Lecture 2 & 3: Machine Learning and Large Language Models (LLMs)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
The Era of Big Data
The widespread use of various digital systems leads to the era of “big data”
We are both producers and consumers of data
Data is informative
We need “big theory” to convert data to knowledge
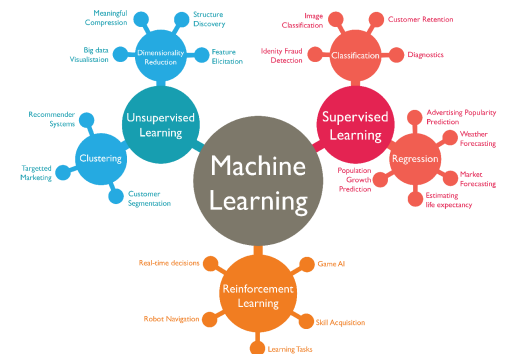
Machine Learning
Machine learning is programming computers to optimize a performance criterion using example data or past experience
Learning general models from a data of particular examples
Advantages:
Ability to review large volumes of data and identify patterns and trends that might not be apparent to a human
Improves the accuracy over time
No need for human intervention (automation)
Categories of Machine Learning
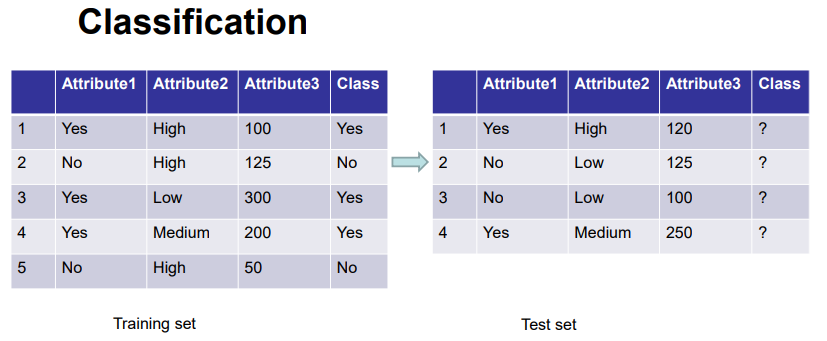
Classification
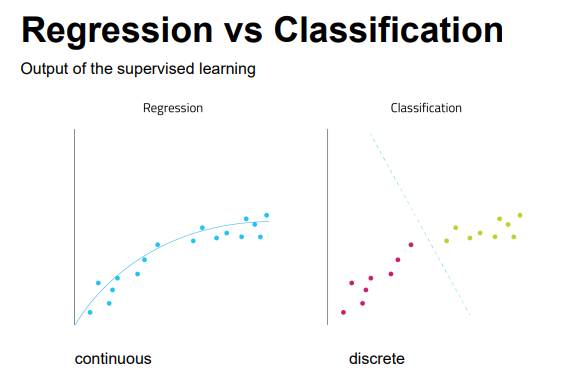
Classification is the task of assigning objects to one of several predefined categories
Given a collection of records (training set)
Each record is by characterized by a tuple (x,y), where x is the attribute set and y is the class label
Task: learn a model that maps each attribute set x into one of the predefined class labels y
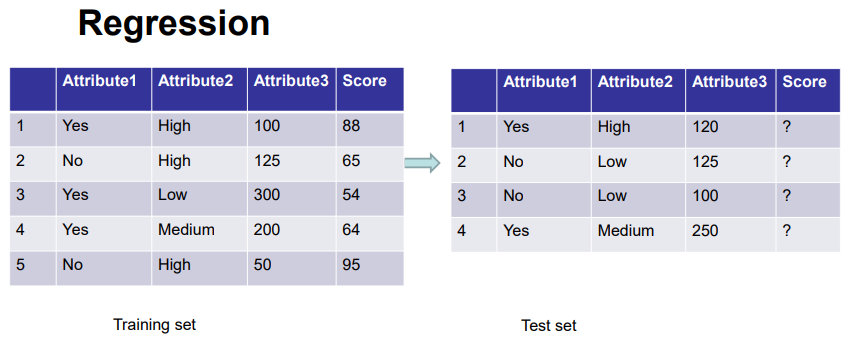
Regression
