AP BIO EXAM REVIEW :)
1/224
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
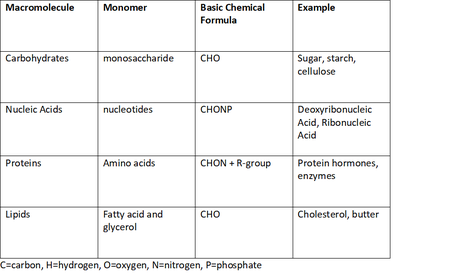
Identify the elements that make up nearly all living matter.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur
Differentiate between a solute, solvent and solution.
Solute- what’s being dissolved (Ex: salt)
Solvent- what it’s being dissolved in (Ex: water)
Solution- the mixture/result (Ex: salty water)
Describe covalent bonds
2 or more atoms sharing electrons forming molecules and compounds
Describe ionic bonds
the attraction between oppositely charged atoms that transfer electrons
How are hydrogen bonds different from other types of bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are weak bonds. The positive hydrogen atom is attracted to an electronegative atom
How does electronegativity affect the interactions between water molecules?
When hydrogen bonds to an electronegative atom, the electrons aren’t shared equally causing hydrogen to be positive while oxygen is negative
What would happen to the properties of water if oxygen and hydrogen had the same electronegativity?
The properties of water would no longer function because they would no longer attract
Name the properties of water
polarity, cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, temperature control, density, universal solvent and capillary action
Polarity
Water is a polar molecule because it has an unequal sharing of electrons.
Cohesion
water attracts to other water molecules causing surface tension
Adhesion
water clings to other molecules and surfaces
Capillary Action
the upward movement of water due to adhesion being greater than cohesion
Temperature Control
Water moderates temperature because when heat is absorbed it breaks hydrogen bonds and when heat is released hydrogen bonds form
Density
when cold, water becomes less dense because hydrogen bonds slowdown breaking bonds but when hot, water speeds up.
Universal solvent
Water is versatile meaning its polar molecules can dissolve both ions and other polar molecules
Explain two ways in which the properties of water benefit organisms.
Capillary action allows for the transportation of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves of plants.
Temperature stabilizes the ocean temperature helping Marine life.
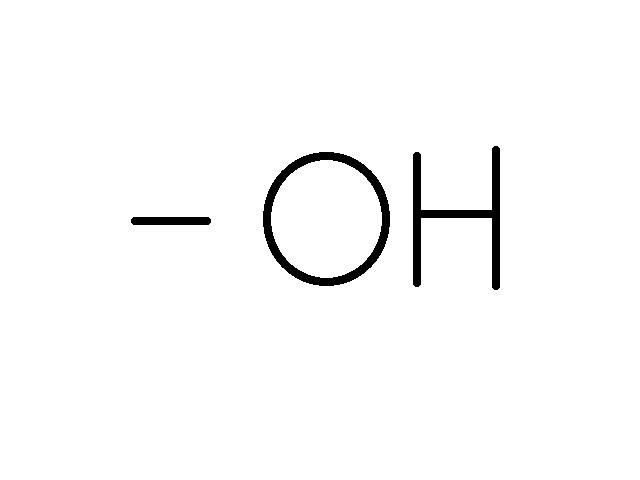
What is the functional group?
Hydroxyl
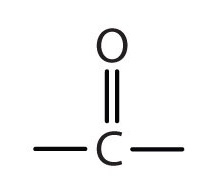
What is the functional group?
Carbonyl
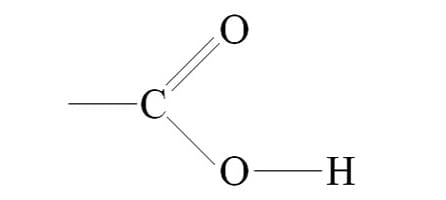
What is the functional group?
Carboxyl
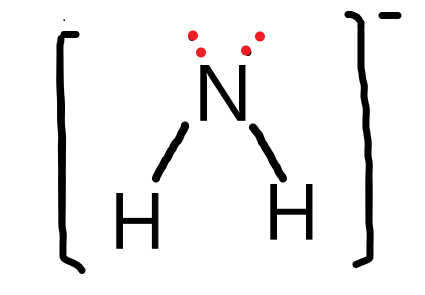
What is the functional group?
Amino
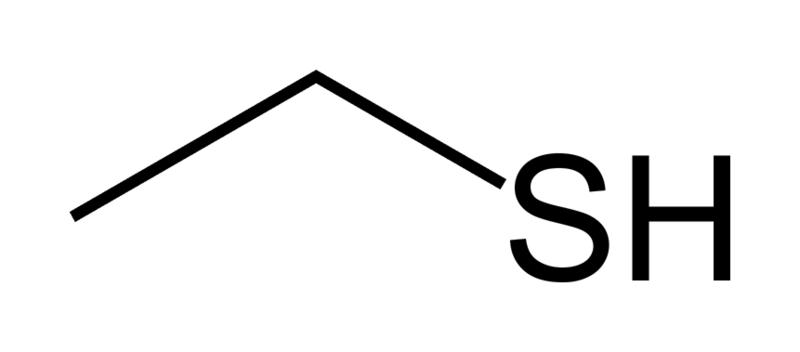
What is the functional group?
