Lesson 4 BSC2085 LAB
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Axial Skeleton
Composed of three main parts: Skull, Vertebral column, and Bony Thorax.
Cranium
The upper part of the skull that houses the brain.
Two major areas of Cranium
- cranial vault
- cranial floor
Cranial Vault
The superior, lateral, and posterior walls of the skull.
Cranial Floor
Contains three concavities: anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae.
Fossae
The plural of fossa, referring to the concave depressions in the cranial floor.
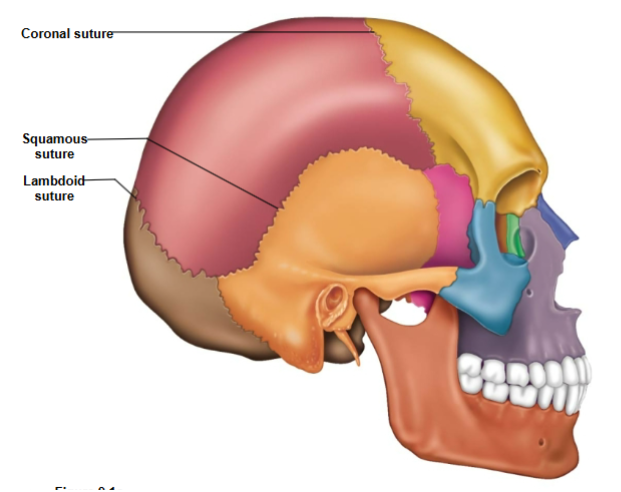
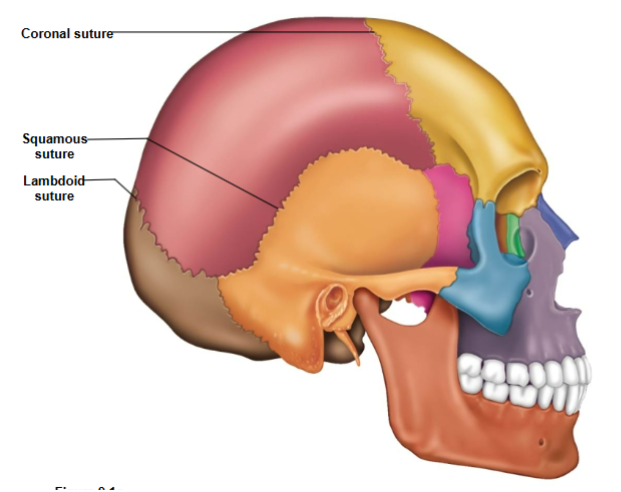
Coronal Suture
Connects the frontal bone to the parietal bone.
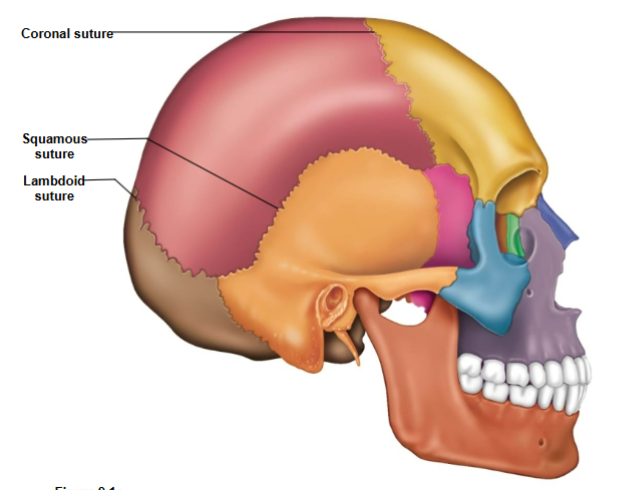
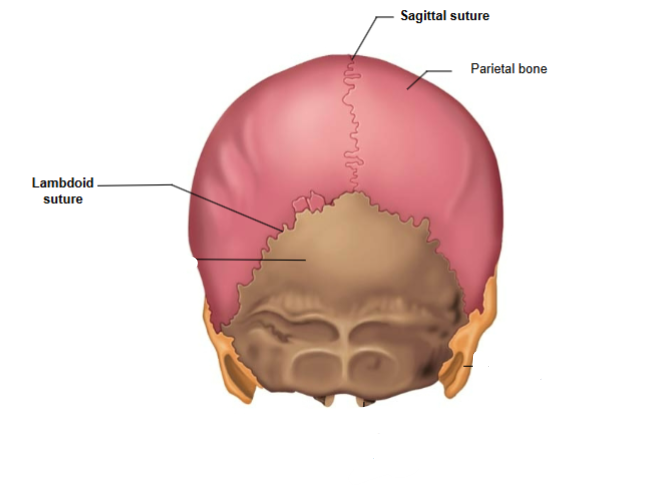
Lambdoid Suture
Connects the parietal bone to the occipital bone.
