APWH Unit 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Diaspora
The dispersion of any people from their original homeland.
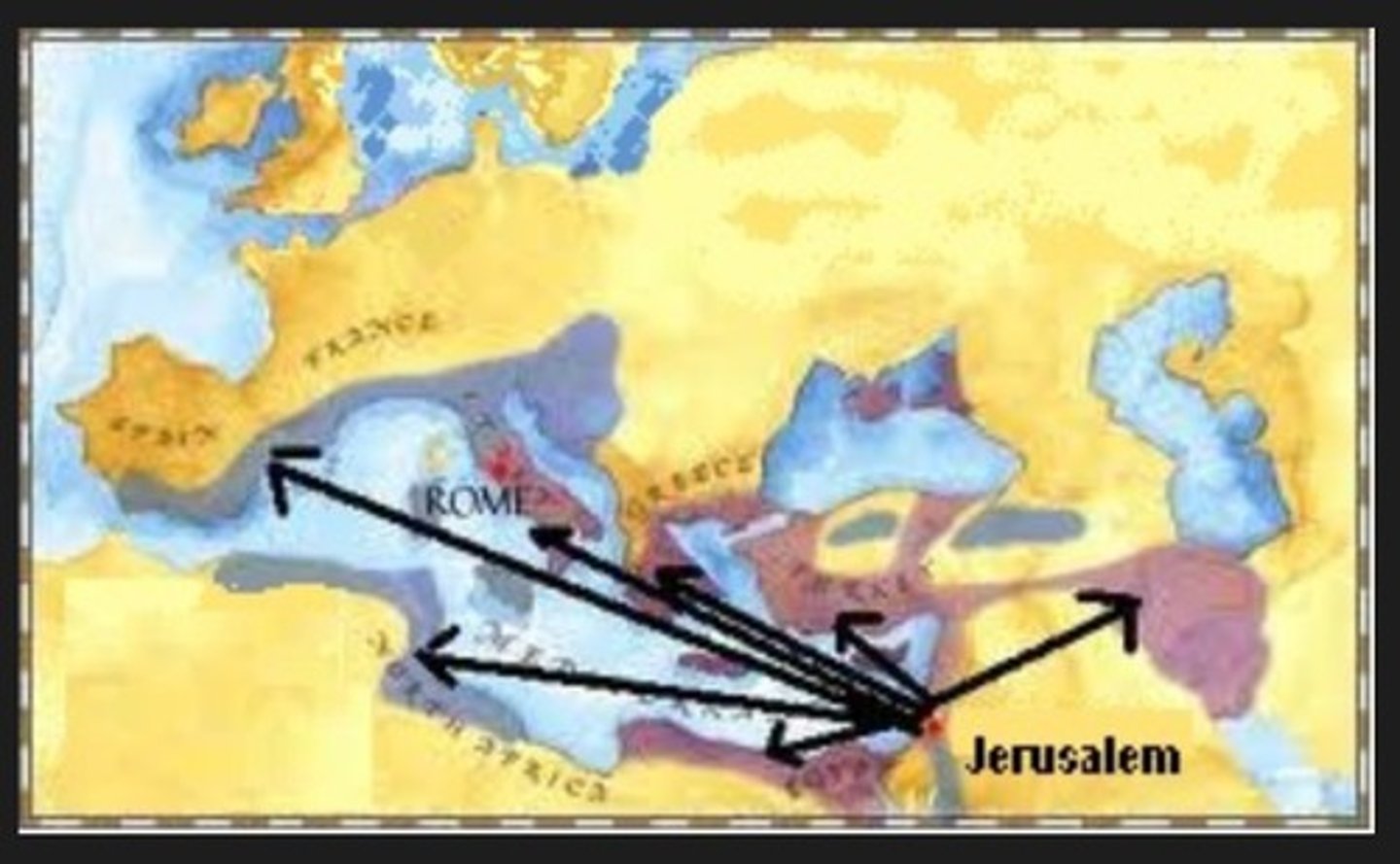
Judaism
The monotheistic religion of the Jews.

Hinduism
A major religious and cultural tradition of South Asia, which developed from Vedic religion.

Confucianism
A system of philosophical and ethical teachings founded by Confucius and developed by Mencius.

Buddhism
A widespread Asian religion or philosophy, founded by Siddartha Gautama in northeastern India in the 5th century BC.

Devshrime
Ottoman Empire practice of forcibly recruiting soldiers and bureaucrats from among the children of their Balkan Christian subjects.
Sultanates
The territory or a country ruled by a sultan (a Muslim king/sovereign)

Ibn Battuta
A Muslim Berber Moroccan scholar, and explorer who widely travelled the medieval world. Over a period of thirty years, Ibn Battuta visited most of the Islamic world and Asia.

