Chapter 15 - Practice Questions (POOL)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
An increase in blood pressure would be sensed by either the aortic or carotid (Click to select) chemoreceptors baroreceptors thermoreceptors . The reflex response would be a(n) (Click to select) increase decrease in sympathetic signals and a(n) (Click to select) decrease increase in parasympathetic signals.
baroreceptors
decrease
increase
The changes in the signals to the heart would cause a(n) (Click to select) decrease increase in the heart rate and a(n) (Click to select) decrease increase in the stroke volume. These two changes would result in a(n) (Click to select) decrease increase in cardiac output, and thus a return of blood pressure to normal limits.
decrease
decrease
decrease
At the same time, there would be a(n) (Click to select) decrease increase in sympathetic signals to the blood vessels, resulting in (Click to select) vasoconstriction vasodilation . The change in blood vessel diameter would cause a(n) (Click to select) decrease increase in the peripheral resistance and a subsequent decrease in blood pressure back to normal limits.
decrease
vasodilation
decrease
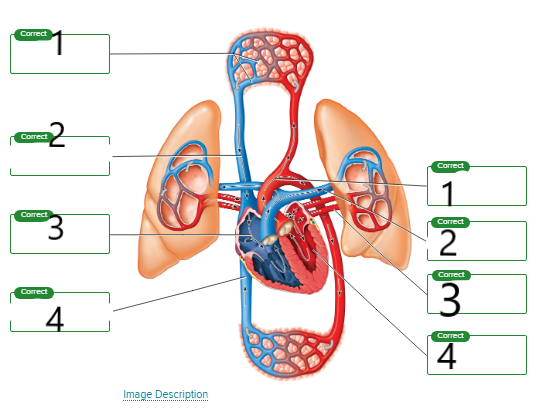
label the image
Left
systemic capillaries
superior vena cava
right atrium
inferior vena cava
Right
aorta
pulmonary artery
pulmonary vein
left ventricle
What valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Multiple Choice
Aortic valve
Tricuspid valve
Pulmonary valve
Bicuspid valve
Tricuspid valve
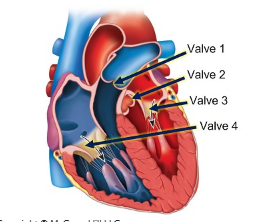
Identify the functions of each of the four valves of the heart indicated in the figure.
prevents backflow of blood from the systemic circuit
prevents backflow of blood to the left atrium
prevents backflow of flood to the right atrium
prevents backflow from the pulmonary circuit
valve 2
valve 3
valve 4
valve 1
After entering the right atrium, the furthest a red blood cell can travel before reaching the right atrium again is the __________Blank.
Multiple Choice
ascending aorta
inferior vena cava
left atrium
pulmonary trunk
inferior vena cava
Name the innermost layer of an artery wall.
Multiple Choice
Vasa vasorum
Tunica media
Endothelium
Tunica externa
Endothelium
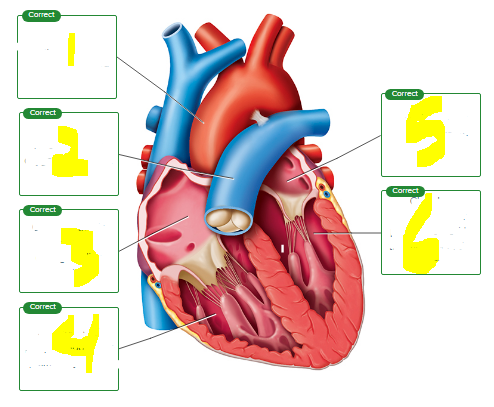
Drag the labels to the location of the structure being described.
chamber that pumps blood to the pulmonary circuit
vein carrying oxygen poor blood
artery carrying oxygen rich blood
chamber that is first to depolarize during cardiac cycle
first chamber to receive oxygen-rich blood
artery carrying oxygen poor blood
chamber responsible for pumping blood to the majority of the body
vein carrying oxygen-rich blood
artery carrying oxygen rich blood
artery carrying oxygen poor blood
chamber that is first to depolarize during cardiac cycle
chamber that pumps blood to the pulmonary circuit
first chamber to receive oxygen-rich blood
chamber responsible for pumping blood to the majority of the body
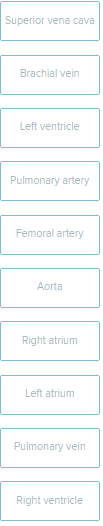
Place the following cardiovascular structures in the appropriate category indicating whether they carry oxygen-rich or oxygen-poor blood.
