Air Quality Management and Pollution Measurement Techniques
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
Airshed
Region with similar climate affecting pollutant diffusion.
Primary Pollutants
Directly emitted pollutants from sources like vehicles.
Carbon Monoxide
Colorless gas from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels.
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds contributing to air pollution and smog.
Nitrogen Oxides
Gases formed from combustion, contributing to smog.
Airborne Lead
Toxic metal from industrial processes and vehicle emissions.
Particulate Matter
Mixture of solid and liquid particles in the air.

Sulfur Oxides
Gases from burning fossil fuels, causing acid rain.
Chlorofluorocarbons
Chemical compounds harmful to the ozone layer.
Mercury
Toxic heavy metal released from industrial activities.
Secondary Pollutants
Pollutants formed by chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
Acid Droplets
Liquid particles containing sulfuric and nitric acids.
Photochemical Oxidants
Pollutants like ozone formed by sunlight-driven reactions.
Total Suspended Solids (TSP)
Measure of all particles suspended in air.
Particulate Matter 10 (PM10)
Particles with diameter less than 10 micrometers.
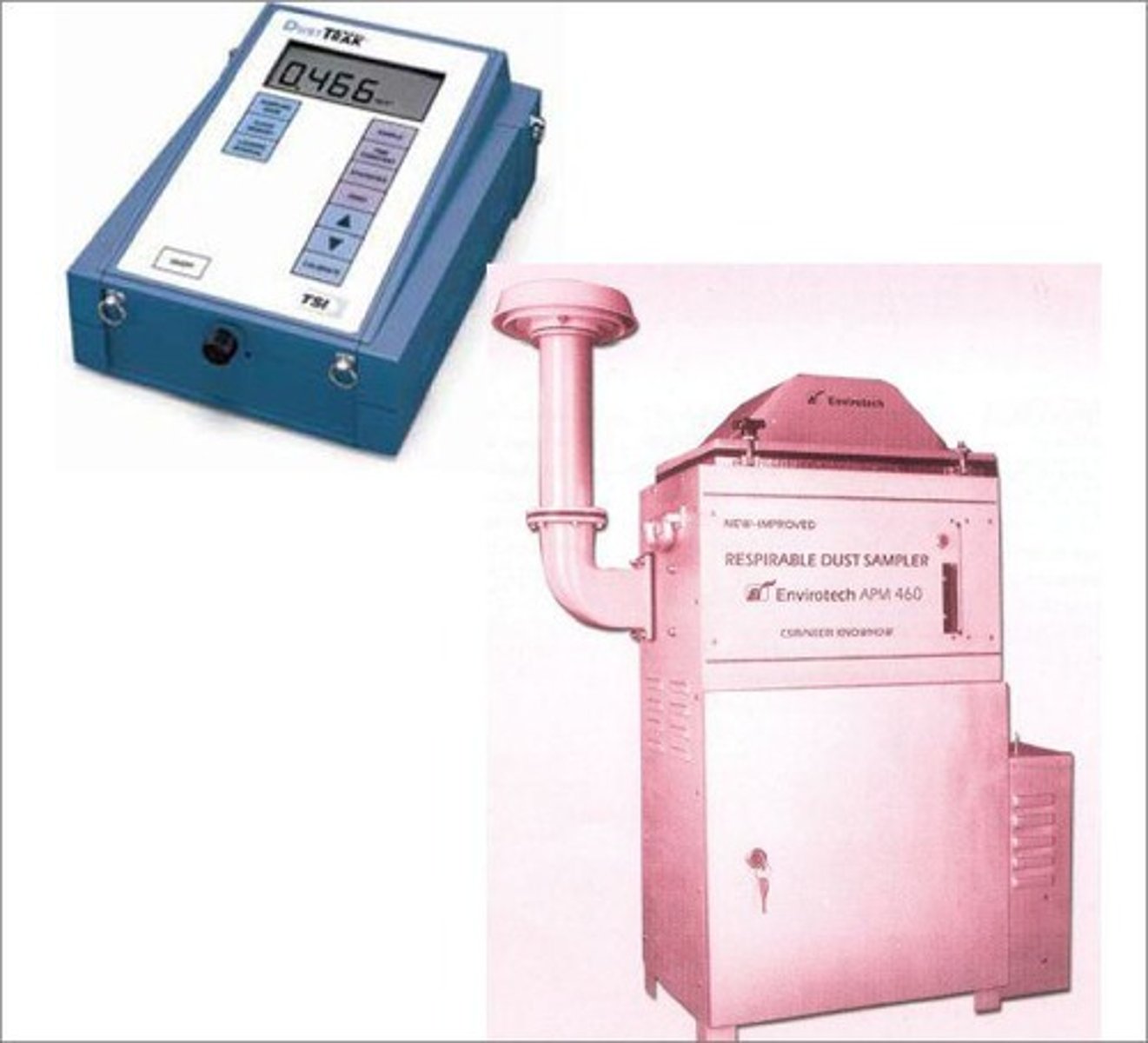
High-Volume Sampler
Instrument for collecting air samples over time.