Sufism
A version of Islam characterized by mystecism and strong self-dicipline

Song Dynasty
An imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279.
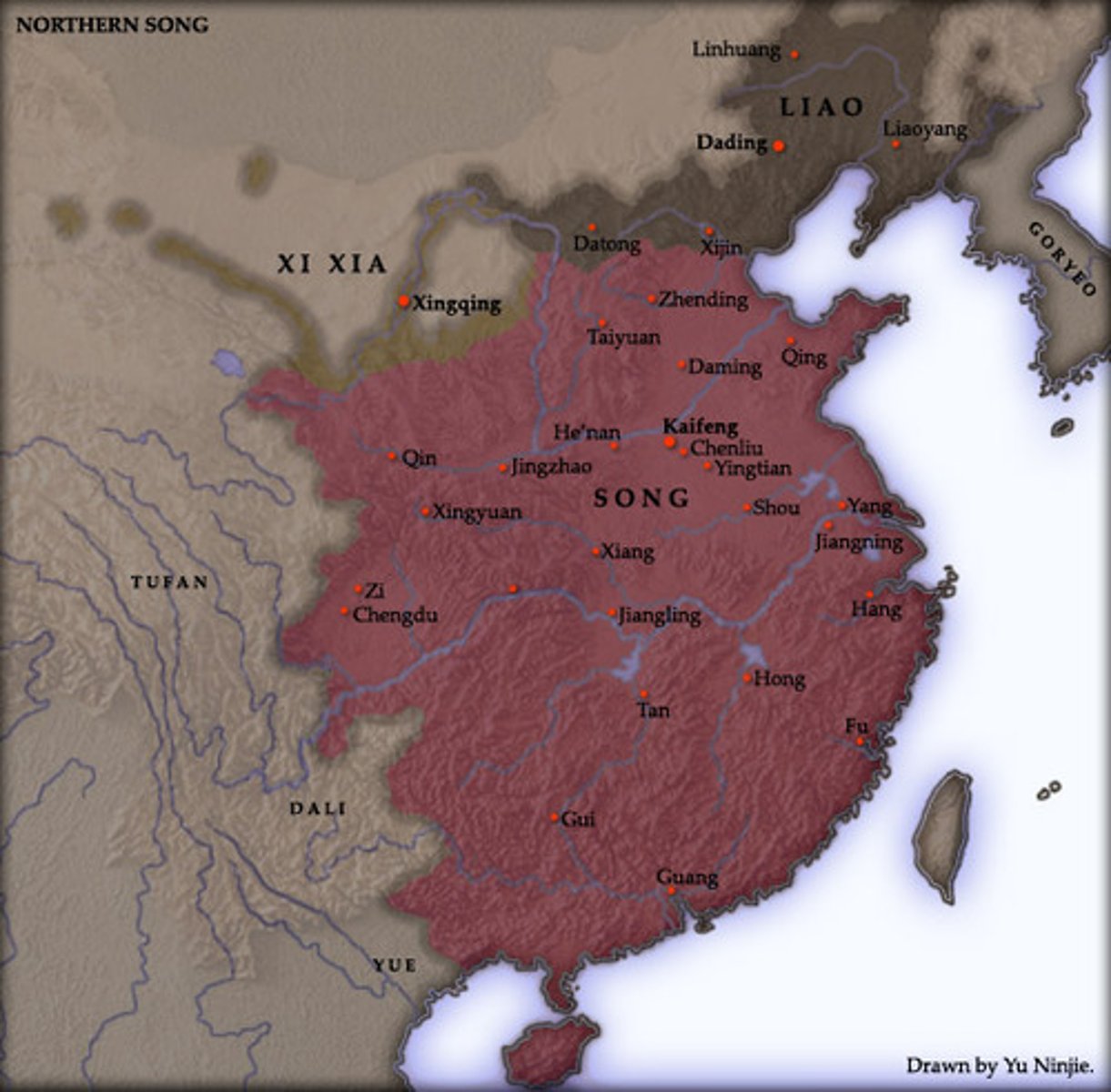
Civil Service Examination
An exam designed to select the most studious and learned candidates for appointment as bureaucrats in the Chinese government. This system governed who would join the bureaucracy between 650 CE and 1905, making it the world's longest-lasting meritocracy.

Ghengis Khan
The founder and first Great Khan and Emperor of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death.

Zheng He
A Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He commanded expeditionary treasure voyages to Asia, India, and Africa from 1405-1433.

Majapahit Empire
A Javanese Hindu-Buddhist maritime (sea) empire in Southeast Asia, based on the island of Java (part of modern-day Indonesia), that existed from 1293 to circa 1517.
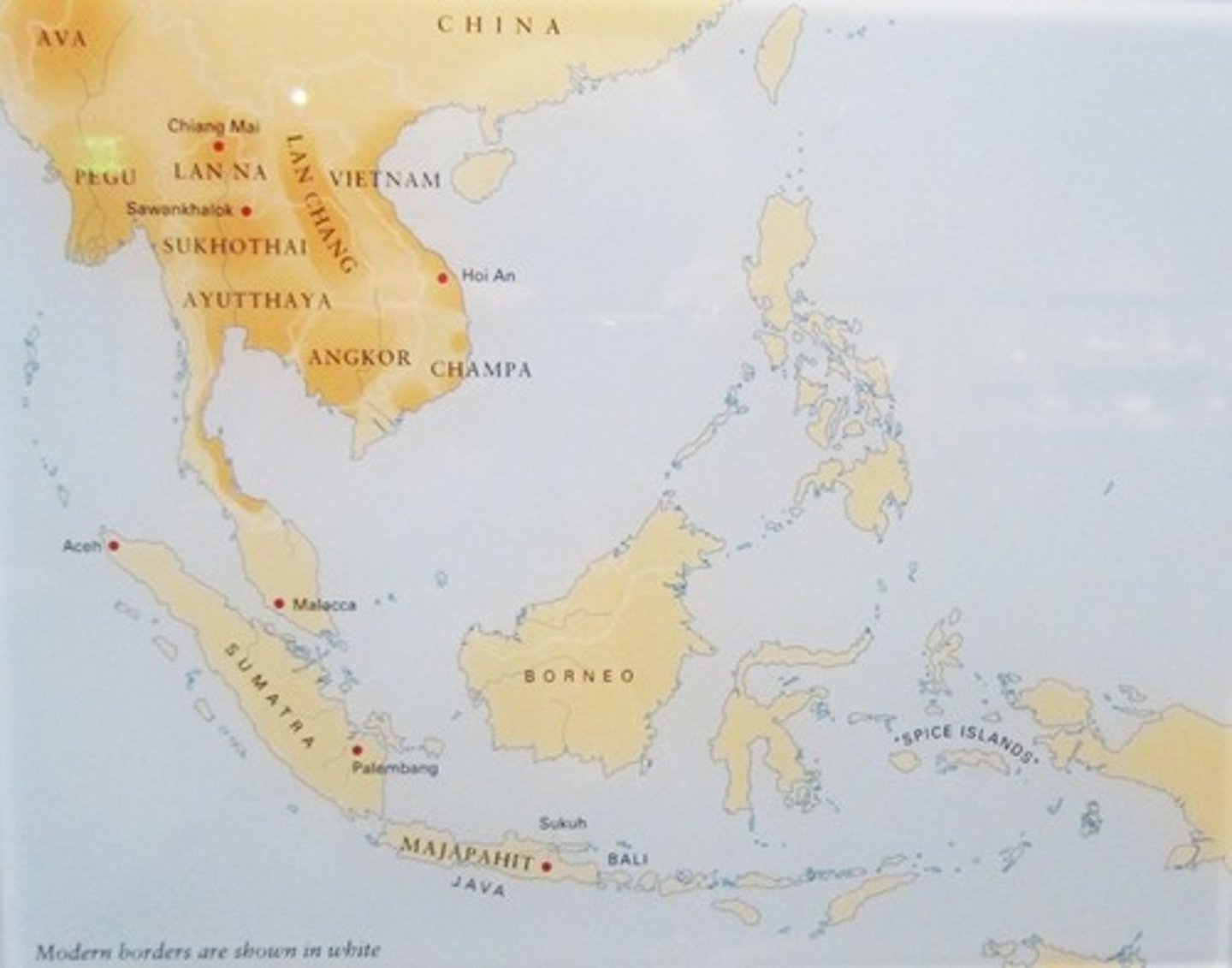
Marco Polo
a Venetian merchant, explorer, and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. Through his appointment to Kublai Khan's court, he described to Europeans the culture of Chine and the wealth/size of the Mongol Empire and Yuan Dynasty.

