i hate anatomy ❤️
1/683
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
684 Terms
What 2 things are contained within the endocrine system?
Ductless glands + endocrine tissues
What does the endocrine system secrete into blood?
Hormones
What is a target cell?
Cell with receptor specific for a hormone
What are the 3 hormone classes?
Steroids, hormones derived from amino acids, peptide/protein hormones
What are steroids synthesized from?
Cholesterol
What are 3 examples of steroid hormones?
Testosterone, estrogen, vitamin D
Tyrosine, an amino acid, has hormones that derive from it (2nd hormone class). What 3 hormones are derived from it?
Thyroxine/T4, epinephrine (adrenaline), norepineprine (noradrenaline)
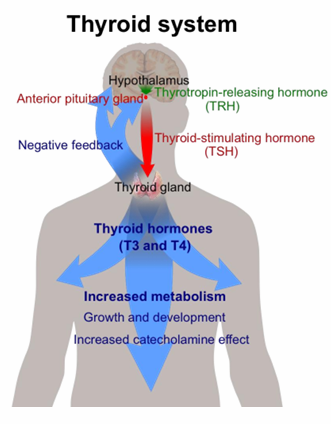
What gland does thyroxine/T4 hormone come from (+ what it controls)?
A thyroid gland hormone that controls metabolism, growth and development
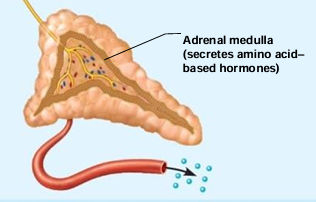
What are epinephrine (adrenaline) + norepinephrine (noradrenaline) secreted by?
Adrenal medulla
Peptide + protein hormones are chains of amino acids. What type of bonds hold amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
Peptide hormone is _____ chains of linked amino acids, while protein hormone is _____ chains of linked amino acids
“short,” “long”
What are 4 examples of peptide + protein hormones?
Oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), growth hormone (GH), insulin
What are the 4 glands with no other function?
Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands
Where is the pituitary gland found?
Suspended from hypothalamus in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
What are the 2 lobes of the pituitary gland?
Anterior pituitary, posterior pituitary
What is the anterior pituitary hormone secretion regulated by?
Hormones released by the hypothalamus
What are the 5 hormones the anterior pituitary secretes?
Growth hormone (GH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
What reproductive hormone does the anterior pituitary secrete?
Prolactin (PRL)
What 2 things does the growth hormone (GH) affect?
Growth + metabolism
What does the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) do?
Stimulates secretion of thyroid
What does the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) do?
Stimulates secretion of steroids from adrenal gland
What 3 things does the luteinizing hormone (LH) do?
Stimulates ovulation, formation of corpus luteum in ovary, and testosterone production
The luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulates testosterone production by?
Interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells in testes
What does the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) do?
Stimulates sustentocytes + follicle cells
What does prolactin/PRL (the reproductive hormone of the anterior pituitary) do?
Stimulates milk production by mammary glands
What type of tissue is the posterior pituitary made of?
Nervous tissue
What is the posterior pituitary an extension of?
The hypothalamus
What 2 hormones are produced in the hypothalamus, but stored + secreted from the posterior pituitary?
Oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
What 2 things does oxytocin do?
Stimulates uterine contractions + milk ejection
What does the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) do?
Enhances water reabsorption by collecting duct in kidney(s)
Where is the thyroid gland found?
On the anterior surface of the superior portion of the trachea (inferior to larynx)
What do people say the thyroid gland is shaped like?
Butterfly shaped
What are the 2 components of the histology of the thyroid gland?
Follicles, parafollicular cells
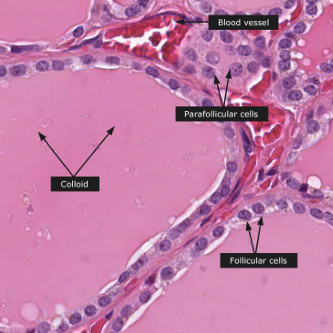
What do follicles of the thyroid gland produce?
T4
What does T4 turn to in target cells?
Active T3
Where are parafollicular cells found?
Between follicles
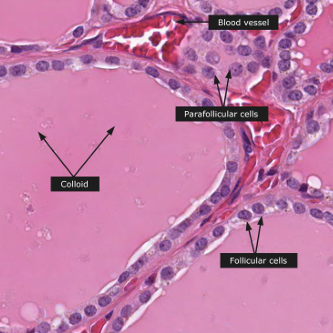
What do parafollicular cells secrete?
Calcitonin
What are the effects of calcitonin in the body?
⬆Ca+ uptake into bone (bone formation), which lowers blood Ca+
How many parathyroid glands are there typically + where?
4 glands embedded in posterior thyroid
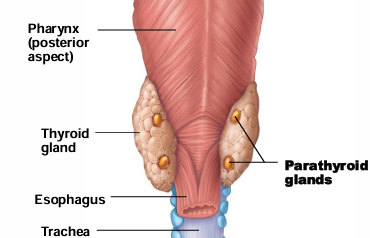
What do parathyroid glands secrete?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
The parathyroid hormone (PTH) acts on bone and kidneys for what purpose?
To increase blood Ca+ levels
Where are adrenal glands found?
On the superior surface of each kidney
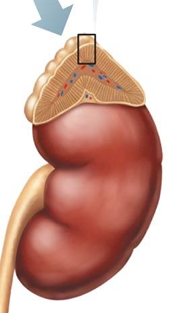
What are the 2 parts of adrenal glands?