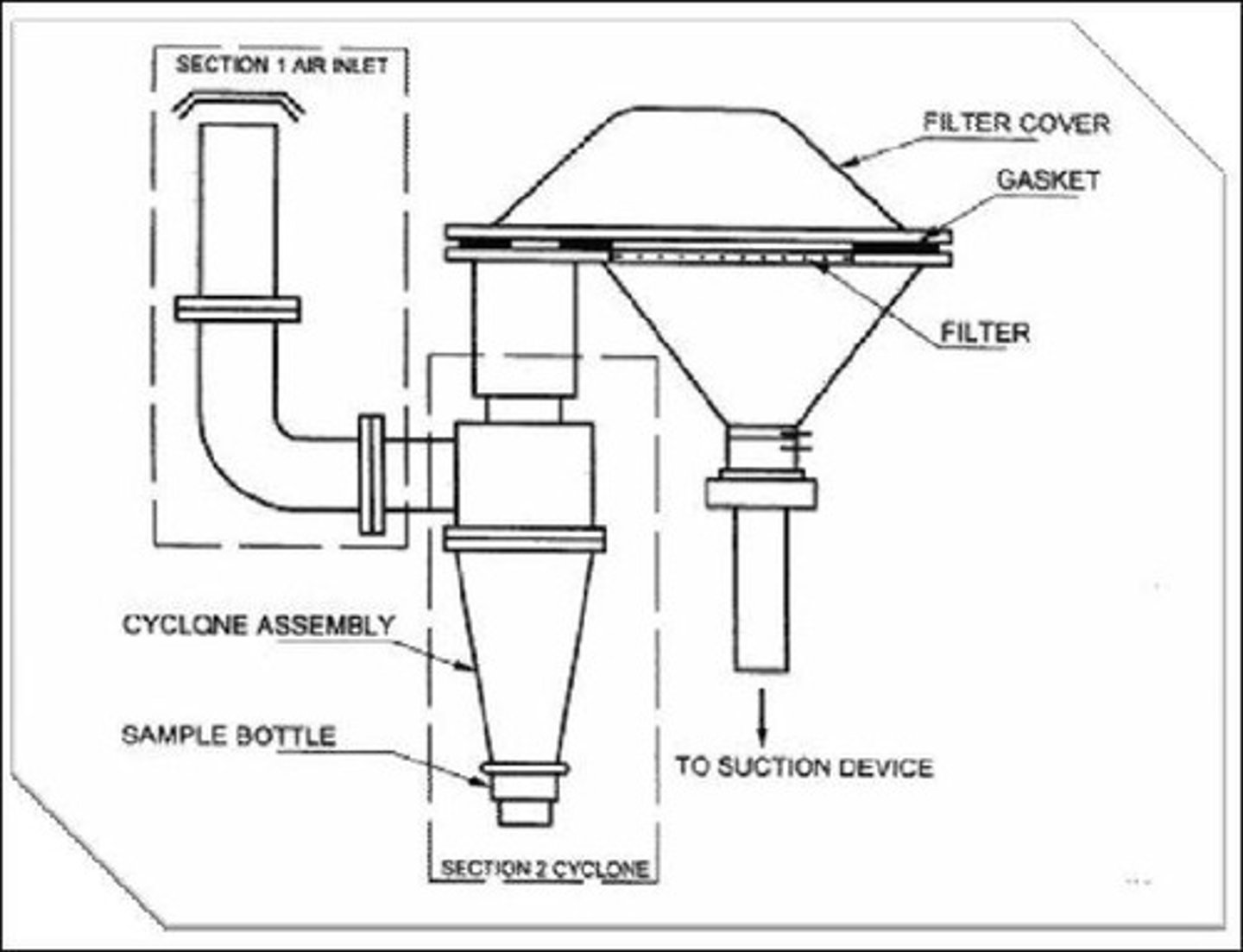
Gravimetric Method
Technique for measuring mass of collected air samples.