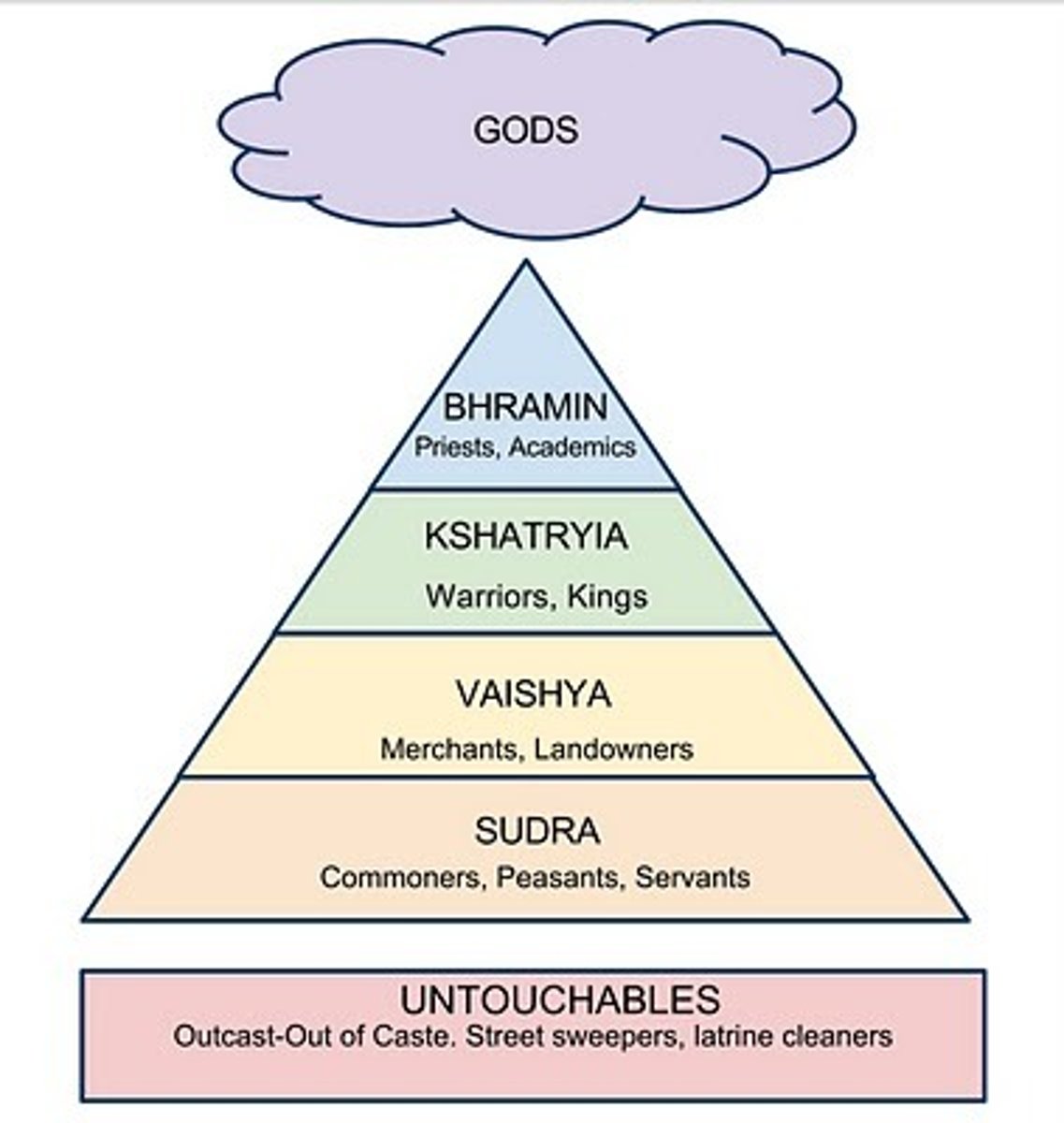
Caste System
A heirarchical system that segments society into groups.Membership is determined by birth, and can affect one's living area, occupation, and marriage opportunities. The four classes were the Brahmins (priestly people), the Kshatriyas (also called Rajanyas, who were rulers, administrators and warriors), the Vaishyas (artisans, merchants, tradesmen and farmers), and Shudras (labouring classes). Another group outside the system were the untouchables.
Mali Empire
The largest empire in West Africa from c. 1235 to 1670. Reknowned for the wealth of its rulers, such as Mansa Musa and storytellers known as griots.
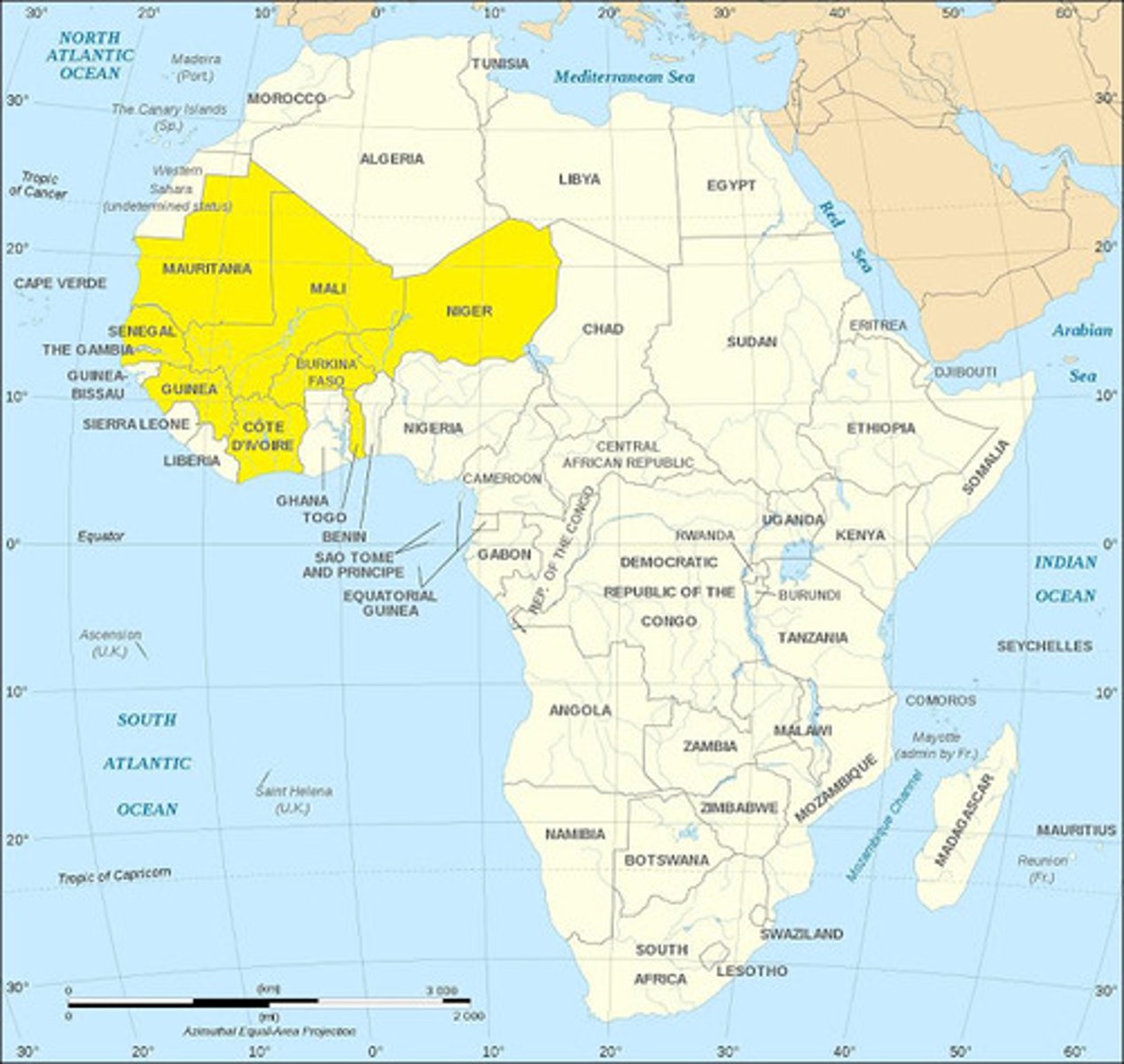
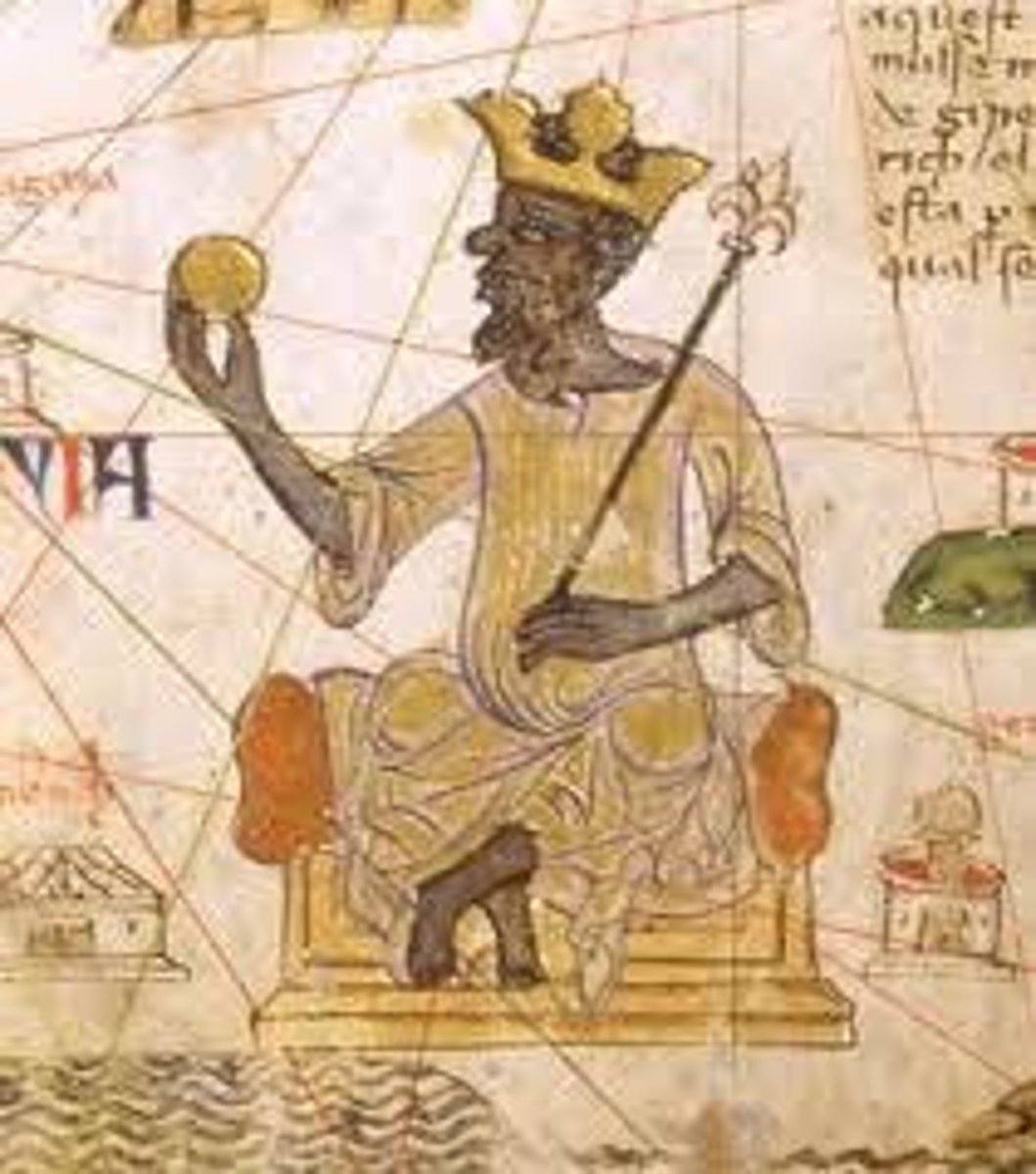
Mansa Musa
The tenth Mansa (sultan) of the Mali Empire. Known as the wealthiest person in the world due to the empire's gold production. Known to the world due to his Hajj

