developmental trauma
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what is trauma?
result of overwhelming stress that exceeds one’s ability to cope
or overwhelms person resources
usually, there is enough space to absorb extra stressors
without basic needs, people cannot feel safe
true
without basic needs, the threat system stays activated
what do safe attachments allow us to do?
learn about ourselves
emotional regulation
template for healthy relationships
conflict resolution
what does scaffolding allow us to do?
challenging prior learning in a safe and guided way
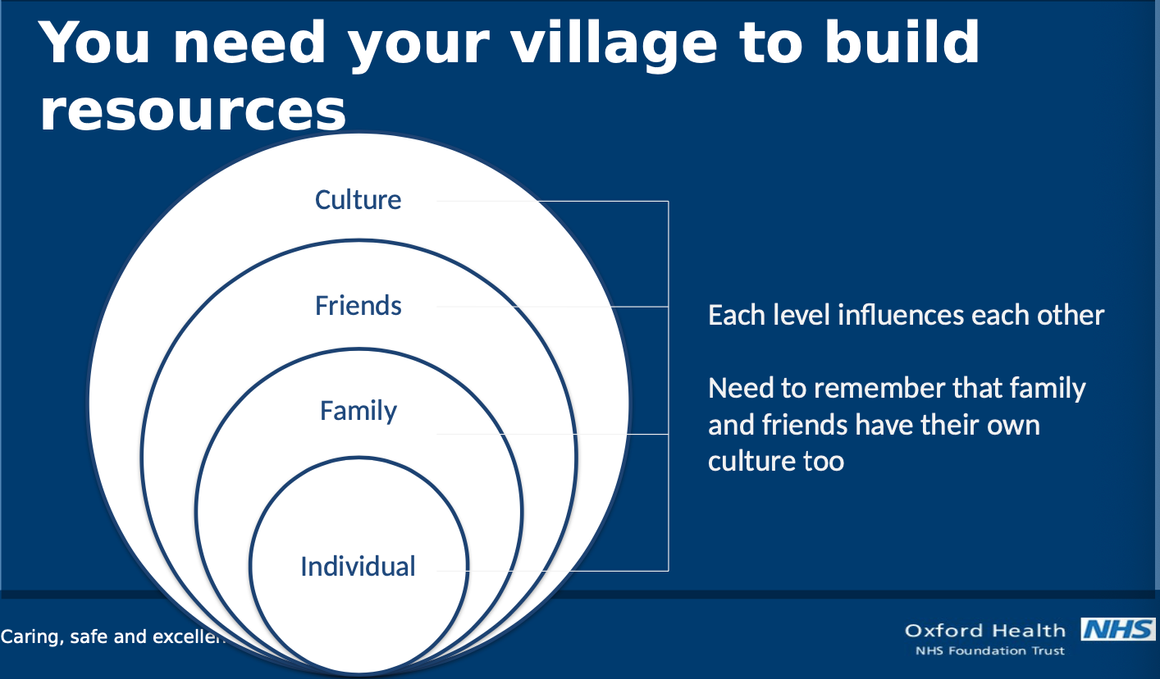
there are multiple levels to build social resources
true
individual, family, friends, and culture
each level influences each other
need to remember that family and friends have their own culture too
during adolescence, you start learning about the needs of other people (mentalising) and understanding risks as well as adult
true
starting to learn about the needs of other people: mentalising
understanding and evaluating risks as well as adults
what are the frontal lobes implicated in?
planning
attention
concentration
impulse control
organisation
mental flexibility
judgement
novel problem solving
what is the brain structure that is most sensitive during adolescence?
frontal lobes
what is mentalising?
ability to understand that others have thoughts and feelings that are different to our own
why is attachment important?
