Understanding Fraud: Types, Prevention, and Detection
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Fraud
Wrongful deception for financial or personal gain.
Ponzi Scheme
Returns to investors come from new investors.
Confidence
Critical element for successful fraud.
Employee Fraud
Fraud committed against an organization by employees.
Fraud on Behalf of Organization
Fraud typically committed by executives.
Occupational Fraud
Misuse of occupation for personal enrichment.
ACFE
Association of Certified Fraud Examiners.
Asset Misappropriation
Theft or misuse of organizational assets.
Corruption
Fraudsters misuse influence for personal benefit.
Fraudulent Financial Statements
Falsification of an organization's financial records.
Employee Embezzlement
Most common occupational fraud type.
Vendor Fraud
Fraud perpetrated by vendors against organizations.
Customer Fraud
Fraud committed by customers against organizations.
Direct Fraud
Employee steals cash or assets directly.
Indirect Fraud
Employee takes bribes or kickbacks.
Fraud Triangle
Three elements: pressure, opportunity, rationalization.
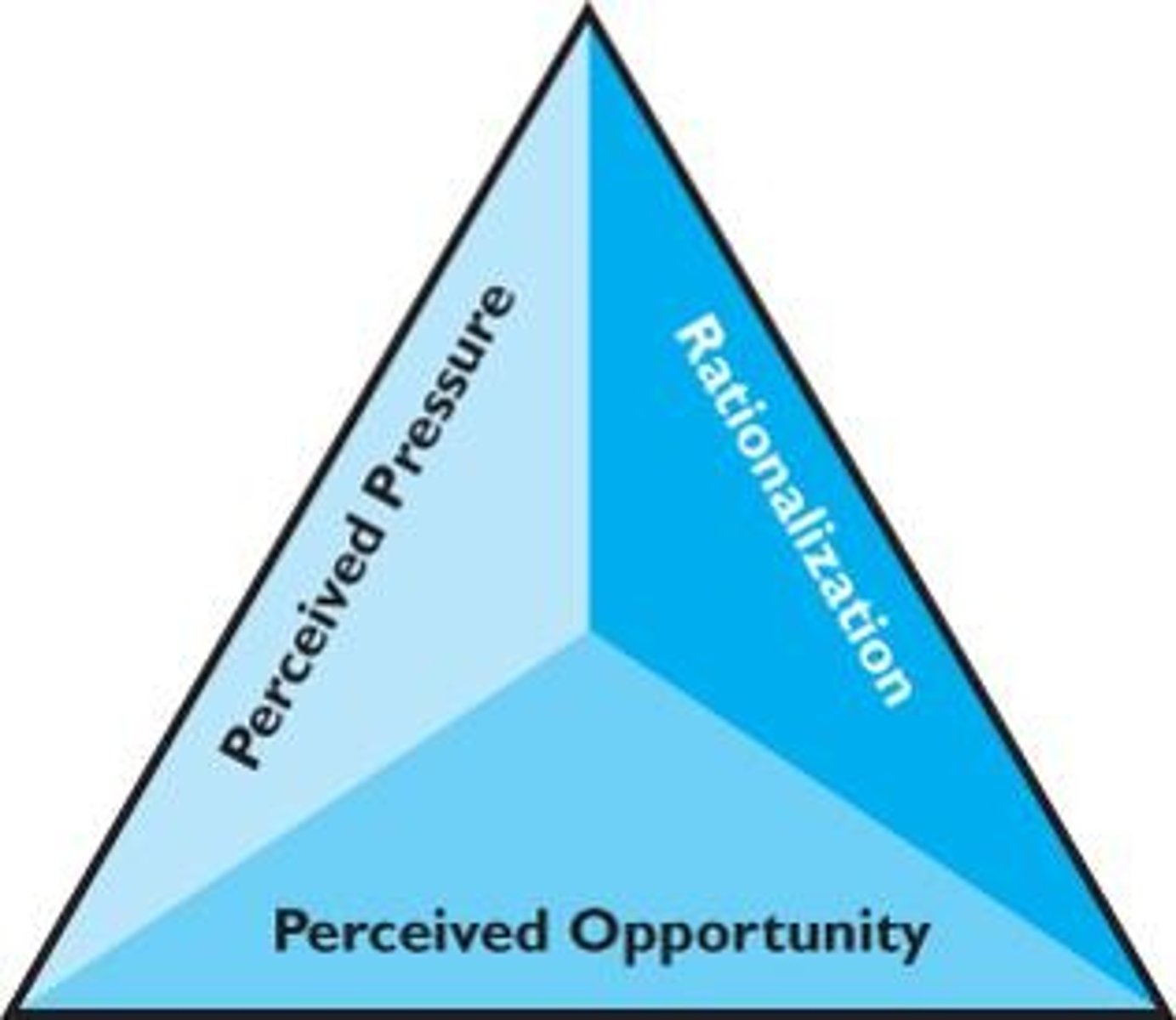
Perceived Pressure
Real or perceived pressure by the perpetrator.