Hausa Kingdom
The Hausa Kingdom, also known as Hausa Kingdoms or Hausaland, was a collection of states started by the Hausa people, situated between the Niger River and Lake Chad (modern day northern Nigeria).
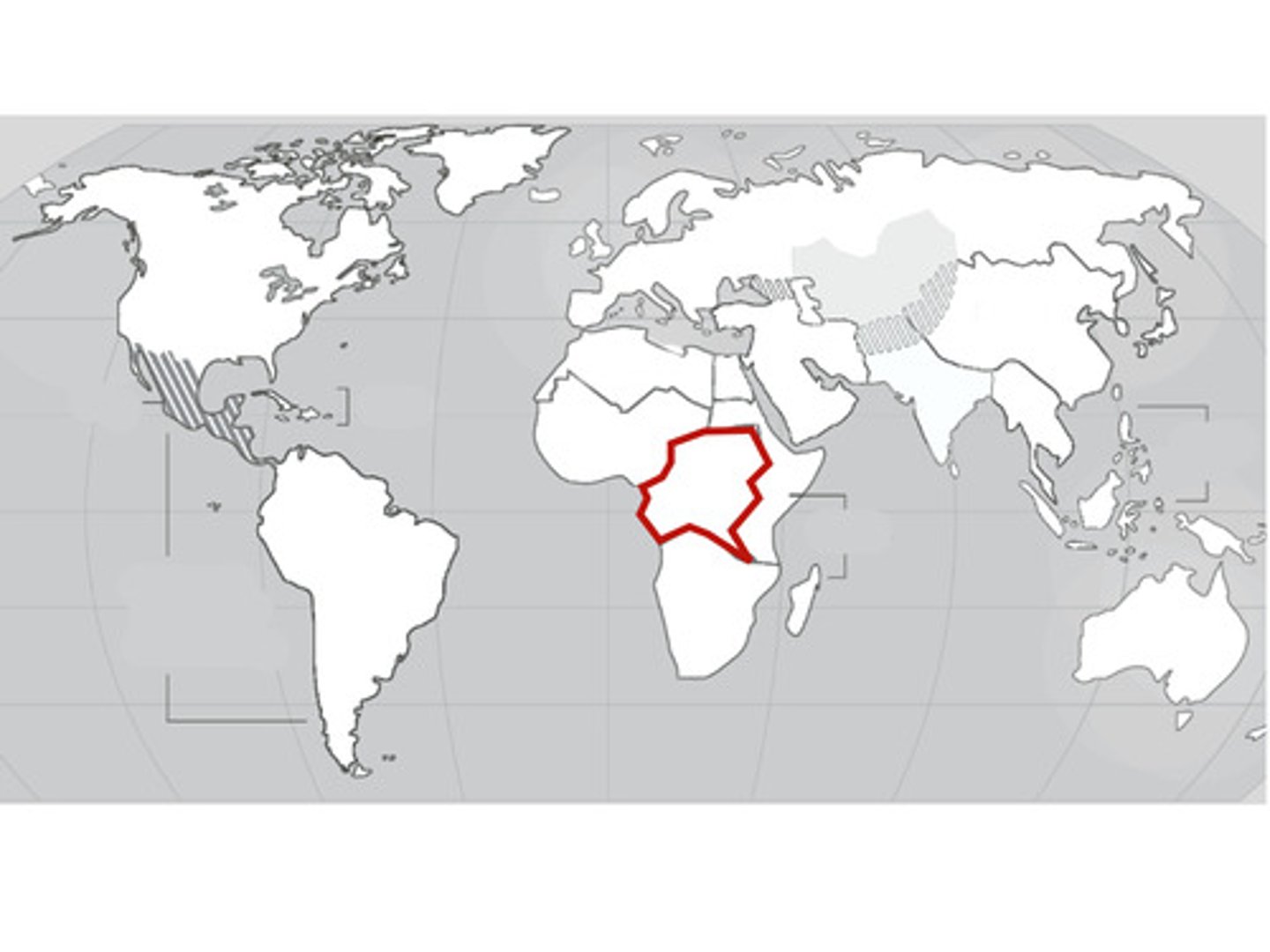
Hajj
The Muslim pilgrimage to Mecca that takes place in the last month of the year, and that all Muslims are expected to make at least once during their lifetime.

