Earth and Space Sciences Exam Review
1/124
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Striations
As glaciers grind over the surface bedrock, they leave behind deep scratches in the rock and the scratches record the direction of ice flow in the rock
Examples of igneous rock
Pumice, Granite, Vesicular basalt, Diorite
Seismograph
records intensity/energy of seismic waves to determine the intensity of the earthquake or map out the earth's interior
examples of metamorphic rock
Schist, Marble, Slate, Gneiss
Weathering
the process of decomposing, breaking up, or changing the color of rocks
Erosion
the movement of weathered materials due to natural forces such as wind, water and ice
examples of sedimentary rocks
Limestone, Conglomerate, Siltstone, Sandstone
intrusions
a body of igneous (created under intense heat) rock that has crystallized from molten magma. Ex. dikes, batholiths, and sills.
Dike
a sheet like intrusion that cuts across layering
Batholith
form by multiple intrusions in the same region
Sill
a sheet like intrusion that forms parallel to the country rock
Geologic time scale
The history of the earth divided into eons, eras, periods, and more based on fossil records of animals and plants that lived during earth time period.
Uniformitarianism
the processes that happen in the present are similar to the processes that occurred in the past. Ex. Faulting, Folding, Erosion
P-waves
Fastest seismic waves, traveling at about 6 to 7 km/s, compression and expansion motion, Bend when traveling through different layers, Slow down in the liquid core, creating a shadow zone.
S-waves
Slow, traveling at about 3.5 km/s, perpendicular motion, Can only travel through solids, Disappear at the mantle core boundary.
layers of the earth
core, mantle, crust
Types of plate boundaries
divergent, convergent (subduction or collision), transform.
epochs of Radiation era
plank, GUT, inflationary, electroweak, quark, Hadron, lepton, nuclear
epochs of Matter era
atomic, galactic, stellar
Eras after the Big Bang
Radiation and Matter
Life cycle of a low mass star
nebula, protostar, main sequence star, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, black dwarf
Life cycle of a high mass star
nebula, protostar, main sequence star, super red giant, black hole or neutron star
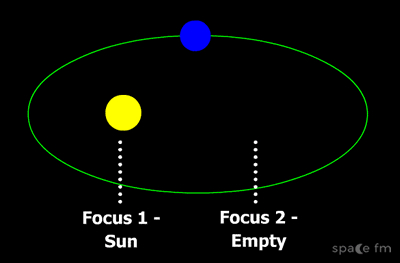
Keplers 1st law of planetary motion
Planets have elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus
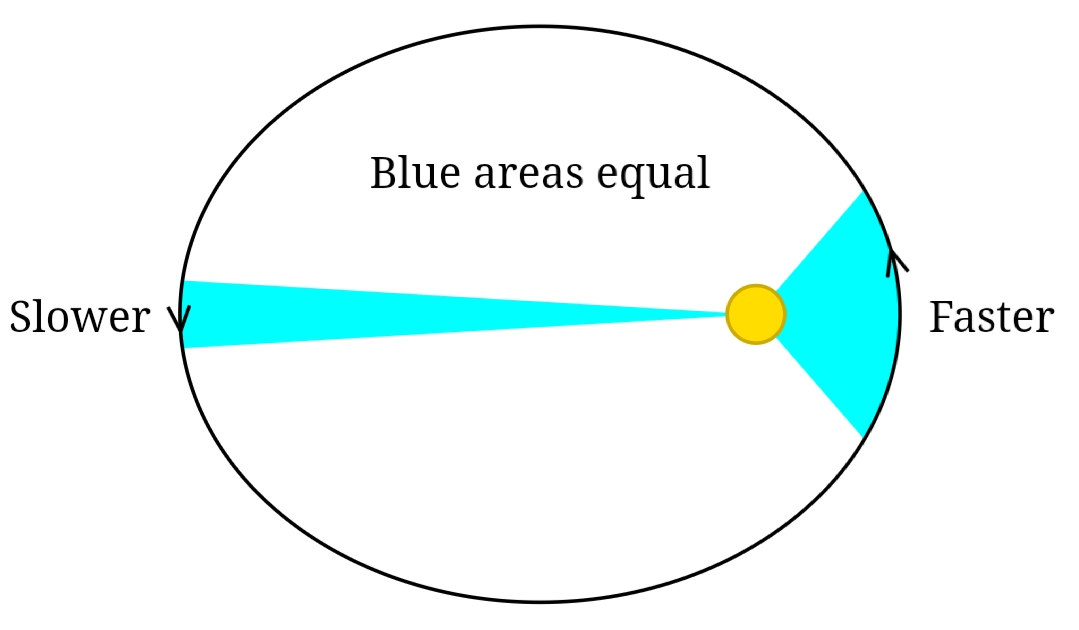
Kepler’s 2nd law of planetary motion
A line drawn between the sun and a planet will sweep out equal areas of space in equal amounts of time. This indicates that planets speed up as they approach the sun.