Regression analysis is a statistical method that helps us to analyze and understand the relationship between two or more variables of interest
The process that is adapted to perform regression analysis helps to understand which factors are important, which factors can be ignored, and how they are influencing each other
Task: learn a model that maps each attribute set into a continuous value
Regression vs. Classification
Clustering
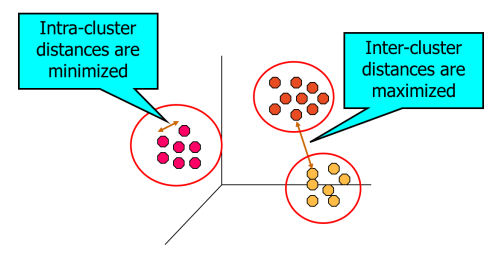
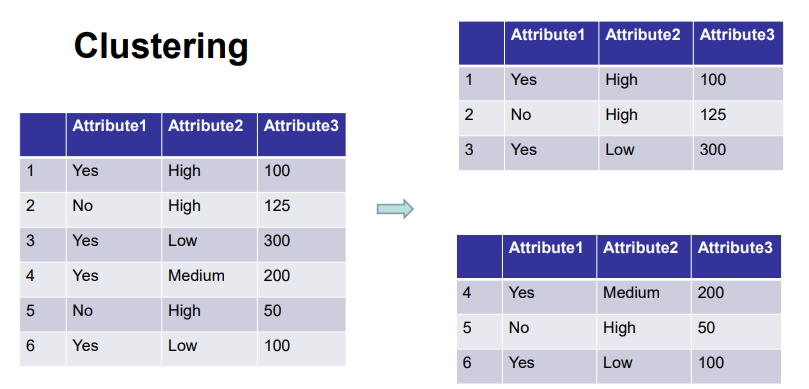
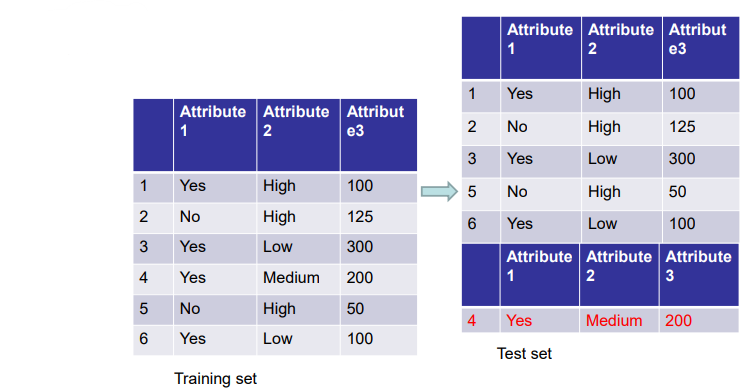
Clustering is finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar (or related) to one another and different from (or unrelated to) the objects in other groups
Examples Spam filters, marketing and sales, and identifying fraudulent or criminal activities
Unsupervised Outlier Detection
An outlier is an observation which deviates so much from the observations as to arouse suspicions that it was generated by a different mechanism
Semantically close to audit terminology such as audit exceptions and transaction anomalies
Often contains useful information about abnormal characteristics of the systems and entities
Abnormal debit/credit amount, occurrence time, counterparty
Possible reasons: mechanical faults, changes in system behavior, fraudulent behavior, human error, etc.