carries oxygen poor
superior vena cava
brachial vein
pulmonary artery
right atrium
right ventricle
carries oxygen rich blood
left ventricle
femoral artery
aorta
left atrium
pulmonary vein
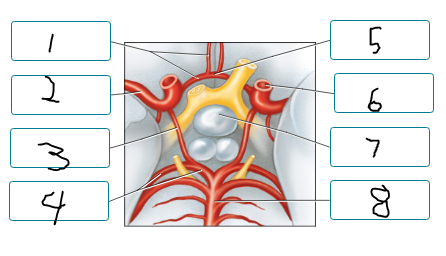
Label the arteries of the cerebral arterial circle and nearby structures.
anterior cerebral a.
middle cerebral a.
posterior communicating a.
posterior cerebral a.
anterior communicating a.
internal carotid a.
pituitary gland
basilar a.
What site is commonly used to feel a pulse?
Multiple Choice
Aorta in the chest
Internal jugular vein in the neck
Radial artery on the wrist
Subclavian artery in the neck
Radial artery on the wrist
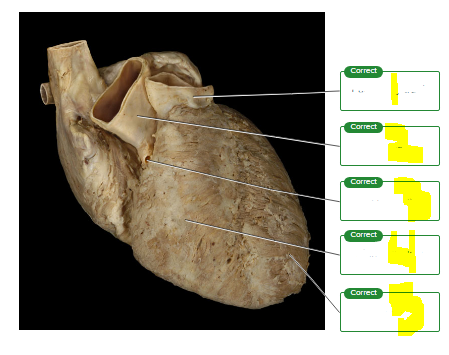
Label the features of the heart seen on the external surface.
pulmonary trunk
aorta
right coronary
right ventricle
left ventricle
Arterial blood pressure can be changed by several factors. The (Click to select) cardiac output peripheral resistance blood volume blood viscosity is the combined amount of formed elements and plasma in the vessels. If this increases, blood pressure will (Click to select) decrease increase .
blood volume
increase
The friction between the blood and the vessel walls creates a force called (Click to select) blood volume preload blood viscosity peripheral resistance . One major component of this force is the diameter of blood vessels. If vessels constrict, the result is an (Click to select) decrease increase in resistance and (Click to select) decrease increase in blood pressure.
peripheral resistance
increase
increase
The inherent resistance to blood flow is called (Click to select) blood viscosity peripheral resistance blood volume preload . A major determining factor is the amount of blood cells relative to the water volume in blood. If blood cell counts increase, blood pressure will (Click to select) decrease increase to help push the thicker blood.
blood viscosity
increase
explanation: Arterial blood pressure is dependent on the heart (cardiac output), the blood (viscosity), and the blood vessels (diameter/resistance).
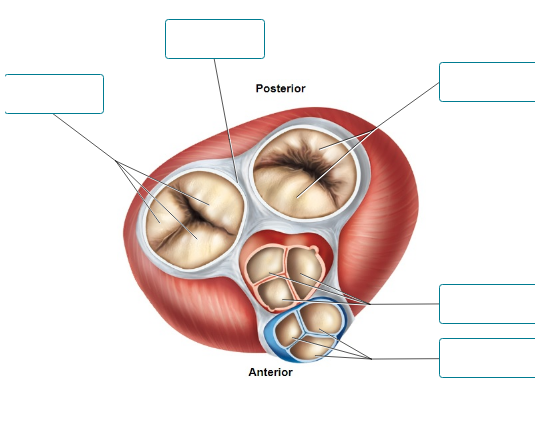
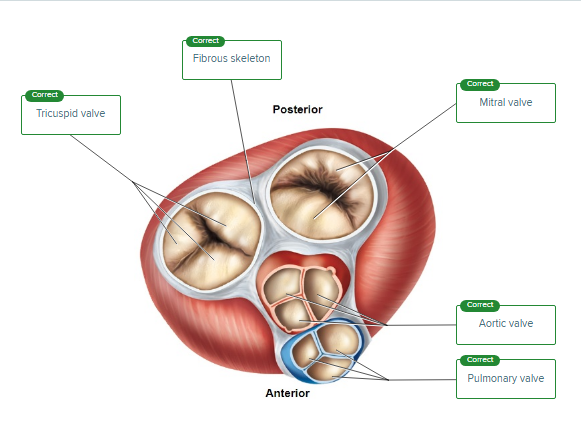
This image is a superior view of a transverse section of the heart. Label the structures shown.
