QC/QA (IPS2)
1/1090
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1091 Terms
A
Combination of attributes which when compared to a standard, serves as a basis for measuring the uniformity of a product and determines its degree of acceptability.
a. Quality
b. Quality control
c. Quality assurance
A
The sum of all factors which contribute directly or indirectly for the safety, effectiveness, and reliability of the product.
a. Quality
b. Quality control
c. Quality assurance
B
Tool which gives the assurance that a product conforms to standards and specification through a system of inspection, analysis and action.
a. Quality
b. Quality control
c. Quality assurance
C
The activity of providing to all concerned, the evidence needed to
establish confidence that the activities relating to quality are being
performed adequately.
a. Quality
b. Quality control
c. Quality assurance
A
Inspect the raw materials, packaging materials, and the product itself before its release.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
B
Name of the department for quality monitoring.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
A
Solely under the scope of Quality Assurance.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
E
Quality control functions in a small company except:
a. Analysis Function
b. Monitor Function
c. Record Review & Release Function
d. Audit Function
e. None
A
In a small drug company, QC has the audit function; if it's a large drug company then the audit function is no longer part of the functions of their QC department.
a. True
b. False
F
Five sections of quality control except:
a. Specification and assay development
b. Central release section
c. Chemical control
d. Inspection and checking section
e. Biological and microbiological section
f. Packaging section
B
Establish systems for ensuring the quality of the product.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
B
Responsible for ensuring that the quality policies adopted by a company are followed.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
B
It serves as the contact with regulatory agencies.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
B
Final authority for product acceptance or rejections.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
B
It helps to identify and prepare the necessary standard operation procedures replated to the control of quality.
a. Quality control
b. Quality assurance
B
An undesirable characteristics of a product. Failure to conform to specification.
a. Under-quality
b. Defects
c. Damage
d. Reject
A
Classification of defects according to measurability
I. Variable defect
II. Attribute defect
III. Critical defect
IV. Major defect
V. Minor defect
VI. Ocular defect
VII. Internal defect
VIII. Performance defect
a. I, II
b. III, IV, V
c. VI, VII, VIII
B
Classification of defects according to seriousness or gravity
I. Variable defect
II. Attribute defect
III. Critical defect
IV. Major defect
V. Minor defect
VI. Ocular defect
VII. Internal defect
VIII. Performance defect
a. I, II
b. III, IV, V
c. VI, VII, VIII
C
Classification of defects according to nature
I. Variable defect
II. Attribute defect
III. Critical defect
IV. Major defect
V. Minor defect
VI. Ocular defect
VII. Internal defect
VIII. Performance defect
a. I, II
b. III, IV, V
c. VI, VII, VIII
A
A defect which can be measured directly by instruments giving dimensions of length, weight, height, thickness, concentration, volume, viscosity pH or size particles.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
B
A defect which cannot be measured directly by instruments. It shows mainly the conformance or nonconformance of the material to specifications.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
C
A defect which may endanger life or property and may render the product non-functional.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
D
A defect which may affect the function of the object and therefore may render the product useless.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
E
A defect which does not endanger life or property nor will it affect the function but remains a defect since it is outside the prescribed limits.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
A
Balance - weight
pH meter - pH
Viscometer - viscosity
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
B
Judging only by color, odor, clarity.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
C
Absence of warning in a label for a potent drug.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
D
The presence of a crack in a bottle.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
E
Slight deviation of the color of the label from the color standards.
a. Variable defect
b. Attribute defect
c. Critical defect
d. Major defect
e. Minor defect
C
A defect that is visible.
a. Major defect
b. Minor defect
c. Ocular defect
d. Internal defect
e. Performance defect
D
A defect which is not seen although present.
a. Major defect
b. Minor defect
c. Ocular defect
d. Internal defect
e. Performance defect
E
A defect in function.
a. Major defect
b. Minor defect
c. Ocular defect
d. Internal defect
e. Performance defect
C
Foreign particulate
a. Major defect
b. Minor defect
c. Ocular defect
d. Internal defect
e. Performance defect
D
A sub-potent drug product
a. Major defect
b. Minor defect
c. Ocular defect
d. Internal defect
e. Performance defect
E
A suppository that does not melt at body temperature.