Perceived Opportunity
Ability to conceal the fraud.
Rationalization
Justifying fraud as acceptable behavior.
Fire Triangle
Elements of fraud prevention: pressure, opportunity, rationalization.
Financial Pressures
Monetary issues causing stress leading to fraud.
Vice Pressures
Addictions or personal vices prompting fraudulent behavior.
Work-Related Pressures
Job stress or dissatisfaction influencing fraud.
Other Pressures
Various external factors contributing to fraudulent actions.
Fraud Opportunity Factors
Six factors increase chances of committing fraud.
Internal Control
Framework ensuring reliability, efficiency, and compliance.
COSO
Committee aiding businesses in internal control enhancement.
COSO Framework
Standard for auditing internal controls over financial reporting.
Control Environment
Foundation of internal control, influenced by management's tone.
Management's Role
Leads by example, modeling appropriate behaviors.
Effective Communication
Critical for conveying appropriate conduct and training.
Organizational Structure
Clear responsibilities enhance accountability and control.
Internal Audit Department
Cornerstone of governance, deters fraudulent activities.
Tone at the Top
Management's attitude towards internal controls affects culture.
Audit Trail
Documentation supporting transactions to detect fraud.
Control Activities
Procedures ensuring employee actions align with goals.
Segregation of Duties
Dividing responsibilities to reduce fraud risk.
Authorizations
System ensuring transactions are approved appropriately.
Physical Safeguards
Protecting assets from theft through physical means.
Independent Checks
Verification processes to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Documents and Records
Maintaining accurate records for accountability and auditing.
SAPID Acronym
Reminds of five control activities: S, A, P, I, D.
Preventive Controls
Activities designed to stop fraud before it occurs.
Detective Controls
Activities that identify fraud after it occurs.
Disciplining Fraud Perpetrators
Necessary to deter repeat offenses in fraud cases.
Audit Oversight
Board of Directors' role in monitoring management.
Compliance with Laws
Ensuring operations adhere to legal regulations.
Asymmetrical Information
One party has information that another lacks.
Fraud Power
Types of influence used by fraud perpetrators.
Reward Power
Convincing victims of benefits from fraud participation.
Coercive Power
Instilling fear of punishment for non-participation.
Perceived Expert Power
Influencing others based on claimed expertise.
Legitimate Power
Convincing others of one's rightful authority.
Referent Power
Relating to potential co-conspirators for influence.
COSO Framework
Five components for effective internal control systems.
Control Environment
Foundation of an organization's internal control system.
Risk Assessment
Identifying and managing areas of potential risk.
Control Activities
Policies and procedures to mitigate risks.
Information and Communication
Sharing relevant information for effective controls.
Monitoring Activities
Assessing internal control performance over time.
Segregation of Duties
Separating responsibilities to prevent fraud opportunities.
Authorization
Approval processes for transactions and activities.
IT Processing Controls
Controls over data processing and security.
General Controls
Controls over data center and network operations.
Application Controls
Controls for individual accounting applications.
Fraud Prevention
Activities aimed at stopping fraud before it occurs.
Fraud Detection
Identifying symptoms or indicators of fraud.
Ethical Maturity Model (EMM)
Framework explaining unethical decision-making.
Independent Checks
Auditor evaluations to detect fraud.
Fraud Symptoms
Indicators associated with potential fraudulent activity.
Fraud Detection Methods
Three primary ways to identify fraud.
Whistle-blower Mechanism
Anonymous reporting system for fraud suspicions.
Predication
Foundation for starting a fraud investigation.
Purpose of Investigation
To determine if fraud or error exists.
Types of Evidence
Classified by evidence type produced during investigations.
Testimonial Evidence
Information gathered from interviews and interrogations.
Documentary Evidence
Evidence from written or digital sources.
Physical Evidence
Tangible items linked to dishonest acts.
Personal Observation
Evidence sensed by investigators through observation.
Fraud Motivation Triangle
Search for pressures, opportunities, and rationalizations.
Fraud Elements
Three components: theft, concealment, and conversion.