Label the structures of the capillary bed.
precapillary sphincter
arteriole
artery
capillary
vein
venule
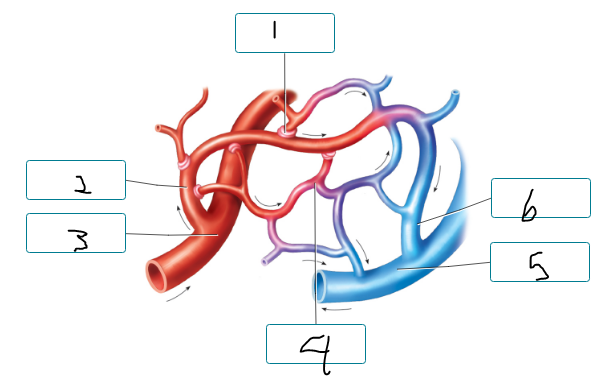
Indicate whether each structure is part of the systemic circuit or the pulmonary circuit.
systemic: vc, femoral arteries, carotid arteries, aorta
pulmonary: the rest
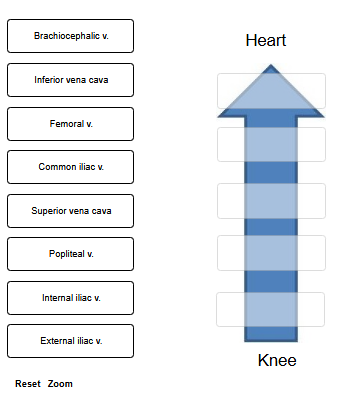
Using the terms provided, trace a drop of blood from the posterior side of the knee back to the heart.
Not all labels will be used.
heart
inferior vena cava
common iliac v.
external iliac v.
femoral v.
popliteal v.
knee
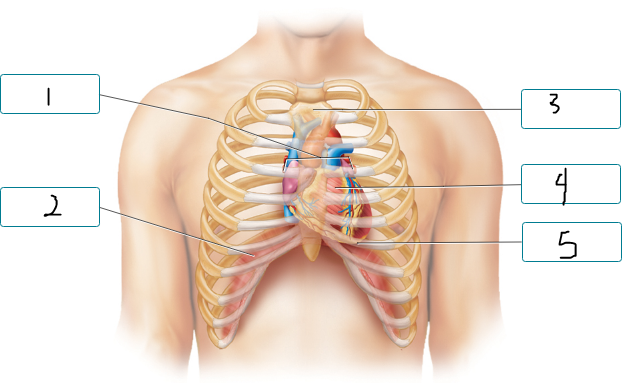
Label the figure indicating the location of the heart and other structures.
base of heart
diaphragm
sternum
heart
apex of heart
The outer layer of the pericardium is called the (Click to select) epicardium fibrous pericardium parietal pericardium visceral pericardium and is composed of dense connective tissue.
The (Click to select) epicardium fibrous pericardium parietal pericardium visceral pericardium lines the previous layer and secretes (Click to select) blood mucus plasma serous fluid .
The fluid is contained within the (Click to select) heart chambers myocardial interstitial space pericardial cavity thoracic cavity .