Swahili
A Bantu language widely used as a lingua franca (a common language created between speakers of different native languages) in East Africa and having official status in several countries.
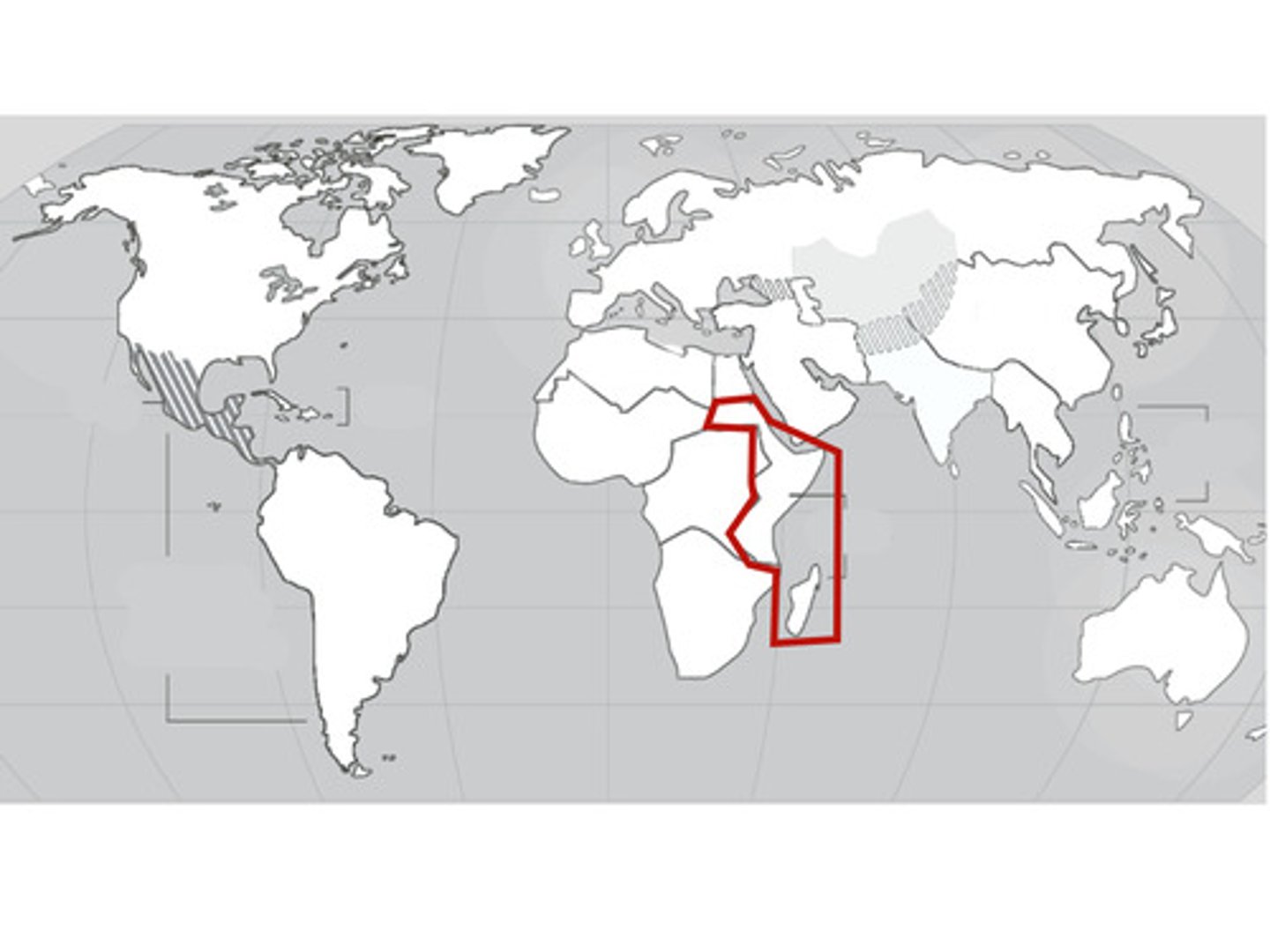
Syncretism
The amalgamation (merging) of different religions, cultures, or schools of thought.