Sagittal Suture
Connects the left and right parietal bones.
Squamous Suture
Connects the parietal bone to the temporal bone.
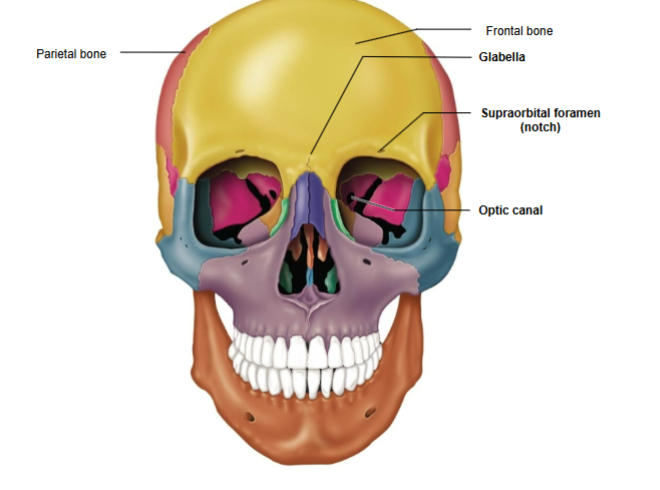
Frontal Bone
The bone forming the forehead and upper part of the eye sockets.
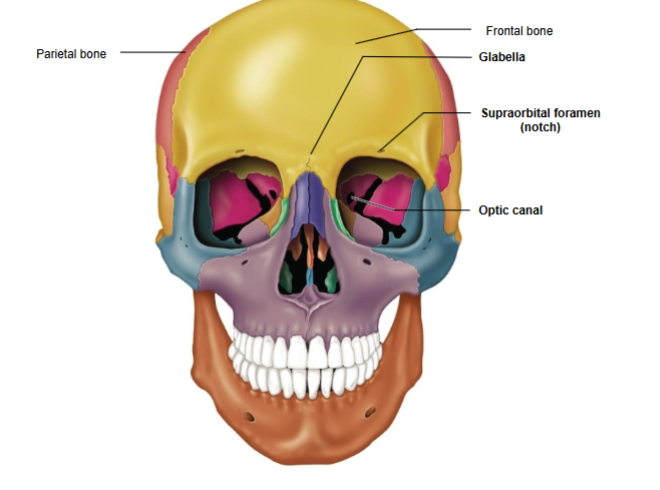
Frontal bone components
Glabella and Supraorbital foramen (notch)
Glabella
Located between the orbital cavities.
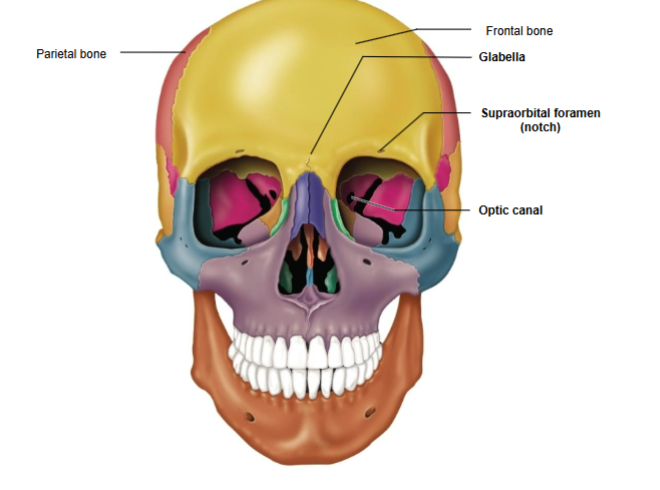
Supraorbital Foramen (Notch)
Opening above each orbit, serving as a passageway for blood vessels and nerves.