Volumetric-Filtration
Method sampling air through a filter at known flow.
Sampling Frequency Guidelines
24 hours at least a week, making 104 samples a year
Sampling Location Guidelines
Recommendations for optimal placement of sampling equipment.
Flow Rate
Volume of air sampled per unit time, measured in liters.
Total Volume of Air Sampled (TVA)
Total air volume collected during sampling period.
SPM Concentration Formula
Calculates SPM in μg/m³ using mass difference.
Total Suspended Particulates (TSP)
Refers to all airborne particles captured in air.
Air Quality Levels
Categorizes air quality based on particulate matter.
Good Air Quality
0 - 80 μg/m³; no health concerns.
Fair Air Quality
81 - 230 μg/m³; minor health concerns possible.
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
231 - 349 μg/m³; sensitive individuals should limit exposure.
Very Unhealthy Air Quality
350 - 599 μg/m³; vulnerable groups should stay indoors.
Acutely Unhealthy Air Quality
600 - 899 μg/m³; outdoor exertion should be limited.
Emergency Air Quality Level
900 μg/m³ and above; everyone should stay indoors.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Colorless gas detectable by taste/smell, 1,000-3,000 μg/m³.
SO2 Source
Primarily from fossil fuel combustion.
Sulfate Aerosols Formation
Occurs when SO2 reacts with atmospheric substances.
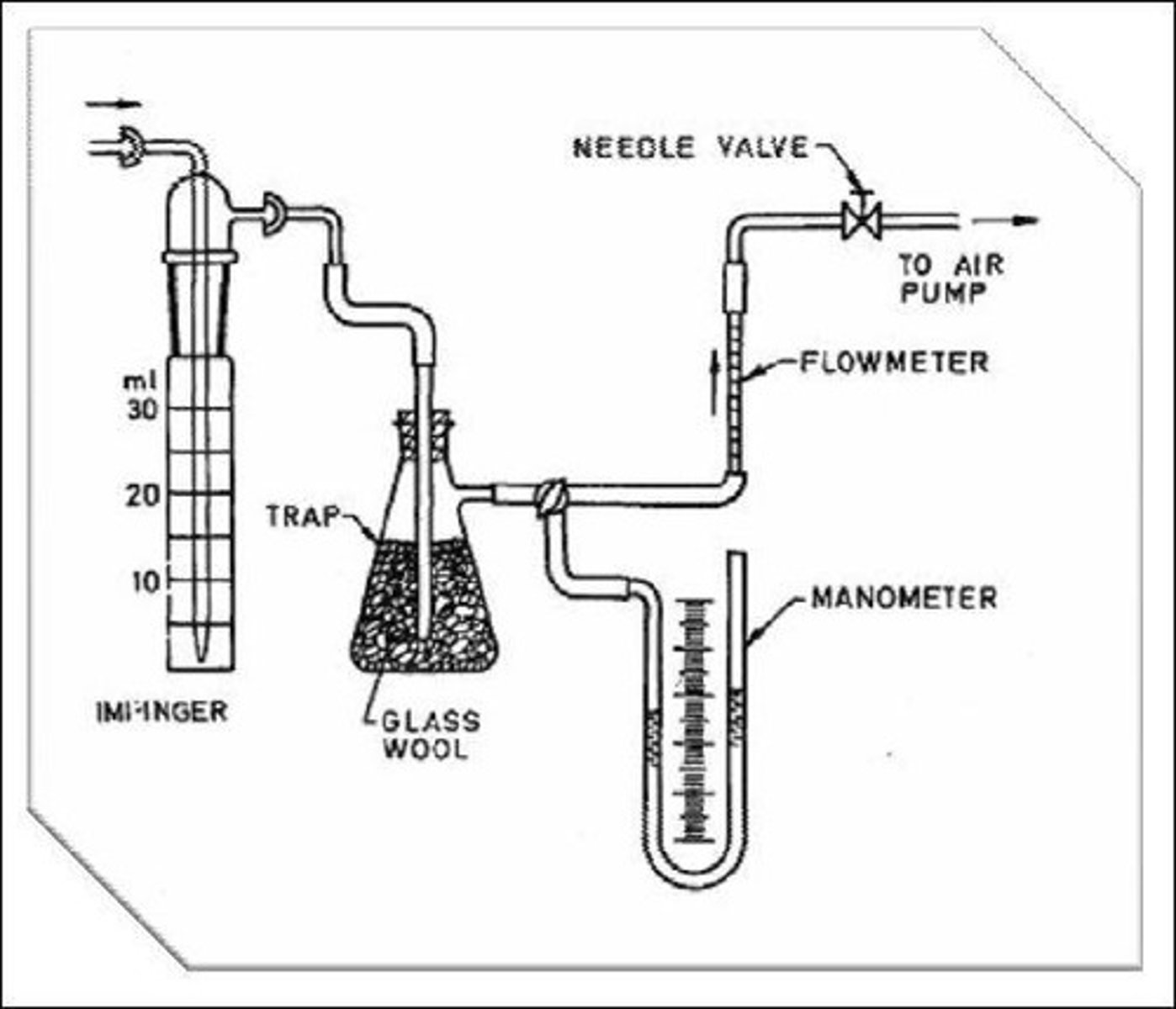
Gas Bubbler
Instrument for sampling gases, especially SO2.