Cysteine
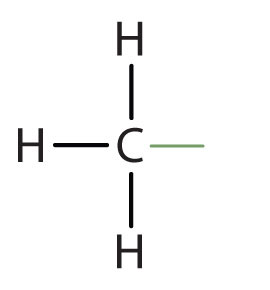
What is the functional group?
Methyl
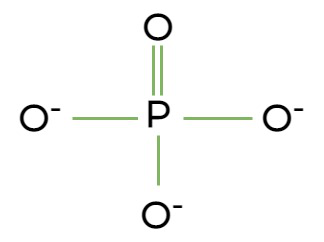
What is the functional group?
Phosphate
What makes carbon such a versatile element?
Carbon can form single, double and triple covalent bonds
How do functional groups affect the structure and behavior of organic molecules?
Functional groups change the structure by attaching to the carbon skeleton and they impact the behavior by giving specific properties to the organic molecules.
What is the difference between hydrocarbons and other organic molecules?
Hydrocarbons only consist of hydrogen and carbon while other organic molecules can contain other elements.
Differentiate between hydrolysis and dehydration reaction
Hydrolysis: adding H2O to break bonds
Dehydration: removing H2O to make bonds
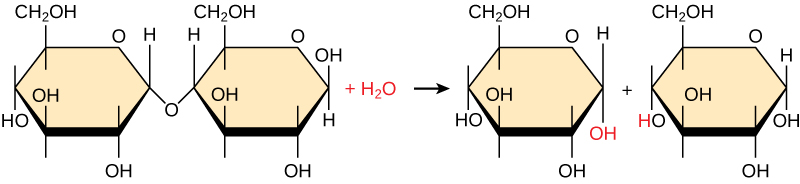
Is the reaction hydrolysis or dehydration?
Hydrolysis
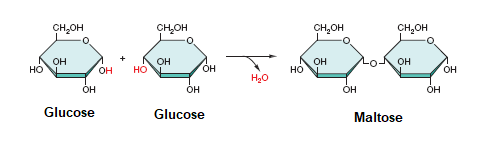
Is the reaction hydrolysis or dehydration?
Dehydration
How many monomers of protein are there?
20 Amino Acids
Structure of an amino acids
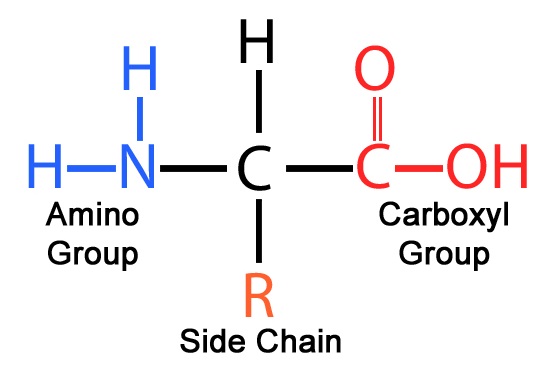
How do the R groups of amino acids contribute to protein structure?
R groups give Amino Acids distinct characteristics
Explain the structure of a phospholipid
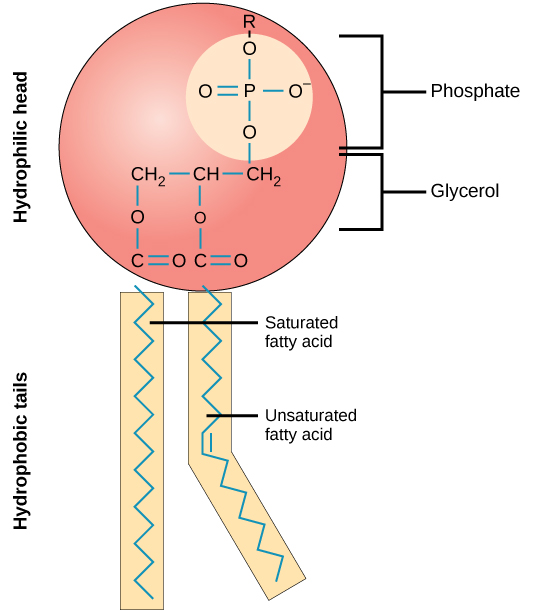
Where is the nonpolar region of a phospholipids?
The hydrophobic tails
Where is the polar region of phospholipids?
The hydrophilic heads
Where are phospholipids found in the cell and what are their role?
