BIO 212 Q6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
1
New cards
What two domains are prokaryotes divided into?
bacteria and archaea
2
New cards
Prokaryotes thrive ___
almost everywhere
3
New cards
Most prokaryotes are ___
unicellular
4
New cards
What are the three most common shapes (colonies)?
spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals
5
New cards
spheres
cocci
6
New cards
rods
bacilli
7
New cards
An important feature of nearly all prokaryotic cells is their
cell wall
8
New cards
What is a cell wall made out of?
cellulose or chitin
9
New cards
What is the function of the cell wall?
maintains cell shape and protects the cell
10
New cards
Scientists use the **___** to classify bacteria by cell wall composition
gram stain
11
New cards
What color is a gram-positive bacteria?
Purple
12
New cards
Gram-positive bacteria have simpler walls with a
large amount of peptidoglycan
13
New cards
What color is a gram-negative bacteria?
Pink
14
New cards
Gram-negative bacteria have
less peptidoglycan and a toxic outer membrane
15
New cards
Many antibiotics target ____ and damage bacterial ___
peptidoglycan, cell walls
16
New cards
gram-negative bacteria are more likely to be
antibiotic resistant
17
New cards
Most motile bacteria propel themselves by
flagella
18
New cards
Many of the flagella’s proteins are
modified versions of proteins that perform other tasks in bacteria
19
New cards
exaptation
existing structures take on new functions through descent with modification
20
New cards
The prokaryotic genome has less DNA than the
eukaryotic genome
21
New cards
Most of the prokaryotic genome consists of a
circular chromosome
22
New cards
Where is the chromosome located?
nucleoid region
23
New cards
plasmids
smaller rings of DNA that some bacteria have
24
New cards
Key feature of prokaryotic reproduction (1)
They are small
25
New cards
Key feature of prokaryotic reproduction (2)
reproduce by binary fission
26
New cards
Key feature of prokaryotic reproduction (3)
have short generation times \[1-3 hours\]
27
New cards
What are the three factors that contribute to prokaryotic genetic diversity?
rapid reproduction, mutation, genetic recombination
28
New cards
Mutation rates during binary fission are low, but because of rapid reproduction
mutations can accumulate rapidly in a population
29
New cards
high diversity from mutations allows for
rapid evolution
30
New cards
Prokaryotic DNA from different individuals can be brought together by
transformation, transduction, conjugation
31
New cards
transformation
A prokaryotic cell can take up and incorporate foreign DNA from the surrounding environment
32
New cards
Transduction
the movement of genes between bacteria by bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria)
33
New cards
Conjugation
the process where genetic material is transferred between prokaryotic cells
34
New cards
genetic material is transferred through the
sex pilus
35
New cards
Prokaryotes can be categorized by how they obtain
energy and carbon
36
New cards
Phototrophs
obtain energy from light
37
New cards
Chemotrophs
obtain energy from chemicals
38
New cards
Autotrophs
require CO2 as a carbon source
39
New cards
Heterotrophs
require an organic nutrient to make organic compounds
40
New cards
Obligate aerobes
require O2 for cellular respiration
41
New cards
Obligate anaerobes
poisoned by O2
42
New cards
What processes do obligate anaerobes use?
fermentation or anaerobic respiration
43
New cards
Facultative anaerobes
can survive with or without O2
44
New cards
What led to the splitting of prokaryotes into bacteria and archaea?
Molecular systematics
45
New cards
Archaea share
certain traits with bacteria and other traits with eukaryotes
46
New cards
extremophiles
archaea that live in extreme environments
47
New cards
extreme halophiles
live in highly saline environments
48
New cards
extreme thermophiles
thrive in very hot environments
49
New cards
What does *Chlamydia trachomatis* cause?
Blindness
50
New cards
What does *Borrelia burgdorferi* cause?