Pararosaniline Method
Laboratory method for analyzing sulfur dioxide.
Sampling Location Guidelines
3 to 10 m above ground, away from disturbances.
Sampling Frequency Guidelines
At least twice a week, totaling 104 samples/year.
Absorbing Reagents Preparation
Mix mercuric chloride and sodium chloride in water.
Sampling Train Setup
Connect gas bubblers securely to the sampling system.
Flow Rate Adjustment
Set to 2 liters/min during sampling.
Calibration Curve
Standard solution of SO2 for absorbance measurement.
Spectrophotometer Use
Measures absorbance at 540 nm for SO2 analysis.
Absorbance
Measurement of light absorbed by a sample.
Calibration Curve
Graph relating absorbance to concentration.
Concentration
Amount of substance per volume, measured in μg.
Flow Rate
Volume of air sampled per time unit.
Total Volume of Air Sampled (TVA)
Calculated using flow rate and time.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Toxic gas from fossil fuel combustion.
Good Air Quality
SO2 levels between 0.000 and 0.034 ppm.
Fair Air Quality
SO2 levels between 0.035 and 0.144 ppm.
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
SO2 levels between 0.145 and 0.224 ppm.
Very Unhealthy
SO2 levels between 0.225 and 0.304 ppm.
Acutely Unhealthy
SO2 levels between 0.305 and 0.604 ppm.
Emergency Air Quality
SO2 levels between 0.605 and 0.804 ppm.
Gas Bubbler
Instrument for sampling gas concentrations.
Griess-Saltzman Method
Chemical analysis method for nitrogen dioxide.
Chemiluminescence Method
Technique for measuring gas concentrations using light.
Sodium Hydroxide
Base used in absorbing reagent preparation.
Sodium Arsenite
Chemical used in gas absorption analysis.
Sampling Frequency
Minimum of 104 samples annually recommended.
Sampling Location Guidelines
Positioned 3 to 10 m above ground level.
Absorbing Reagent Preparation
Mix sodium hydroxide and sodium arsenite in water.
Flow Rate Adjustment
Set to 0.2 liters per minute for sampling.
Interference Elimination
Use hydrogen peroxide to convert SO2 to sulfate.
Sampling Train
Transport device for environmental samples safely.
Controlled Conditions
Stable environment for preserving sample integrity.
Calibration Curve
Graph showing absorbance versus concentration relationship.
Standard Solution
Known concentration used for calibration in experiments.
Absorbing Reagent
Chemical added to samples to facilitate measurement.
Pararosaniline Method
Method of analysis for sulfur dioxide parameter
Spectrophotometer
Instrument measuring light absorbance at specific wavelength.