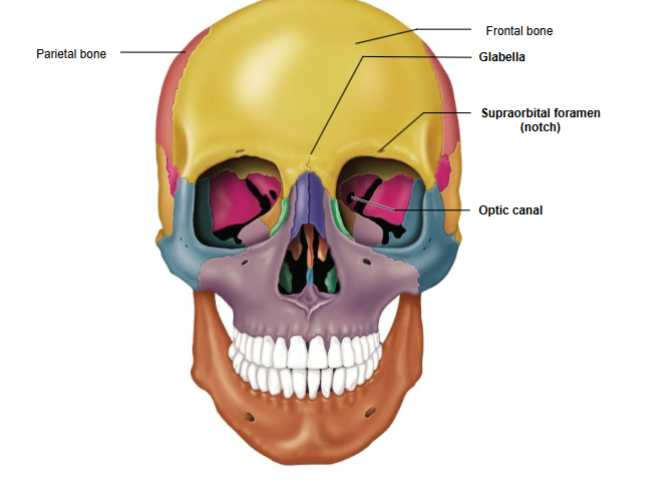
Parietal Bone
Forms the sides and roof of the cranium.
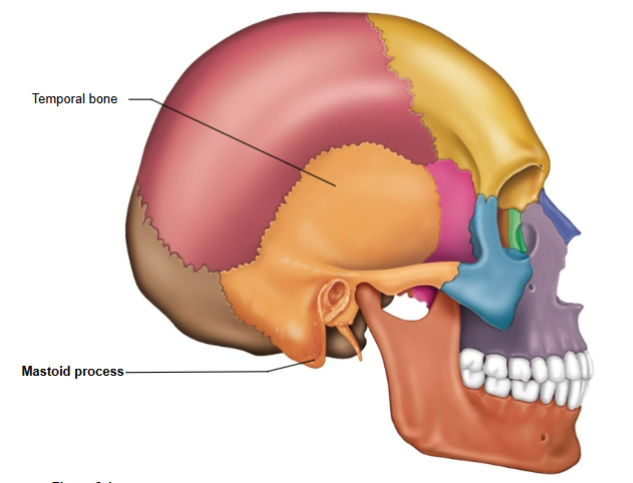
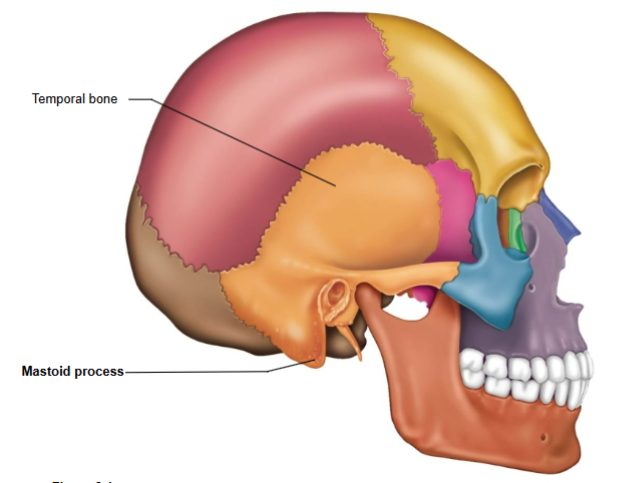
Temporal Bone
Bone located at the sides and base of the skull.