Covering the outer surface of the wall of the heart is the (Click to select) visceral pericardium parietal pericardium fibrous pericardium , which is also called the (Click to select) myocardium epicardium endocardium .
fibrous pericardium
parietal pericardium, serous fluid
pericardial cavity
visceral pericardium, epicardium
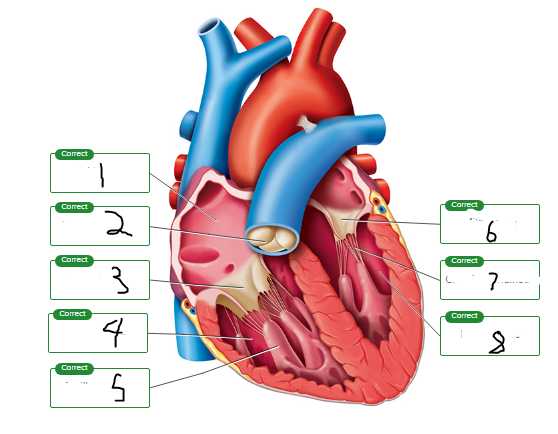
Label the chambers and valves seen in a frontal section of the heart.
right atrium
pulmonary valve
tricuspid valve
right ventricle
papillary muscle
mitral valve
chordae tendineae
left ventricle
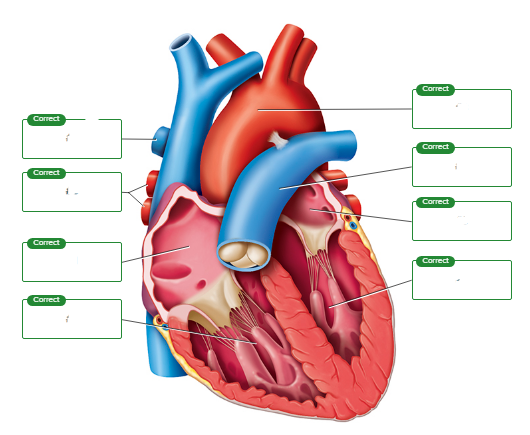
Correctly sequence the pathway of blood flow through the heart, starting with #1 as blood enters the heart from the venae cavae. (Note that the lungs are not a numbered structure in this sequence.)
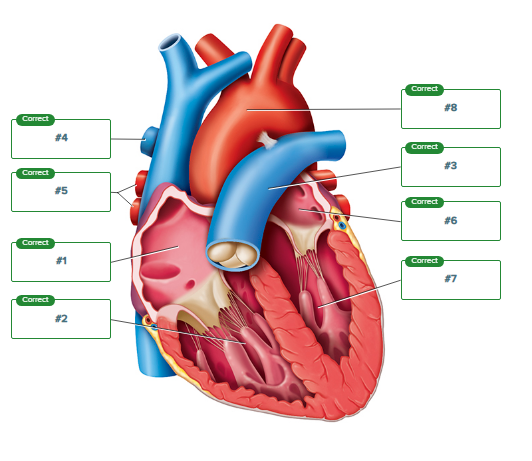
What is the function of chordae tendineae?
Multiple Choice
Carry electrical signals through the ventricular myocardium
Open the AV valves during atrial contraction
Prevent the cusps of the AV valves from moving up into the atria
Generate force to push blood through the heart
Prevent the cusps of the AV valves from moving up into the atria
explanation: The chordae tendineae run between the papillary muscles and AV valves. The chordae tendineae are pulled taut when the papillary muscles in the ventricle contract.
The myocardium of the heart receives blood through the coronary vessels, which are branches off of the (Click to select) aorta coronary sinus right atrium superior vena cava .
aorta
The (Click to select) right coronary left coronary artery is found between the right atrium and right ventricle. This artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle as well as the posterior side of the left ventricle.
right coronary
The (Click to select) left coronary right coronary artery is relatively short, and divides into two major arteries. These arteries supply the anterior walls of both ventricles and the walls of the left atrium.
left coronary
All the myocardial capillaries drain into cardiac veins, which in turn drain into a large (Click to select) coronary sinus left atrium posterior interventricular vein right atrium found on the (Click to select) anterior posterior surface of the heart. This enlarged vein empties into the (Click to select) left atrium right atrium inferior vena cava superior vena cava of the heart.
coronary sinus
posterior
right atrium
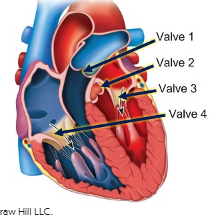
For each of the four valves of the heart labeled in the figure, indicate the names that are used.
tricuspid valve
left atrioventricular valve
right semilunar valve
right atrioventricular valve
bicuspid valve
aortic valve
pulmonary valve
left semilunar valve

Swelling of the hand could be caused by a thrombosis (blood clot) in the __________Blank vein.