a. Major defect
b. Minor defect
c. Ocular defect
d. Internal defect
e. Performance defect
E
Sources of variation except:
a. Materials
b. Machines
c. Methods
d. Men
e. None
f. All
A
Internal factor for assuring safety and therapeutic efficacy of drugs
a. General principles of Total Quality Control in the drug Industry
b. Current Good Manufacturing Practices
c. International Harmonized Guidelines
A
Established & implemented by Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association in 1967.
a. General principles of Total Quality Control in the drug Industry
b. Current Good Manufacturing Practices
c. International Harmonized Guidelines
A
All drug makers since 1967 must have QA department responsible for controlling all the products they manufactured.
a. General principles of Total Quality Control in the drug Industry
b. Current Good Manufacturing Practices
c. International Harmonized Guidelines
B
External factor for assuring safety and therapeutic efficacy of drugs.
a. General principles of Total Quality Control in the drug Industry
b. Current Good Manufacturing Practices
c. International Harmonized Guidelines
B
Established & implemented by Food & Drug Administration.
a. General principles of Total Quality Control in the drug Industry
b. Current Good Manufacturing Practices
c. International Harmonized Guidelines
A.
Mandated quarter of the month visits by FDA in manufacturing sites
a. Administrative Order No. 220 series of 1974.
b. Administrative Order No. 13 series of 2005.
c. Administrative Order No. 320 series of 1974.
d. Administrative Order No. 24-0017 series of 2000.
A
Scope of Administrative Order No. 220 series of 1974.
Organization and Personnel
Buildings and Facilities
Equipment
Components & Drug Product Containers and Closures
Production & Process Control
Packaging, Labelling Control
Holding and Distribution
Laboratory Control
Record and Reports
Returned & Salvaged Drug Products
a. True
b. False
E
Non compliance to CGMp could result in
a. Quality Variation
b. Contamination
c. Aging & improper care
d. Mix-ups and Errors
e. All
f. None
D
Main objective of CGMP is to produce a product that is except;
a. Safe
b. Pure
c. Effective
d. Highly profitable
e. None
A
The monitoring of quality by application of statistical methods in all stages of production.
a. Statistical quality control
b. Statistics
c. Sampling
d. Population
e. Sample
B
Collection of data or numbers, and with the use of mathematics, can analyze and interpret these data for the purpose of making meaningful decisions.
a. Statistical quality control
b. Statistics
c. Sampling
d. Population
e. Sample
C
Process of removing appropriate number of items from a population in order to make inferences to the entire population
a. Statistical quality control
b. Statistics
c. Sampling
d. Population
e. Sample
D
Is the totaling of all actual or conceivable items of a certain class under consideration.
a. Statistical quality control
b. Statistics
c. Sampling
d. Population
e. Sample
E
Is a finite number of objects selected from a population.
a. Statistical quality control
b. Statistics
c. Sampling
d. Population
e. Sample
E
Common sampling plans except
a. 100% Inspection
b. Random sampling
c. Government sampling or Military standard
d. All
e. None
A
Used to minimize errors but normally and practically cannot be attained due to personnel fatigue and other human related factors. Usually applied to parenteral products.
a. 100% Inspection
b. Random sampling
c. Government sampling or Military standard
B
Sampling plan using the square root system
a. 100% Inspection
b. Random sampling
c. Government sampling or Military standard
C
N=50. Find the number of sample
a. 5
b. 7
c. 8
d. 10
C
Originated by a committee from military agencies of the USA, Great Britain and Canada. A table indicate how many sampling numbers can be used depending on the number of procured items from the supplier.
a. 100% Inspection
b. Random sampling
c. Government sampling or Military standard
A
Military standard
a. 105 D & ABC-STD105 D
b. 105 H & EFG-STI105 E
c. 110 D & ABC-STD110 D
d. 110 H & EFG-STI110E
A
Included in the four basic standards to be specified in the construction of statistical sampling plan.
I. AQL - Acceptable Quality Level
II. UQL - Unacceptable Quality Level
III. Producer's risk (α)
IV. Consumer's risk (ß)
a. I, II, III, IV
b. I, II
c. I, II, III
d. III, IV
A
For the weight variation, when 1-2 tablets don't comply with the requirement, then it will still be accepted
a. True
b. False
A.
In weight variation, if there are 3-4 tablets that didn't comply, it won't immediately be rejected for there'll be a conduction of the 2nd trial that is called double sampling.
a. True
b. False
A.