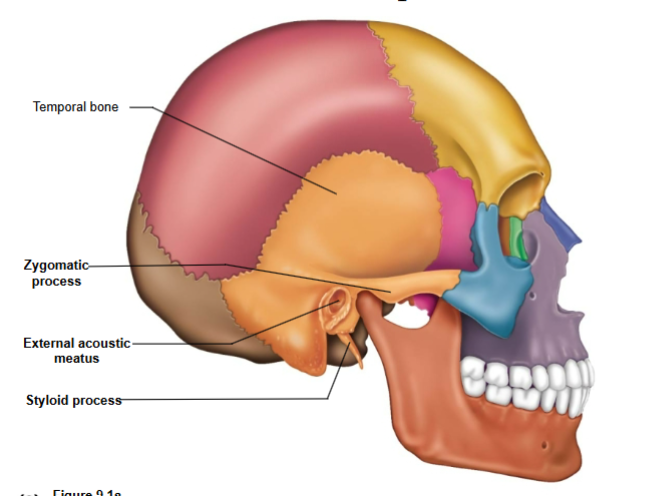
Regions of the temporal bone
Squamous region, tympanic region, mastoid region, petrous region
Squamous region contains
Zygomatic process
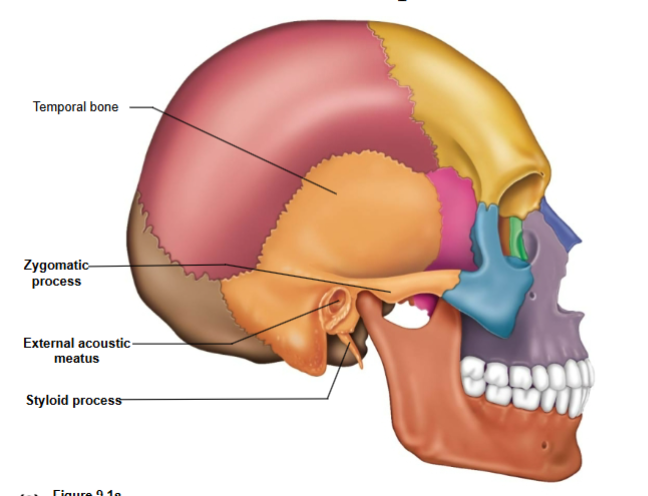
Tympanic region contains
External acoustic meatus- ear canal
Styloid process- ligament attachment site
Mastoid region contains
Mastoid process- a muscle attachment site located on the temporal bone.
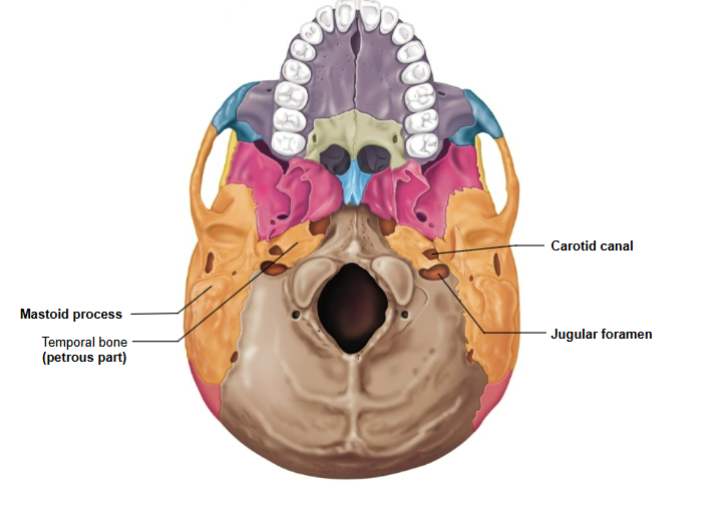
Petrous region contains
Jugular foramen- passage for jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI
Carotid canal- passage for internal carotid artery
Internal acoustic meatus- passage for cranial nerves VII and VIII
Occipital associated structures
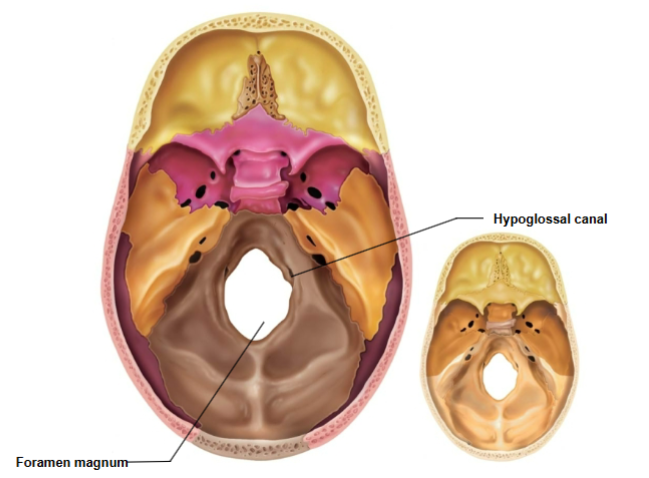
Foramen magnum
Occipital condyles
Hypoglossal canal
Foramen magnum
Where the spinal cord enters the cranium to connect to the brain
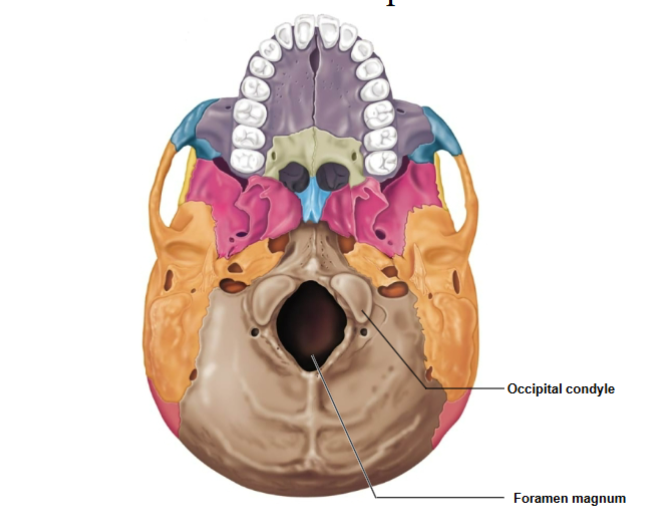
Occipital Condyles
Articulation site with the 1st cervical vertebra (atlas).