Phospholipids are found in the plasma membrane and their job is to select what enters and exits the cell.
What are polysaccharides? What are their monomers?
Polysaccharides are polymers with lots of sugars joined together due to dehydration. Their monomers are monosaccharides, which are simple sugars like glucose.
What important roles do polysaccharides play in plants? What about for animals?
In plants polysaccharides store starch while in animals they store glycogen in the liver and muscle cells.
How does saturation affect fatty acid structure/function?
Saturated fatty acids make the plasma membrane rigid while unsaturated fatty acids give the plasma membrane more fluidity.
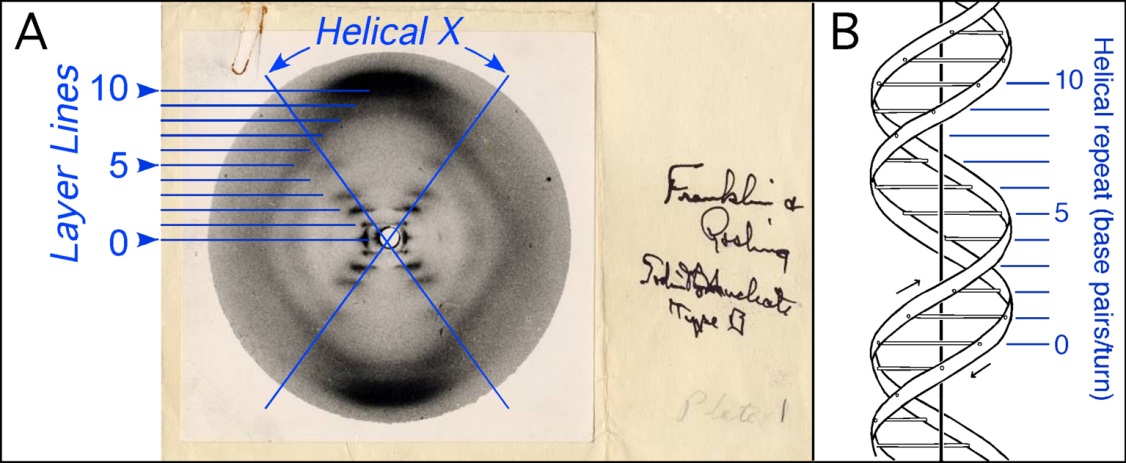
How was the double helix structure of DNA discovered?
With X-ray crystallography
What forms the backbone of DNA?
The backbone is made of deoxyribose connected to phosphates.
Why are DNA strands anti-parallel?
DNA grows in opposite directions due to the opposite orientation of the sugar molecule in them which allow the bases to be complementary.
What determines the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of the amino acids
How does the primary structure of a protein affect the other structural levels?
The primary structure of protein determines the secondary structure which then determines the tertiary which ends up impacting the quaternary structure.
Would the function of a protein change if the amino acid sequence changed?
The function would change because the amino acid sequence gives the protein specific characteristics which will be changed if the amino acid sequence is disrupted.
Primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids in a protein
Secondary structure
three dimensional coil creating helix and beta pleated sheets
Tertiary structure
3D shape caused by interactions between the R groups of amino acids
Quaternary Structure
Two or more protein chains arranged together
What causes a protein to denature? What happens to a protein if it is denatured?
Outside stressors like temperature and pH denature proteins. When a protein dentures its hydrogen bonds break.
What macromolecule would both starch and cellulose be considered?
They are both polysaccharides but starch is a storage polysaccharide that gets stored in plants while cellulose is a structural polysaccharide that forms the plants cell wall.
True or false: a change in a protein’s structure will change the proteins function?
True! Shape determines function
Identify the three components of a nucleotide.
nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and phosphate
What is a monomer called if it is lacking a phosphate group?
It is called a nucleoside because it only has a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base.
What are the nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides?
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil
List the purines
Adenine and Guanine
List the pyrimidines
Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil
What does it mean that DNA is antiparallel?
The base pairs are connecting to distinct locations on the sugar.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA
DNA: double stranded, no Uracil, deoxyribose, helix, stores genetic information
RNA: single stranded, has no Thymine, ribose, codes for amino acids and is a messenger
Where can DNA be found in a cell? What about RNA?
DNA is found in the nucleus while RNA is found in the cytoplasm
What functional groups define the 5’ end of DNA?
Nucleotide units that are connected with covalent bonds to form a linear molecule
What functional groups define the 3’ end of DNA?
Ends with nitrogenous bases perpendicular to the phosphate backbone
What organelles are in animal cells, but not in plant cells?
Lysosomes, centrosomes and the flagella
What organelles are in the plant cells but not in animal cells?
Chloroplast, central vacuole, cell wall and plasmodesmata
How do ribosomes help carry out instructions encoded in DNA?
