Campbell Biology Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
fermentation
a catabolic process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid
aerobic respiration
a catabolic pathway that consumes oxygen gas and organic molecules, producing ATP
cellular respiration
the catabolic pathways of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, which break down organic molecules for the production of ATP
redox reaction
a chemical reaction involving the complete or partial transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another
oxidation
the loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction
reduction
the addition of electrons to a substance involved in a redox reaction
reducing agent
the electron donor in a redox reaction
oxidizing agent
the electron acceptor in a redox reaction
NAD+
a coenzyme that can accept an electron and acts as an electron carrier in the electron transport chain
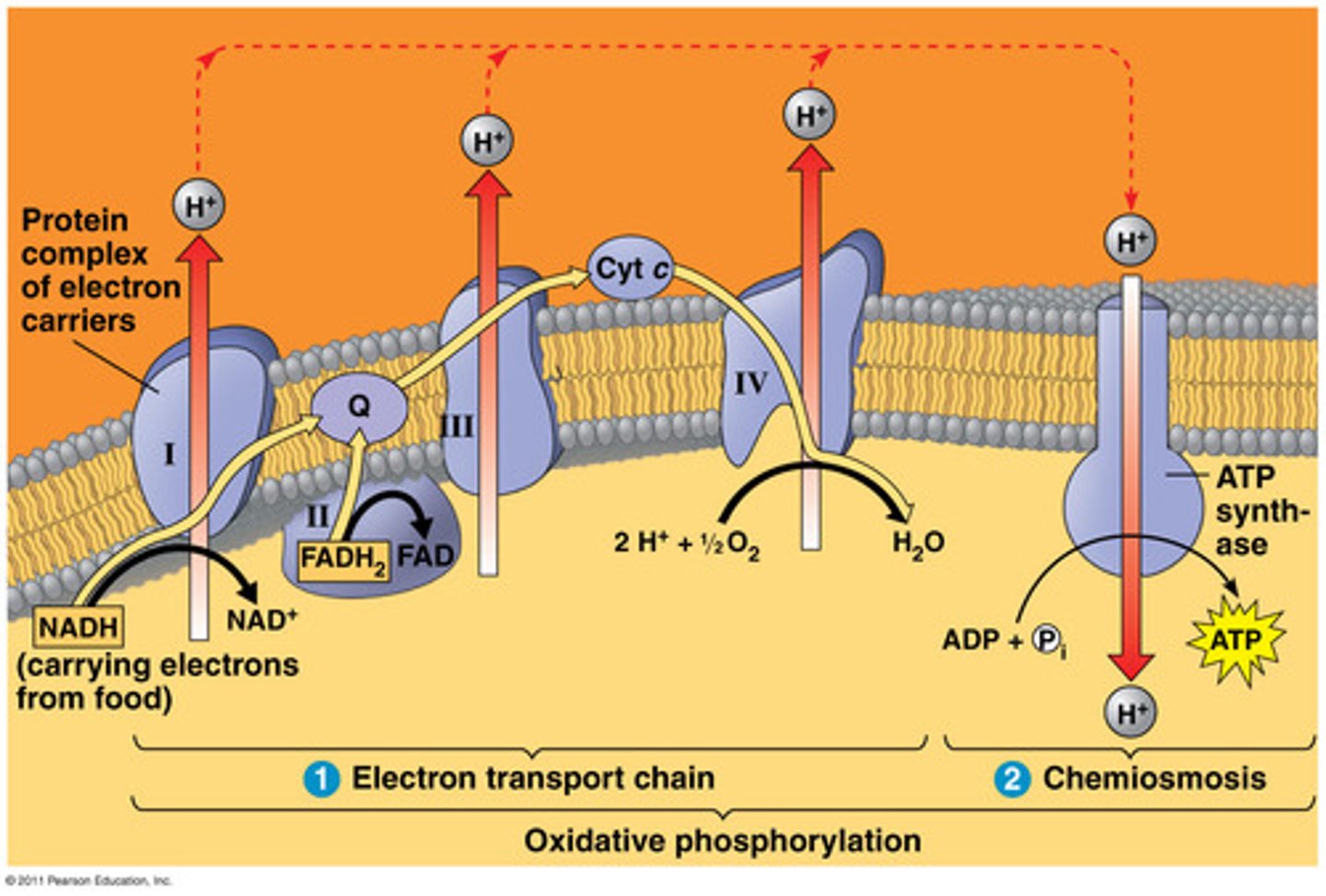
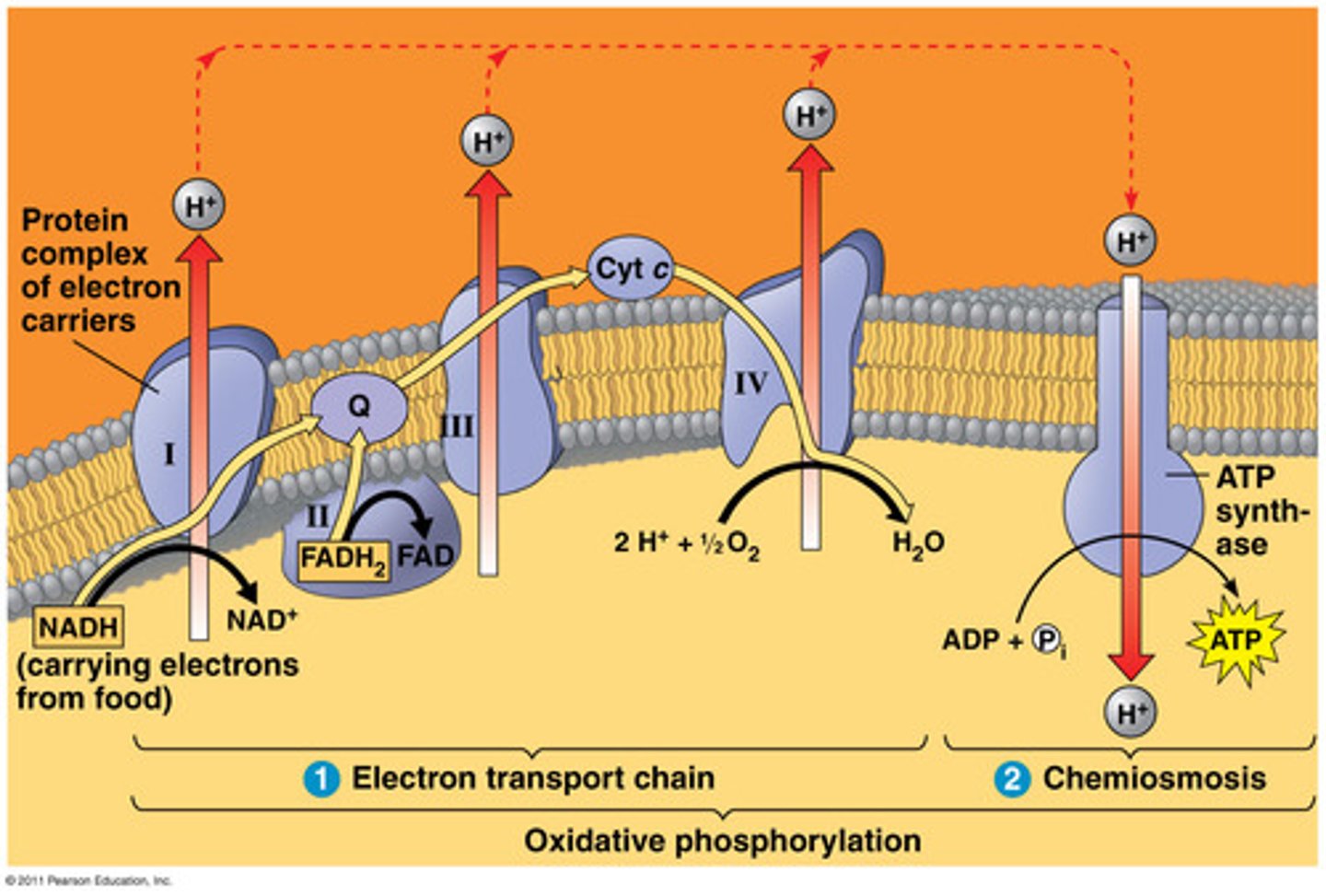
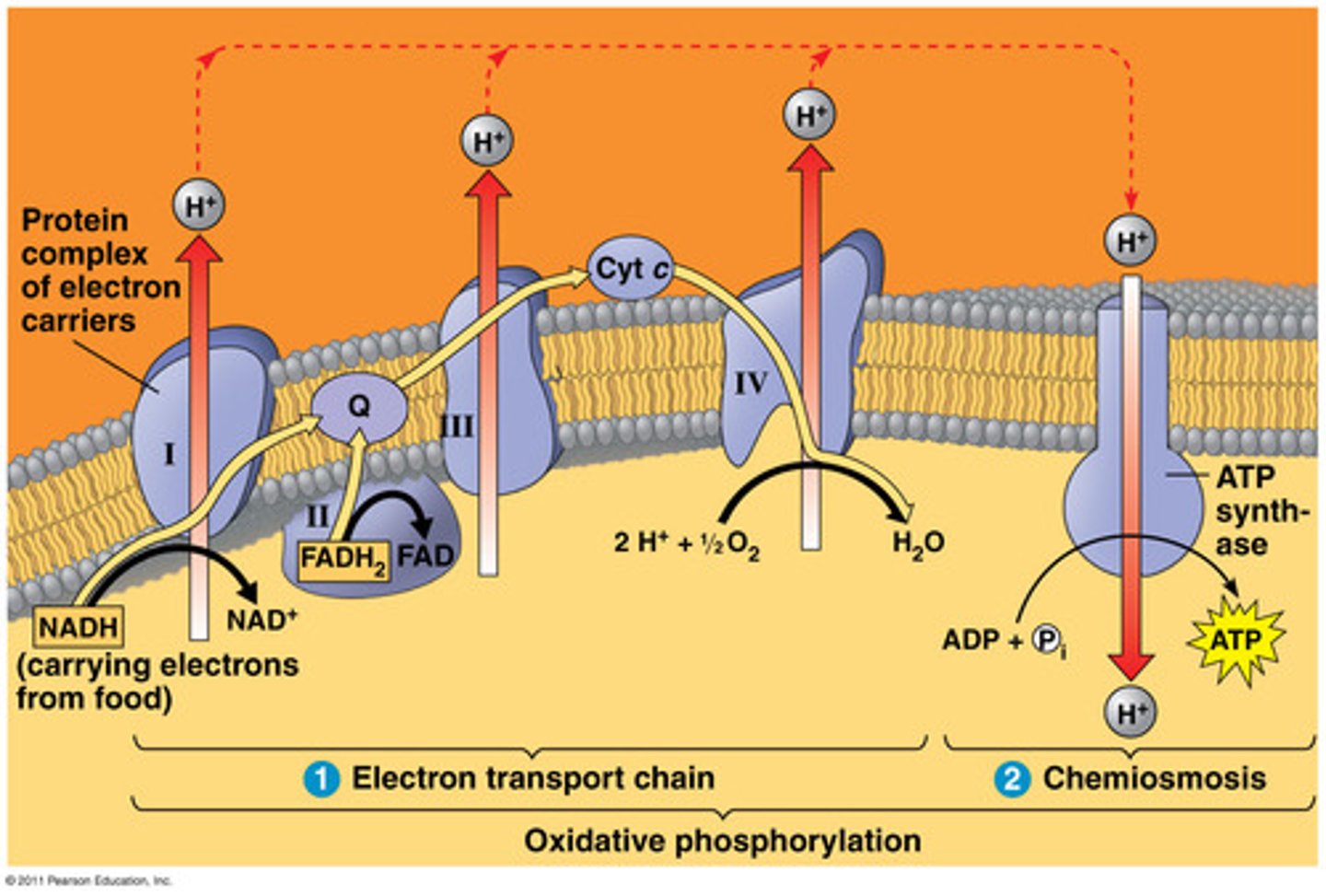
electron transport chain
a sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP
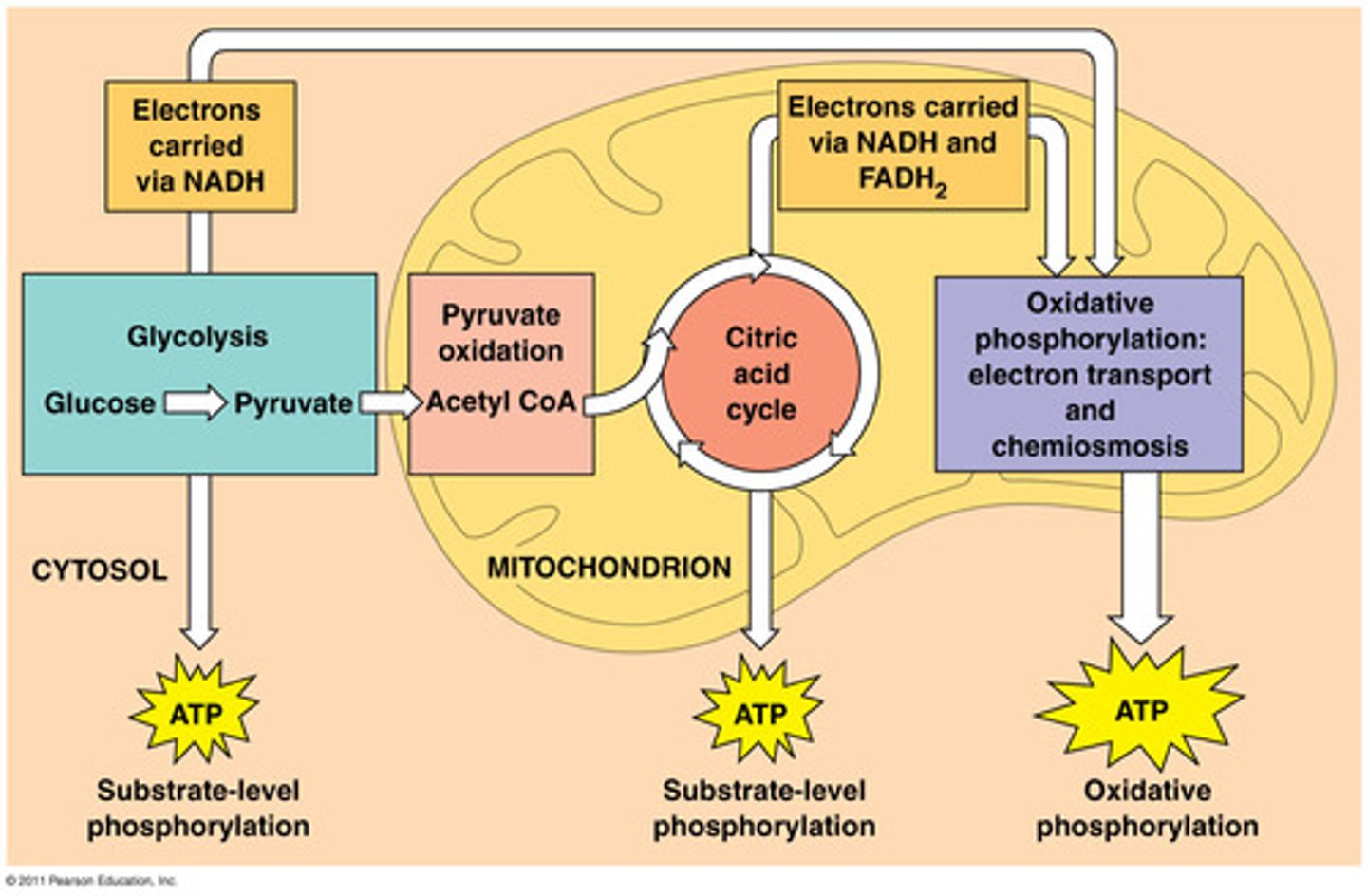
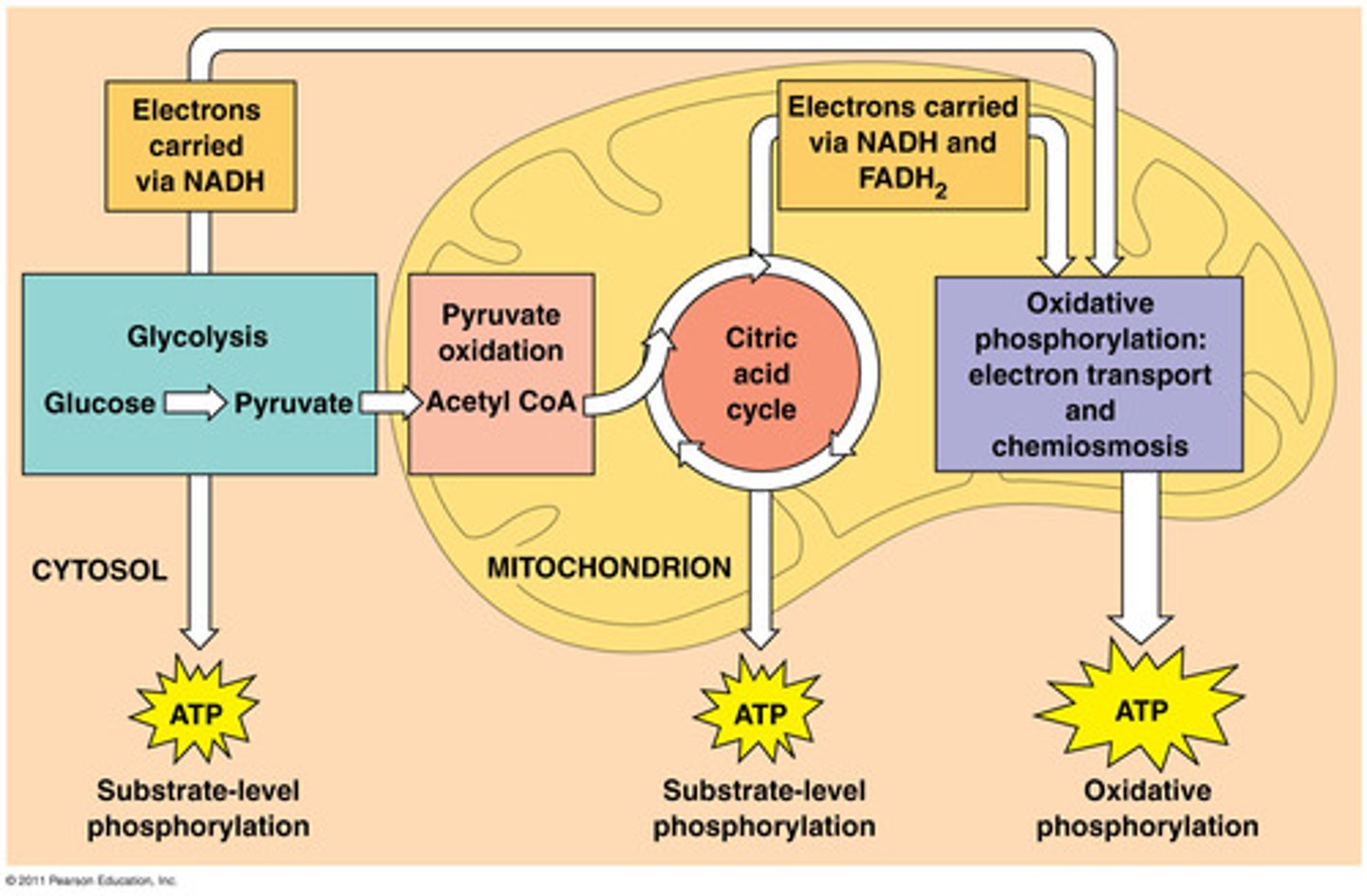
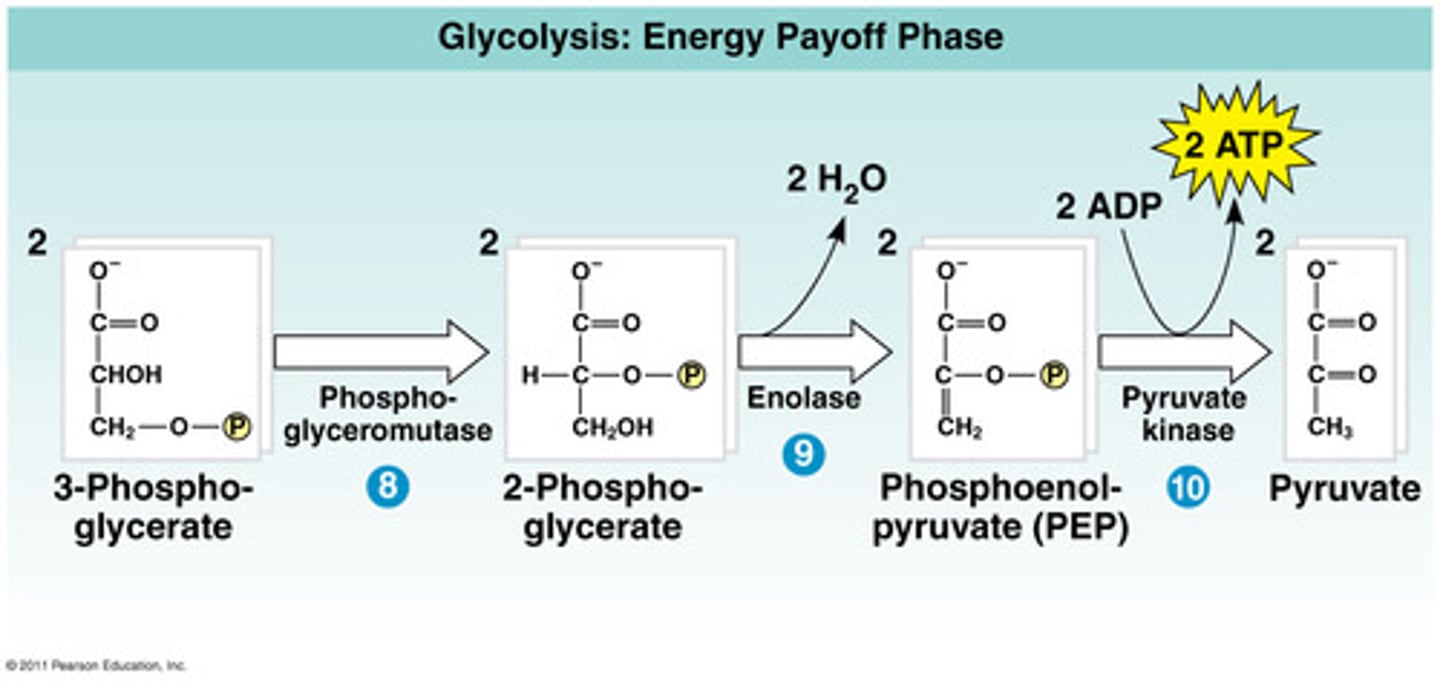
glycolysis
the splitting of glucose into pyruvate; serves as the starting point for fermentation or cellular respiration
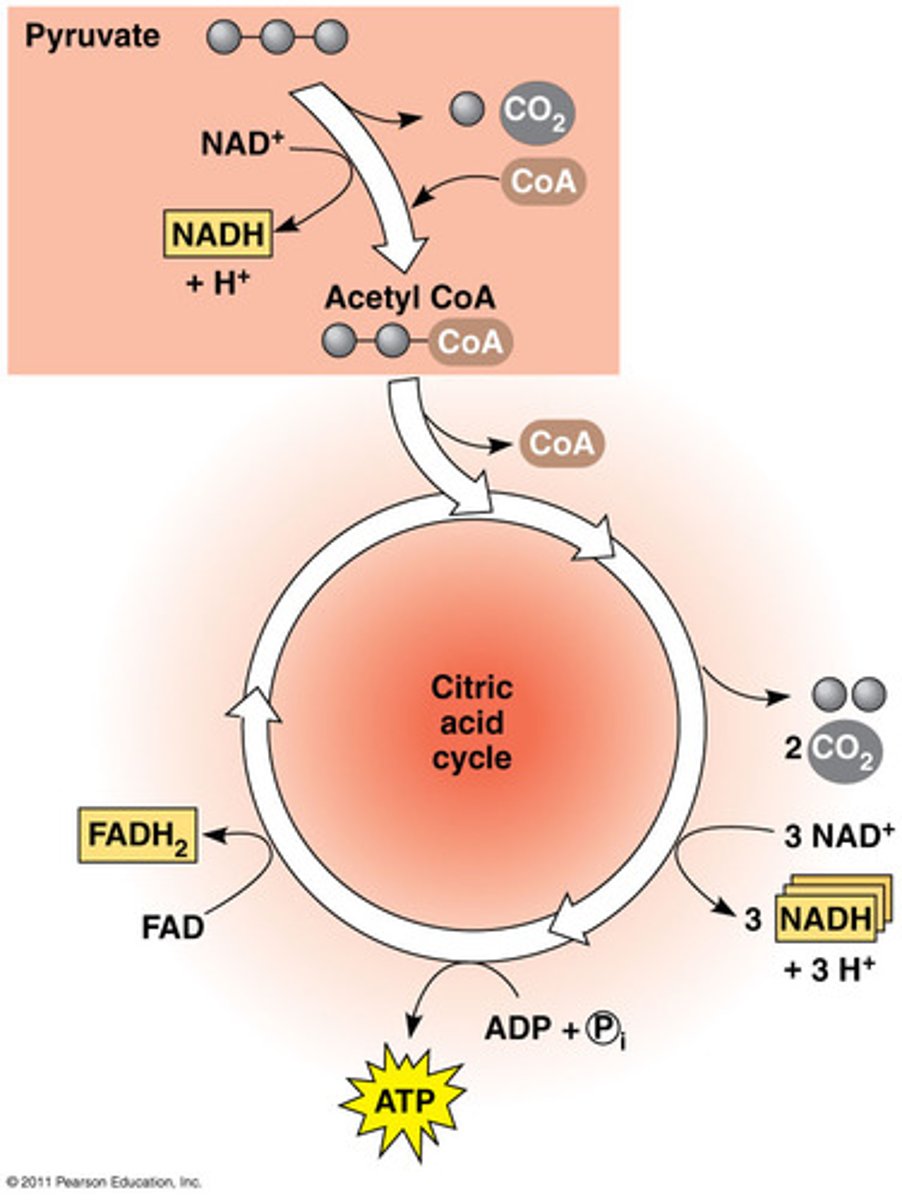
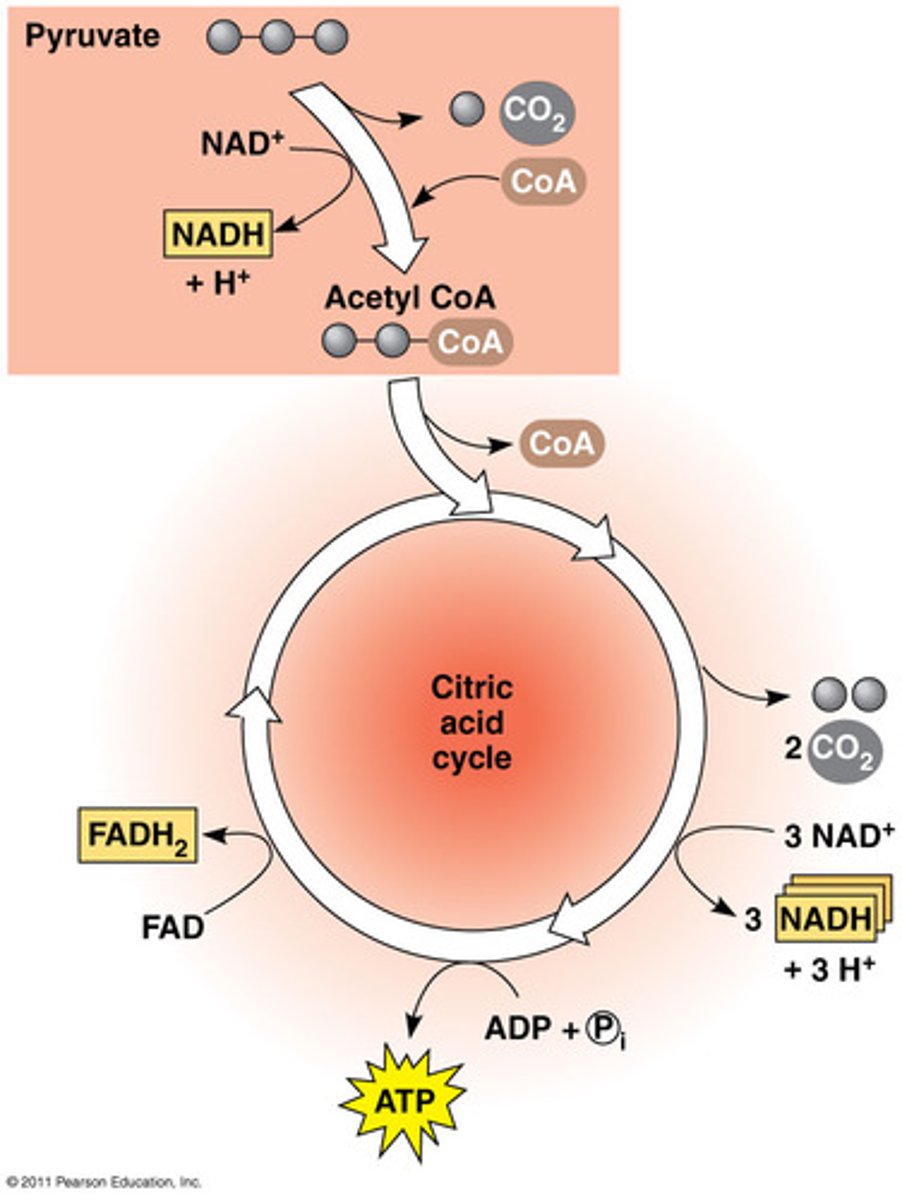
citric acid cycle
an eight-step series of reactions that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules by oxidizing pyruvate to carbon dioxide