Multiple Choice
dorsal pedal
internal jugular
brachial
popliteal
brachial
explanation:
A thrombosis is a blood clot that can prevent the flow of blood in a vessel. As a result, blood would backup in previous vessels and structures that were drained by those vessels.
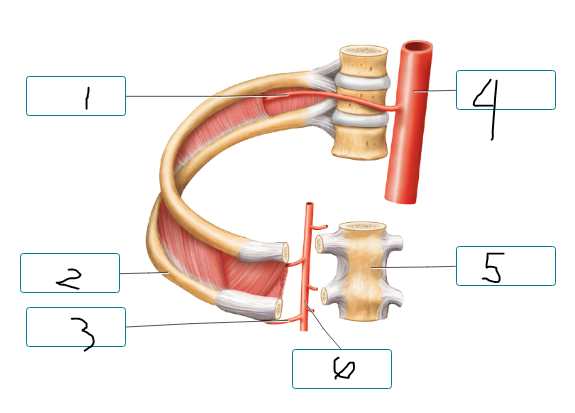
Label the arteries of the thoracic wall and nearby structures.
posterior intercostal a.
rib
anterior intercostal a.
thoracic aorta
sternum
internal thoracic a.
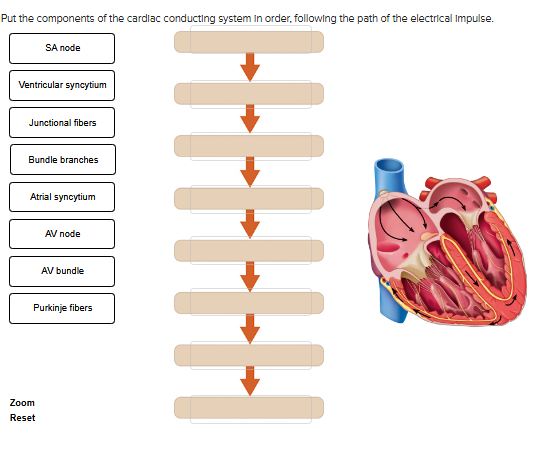
Put the components of the cardiac conducting system in order, following the path of the electrical impulse.
SA node
atrial syncytium
junctional fibers
av node
av bundle
bundle branches
purkinje fibers
ventricular syncytium
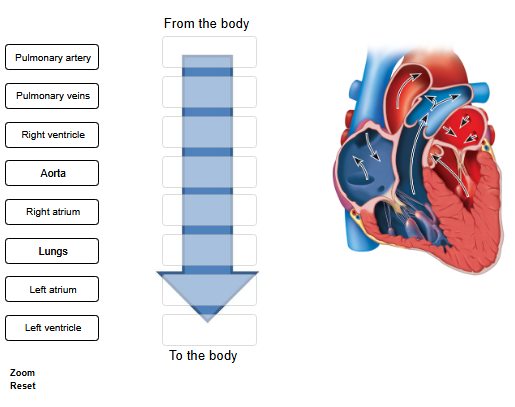
Place the following structures in order through which the blood flows.
right atrium
right ventricle
pulmonary artery
lungs
pulmonary veins
left atrium
left ventricle
aorta
Complete the sentences, tracing a drop of blood from the heart to the left thumb.
The blood leaves the heart through the (Click to select) aorta brachiocephalic trunk common carotid a. subclavian a. .
The (Click to select) first second third branch off the aorta takes blood to the left arm and is called the (Click to select) axillary a. brachiocephalic trunk common carotid a. subclavian a. .
Next, blood flows through the (Click to select) axillary a. brachial a. brachiocephalic trunk subclavian a. , located anterior to the scapula.
In the medial side of the arm, the artery continues as the (Click to select) axillary a. brachial a. radial a. ulnar a. .
Blood going to the thumb would then travel through the (Click to select) brachial a. popliteal a. radial a. ulnar a. in the lateral side of the forearm.
aorta
third, subclavian a.
axillary a.
brachial a.
radial a.
Complete the sentences with the appropriate artery name, tracing a drop of blood from the heart to the sole of the foot.
The blood leaves the heart through the (Click to select) aorta brachial a. brachiocephalic a. femoral a. .
Once in the lower abdomen, the aorta branches into a right and left (Click to select) common iliac a. external iliac a. femoral a. subclavian a. .