attachments early in life are how we develop an understanding of how to be in this world
attachment during our teenage years is the same to early childhood
false
attachments during teenage years is different to early childhood
there is individuation from the home and peer social life
experimentation in peer, non-home groups
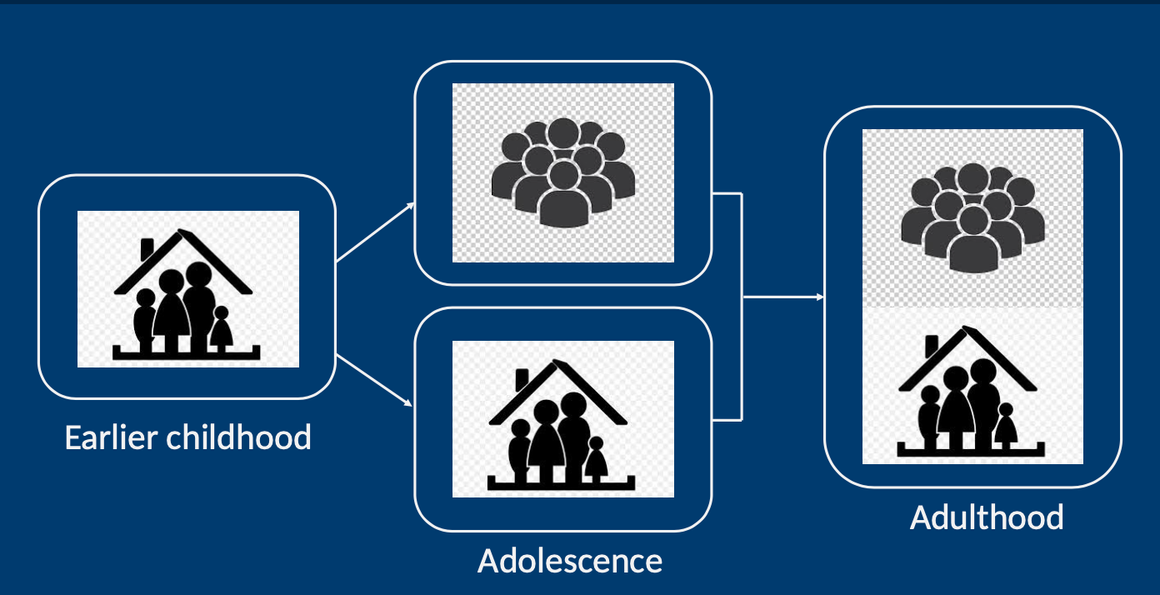
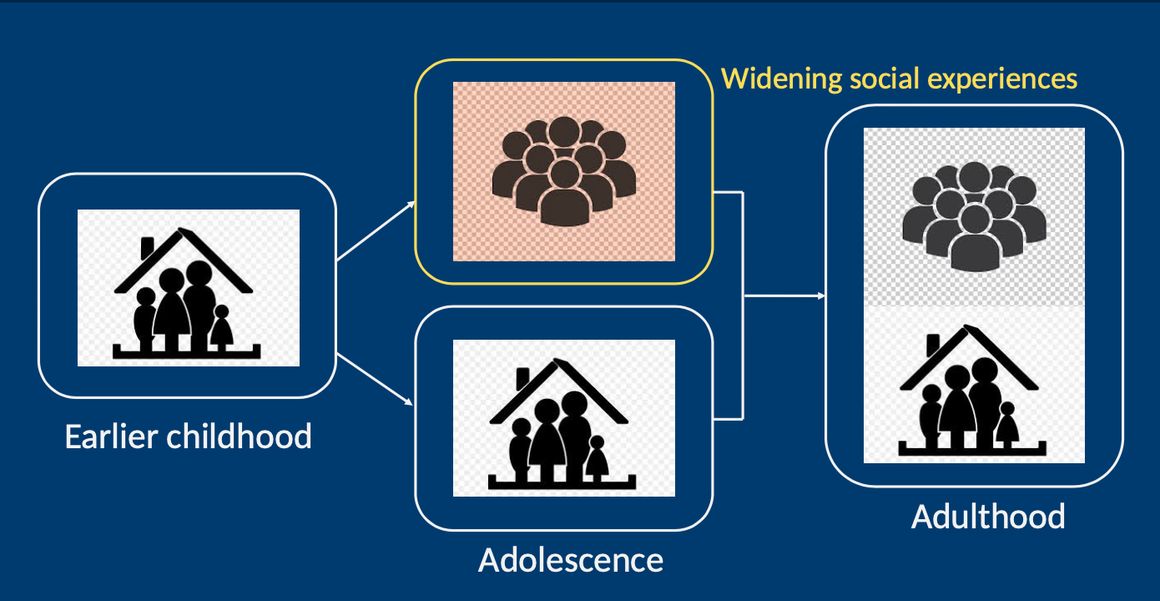
what attachment changes occur from teenagehood to adulthood?
during teen years, there is a widening of social experiences
by adulthood, we come to a core sense of self that is more or less consistent between the home and outer social life
social connections are key to mental wellbeing
true
social connections, quality in particular, is related to mental wellbeing
may buffer negative impacts of stressful events
what biopsychosocial factors are affected by trauma?
biochemistry
the individual’s psychology
social context
environmental context
trauma has impact on a biopsychosocial level
true
also has an effect on who you end up associating with: social and environmental
what parts of the brain reduces in activity during threat?
prefronal cortex: thinking part of the brain
hippocampus: sorts through facts
what parts of the brain increases in activity during threat?
the amygdala acts as the alarm system and becomes more activated during threat
what are forms of ACEs?