Kepler’s 3rd law of Planetary Motion
Planets that are closer to the sun have smaller orbits and shorter periods. “The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit”

layers of the sun/solar atmosphere
core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona
Features of Galaxies
bulge, disk, halo
Types of galaxies
spiral (barred spiral or spiral), elliptical, irregular, peculiar, lenticular
Types of plate boundaries
Divergent (mid atlantic ridge), subduction (Mariana islands, western coast of south america), collision (himalayas), transform (san andreas fault)
Layers of the earth
solid metal inner core, liquid metal outer core, liquid lower mantle, liquid upper mantle, solid crust
Continental drift
the gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface through geological time.
The name of Wegener's "supercontinent"
Pangea
Types of volcanoes
Shield Volcanoes (broad bases), Cinder Cones(simple, magma hardens before hitting ground), Composite Volcanoes (layers of material from one vent)
Rift valleys
a large elongated depression with steep walls formed by the downward displacement of a block of the earth's surface between nearly parallel faults or fault systems.
Richter scale
Measures the magnitude of an earthquake based on seismic wave amplitude.
Mercalli scale
Measures the intensity of an earthquake based on its observed effects.
Pangea
The supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras, around 335 million years ago.
Formation of Pangea
about 300 million years ago Gondwana and the small landmasses converged to form Pangea.
destruction of Pangea
Gondwana and Laurasia split off, and eventually split into today's continents.
Chemical Weathering
chemical changes in the minerals of the rock, or on the surface of the rock, that make the rock change its shape or color.
Causes of chemical weathering
Carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, and acids.
Mechanical weathering
the process of breaking a large rock into smaller pieces without changing the minerals in the rock
causes of mechanical weathering
frost, ice, plant roots, running water, or heat from the sun.
Focus
The exact point within the Earth where an earthquake begins
Epicenter
The point on the Earth's surface directly above where an earthquake originates
Hypocenter
Another term for the focus, the point within the Earth where an earthquake originates.
Shadow zone
A region where P-waves do not reach due to their slowdown in the liquid outer core.
ring of fire
a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes around the edge of the pacific ocean including chile, mexico, US, antarctica russia, japan, new zealand, papua new guinea, indonesia, etc.
Laccolith
magma intrusions that cool before reaching the surface, causing a dome shape
Joint
a break in the natural origin of a rock body that has little displacement
Faults
a discontinuity in the natural origin of a rock body that has significant displacement
Drumlins
a low oval mound or small hill, typically one of a group, consisting of compacted boulder clay molded by past glacial action.
Morraines
a mass of rocks and sediment carried down and deposited by a glacier, typically as ridges at its edges or extremity.
Characteristics of minerals
hardness, cleavage, streak, luster, magnetism, fracture
Conchoidal
denoting a type of fracture in a solid (such as flint or quartz) that results in a smooth rounded surface resembling the shape of a scallop shell.
Splintery
liable to produce or break into splinters.
irregular (characteristic of fractures)
stone that is cut to or quarried in different shapes and/or sizes.
Lithosphere
the brittle crust and uppermost mantle
Asthenosphere
a solid but it can flow, like toothpaste. The lithosphere rests on the asthenosphere.
Types of fossils
Original remains, replaced remains, molds and casts, trace fossils, carbonaceous films
replaced remains
Remains are slowly replaced by rock forming minerals molecule by molecule. This occurs in fossil bones, teeth, shells
molds and casts
Plant, leaf or insect is buried in mud or sediments, it's hard body parts become a fossil as the sediments become rock. The fossil later dissolves and leaves mold (a hollow depression), If minerals fill in the mold it forms a cast
trace fossils
Trails, footprints, tracks, burrows, bite marks on trilobites
Carbonaceous films
Remains of animals and plants are affected by temperature and pressure as sediments are deposited. The conditions cause the carbon compounds to chemically change. The carbonizing process results in the thin film of carbon
Plutonic features
Comet composition
core: is mostly made up of ice but has some dust and rock particles
coma: ice sublimates due to solar heat
Gas tail: made of lightweight gasses that often appear blue
Dust tail: made of heavier particles like dust and rock particles
Comet location of origin
The oort cloud
Asteroid Composition
Made of rock and metal, no ice because it formed closer to the sun than comets. Sometimes has organic material.