oxidative phosphorylation
the production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain
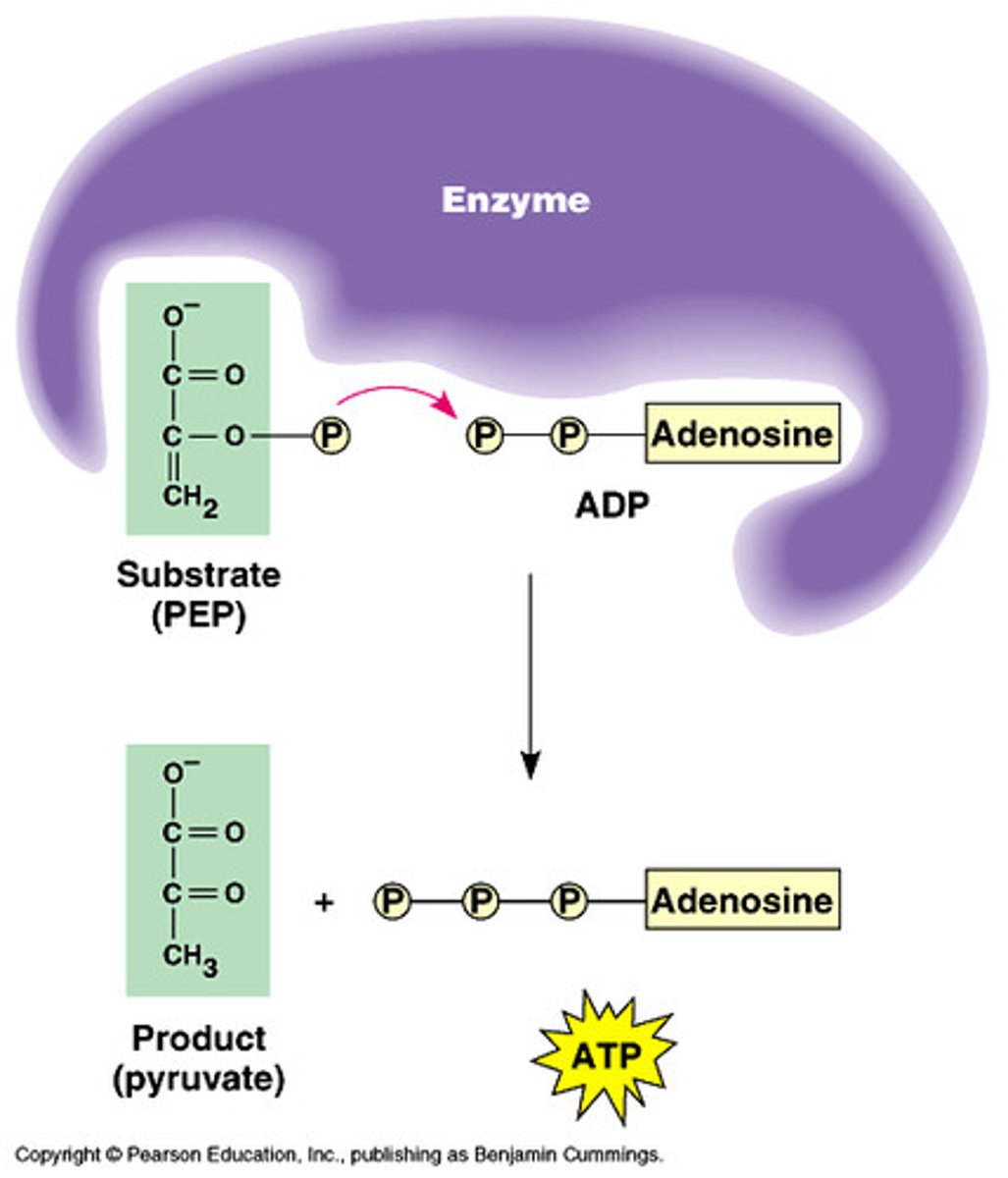
substrate-level phosphorylation
the formation of ATP by an enzyme directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism
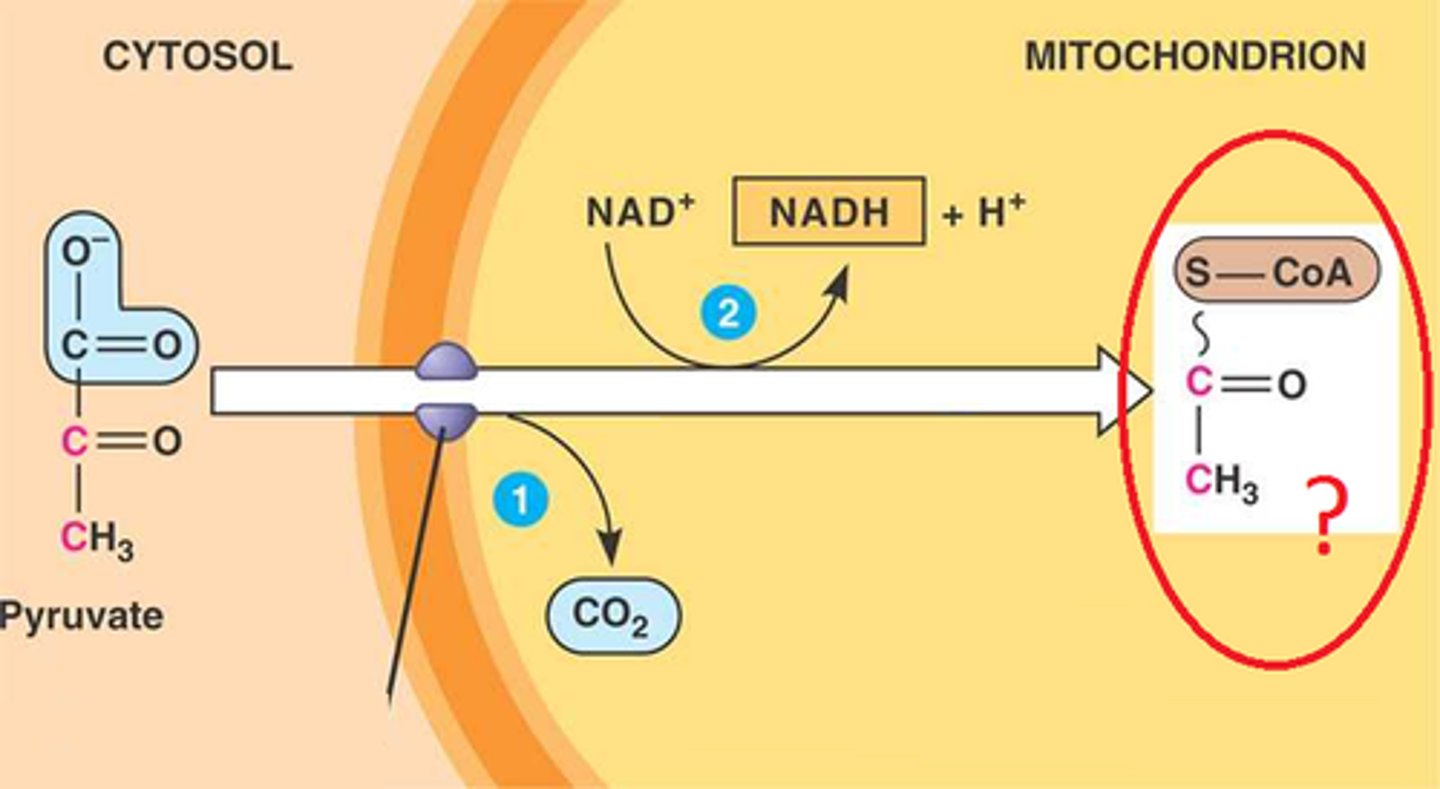
acetyl CoA
the entry compound for the citric acid cycle in cellular respiration, formed from a fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme
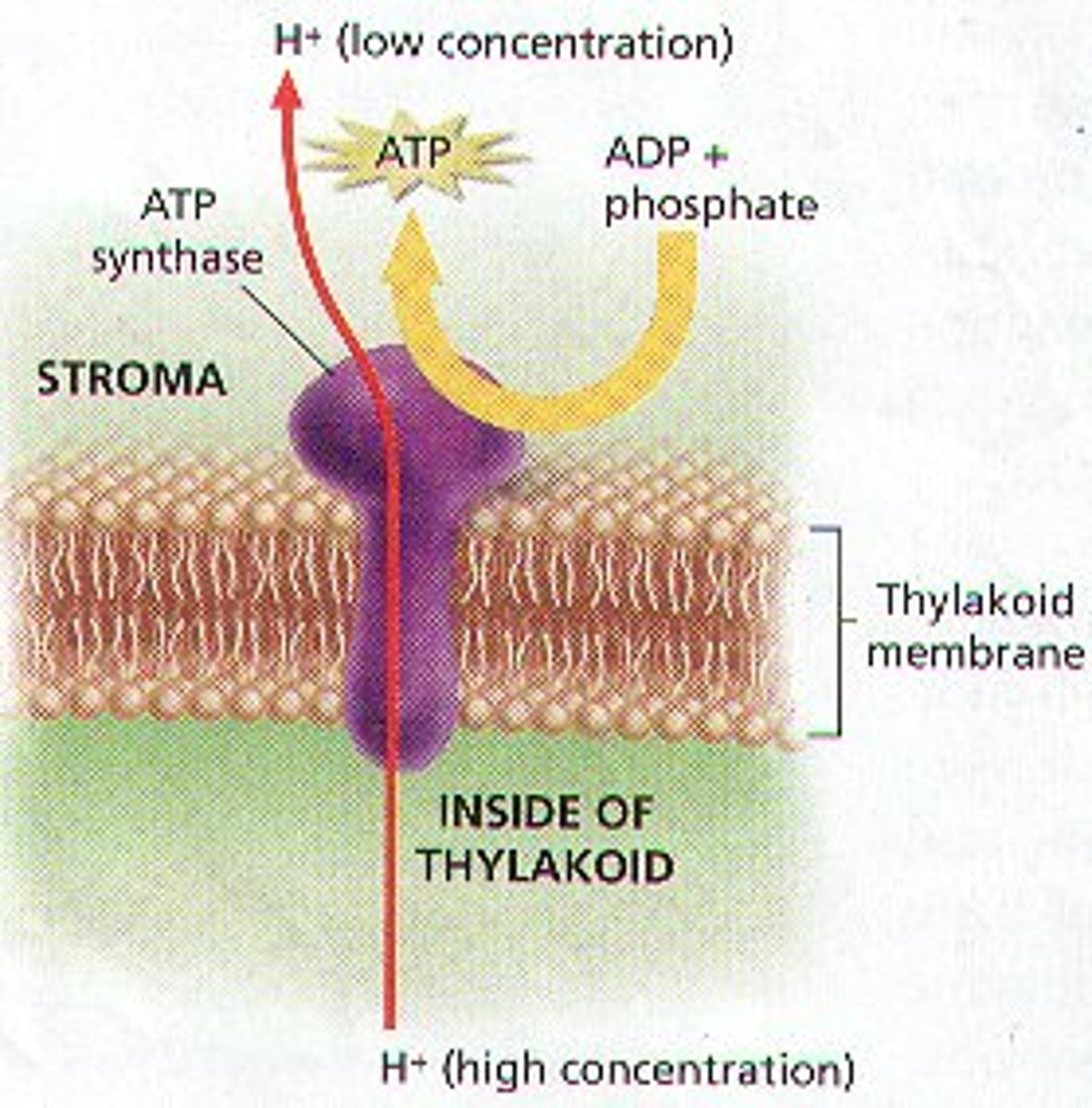
ATP synthase
enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate; uses the energy of a hydrogen ion (proton) concentration gradient to make ATP
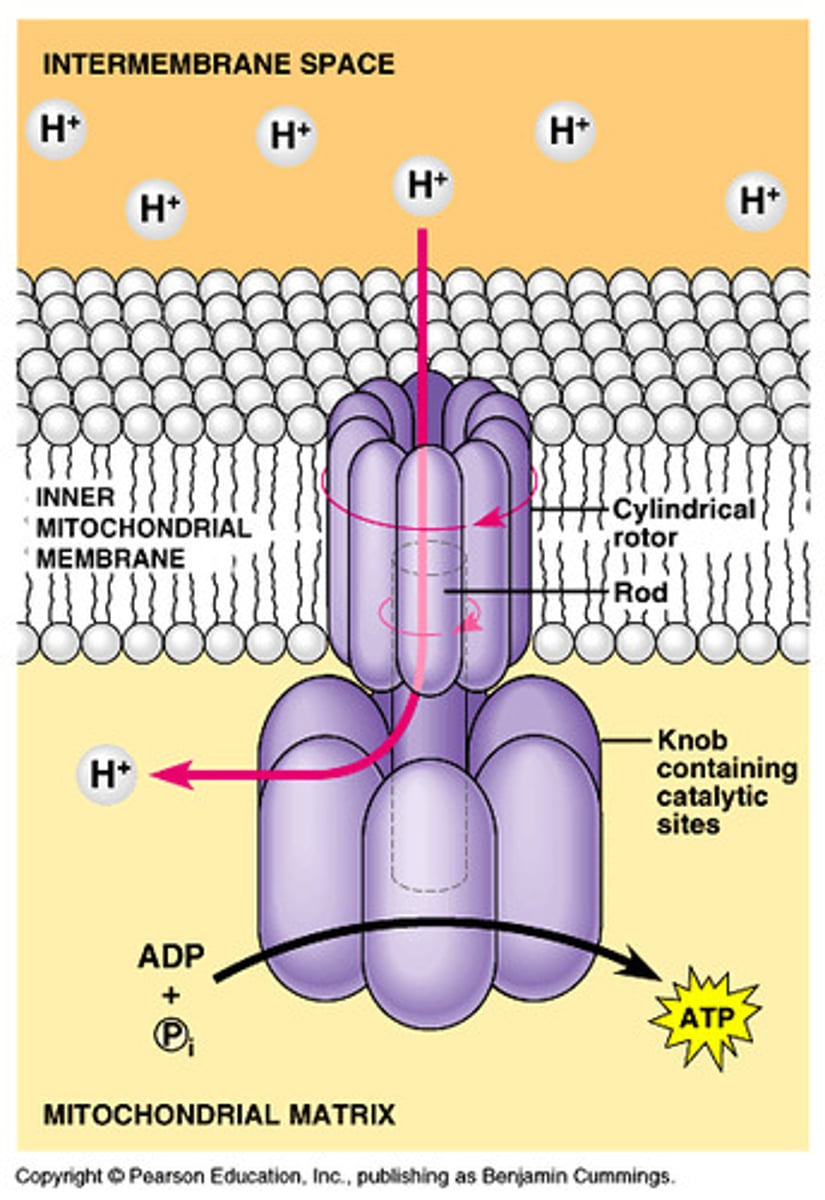
chemiosmosis
an energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work, such as the synthesis of ATP
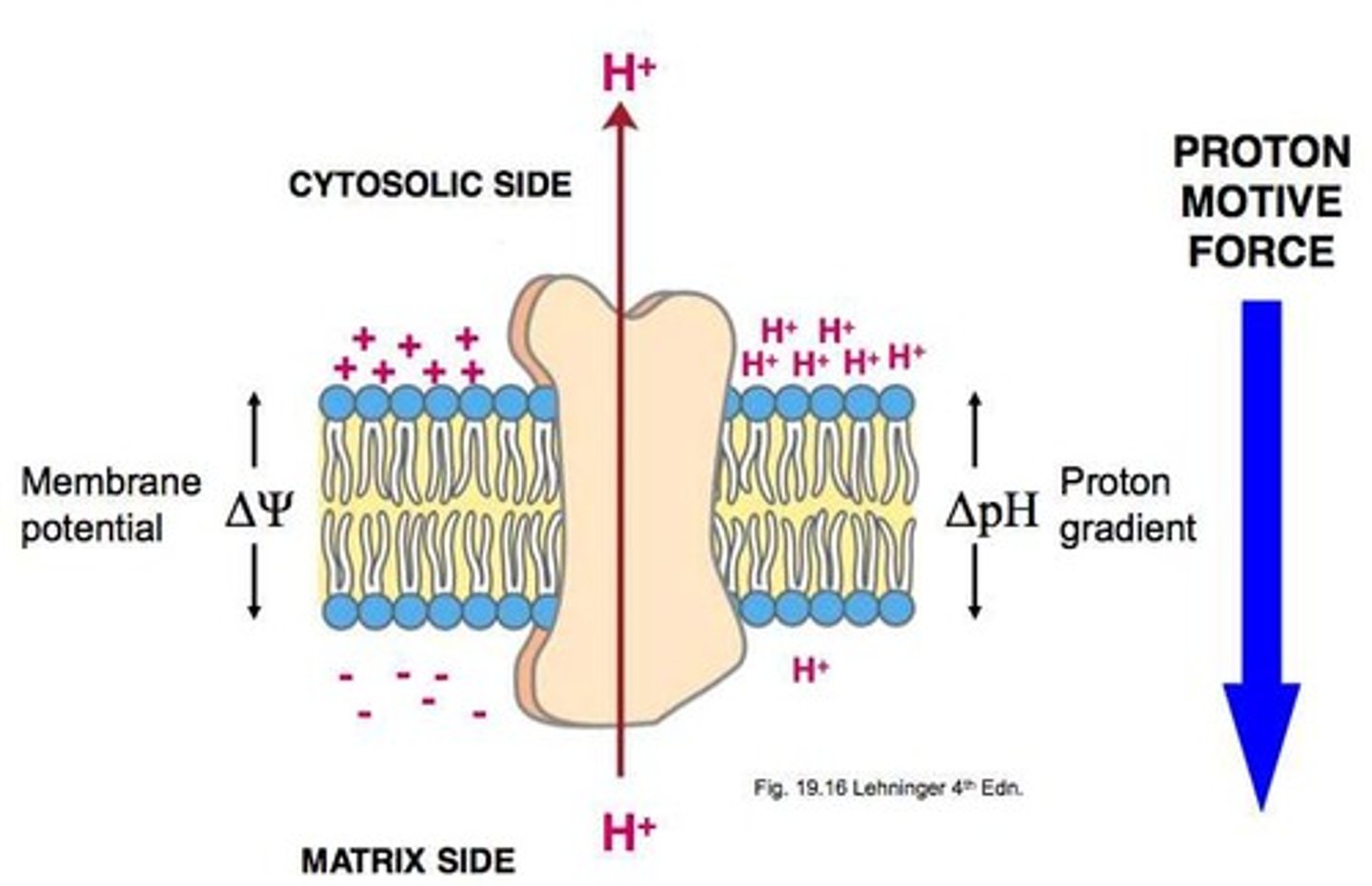
proton-motive force
the potential energy stored in the form of an electrochemical gradient, generated by the pumping of hydrogen ions across biological membranes during chemiosmosis
obligate anaerobes
carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2