These arteries then branch, and blood going to the leg travels through the (Click to select) internal iliac a. external iliac a. to the lower limb.
Next, blood flows into the (Click to select) external iliac a. femoral a. internal iliac a. popliteal a. , which is found in the medial thigh.
This artery becomes the (Click to select) anterior tibial a. deep femoral a. external iliac a. popliteal a. , which is located in the posterior knee region.
The artery then branches. Blood traveling to the sole of the foot would travel in the (Click to select) anterior tibial a. deep palmar arch dorsalis pedis a. posterior tibial a. .
aorta
common iliac a.
external iliac a.
femoral a.
popliteal a.
posterior tibial
The __________Blank ventricle pumps blood to the pulmonary circuit, while the __________Blank ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circuit.
Multiple Choice
left; right
right; left
right; left
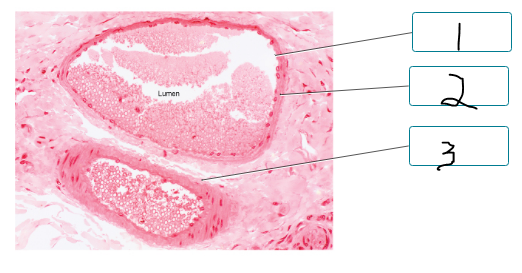
Label the components of the walls of the artery and vein.
endothelium of tunica interna
tunica media
tunica externa
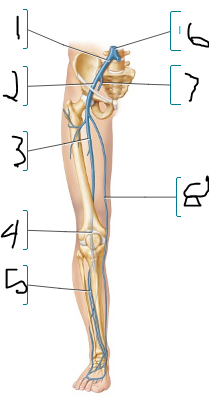
common iliac v
external iliac vein
femoral
popliteal
anterior tibial
inferior vena cava
internal iliac
great saphenous v

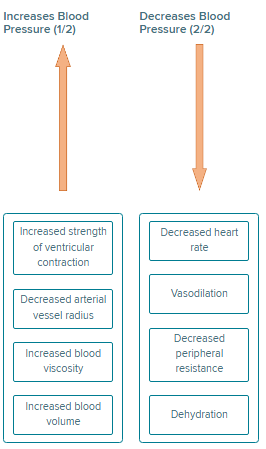
Indicate whether each condition would increase or decrease arterial blood pressure, if all other factors remaining unchanged.
Explanation: Arterial blood pressure is the force of blood against arterial walls. It is created by ventricular contraction. Its value depends on a variety of factors. Blood pressure drives blood flow through the body from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
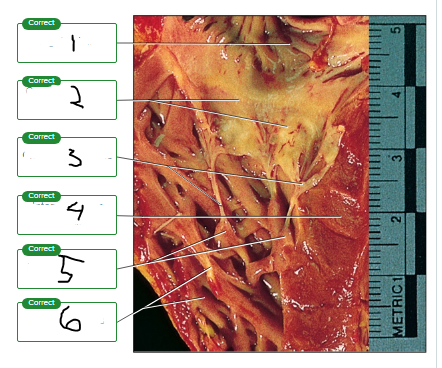
Label the photograph of the tricuspid valve.
right atrium
cusps of tricuspid valve
chordae tendineae
interventricular septum
papillary muscles
muscle ridges
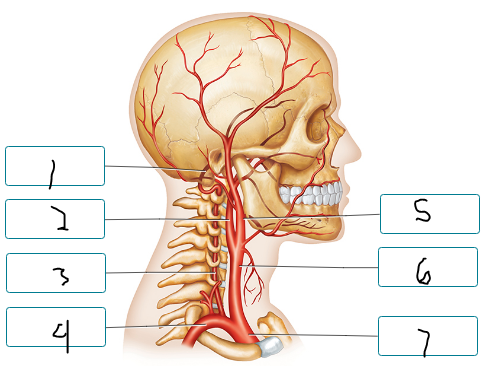
Label the arteries of the head and neck.
basilar a.
internal carotid a.
vertebral a.
subclavian a.
external carotid a.
common carotid a.
brachiocephalic trunk
Complete the following sentences describing the location of the heart.