maltreatment
violence and coercion
adjustment
prejudice
household or family adversity
inhumane treatment
adult responsibilities
bereavement and survivorship
those with 4+ ACEs experience a myriad of health-harming behaviours, poorer mental and physical health outcomes in adulthood compared to those without
true
2x more likely to binge drink and have a poor diet
3x more likely to be a current smoker
4x more likely to have low levels of mental wellbeing and life satisfaction
5x more likely to have had underage sex
6x more likely to have an unplanned pregnancy
7x more likely to have been involved in violence
11x more likely to have used illicit drugs
11x more likely to have been incarcerated
all individuals with 4+ ACEs will suffer detrimental impacts in adulthood
false
on a population level, the more things you go through, the more impact you experience
however on an individual level, some may fare much better: individuals work differently from populations
shame is a form of internal threat
true
activates our threat system from the inside
fear that the worst thing about ourselves will be revealed and no one would want to know us
stems from the threat of potential rejection from others
what is the window of tolerance?
a window in which we are able to cognitively and emotionally engage with what is going on around us
cortisol and adrenaline limits this window → only threat processing becomes available (amygdala)
hypoarousal shuts down thinking and fact sorting (PFC and hippocampus)
what are the 5 main responses to threat?
fight
appease (friend)
flight/flee
freeze
flop
there is a dose-response effect of trauma
true
the more trauma, the more the impact it has on your development
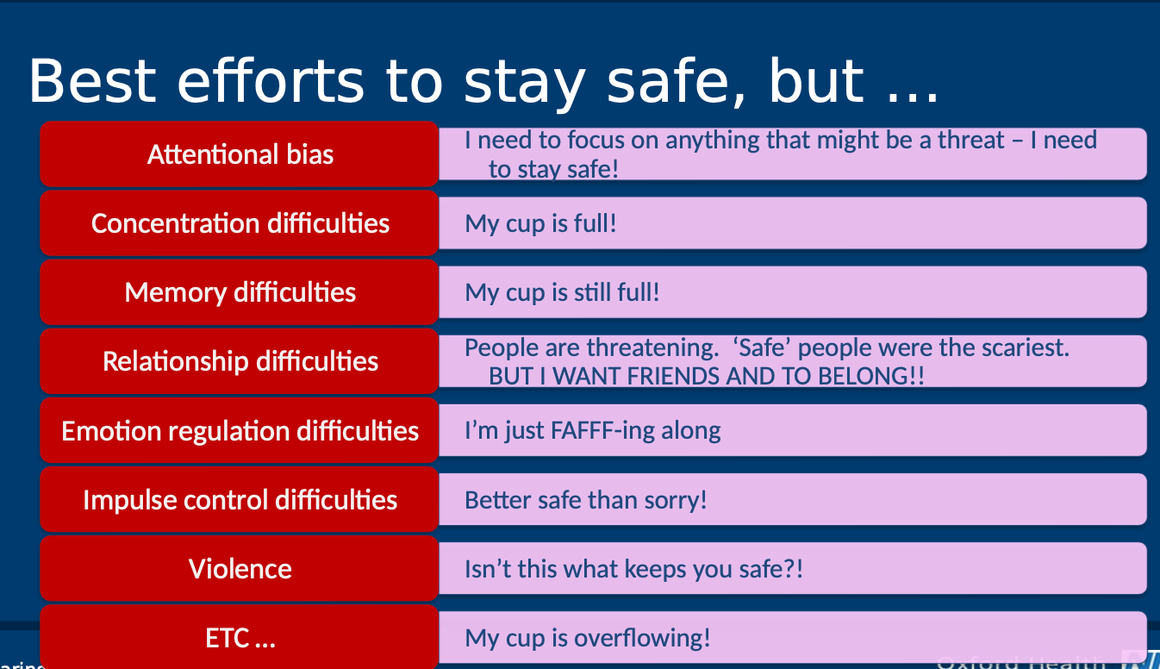
what are some ways in which a small window of tolerance can impact your cognition and behaviour?
attentional bias toward threat
concentration difficulties
memory difficulties
relationship difficulties: people are scary, even safe people
emotional regulation difficulties: using FAFFF
impulse control difficulties: better safe than sorry
how do breakdown of resources occur in developmental trauma?
loss of healthy attachment →
fewer opportunities to learn emotional and social competencies →
lack perceived support from the community →
fewer resources to overcome adversity
a loss of healthy attachment leads to a loss of social competence
true
after a loss of healthy attachment, there are fewer opportunities to learn emotional and social competencies
fewer emotional and social competence can lead to compensation by developing adaptive coping strategies
false
fewer emotional and social competence can lead to lack of perceived support (differences in what they feel is true support vs. the support they are getting)
lack of perceived support from the community leads to fewer resources to overcome adversity
true
loss of healthy attachment leads to a cycle as losing perceived support and resources to overcome adversity
a sense of safety can be established even when threat responses predominate
false
there is no sense of safety when threat responses predominate
every experience can shape our psychology
true
every new experience creates new connections in the brain
repeated experineces strenghten the connections
unused connections disappear if not used
what effect does childhood trauma have on the threat system?