Aztecs/Mexicas
A member of the indigenous people dominant in Mexico before the Spanish conquest of the 16th century.

Tribute System
The conquered regions paid tribute to the emperor and the Aztec citizenry paid taxes (with the exception of priests, nobles, minors, orphans, invalids, and beggars).

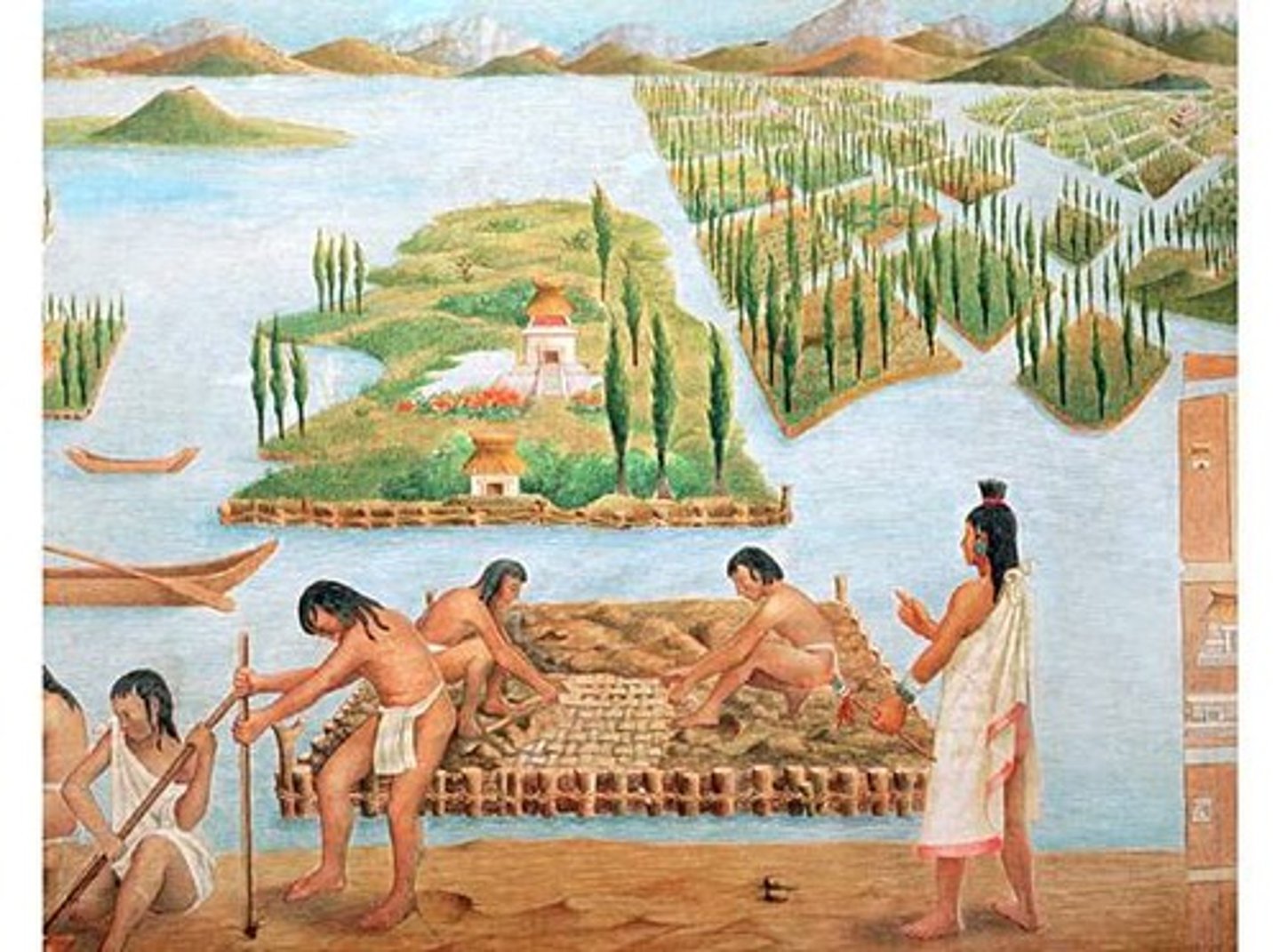
Chinampas
An agricultural technique that relies on small, rectangular areas of fertile land to grow crops which float on lakes.

Monarchies
a sovereign (supreme ruler) head of state, especially a king, queen, or emperor.
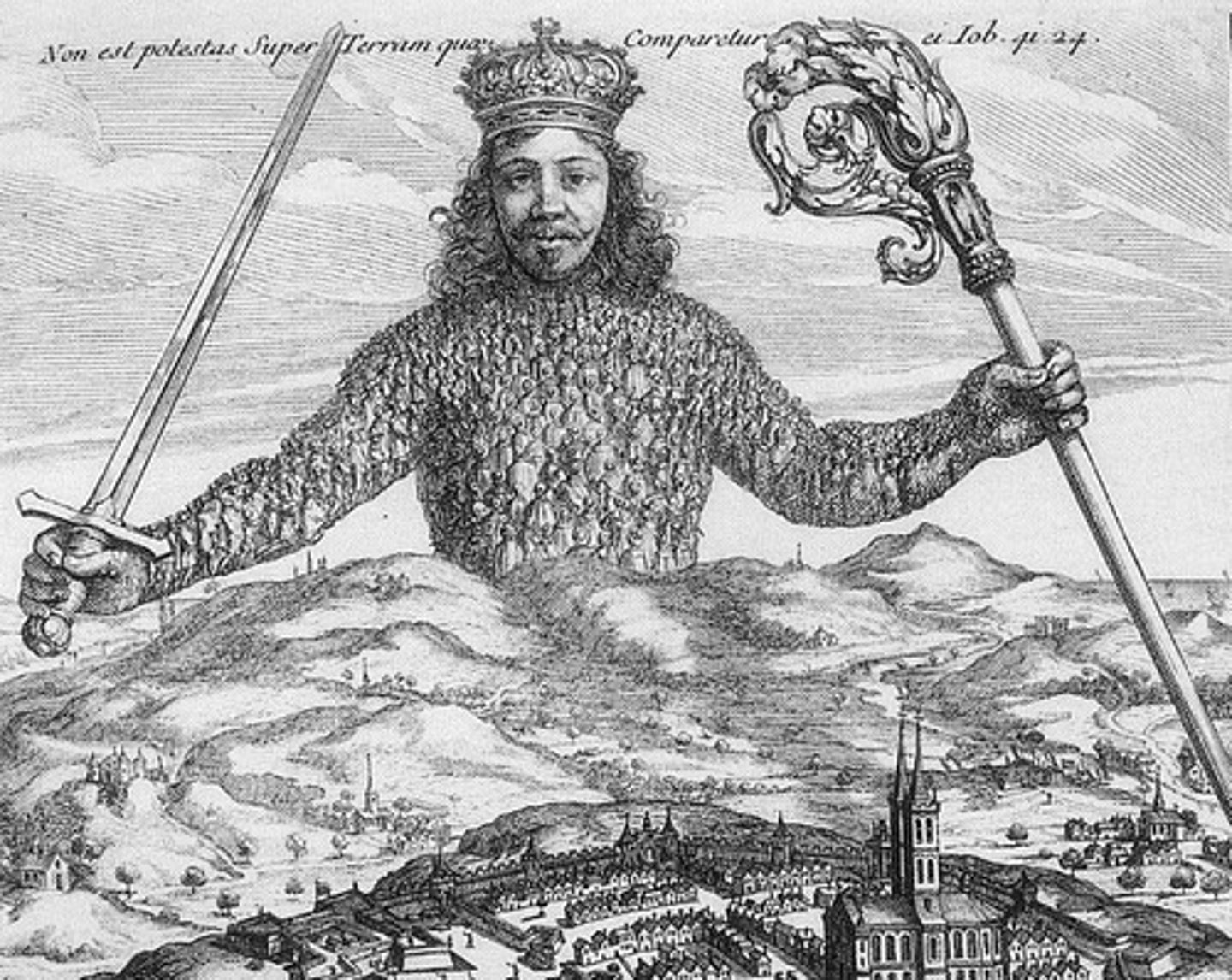