Lyme disease
51
New cards
Plant chloroplasts likely evolved from
cyanobacteria
52
New cards
cyanobacteria
photoautotrophs that generate O2
53
New cards
Plant chloroplasts likely evolved from cyanobacteria by the process of
endosymbiosis
54
New cards
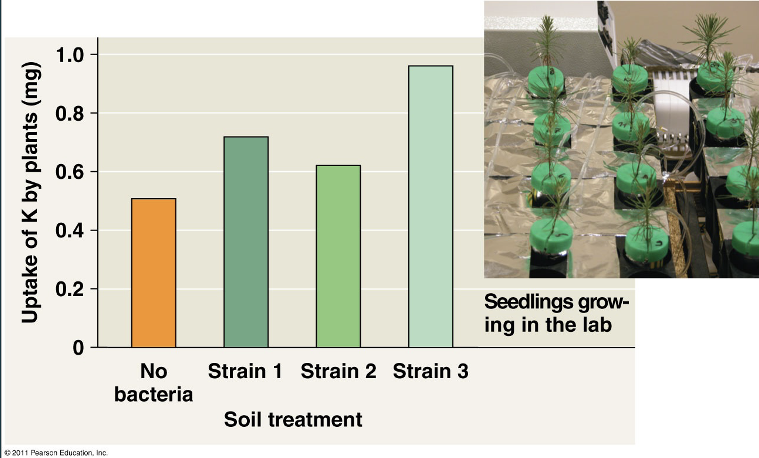
Prokaryotes play a major role in the ___ between the living and nonliving components of ecosystems
recycling of chemical elements
55
New cards
Chemoheterotrophic prokaryotes function as
decomposers
56
New cards
Symbiosis
ecological relationship in which two species live in close contact
57
New cards
prokaryotes often form symbiotic relationships with
larger organisms
58
New cards
mutualism
both symbiotic organisms benefit
59
New cards
commensalism
one organism benefits while neither harming nor helping the other in any significant way
60
New cards
parasitism
organism harms but does not kill its host
61
New cards
pathogens
parasites that cause disease
62
New cards
vectors
parasites that transmit disease
63
New cards
Prokaryotes are the principal agents in
bioremediation
64
New cards
bioremediation
the use of organisms to remove pollutants from the environment
65
New cards
The Romans thought the malaria was caused by
bad air from swamps
66
New cards
What did the Romans do to prevent malaria?
drain swamps
67
New cards
Malaria can be
asymptomatic
68
New cards
What are the classic symptoms of malaria?
fever, chills, sweating, headaches, muscle pains
69
New cards
What are the severe symptoms of malaria?
cerebral malaria, anemia, kidney failure
70
New cards
What factor affects the severity of symptoms? (1)
the species of Plasmodium
71
New cards
What factor affects the severity of symptoms? (2)
the victims genetic background
72
New cards
What factor affects the severity of symptoms? (3)
acquired immunity
73
New cards
Who discovered malaria?
Charles Laveran
74
New cards
Who discovered the mode of transmission of malaria?
Ronald Ross
75
New cards
What is the mode of transmission of malaria?
Anopheles mosquito
76
New cards
What are the four species of Plasmodium that causes malaria?
P. falciparum, P. vivax, P.ovale and P. malariae
77
New cards
P. falciparum cases are often
fatal and is responsible for most deaths
78
New cards
Both ___ and ___ can go dormant, hiding out in the liver
*Plasmodium vivax*, *P. ovale*
79
New cards
P. malariae causes a
long-lasting infection
80
New cards
Plasmodium has two hosts:
mosquitoes and humans
81
New cards
Where does sexual reproduction take place?
In the mosquito
82
New cards
When is malaria transmitted to humans?
when the mosquito takes a blood meal
83
New cards
In the salivary gland the parasite cuts off the mosquito’s
anticoagulant supply
84
New cards
What does cutting off the anticoagulant supply do?
this makes it harder for the mosquito to feed
85
New cards
As a result of the anticoagulant
an infected mosquito is twice as likely to bite two people in a single night as an uninfected mosquito
parasite is spread more widely
parasite is spread more widely
86
New cards
In humans, the Plasmodium helps the mosquito feed by
releasing chemicals that slow clotting
87
New cards
What does slowed clotting do?
increase the chances of the mosquito feeding successfully and sucking up the parasite