|
thoracic cavity
lungs, vertebral column, sternum
base
apex, fifth
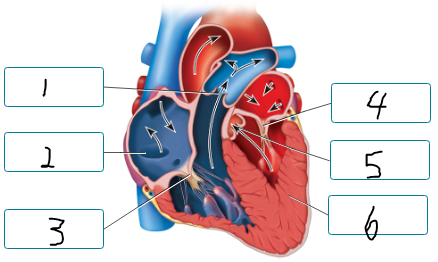
The figure illustrates the heart during ventricular systole and atrial diastole. Label the positioning of the valve cusps during this phase of the cardiac cycle.
pulmonary valve open
atrium in diastole
tricuspid valve closed
mitral valve closed
aortic valve open
ventricle in systole
explanation: When ventricular pressure exceeds arterial pressure during ventricular systole, the semilunar valves open allowing blood to flow from the ventricles into arteries.
The left ventricle pushes blood into what vessel(s)?
Multiple Choice
Pulmonary veins
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Venae cavae
aorta
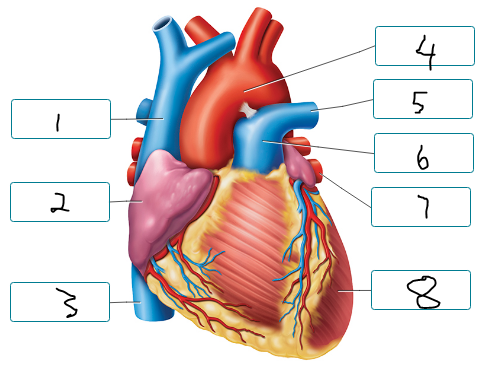
Label the structures seen in an anterior view of the heart.
superior vena cava
right atrium
inferior vena cava
aorta
pulmonary artery
pulmonary trunk
pulmonary vein
left ventricle
A rise in blood pressure detected by baroreceptors would result in a(n) __________Blank in heart rate due to __________Blank stimulation.
Multiple Choice
decrease; sympathetic
increase; sympathetic
increase; parasympathetic
decrease; parasympathetic
decrease; parasympathetic
Complete the following sentences about the functioning of the valves.
|
right, left, atrioventricular valve
chordae tendineae, papillary muscles
contract, taut
prevent the valves from pushing up into the aorta
Which equation states the relationship between blood pressure (BP), peripheral resistance (PR), and cardiac output (CO)?
Multiple Choice
CO = PR x BP
CO = PR / BP
BP = CO / PR
BP = CO x PR
BP = CO x PR
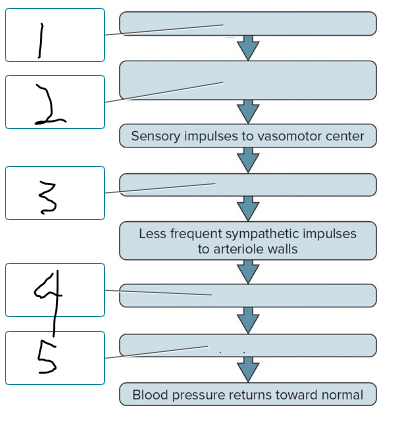
This flow diagram shows the result of stimulation of the baroreceptor reflex in response to an increase in blood pressure. Place the labels in the correct order.
rising blood pressure
stimulation of baroreceptors
vasomotor center inhibited
vasodilation of arterioles
decreased peripheral resistance
What abdominal blood vessel is indicated in the figure?