In weight variation 3% or less defective tablets are still accepted.
a. True
b. False
A
Is the risk of error on the probability of rejecting a good batch.
a. Producer's risk (α)
b. Consumer's risk (ß)
c. Profit loss risk
B
Is the risk of error on the probability of accepting a defective batch.
a. Producer's risk (α)
b. Consumer's risk (ß)
c. Cost-effectiveness risk
D
Two basic types of quality control chart
a. Variable chart
b. Attribute chart
c. Characteristic chart
d. a and b
e. a and c
f. b and c
A
Several samples are tested and distribution of measurements can, in a sense, measure degrees of defectiveness. A chart using actual records of numerical measurements on a full continuous scale such as meter, grams, liter.
a. Variable chart
b. Attribute chart
B
Each sample inspected is tested to determine whether it conforms to requirements. It is the so-called "go" or "no-go" situation.
a. Variable chart
b. Attribute chart
B
Makes use of discrete data classifying the number of items conforming and the number of items failing to conform to any specified requirements.
a. Variable chart
b. Attribute chart
A
Variable chart
I. Mean (X) chart
II. Range (R) chart
III. (Fraction defective) P-Chart
a. I, II
b. I, III
c. I, II, III
d. III only
e. I only
D
Attribute chart
I. Mean (X) chart
II. Range (R) chart
III. (Fraction defective) P-Chart
a. I, II
b. I, III
c. I, II, III
d. III only
e. I only
A
The square root of the quantity (sum of squares of deviation of individual results from the mean, divided by one less than the number of results in the set).
a. Standard deviation
b. Relative standard deviation
A
a. Standard deviation
b. Relative standard deviation
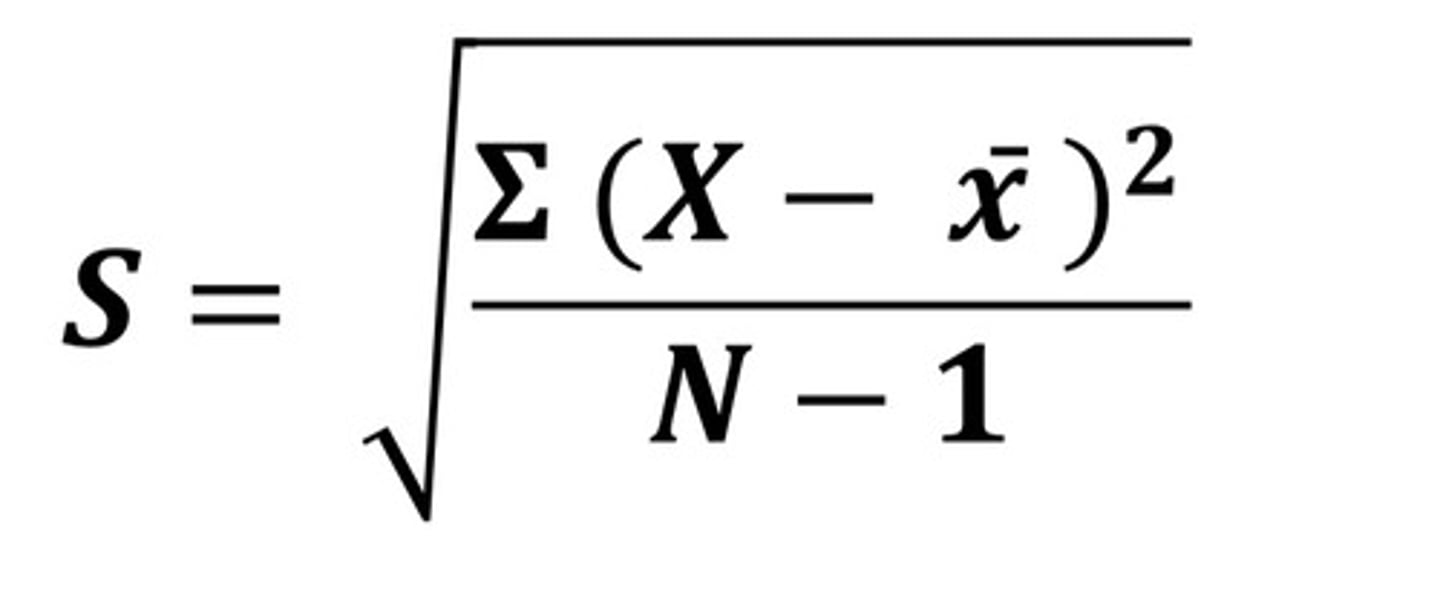
B
The one tells us how far the UCL and LCL with the target value or average or center value.