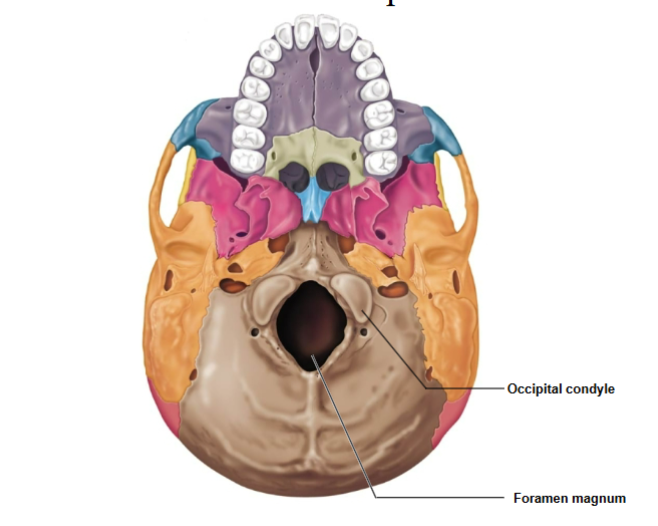
Hypoglossal Canal
Passage for cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal nerve).
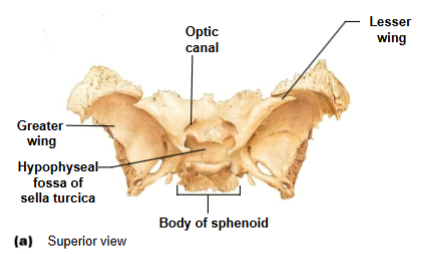
Sphenoid bone associated structures
Greater wings- part of orbital cavity
Sella turcica- midline of sphenoid bone
Lesser wings- anchors dura mater
Optic canals- opening at base of lesser wings for cranial nerve II
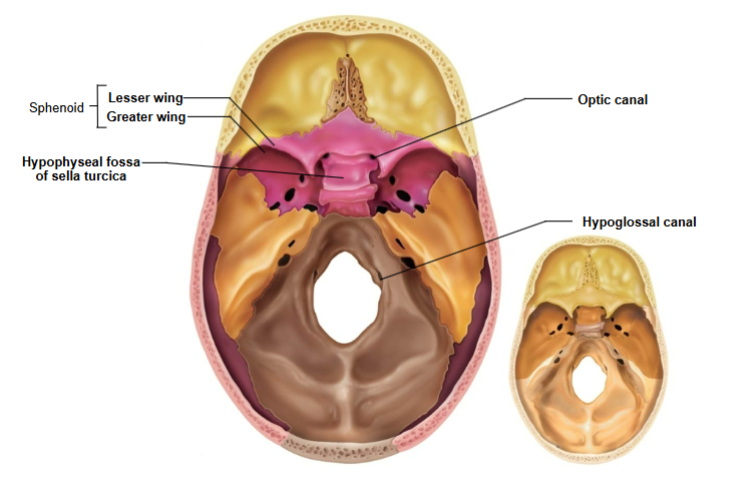
Hypophyseal fossa
Houses the pituitary gland; part of sella turcica
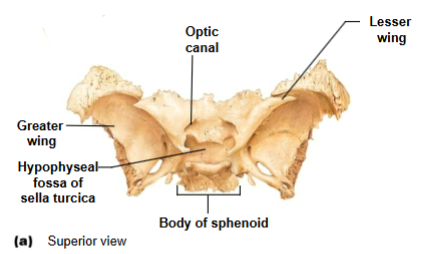
Optic canals
Openings at base of lesser wings for cranial nerve II (optic nerve)
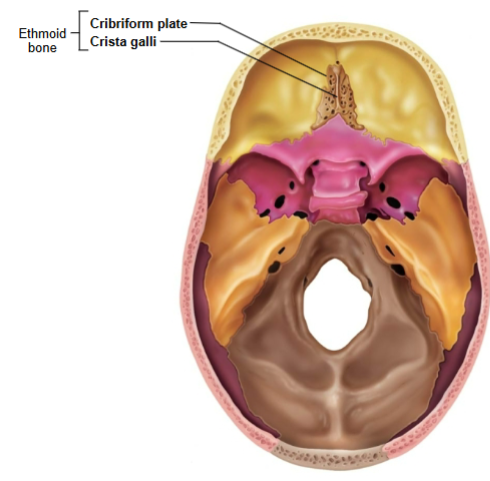
Ethmoid bone
Crista galli and Cribriform plate
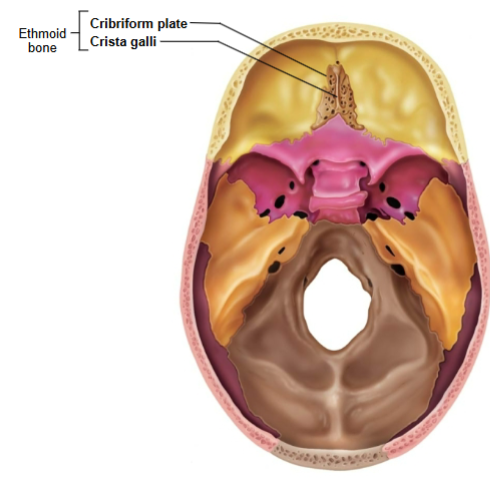
Crista galli