Ribosomes transcript mRNA and translate the genetic code into a specific strand of amino acids.
If a cell has a high rate of protein synthesis, what organelle would you expect to have a large number of?
You would expect there to be a large amount of ribosomes because they are in charge of synthesizing proteins.
What is the difference between the rough and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough er synthesis proteins and contains ribosomes while the smooth er detoxifies poison, alcohol, and other foreign agents
What are the main differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes are single celled while eukaryotes are membrane bound and contain a nucleus
Describe the endomembrane system
It is a group of organelles working together
What is the path of a protein from mRNA to the the final destination?
Ribosome-Rough ER-Golgi-Vesicles-Around the Cell
How is the Golgi Complex similar to UPS?
The Golgi organizes and transports proteins just like UPS does
True or false: Since plant cells get their energy from photosynthesis they don’t need the mitochondria?
This is false because plants use both the mitochondria and the chloroplast to get their energy.
Differentiate between the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
Light dependent reactions occur in the mitochondrial matrix and makes glucose while the Calvin Cycle occurs in the luminal space (the mitochondria’s membrane) and transports electrons to make the electron gradient.
Identify the location where each process occurs:
-Light dependent reactions
-Calvin Cycle
-Krebs Cycle
-ATP Synthesis
-Electron Transport Chain
-Light dependent reactions occurs in the stroma of a chloroplast
-Calvin Cycle occurs in the mitochondria’s membrane
-Krebs Cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
-ATP Synthesis occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
-Electron Transport Chain occurs in the mitochondria’s membrane
Why are pigments like chlorophyll, important to plants?
Pigments help plants photosynthesize (turn light energy into chemical energy)
How should the surface area to volume ratio be in order for cells to optimize the exchange of material through the plasma membrane?
The SA:V should be large in order for the cell to have easier diffusion and be more efficient
What problems would occur if a single cell were to keep getting larger over time?
The cell could stop functioning, rupture or shrink
Why is the plasma membrane often refereed to as a fluid mosaic model?
That is due to the plasma membrane being made of many macromolecules like a mosaic
What is the purpose of the plasma membrane?
To select what enters and exits the cell and to give the cell structure
What is the difference between unsaturated and saturated tails of phospholipids?
Unsaturated tails- are flexible, maintain fluidity and are caused by cholesterol
Saturated tails- are rigid and have little to no fluidity
What causes the kinks in the tails of phospholipids?
Cholesterol
What molecule embeds itself within the membrane and affects fluidity? How does it affect fluidity?
Cholesterol embeds itself into the membrane and kinks the phospholipid tails allowing for fluidity to occur even during sudden temperature changes.
Differentiate between integral and peripheral proteins.
Integral are in the inside of the membrane while peripheral are on the outside.
What does it mean that the plasma membrane is selectively permeable?
It selects what enters and exits the cell.
What qualities of the plasma membrane make it selectively permeable?
Its lipid bilayer (hydrophobic inside and hydrophilic outside)
Are nonpolar molecules hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
They are hydrophobic making it easier for them to enter the cell.
Are polar molecules hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
They are hydrophilic making it harder for them to enter the cell.
Identify the following as polar or non-polar:
-carbon dioxide
-ions
-oxygen
-water
-glucose
-carbon dioxide is nonpolar
-ions are polar
-oxygen is nonpolar
-water is polar
-glucose is nonpolar
True or false: If plant cells have a cell wall, then they cannot exchange material through their plasma membrane.
False, both work together to select what enters and exits the cell.
What are cell walls composed of?
Plasmodesmata ( windows in the cell wall)
What kind of cells have a cell wall? What is the purpose of the cell wall?
Plant cells have a cell wall which provides protection, support and regulates water.
What are the main differences between passive and active transport?
Passive transport does not require energy because it follows the concentration gradient while active transport requires energy because it goes against the concentration gradient.
Imagine a room is a cell and someone bring freshly popped popcorn (gas molecule) and the smell slowly drifts through the room. What type of diffusion is this an example of?
Passive transport because the scent is going from a high concentration to a low concentration.
Fill in the blank:
In passive transport, molecules move from ___ to ___ concentration
In passive transport, molecules move from low to high concentration
How are molecules able to go through diffusion?
Molecules are able to go through diffusion due to channels and pumps
How is it possible that animal cells have a high internal concentration of potassium in comparison to their external environment?
This is due to the sodium potassium pumps which regulates the input and output of sodium and potassium by removing 3 sodium for every 2 potassium that enter.
What molecule is necessary for active transport?
ATP
What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?
Exocytosis- the secretion of molecules via vesicles that fuse to the plasma membrane
Endocytosis- the intake of molecules from vesicles fused from the plasma membrane
Is facilitated diffusion a type of active or passive transport?
It is passive because it doesn’t need ATP meaning molecules diffuse easily