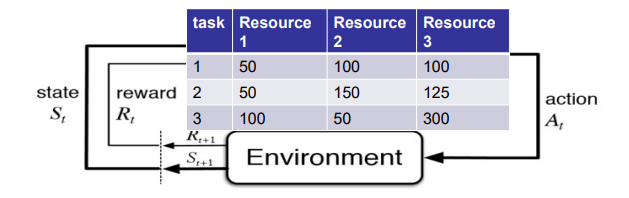
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a machine learning training method based on rewarding desired behaviors and/or punishing undesired ones
In general, a reinforcement learning agent is able to perceive and interpret its environment, take actions and learn through trial and error (e.g., resource management)
Machine Learning Improve Expert Systems
Expert system (rule-based): rather than attempting to identify new patterns and classify data based on statistics or operational experience, they are designed to replicate the problem-solving process of experts in the field
Always based on known rules
A direct application of existing knowledge
Do not attempt to learn directly from the data
Rule-based machine learning (RBML) is a term in computer science intended to encompass any machine learning method that identifies, learns, or evolves 'rules' to store, manipulate or apply

Comments on Adopting Machine Learning
Computers are able to create the system
Learning from the data
The key to success of machine learning applications:
Enough data
Less noisy
Limited time and money
Traditional methods and machine learning can benefit each other
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large language models (LLMs) are a type of artificial intelligence model designed to understand and generate human-like text
They are based on a type of neural network called a transformer, which uses self-attention mechanisms to understand the context and meaning of words in a sentence
A form of task-specific AI, but is highly versatile in natural language processing tasks
Not true AGI but exhibits signs of “General understanding” within the realm of language
Leverages vast amounts of text data to generate coherent and contextually relevant responses
Impressive but limited: lacks consciousness, reasoning like humans, or broad adaptability outside of language
The Development of GPT Models
GPT-2 & Training Controversy
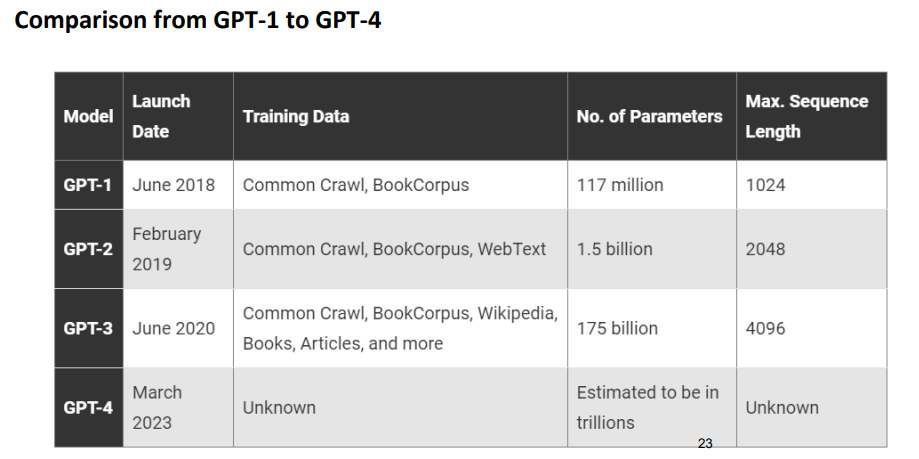
GPT-2, introduced in 2019, was a more sophisticated version with 1.5 billion parameters
It was capable of generating longer and more coherent text
The release of GPT-2 sparked controversy due to concerns about potential misuse for generating fake news and misleading content
GPT-3 & GPT-3.5 Turbo (ChatGPT)
GPT-3, introduced in 2020, was the most advanced model yet, with 175 billion parameters.
It was trained on an enormous corpus of text data, including books, articles, and web pages
GPT-3.5 Turbo (ChatGPT) is a conversational AI model that can engage in human-like conversations, trained on a large corpus of conversational data
GPT-4 & Multimodal Training
GPT-4, introduced in 2023, is a multimodal large language model capable of understanding more than text, such as images
It was pretrained to predict the next token using both public data and data licensed from third-party providers, and then fine-tuned with reinforcement learning from human and AI feedback
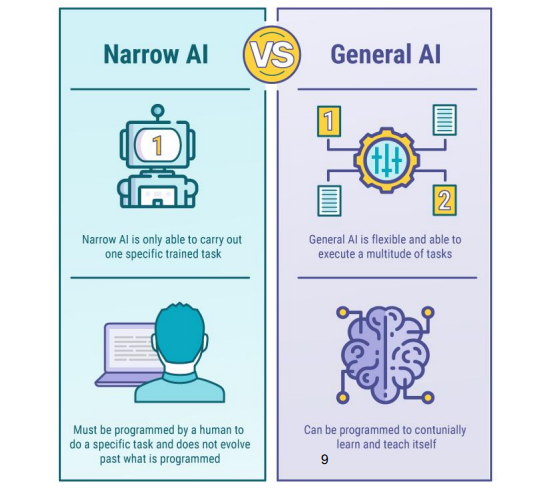
Task-Specific AI vs. General AI
Task-Specific AI (Narrow or Weak AI)
Designed for one specific task
Examples: Siri, facial recognition software
Cannot perform tasks outside its programmed domain
Dominates current AI applications
General AI (Artificial General Intelligence, AGI)
Mimics human cognitive functions
Can perform any intellectual task a human being can
Adaptable to unfamiliar tasks without specific training
Still theoretical; not yet fully realized