are there?
Granulocytes & Agranulocytes
What type of granulocytes are there?
Neutrophils, Eosinophils, & Basophils
How abundant are neutrophils?
Most abundant of all leukocytes
What type of specialist are neutrophils?
Bacteria specialist
What is the method of attack for neutrophils?
They attack bacteria via: degranulation & phagocytosis
How does degranulation work?
Degranulation releases various enzymes and antimicrobial proteins
What does phagocytosis involve?
Phagocytosis involves TLRs and lysosomal enzymes and reactive oxygen species
What type of -phage are neutrophils?
Microphage
How are neutrophils kamikaze microphages?
Main inflammatory cell and they die fighting bacterial infections (pus).
What type of specialist are eosinophils?
Parasite specialist
What type of parasites do eosinophils attack?
They attack endoparasites (especially helminthic worms)
What is the method of attack for eosinophils?
They attach via TLRs, and release granules containing enzymes (lipases, ribonucleases, deoxyribonucleases) and peroxidases
What is the result after eosinophils attack?
In cell apoptosis and necrosis
What is apoptosis?
Death of cell
What is necrosis?
Death of body tissue
What else do eosinophils contribute to?
To allergic reactions as well
What type of -phage are eosinophils?
Microphage
How abundant are basophils? How large is this granulocyte?
Least abundant, but largest granulocyte.
What is the method of attack for basophils?
They release granules containing histamine, heparin, proteolytic enzymes, and various other chemicals (like Mast cells).
What do basophils contribute to?
They contribute significantly to allergic reactions & inflammatory processes.
What type of agranulocytes are there?
Monocyte, T lymphocyte, & B lymphocyte
What is the origin of T and B lymphocytes?
T and B lymphocyte stem cells originate in lymphoid red bone marrow
What occurs during the maturation of T and B lymphocytes?
They begin developing immunocompetence, self-recognition & self-tolerance.
Where do T lymphocytes mature?
Cells destined to become T cells migrate to and mature in the thymus
What do T lymphocytes differentiate into?
Cytotoxic T Cells, Regulatory T Cells, Helper T Cells, Memory T Cells.
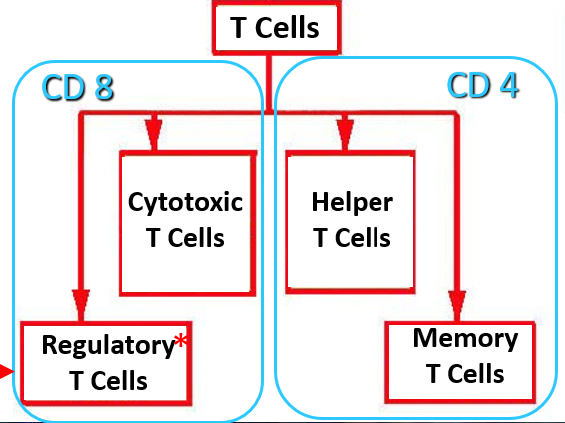
What is another name for Regulatory T Cells?
Suppressor T Cells
Which T Cells are CD 4?
Helper T Cells & Memory T Cells
Which T Cells are CD 8?
Cytotoxic T Cells & Regulatory T Cells
Where do B lymphocytes mature?
B cells stay and mature in the red bone marrow
What do T lymphocytes target/do?
Target viral infected cells, cancerous cells, regulate immune activity, etc
What do B lymphocytes differentiate into?
Plasma cells
What do B Lymphocyte produce when activated?
Antibodies
What do antibodies that originate from B Lymphocytes do?
Neutralize, opsonize, agglutinate, & activate complement
What do Monocytes differentiate into?
Macrophages
How large are Macrophages / Monocytes?
They are the largest leukocytes & primary phagocytic cells in the body
What do Macrophages rely on?
On TLRs, but other factors can significantly enhance phagocytosis
What do Free Macrophages do?
They wander through interstitial spaces, blood, and lymph
What do Fixed Macrophages do?
They are permanent residents of some organs (bone marrow, liver, spleen)
What specificity is Innate Immunity?
Non-specific
What is the response time for Innate Immunity?
Immediate response (1st and 2nd lines)
What type of immunological memory does Innate Immunity have?
No immunological memory
What type of non-specific defenses does the innate immune system have?