Asteroid location
Forms closer to the sun, often found on asteroid belts.
Meteoroid composition
fragments of comets, asteroids, or artificial space debris
Meteoroid location
In space
Meteor composition
fragments of comets, asteroids, or artificial space debris.
Meteor location
Anywhere within earth's atmosphere, at a height of around 80-120 km above the surface.
meteorite composition
fragments of comets, asteroids, or artificial space debris
Meteorite location
Earth's surface
Inner layers of the sun
Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone
Outer layers of the sun
Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona.
Features of the sun
Sunspots, prominences, coronal mass ejections, solar flares
Trends of the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram
main sequence stars are more luminous when they are hotter
Red giants are more luminous than main sequence, but cooler
white dwarf stars are less luminous that main sequence, but they can be hotter
blue/white = hot, red=cool
Spiral galaxies
These galaxies have a flat, rotating disk with spiral arms and a central bulge. They often appear as a pinwheel shape.
Central bulge
A dense, spherical region of stars.
Spiral arms
Regions of active star formation and high concentration of stars, gas, and dust.
Halo
A spherical region surrounding the disk, filled with older stars and globular clusters.
Elliptical Galaxies
These galaxies have a spheroidal shape, with no distinct spiral arms or disk. Older, redder stars dominate, with little to no ongoing star formation. Very little gas and dust compared to spiral galaxies.
Irregular galaxies
These galaxies lack a defined shape, unlike spiral or elliptical galaxies.
Lenticular galaxies
These galaxies are intermediate between elliptical and spiral galaxies. They have a central bulge and a flat disk but lack the spiral arms of a spiral galaxy.
Peculiar galaxies
These galaxies do not fit into the traditional categories of spiral, elliptical, or irregular. They have unusual shapes due to interactions with other galaxies.
Eratosthenes
Measured Earth's Circumference
Found earth-moon distance, earth-sun distance
Hipparchus
Believed in pure observation
Examined precise positions of the stars
Unable to detect parallax
Found procession of the equinoxes
Modern Magnitude system (bright=1st dim=6th)
Ptolemy
Last of great astronomers of Alexandria
Hid in library of Serapeum
Created Ptolemaic Model (explained retrograde using epicycle and different)
Bad model (no universal rule, all planets were independant, too complicated)
Copernicus
First heliocentric model of universe (explained retrograde motion)
Orbits were circular :(
Kepler
Tycho's assistant, inherited all positional data
redefined copernicus's model (eliptical orbits)
laws of planetary motion (planets move in elipse around sun)
Galileo
Delivered final blow to geocentric model
Trouble with catholic church (said objects fall at same rate)
Built his own telescope (observed phases of venus, moon mountains, suspots, moons of jupiter, rings of saturn, etc.)
Roman Catholic Church put him in house arrest
Newton
began development of physics and calculus
Laws of motion
in motion = remain in motion, at rest=at rest
F=ma
every action has an equal and opposite reaction
Laws of gravitation (attracting force is proportional to mass, inversely proportional to distance apart)
North star
polaris, located in ursa minor, northern hemisphere, always above the horizon
Evidence of the big bang
Galaxies are moving farther apart, therefore they were close together before
Element ashes observed are proportional to the predictions using the Big Bang model
CMB, heat and light detected from the first stages of the universe
Law of superposition
within an undisturbed sequence of layers of sedimentary rock, the oldest layer is at the base and that the layers are progressively younger with ascending order in the sequence.
The Hadean Eon
began with the formation of the first rocks on Earth and ended 4 billion years ago. This eon was a time of massive volcanic activity and frequent collisions with asteroids, leading to rapid changes of the planet’s surface.
The Archean Eon
began 4 billion years ago and ended 2.5 billion years ago. During this time, the first areas of continental crust appeared and began coalescing into larger landmasses. These continental cores are known as cratons or shields. Collisions with objects from space and volcanic activity decreased. Life first appeared on Earth during this Eon. The earliest types of fossils to be found in any quantity are traces of microbial mats. A mat of aquatic microbes would trap sediment, and the microbes would grow over the sediment, producing a layered structure. Stromatolites are one well-known type of microbial mat fossil.
Proterozoic Eon
the most recent division of the Precambrian. It is also the longest geologic eon, beginning 2.5 billion years ago and ending 541 million years ago