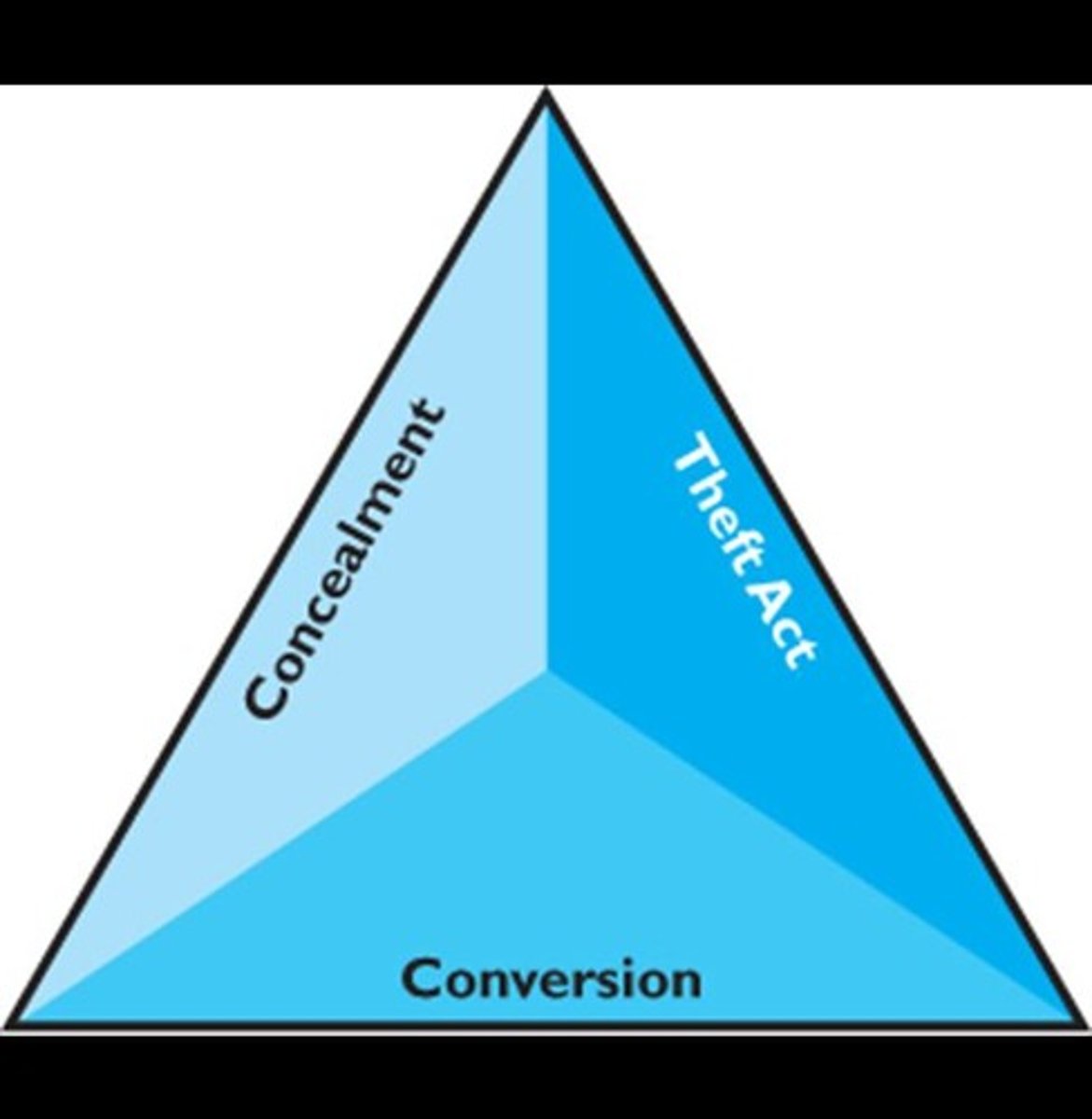
Theft Act
Gathering information on how theft was committed.
Concealment
Focus on hiding methods used by perpetrators.
Conversion
Investigating how stolen goods are spent.
Internal Control Limitations
Factors that undermine effective fraud prevention.
Management Override
Management decisions that bypass internal controls.
Human Errors
Mistakes due to carelessness or misunderstanding.
Collusion
Employees collaborating to bypass internal controls.
Whistle-Blowing System Elements
Key features for effective reporting of misconduct.
Anonymity in Reporting
Protection against retribution for whistle-blowers.
Proactive Fraud Audits
Four steps to identify and investigate fraud risks.
Current Fraud Model
Four stages: incident, investigation, action, resolution.
Fraud
Deceptive act for personal gain.
Positive Tone at the Top
Management's commitment to ethical behavior.
Education and Training
Informing employees about fraud seriousness.
Integrity Risk Assessment
Evaluating potential fraud risks in operations.
Internal Control System
Processes to safeguard assets and ensure accuracy.
Reporting System
Mechanism for reporting suspected fraud incidents.
Monitoring System
Continuous oversight to detect fraud activities.
Proactive Fraud Detection
Methods to identify fraud before it occurs.