Lecture 16: Senses- The eye
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What does it mean when the brain becomes aware of a sensory impulse?
sensation
What does it mean when the brain interprets the sensory impulse?
perception
T/F sensory info enters the brain in the same way
true
sensory info results depend on what?
which area of the brain receives info
What is the brains ability to ignore unimportant stimuli known as?
sensory adaptation
What does sensory adaptation result from?
receptors becoming unresponsive or inhibition of nerve impulse
What are the types of sensory receptors?
chemoreceptors
pain receptors
thermoreceptors
mechanoreceptors
photoreceptors
What type of receptors is stimulated by chemical concentration (smell, taste)?
chemoreceptors
What type of receptors is stimulated by tissue damage (all senses)?
pain receptors
What type of receptors is stimulated by temperature change (skin)?
thermoreceptors
What type of receptors is stimulated by pressure or movement (skin, ears)?
mechanoreceptors
What type of receptors is stimulated by light energy (eye)?
photoreceptors
What are the two basic types of sensory categories?
somatic senses
special senses
Receptors of skin, muscles, joints and visceral organs (sense of touch, temp, pressure) fall under what?
somatic senses
What falls under special senses?
nose, tongue, ear, eye
What are the visual accessory organs?
eyelids, lacrimal apparatus, and extrinsic eye muscles
What are eyelids moved by?
orbicularis oculi
What is a thin, translucent membrane that covers the sclera (white), cornea and lines the under surface? Where is it located?
conjuctiva
eyelids
Lacrimal apparatus contains what?
lacrimal duct
lacrimal gland
What secretes tears… moistens, lubricates, and contains antibacterial agent?
lacrimal glands
What connects to nose to drain tears?
lacrimal duct
What is the function of extrinsic eye muscles?
move eyeball
The wall of the eye has ______ tunics (layers)
three
What is part of the fibrous (outer) tunic of the eye?
cornea
sclera
optic nerve
What structure is a transparent dome; helps to focus entering light rays?
cornea
What structure is known as the whites of the eye; continuous with the cornea; muscle attachment?
sclera
What structure transmits electrical impulses from the retina to the brain?
optic nerve
What is part of the vascular (middle) tunic?
iris
pupil
lens
choroid coat
ciliary body
aqueous humor
What structure is a diaphragm regulating amount of light entering the pupil; associated with eye color?
iris
What structure is a circular opening in the center of the iris where light enters; black?
pupil
What structure is located behind the iris/pupil; it focuses light onto the retina?
lens
What is the term for when the lens changes shape to adjust for close or distance vision?
accommodation
What connects lens to ciliary muscles (smooth)… contraction/relax causes accomodation?
suspensory ligaments
What is it called when the cornea and lens bend light waves to focus an image on the retina?
light refraction
What two structures of the eye cause light refraction?
cornea and lens
What is the accommodation mechanism for distance (far)?
thin lens; ciliary muscles relax
What is the accommodation mechanism for close (short distance)?
thick lens; ciliary muscles contract
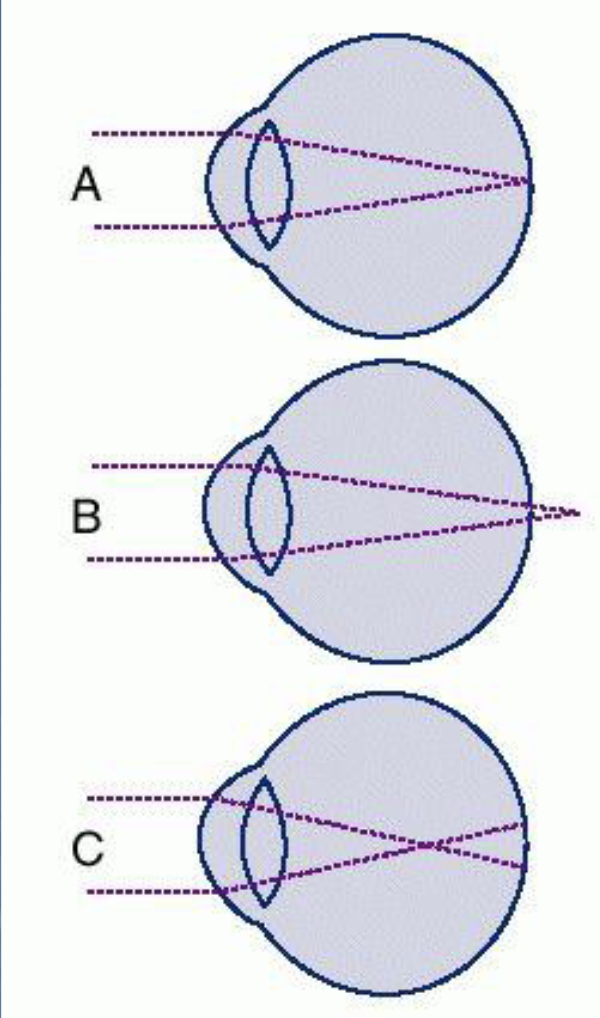
Figure A is a demonstration of what?
normal refraction and accommodation
Why does hyperopia and myopia occur?
due to shape of eye or cornea
Why does presbyopia occur?