facultative anaerobes
carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2; pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic road that leads to two alternative catabolic routes
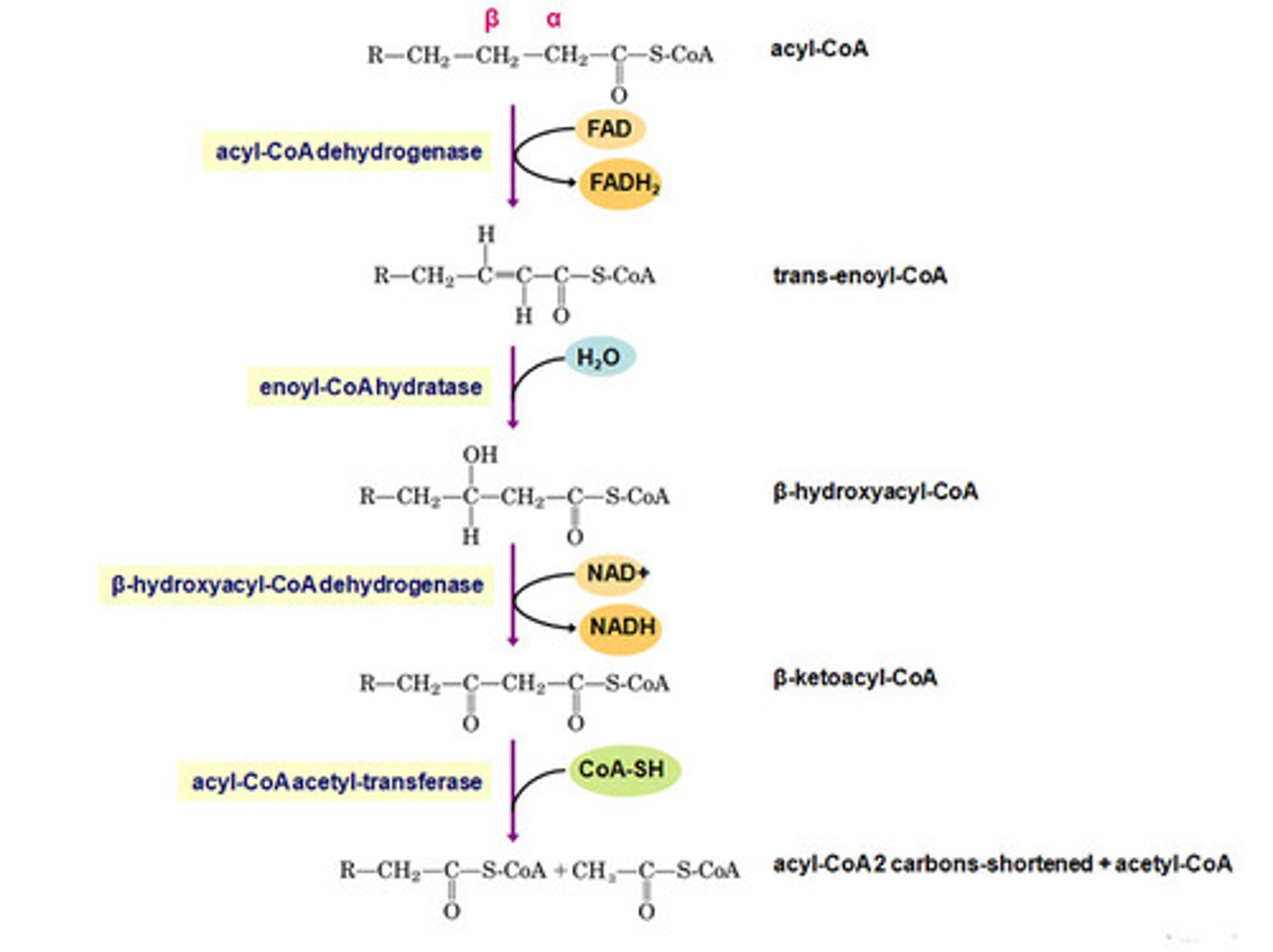
beta oxidation
a metabolic sequence that fatty acids down to two-carbon fragments that enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl CoA
NADH
Oxidized form of NAD that temporarily accepts electrons during cellular respiration
Autotroph
Uses energy from the sun or from oxidation of inorganic substances to make organic molecules from inorganic ones.