a. Standard deviation
b. Relative standard deviation
B
The standard deviation expressed as a fraction of the mean. It is sometimes multiplied by 100 and expressed as a percentage.
a. Standard deviation
b. Relative standard deviation
B
a. Standard deviation
b. Relative standard deviation
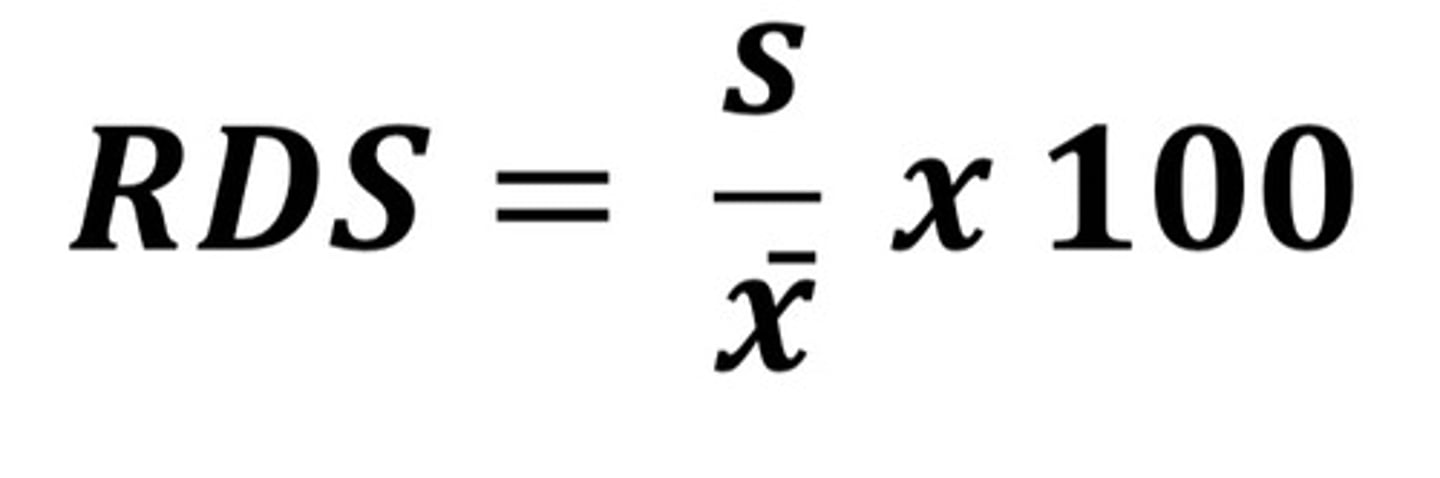
E
Two types of errors in analysis.
I. Determinate error
II. Systematic error
III. Indeterminate error
IV. Random error
a. I, III
b. II, IV
c. I, II
d. III, IV
e. I, II, III, IV
C
Caused by personal, method, and apparatus error.
I. Determinate error
II. Systematic error
III. Indeterminate error
IV. Random error
a. I, III
b. II, IV
c. I, II
d. III, IV
e. I, II, III, IV
D
Manifest themselves by slight variation in a series of observations made by the same observer under identical conditions.
I. Determinate error
II. Systematic error
III. Indeterminate error
IV. Random error
a. I, III
b. II, IV
c. I, II
d. III, IV
e. I, II, III, IV
A
Made by the individual analyst.
Ex. Inability to judge color changes sharply.
a. Personal error
b. Error of method
c. Apparatus error
B
Caused by faulty procedures.
Ex. Incorrect sampling and improper selection of indicator.
a. Personal error
b. Error of method
c. Apparatus error
C
Due to poor construction or calibration.
Ex. Inaccuracy in the calibration of burets, pipets, etc.
a. Personal error
b. Error of method
c. Apparatus error
B
Verification, by data and analysis that the design objectives of a given facility, system, apparatus or procedures are reliably fulfilled in routine operation.
a. Authentication
b. Validation
c. Confirmation
F
Steps involved in validation except.
a. Choosing the desired attributes of the products.
b. Determining specification for those attributes
c. Selecting appropriate processes and equipment
d. Monitoring and testing processes, equipment & personnel while in operation.
e. Examining test procedures themselves to ensure their accuracy and reliability.
f. None
F
Scope of validation except
a. Process Validation
b. Assay Validation
c. Qualification of Manufacturing equipment
d. Validation of existing products by statistical evaluation
e. Cleaning Validation
f. None
A
Measure of reproducibility of data within a series of results. It expresses a degree of agreement among individual test results when procedure/method is applied to homogenous sample.