Barriers, Phagocytes, Fever, Inflammation, Complement, Interferons, & NKCs
What does the innate system use to stop attacks?
Uses the first and/or second lines of defense to stop attacks by pathogens.
What is the 1st line of defense for the innate system?
Surface Barriers which are skin and mucous membranes
What is the main purpose of surface barriers?
To stop bad things from coming in
What else do these surface barriers include for added protection.
Protective chemicals that inhibit or destroy microorganisms
What are the surface barriers in the 1st line of defense?
The Skin & Mucous Membranes
What does the skin provide in the innate immune system?
Acidity, defensin proteins, dermcidin, & sebum
What does the mucous membrane provide in the innate immune system?
Acidity, defensin proteins, enzymes, mucus (mucin), hairs, & cilia
What occurs when surface barriers are breached by wounds?
it triggers an internal 2nd line defenses, which protects deeper tissues
What is the 2nd line of defense for the innate immune system?
Internal Barriers which are WBCs: granulocytes, macrophages, natural killer cells, and antimicrobial proteins
What important role do Internal Barriers play?
These cellular and antimicrobial barriers play important roles in inflammatory responses and fever.
What type of cells are in the 2nd line of defense for innate immune system?
They include granulocytes, macrophages, and NK cells
What are TLRs & PAMPs?
Most innate immune cells utilize Toll-like receptors (TLRs) that identify/bind tightly to structures or patterns (pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PAMPs) on pathogens.
What role do TLRs play in?
TLRs play a central role in triggering immune responses.
What specificity is Adaptive Immunity?
Antigen-specific
What is the response time for Adaptive Immunity?
Lag time from exposure to response (3rd line)
What type of immunological memory does Adaptive Immunity have?
Immunological memory after exposure
What type of response is Adaptive Immunity?
Systemic response
What does Adaptive Immunity provide protection against?
Against specific microbes & pathogens
What type of “immunity” is in Adaptive Immunity?
Cell-Mediated Immunity & Humoral Immunity
What structures are in the 1st line of defense?
Surface Barriers aka skin & mucous membranes
What is the function of the 1st line of defense?
This line of defense inhibits & destroys microorganisms
What structures are in the 2nd line of defense?
Internal Barriers aka granulocytes, macrophages, NK cells, & antimicrobial proteins
What is the function of the 2nd line of defense?
They participate in inflammatory responses & fever
What is the abbreviation for Toll-like receptors?
TLRs
What role do TLRs play?
In triggering immune responses
What do TLRs do to pathogens?
They identify and bind tightly to structures or patterns on pathogen
What are the main phagocytic cells?
Macrophages, neutrophils, & dendritic cells
How do phagocytic cells AIDD?
Adherence
Ingestion
Digestion
Destruction
What is the first step of phagocytosis (Adherence)?
Phagocyte adheres to pathogens or debris using TLRs
How does phagocytosis aid with antigen-presenting / what are antigen presenting cells?
They insert digested pieces of the pathogen into specific membrane proteins for presenting to/activation of other immune cells
What is Opsonization?
Antibodies or complement proteins are opsonin that coat pathogens
What do Opsonization basically do?
Makes pathogens more desirable to destroy
What does Opsonization stick to?
stick to pathogenic cells like glue, making them difficult to adhere
What do interferons do?
Cells infected with viruses can secrete IFNs that “warn” healthy neighboring cells.
What are IFN-a(interferon alpha) & IFN-b(interferon beta) secreted by?
Secreted by virus-infected cells
What is the purpose of IFN-a & IFN-b?
They stimulate production of anti-viral proteins that block viral reproduction and degrade viral RNA
What do IFN-a & IFN-b activate?
NK cells
What are IFN-g(interferon gamma) secreted by?
Secreted by T cells, NK cells, & macrophages
What is the purpose of IFN-g?
Widespread immune mobilizing effects
What do IFN-g activate?
Potent activator of macrophages, but also activates NK cells and T cells.
What do Interferon proteins increase?
Resistance to viral infections & stimulate Macrophages & NKCs
What is a Complement System?
About 20 blood proteins that circulate in blood in inactive form
What proteins does Complement System include?
Proteins C1–C11
What does the Complement System enhance?
Enhances inflammation and directly destroys bacteria & Enhances both innate and adaptive defenses.