Anchors dura mater (leathery connective tissue membrane that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord)
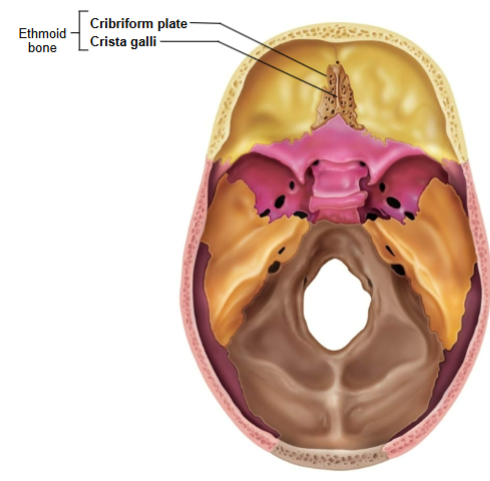
Cribriform plate
Allows olfactory fibers (cranial nerve I) from nasal mucosa to enter the brain
Facial bones
Mandible, Maxilla, Palatine, Zygomatic, Lacrimal, Nasal, Vomer, Inferior nasal conchae
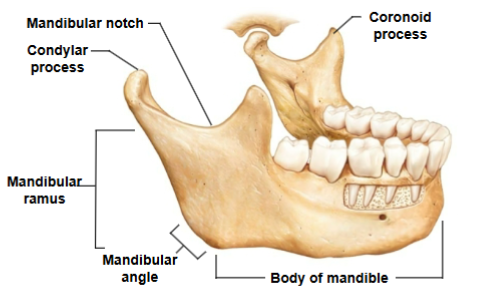
Mandible
Body of mandible, Mandibular ramus, Mandibular angle, Coronoid process, Mandibular notch, Condylar process
Maxilla
Palatine process - anterior part of the hard palate
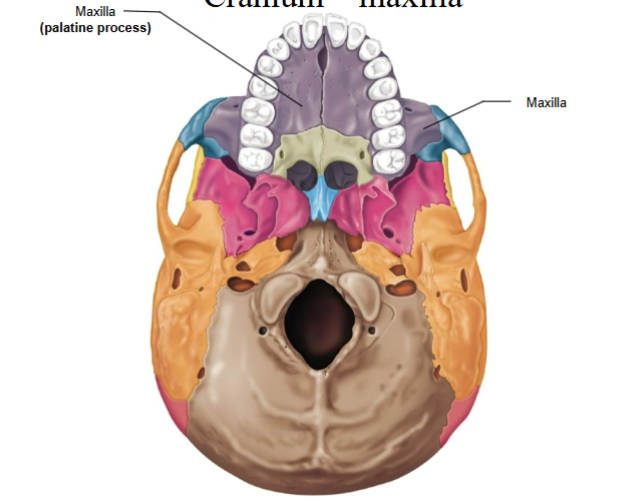
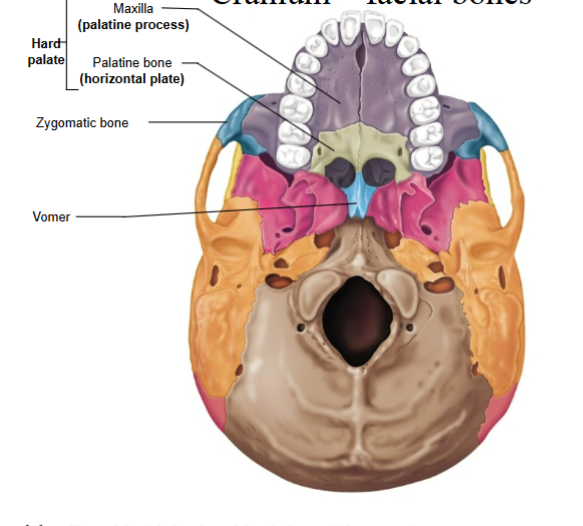
Hard palate
Composed of BOTH the palatine process of the maxilla AND the palatine bone
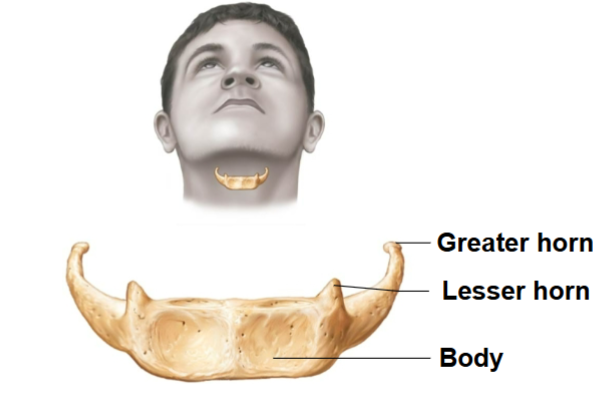
Hyoid bone