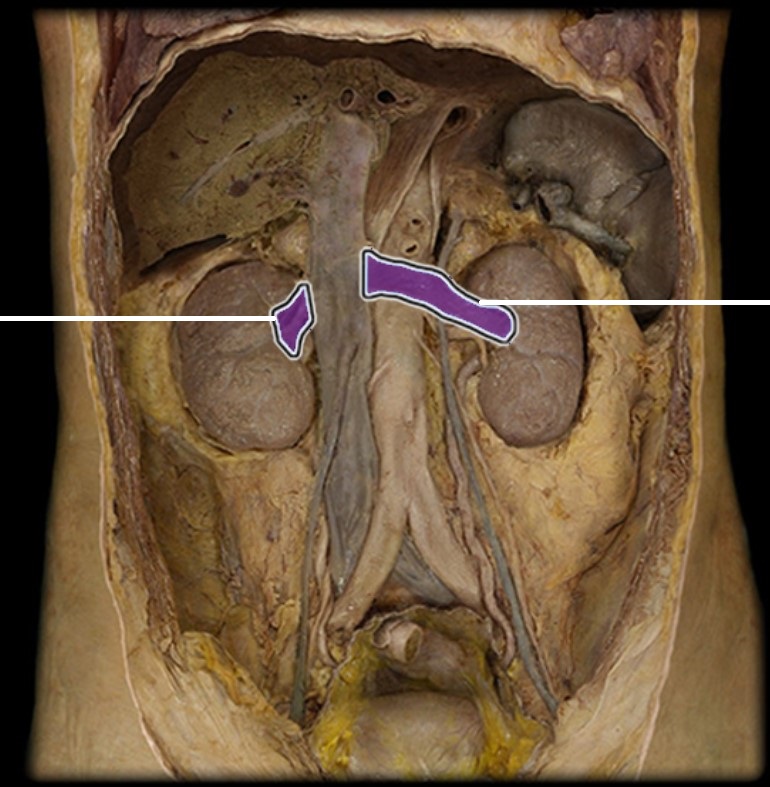
Multiple Choice
Abdominal aorta
Splenic artery
Superior mesenteric artery
Renal artery
Renal artery
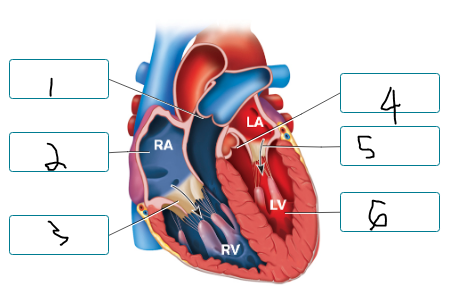
This figure illustrates the heart during ventricular diastole and atrial systole. Label the positioning of the valve cusps during this phase of the cardiac cycle.
pulmonary valve closed
atrium in systole
tricuspid valve open
aortic valve closed
mitral valve open
ventricle diastole
Identify the three vessels that branch off of the aortic arch.
Check All That Apply
Pulmonary trunk
Brachiocephalic artery
Internal jugular vein
Common carotid artery
Subclavian artery
Coronary artery
Brachiocephalic artery
Common carotid artery
Subclavian artery
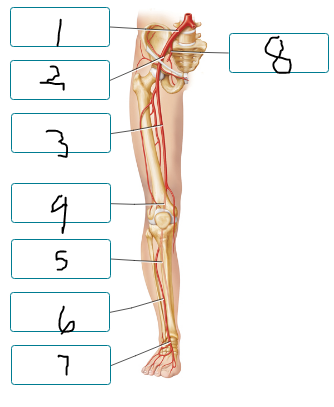
Label the arteries of the lower limb, as seen in the anterior view.
common iliac a
external iliac a
femoral a
popliteal a
posterior tibial a
anterior tibial a
dorsalis pedis a
Complete each sentence describing blood pressure and its measurement.
|
systolic blood pressure
diastolic blood pressure
sphygmomanometer
mmHg
systolic blood pressure
diastolic blood pressure
true or false: If all nerves from the central nervous system to the heart were severed, the heart would stop beating.
false
explanation:
The heart generates its own electrical impulses via the SA node. It does not need innervation from the nervous system to beat. In fact, the heart would beat at a higher frequency if the nerves were severed because the vagus nerves act to slow the heart rate down.
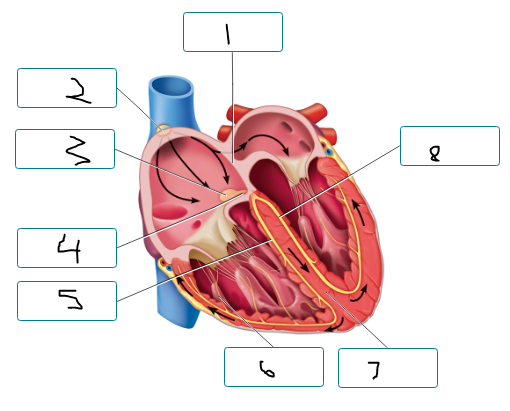
Label the components of the cardiac conduction system.
interatrial septum
SA node
av node
av bundle
right bundle branch
purkinje fiber
interventricular septum
left bundle branch