due to age
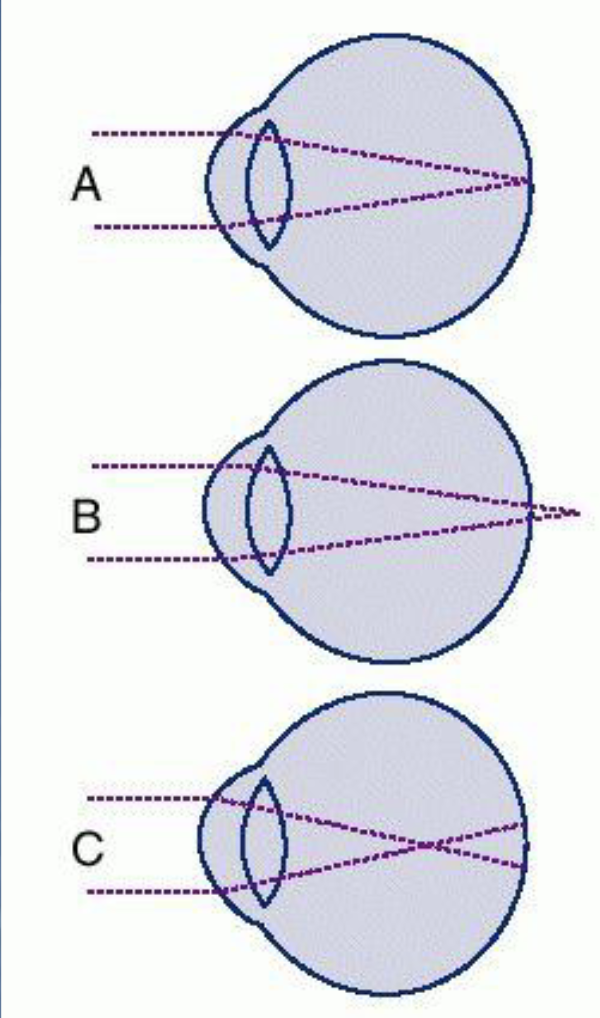
Figure B is a demonstration of what?
hyperopia
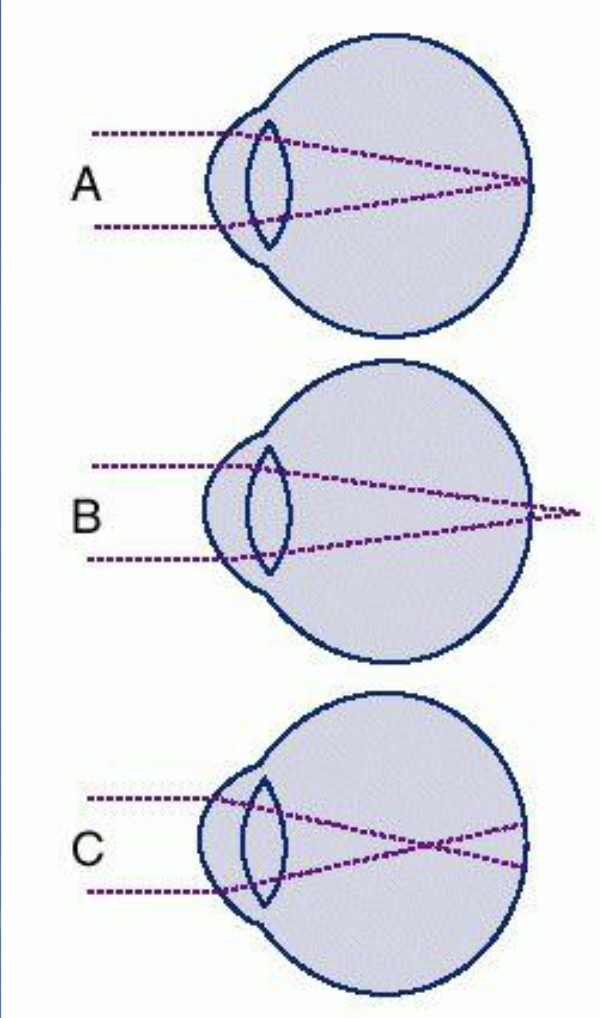
Figure C is a demonstration of what?
myopia
What is hyperopia?
can’t see near (farsighted)
What is myopia?
Can’t see far (nearsighted)
What is the general effect of presbyopia?
reading glasses
What structure lines internal surface of sclera?
choroid coat
vascular
nourished retina
choroid coat has a dark pigment that
absorbs excess light
What structure produces aqueous humor fluid; houses certain muscles?
ciliary body
What structures are part of the nervous (inner) tunic?
retina
fovea centralis
optic disc
vitreous humor
What structure is a multi-layered sensory tissue that lines the back of the eye and captures light rays?
Retina
Photoreceptors are?
rods and cones
What provides colorless vision and vision in dim light; more sensitive to light?
rods
What provides color vision; sharper image?
cones
What is the color blindness test?
Ishihara test
What is the region of the retina that produces the sharpest vision; densely packed with cones?
fovea centralis
What is the area on the retina where the optic nerve attaches; absence of photoreceptors causing a blind spot?
optic disc
Where is the anterior segment located?
between cornea and lens
What is a watery, fluid that gives shape, nourishes the lens and cornea; maintains intraocular pressure?
aqueous humor
The anterior segment contains what kind of humor?
aqueous humor
Where is the posterior cavity?
between lens and retina
What is a jelly like fluid; holds retina in place; maintain intraocular pressure?
vitreous humor
What kind of humor does the posterior cavity have?
vitreous humor
In order, list the structures in which light passes through the eye.
cornea → aqueous humor → pupil/iris → lens → vitreous humor → retina → optic disc → optic nerve → brain
What are the layers (tunics) of the eye?
fibrous (outer) tunic
vascular (middle) tunic
nervous (inner) tunic