hypervigilance or excessive avoidance
what effect does childhood trauma have on the reward system?
less sensitive to rewards over time
what effect does childhood trauma have on the memory system?
lots of negative memories
over-generalisation of negative memories → positive ones get pushed out
why is early intervention important for preventing negative outcomes of developmental trauma?
earlier or multiple traumas have a larger impact on our life course compared to later or single event traumas
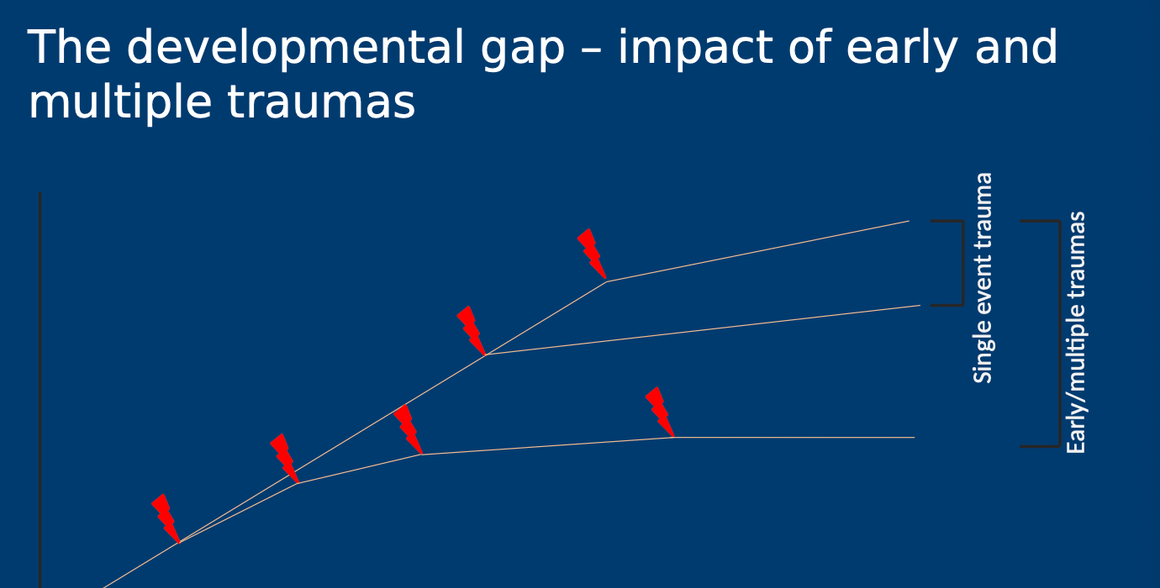
latent vulnerability
neurocognitive and biological systems adapt to early adverse environments that are adaptive in the short term but increases risk of poor outcomes in the future
what impacts do perceived lack of support from others and fewer personal resources to overcome adversity?
learning negative things about ourselves
negative impacts on relationships
perceived future looks bleak
adversity is common, but becomes traumatic if we feel like we are alone
true
perceived lack of social support leads to lowered resouces to cope with effects of early life adversity
how should one approach treating developmental trauma?
feeling of safety is central to treatment of trauma
bringing into balance threat, safety, and drive
understanding what increases sense of safety and decreases sense of threat
trauma informed care has roots in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
true
it is important to establish basic needs before moving onto higher order needs
how should stabilisation be approached in developmentally traumatised individuals?
work with multiagency colleagues
aim to increase external and internal safeties
how should addressing distress be approached in developmentally traumatised individuals?
bringing in evidence or practice-based evidence to work with psychological distress
how should moving forward be approached in developmentally traumatised individuals?
asking how would you like to live your life if you weren’t ruled by fear
it is important to think about who is contributing to the sense of threat and safety outside of the individual
true
it is also important to consider how family, friends and the wider culture contribute to an individual’s sense of threat and safety
the sense of threat and safety is impacted by not only the individual’s cognitions and feelings, but also the influences from the environment
if the person is not safe enough, you must swiftly provide support through someone the YP already trusts and direct intervention
false
you must establish safety first before moving onto any intervention
if the person is safe enough, move to support the YP through someone they trust and/or directly intervene via TFT and resilience building
true
if the person is safe enough, you must move to support the individual using support networks and direct interventions