Adrenal cortex (outer), adrenal medulla (inner)
What tissue type is the adrenal cortex made of?
Epithelial tissue
What does the adrenal cortex secrete?
Steroids only
What are the 3 layers of the adrenal cortex (each layer secretes a different hormone)?
Zona Glomerulosa, Zona Fasciculata, Zona reticularis
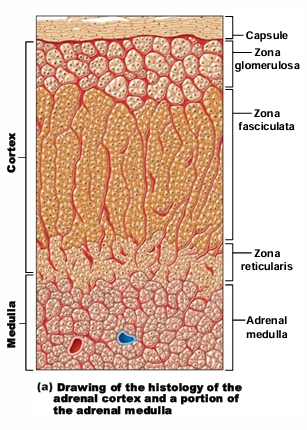
What does Zona Glomerulosa secrete (+ function)?
Mainly aldosterone; salt balance
What does Zona Fasciculata secrete (+ function)?
Mainly cortisol; long-term stress hormone
What does Zona reticularis secrete (+ function)?
Androgens (sex hormones)
What are androgens converted to in other tissues?
Testosterone or estrogens
The adrenal medulla is modified _______ tissue
“nervous”
What are the 2 main hormones of the adrenal medulla?
Epinephrine (80%), norepinephrine (20%)
What are the ~4 hormone secreting cells/tissues in organs that have other functions as well?
Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans, hypothalamus, gonads, others...
What 2 cells are included in pancreatic islets of langerhans?
α-cells, β-cells
What do α-cells secrete (+ function)?
Glucagon; ⬆blood glucose
What do β-cells secrete (+ function)?
Insulin; ⬇blood glucose
The hypothalamus regulates the anterior pituitary via what 3 hormones?
GHRH (GH releasing hormone), GHIH (GH inhibiting hormone), GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone)
GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone) stimulates the release of what 2 hormones?
FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) + LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
The hypothalamus produces hormones stored + secreted by the ________ pituitary
“posterior”
In testes (male gonads), what type of cells secrete what type of hormone?
Interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells; testosterone
In ovaries (female gonads), what 2 types of cells secrete what types of hormones?
Granulosa cells of 2° and vesicular follicles; estrogen
Corpus luteum; estrogen + progesterone
What hormone secreting cells/tissues in organs with other functions are included in the “others” category?
Duodenum, kidney, skin, heart, etc.
What 2 hormones does the duodenum secrete?
Secretin + cholecystokinin (CCK)
What 2 hormones does the kidney secrete?
Renin + erythropoietin (EPO)
What hormone is secreted by the skin?
Vitamin D
What hormone is released by the heart?
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
What are the 2 main functions of the respiratory system?
Air movement in/out of lungs + exchange of gases between lungs/blood
What are the 2 subdivisions of the respiratory system?
Upper respiratory system, lower respiratory system
What does the upper respiratory system consist of?
Nose, nasal cavity, pharynx
What does the lower respiratory system consist of?
Larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, lungs
What does the tissue of the mucosa of the respiratory tract mostly consist of?
Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells sitting on lamina propria
What do goblet cells secrete?
Mucous
What do cilia do to mucous?
Sweep mucous to esophagus where swallowed
What two materials is the nose supported by?
Bone + hyaline cartilage
What is another word for nostrils?
Nares
What are the 3 functions of the nasal cavity?
Airway passage, olfaction (smell), speech
What is the nasal cavity divided by?
The nasal septum
What is the anterior portion of the nasal cavity made of?
Hyaline cartilage
What is the posterior portion of the nasal cavity made of?
Vomer, ethmoid, maxillae, palatine bones
What are the 3 areas of the nasal cavity?
Vestibule, respiratory area, olfactory area
Which area of the nasal cavity is the anterior region?
Vestibule
Describe the vestibule region of the nasal cavity
No mucosa, lined by skin with coarse hair
Which area of the nasal cavity is the posterior region?
Respiratory area
What is the name of the structure(s) in the respiratory area of the nasal cavity that protrude medially from the lateral walls of the cavity?
Chonchae
What are the 3 chonchae called (according to position)?
Superior, middle, inferior

What 2 chonchae are formed by the ethmoid bone?
Superior + middle
What is found in between chonchae?
Nasal meatuses (channels)
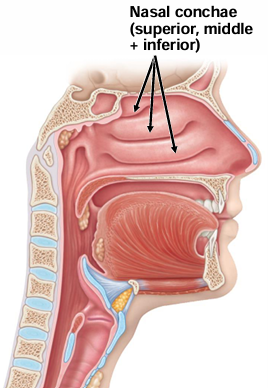
What do chonchae + meatuses cause?
Cause air turbulence to humidify air + knock out dust
What does the nasolacrimal duct connect?
Medial region of eye → inferior nasal meatus
What does the nasolacrimal duct transport from the eyes to the nasal cavity?
Lacrimal fluid
What is lacrimal fluid commonly referred to as?
Tears
What area of the nasal cavity is the roof?
Olfactory area
What type of cell is contained in the mucosa of the olfactory area of the nasal cavity?
Olfactory neurons
What is the purpose of olfactory neurons?
Receptors for sense of smell
What are paranasal sinuses + how many are there in the human body?
8 air filled spaces in skull
The 8 paranasal sinuses are paired left & right in spaces of what 4 bones?
Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillae
Into what area do paranasal sinuses open directly into?
Nasal cavity
What is the function of paranasal sinuses?
Warm + moisten air
What is sinusitis?
Inflammation of mucous membrane due to infection

The pharynx is made of _______ muscle, lined by mucous membrane
“skeletal”