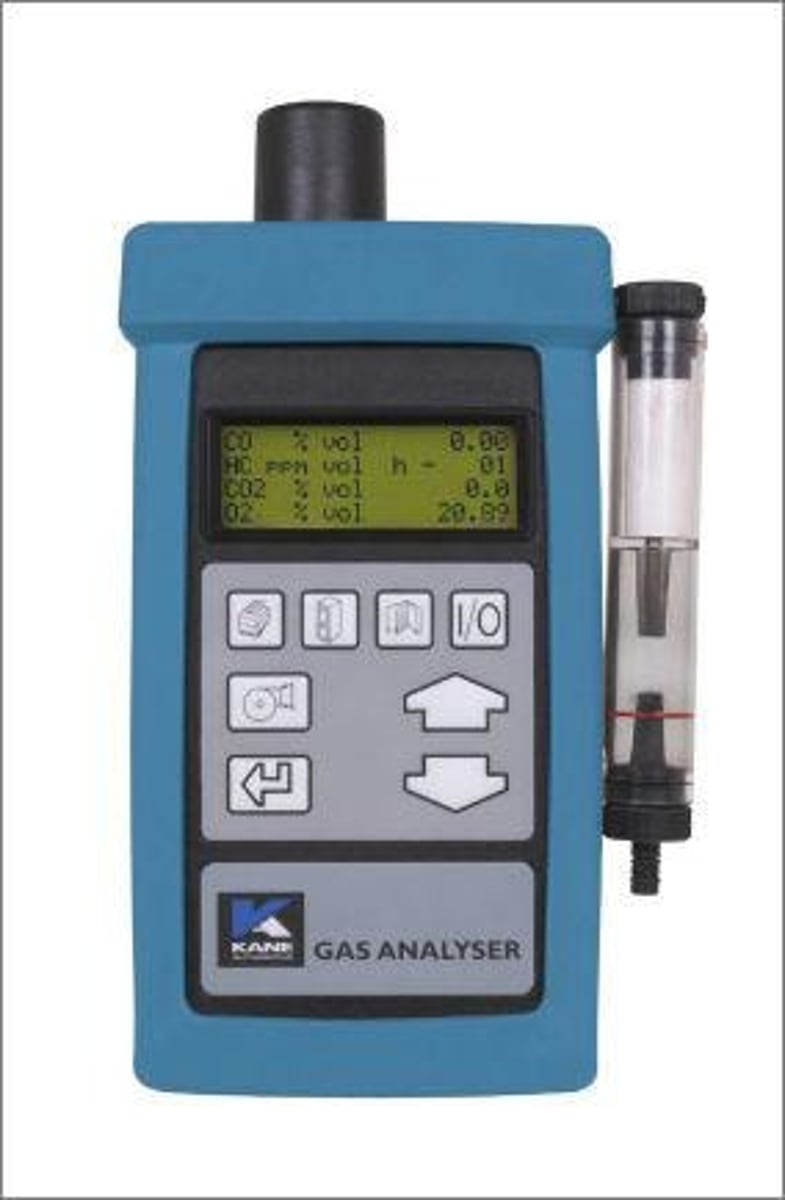

Absorbance Measurement
Quantifying light absorption by a sample solution.
Concentration Determination
Finding substance amount using calibration curve data.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
Pollutant affecting respiratory health and air quality.
Air Quality Levels
Categories indicating pollution impact on health.
Good Air Quality
No harmful pollutants detected in the air.
Fair Air Quality
Acceptable pollution levels; minimal health concerns.
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
Risk for individuals with respiratory conditions.
Very Unhealthy
Significant health risks; limit outdoor activities.
Acutely Unhealthy
High pollution; strict outdoor activity restrictions.
Emergency Air Quality
Severe pollution; everyone should stay indoors.
Secondary Pollutant
Pollutant formed by reactions in the atmosphere.
Ozone (O3)
Common secondary pollutant; harmful to lungs.
Chemiluminescence Method
Technique for measuring ozone concentration in air.
Neutral Buffer Potassium Iodide
Chemical solution used for ozone detection.
Sampling Frequency
Collecting samples at least twice a week.
Wetted Wall Absorber
Device for scrubbing air samples with liquid.
Sodium Thiosulphate
Used for titration in solution analysis.
End Point
Established by comparison with the blue starch-iodine solution
Ozone Mixture Preparation
Combines ozone and air in a polyester bag.
Ozone Decomposition
Gradual breakdown necessitates immediate analysis.
Impinging Method
Analyzes ozone by passing through buffered KI solution.
Spectrometer Method
Determines iodine release during analysis.
Sample Flow Rate
Set at 4 ml/min for solution.
Air Flow Rate
Set at 4 l/min for air.
Calibration Curve
Graph of absorbance versus concentration.
pH Adjustment
Weekly adjustment of solution pH required.
Carbon Filter Change
Replace monthly to maintain air quality.
Ozone Levels
Measured in parts per million (ppm).