Feudalism
The dominant social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were in turn tenants of the nobles, while the peasants (villeins or serfs) were obliged to live on their lord's land and give him homage, labor, and a share of the produce, notionally in exchange for military protection.
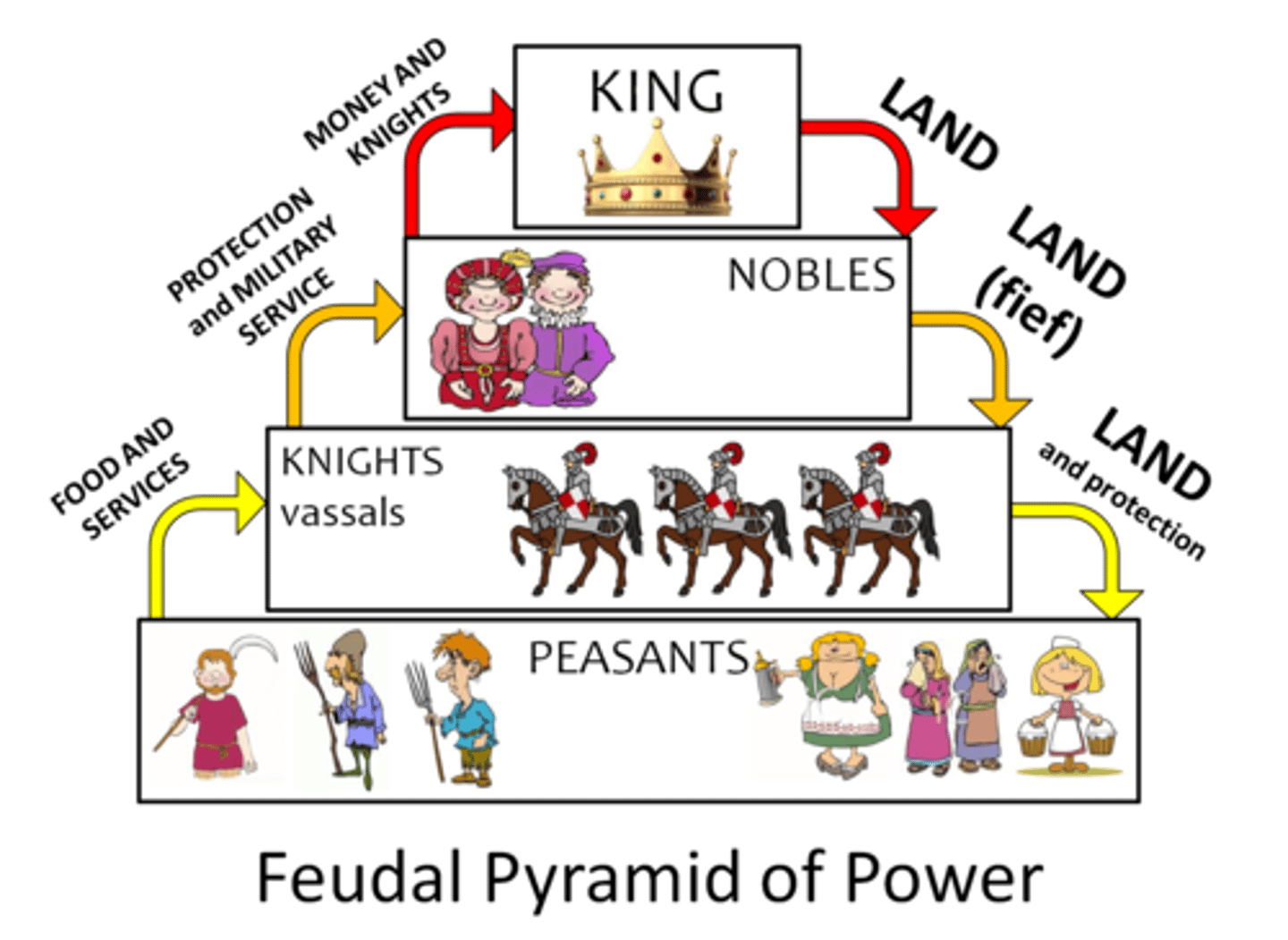
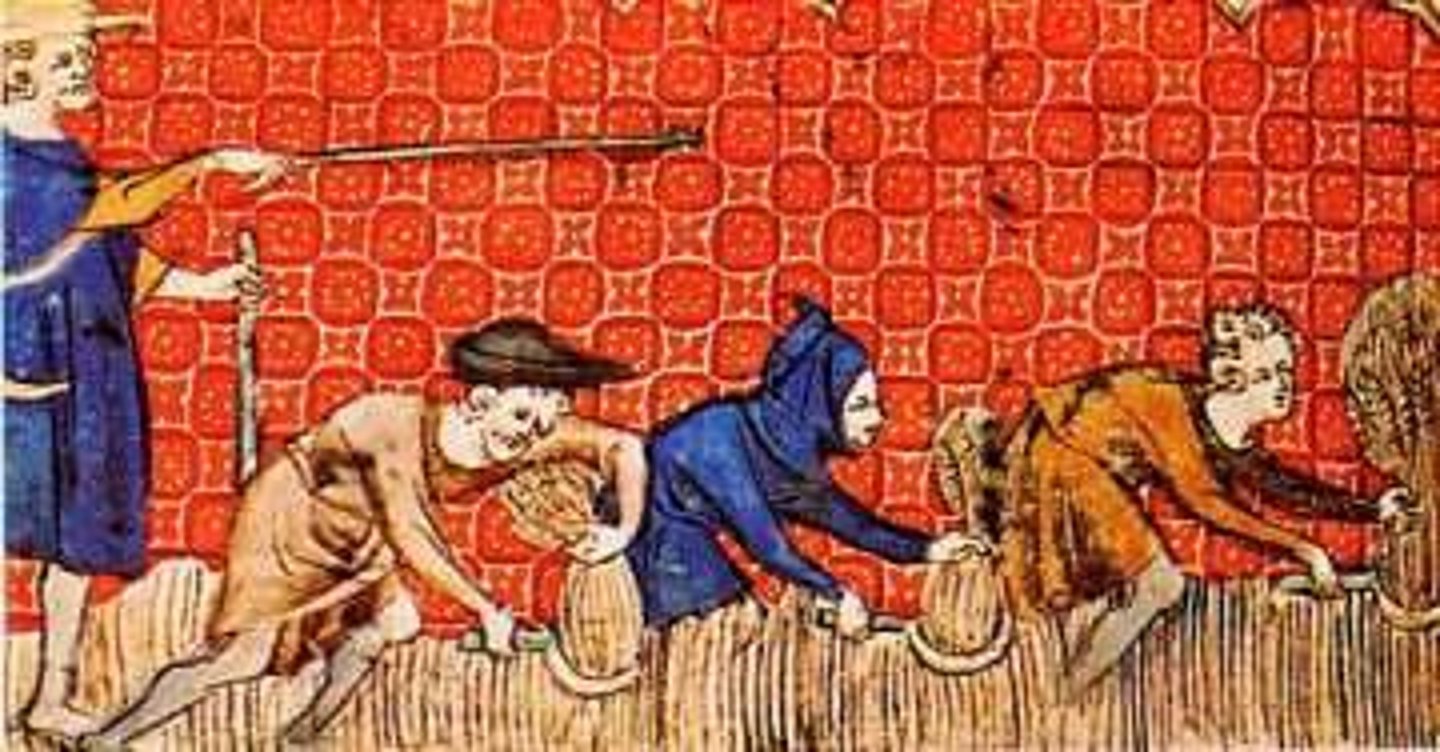
Manorial System
Peasants of medeival Europe were dependent on the land of their lord.

Serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism. A condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude.

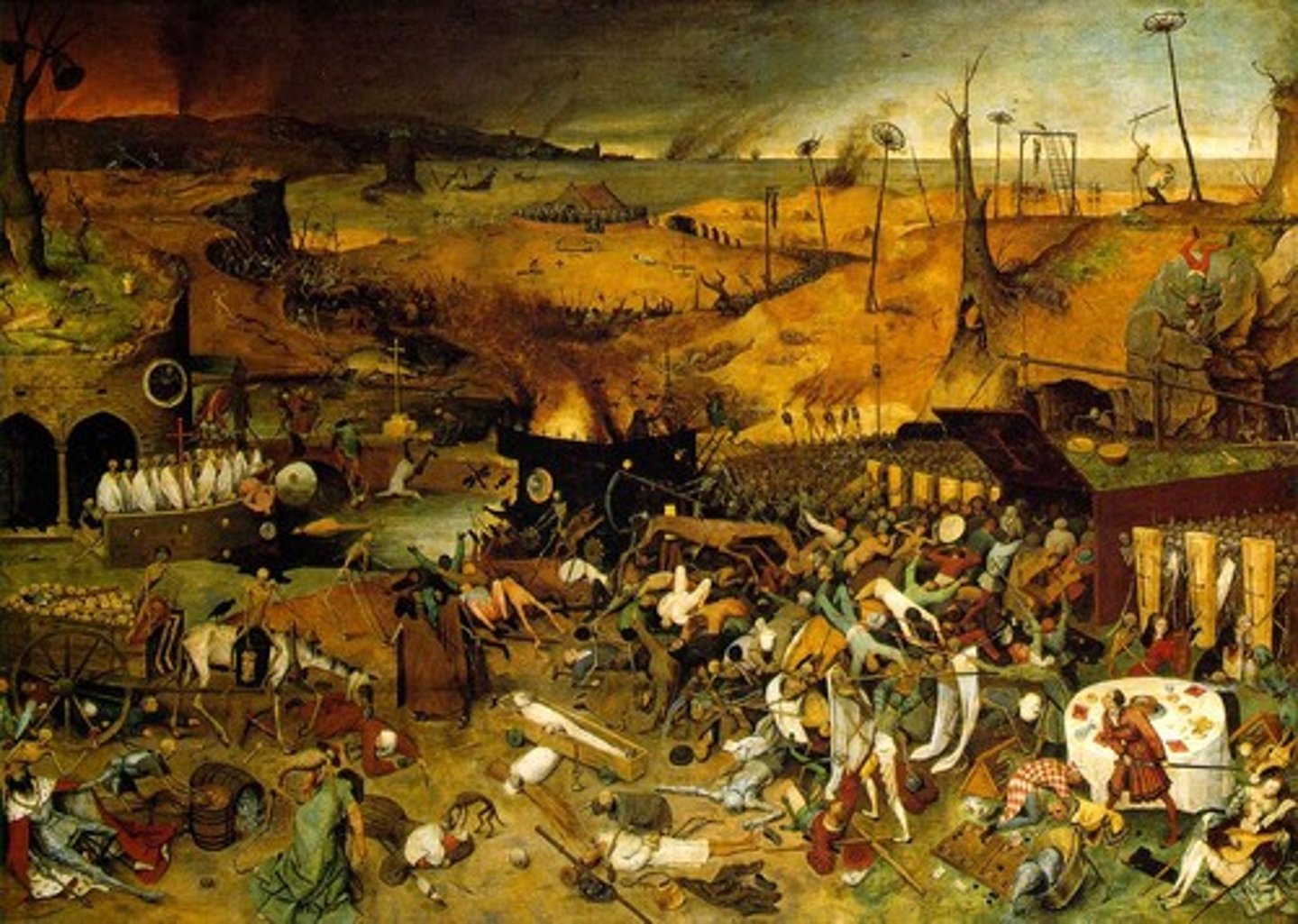
Black Death/ Bubonic Plague
the deadliest pandemic recorded in human history, causing 75-200 million deaths across Eurasia and North Africa. It likely originated in Central/East Asia and spread along the Silk Road from fleas living on black rats.

Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. They had the objective of "recovering" the Holy Land from Islamic rule.