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Selectivity (Specificity)
d. Linearity
e. Range
A
Usually expressed as SD/RSD.
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Selectivity (Specificity)
d. Linearity
e. Range
B
It is used to denote agreement of an experimental result of the agreement of the main value of a series of experimental results with the true value.
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Selectivity (Specificity)
d. Linearity
e. Range
C
Ability of the method to measure accurately the analyte of interest.
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Selectivity (Specificity)
d. Linearity
e. Range
D
Ability of the methods to elicit test results that are directly proportional to the concentration of the analyte.
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Selectivity (Specificity)
d. Linearity
e. Range
B
Law used to graph and determine linearity of a sample.(absorbance= y-axis, against concentration= x-axis)
a. Stoke's Law
b. Beer's Law
c. Gin's Law
E
Lowest and highest level of analyte but the method can determine with reasonable accuracy and precision.
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Selectivity (Specificity)
d. Linearity
e. Range
A
Lowest concentration of the analyte in the sample that the method can detect. Prescribed as percentage or as parts per million.
a. Limit of detection
b. Ruggedness
c. Robustness
d. Sensitivity
B
Degree of reproducibility of test results obtained by analyzing the same sample under variety of normal test conditions such as different analyst instruments, days, reagent, columns & TLC plates.
a. Limit of detection
b. Ruggedness
c. Robustness
d. Sensitivity
C
Is the measure of the capacity of the analytical method to remain unaffected by small but deliberate variations in procedure.
a. Limit of detection
b. Ruggedness
c. Robustness
d. Sensitivity
D
Capacity of the test procedure to record small variations in concentrations.
a. Limit of detection
b. Ruggedness
c. Robustness
d. Sensitivity
A
The application of the procedures quantitative analytical chemistry to the analysis and determination of the purity and quality of drugs and chemicals used in pharmacy.
a. Quantitative Pharmaceutical Chemistry
b. Statistical Quality Chemistry
c. Qualitative Quality Chemistry
E
Method of analysis used in Quantitative Pharmaceutical Chemistry except:
a. Volumetric Method
b. Gravimetric Method
c. Special Method
d. Instrumental Method
e. None
A
Determination of the volume of a solution of known concentration required to react with a given amount of a substance to be analyzed.
a. Volumetric Method
b. Gravimetric Method
c. Special Method
d. Instrumental Method
e. None
A
Chemical reaction involved.
a. Neutralization
b. Precipitation
c. Redox reaction
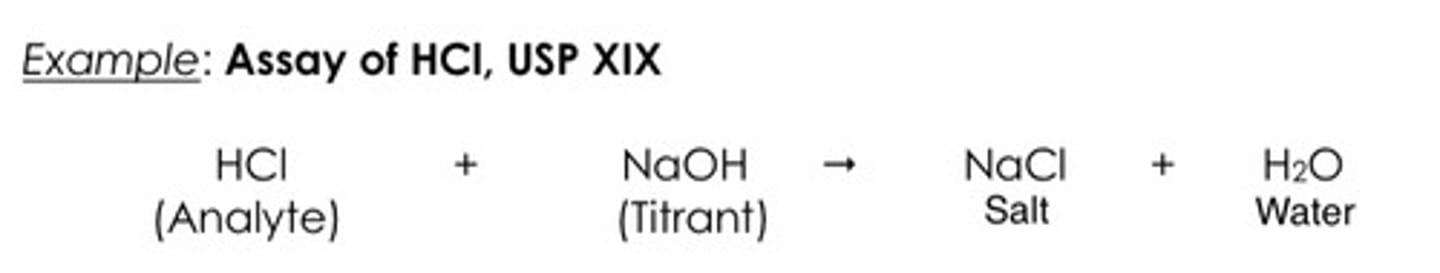
A
The chemical substances being analyzed.
a. Analyte or active constituents
b. Titrant
c. Titration
d. Indicator
B
The solution of known concentration. Examples are 0.1N HCl, 0.5N HSO4, 0.2N NaOH
a. Analyte or active constituents
b. Titrant
c. Titration
d. Indicator
C
The act of adding and measuring the volume of titrant used in the assay.
a. Analyte or active constituents
b. Titrant
c. Titration
d. Indicator