Serves as a point of attachment for many tongue and neck muscles
Paranasal Sinuses
Four skull bones (maxillary, sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal) contain sinuses (mucosa-lined air cavities)
They lighten the skull and act as resonance chambers for speech
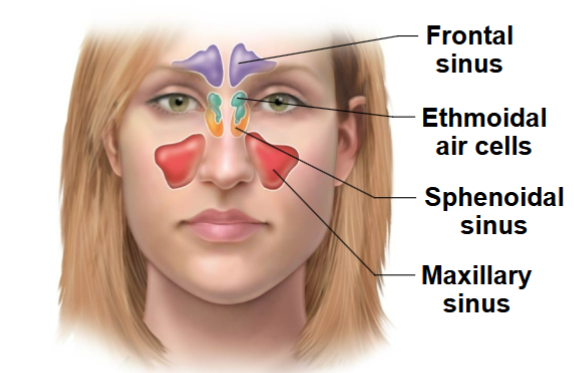
Sinusitis
Inflammation of sinuses (from bacterial infection or allergy)
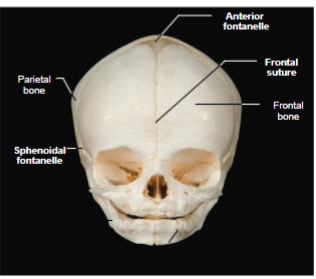
Fetal Skull
Contains areas of fibrous membranes (fontanelles) that allow the skull to compress slightly during birth
Craniosynostosis
Birth defect that causes one or more of the sutures on a baby's head to close earlier than usual. No fontanelles
Fontanelles
Areas of fibrous membranes in the fetal skull that allow for brain growth during late fetal life. Completely ossify by 1.5-2 years old