Heterotrophs
Unable to make there own food, they live on compounds produced by other other organisms. (hetero - "other")
Oxidation
removal of electrons (Hydrogen, adding Oxygen)
Reduction
addition of electrons (Gains Hydrogen)
Redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction happening at the same time.
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Cristae
folds in the inner membrane of mitochondria
Matrix
the space inside the inner membrane of the mitochondria
Intermembrane space
between inner and outer membranes of mitochondrion
Fermentation
final electron acceptor is an organic compound
proton pumps
Active transport of H+ molecules across membranes occurs through
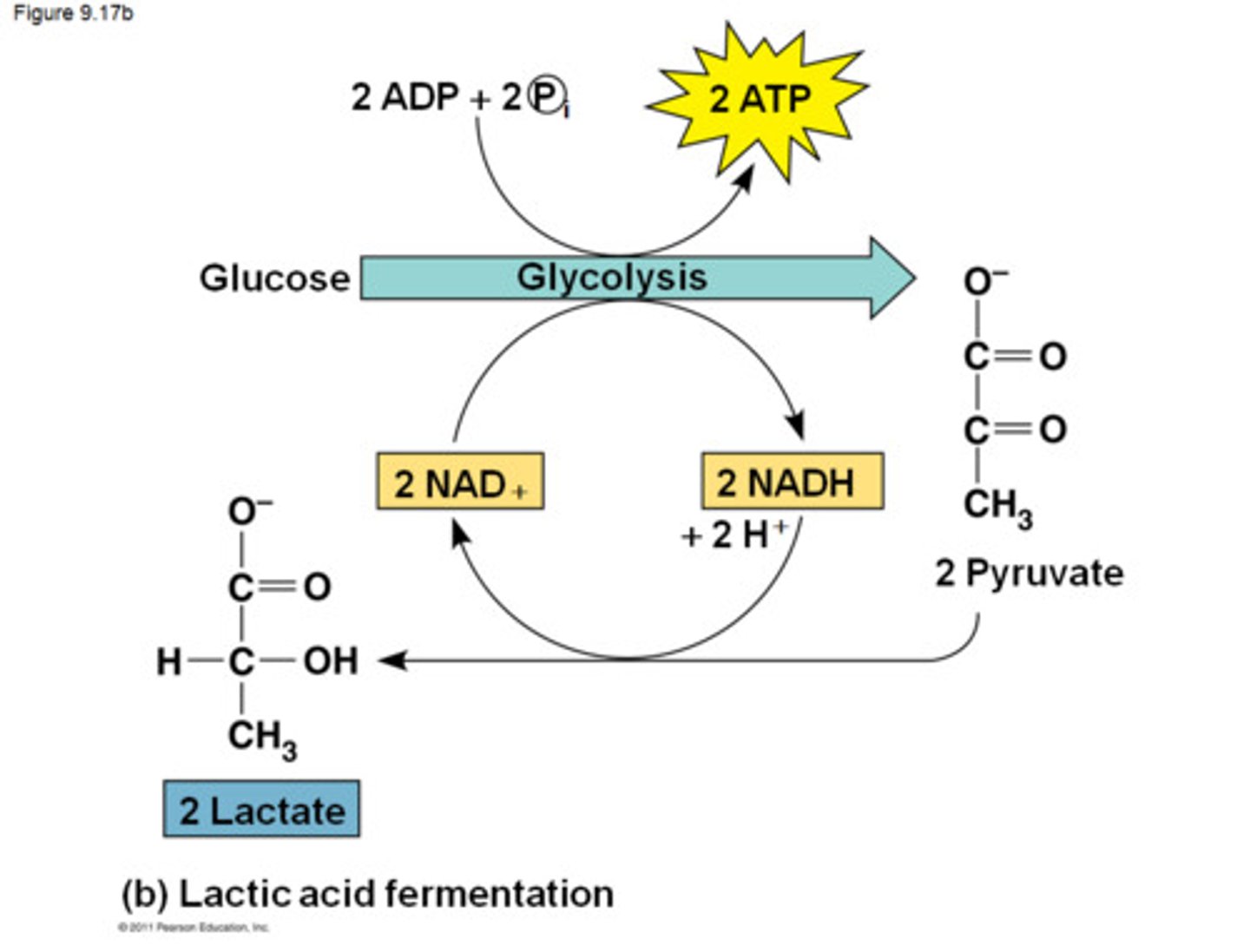
lactic acid fermentation
Glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+ with no release of carbon dioxide.
alcoholic fermentation
Glycolysis releases carbon dioxide from pyruvate, which is converted to acetaldeyde. Acetaldehyde is reduced by NADH to ethanol regenerating the supply of NAD+.