Neurogenic Communication Disorders
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
RHD (right hemisphere damage)
visuospatial deficits/visual neglect
anosognosia
prosodic, inferencing, and discourse deficits
sustained & selective attentions deficits
frontal lobe damage
executive function deficits (planning, problem solving, reasoning)
memory loss, consciousness, impulse control
motor planning candor programming
parietal lobe damage
sensory deficits
difficulty reading/writing, spatial relationships
mathematical deficits
temporal lobe damage
deficits in auditory perception/sensation/integration
categorization difficulties, memory & recognition deficits
Broca’s Aphasia
nonfluent
intact comprehension
impaired repetition
Wernicke’s Aphasia
fluent
impaired comprehension
impaired repetition
Transcortical Motor Aphasia
Nonfluent
intact comprehension
intact repetition
Transcortical Sensory Aphasia
Fluent
Impaired comprehension
Intact repetition
Conduction Aphasia
Fluent
Intact comprehension
Impaired repetition
Mixed Transcortical Aphasia
Nonfluent
Impaired comprehension
Intact repetition
Global Aphasia
Nonfluent
Impaired comprehension
Impaired repetition
Anomic Aphasia
only deficit is word retrieval
Fluent
Intact comprehension
Intact repetition
Broca’s Aphasia site of damage
left frontal lobe in the posterior inferior frontal gyrus (left hemisphere)
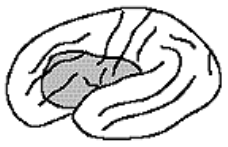
Wernicke’s Aphasia site of damage
left posterior superior temporal gyrus

Transcortical Motor Aphasia site of damage
supplementary motor cortex (anterior to Broca’s area)
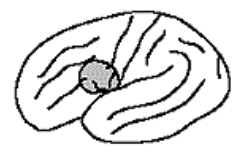
Transcortical Sensory Aphasia site of damage
posterior to wernicke’s area at the temporo-occipital parietal junction

Conduction Aphasia site of damage
supramarginal gyrus of parietal lobe (superior to wernicke’s area)

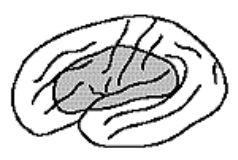
Global Aphasia site of damage
damage to multiple areas & can vary
Flaccid Dysarthria
lower motor neuron
Primary deficit is weakness
hypernasality, nasal emissions, imprecise consonants, breathy, wet, hoarse, monopitch/loud, slow and slurred DDKs, tongue fasciculations
etiologies: stroke, myasthenia gravis,
Spastic Dysarthria
Bilateral UMN
strain-strangled voice, harsh, low pitch, monopitch, excess & equal stress, imprecise consonants
etiologies: CP, bilateral strokes, TBI
Ataxic Dysarthria
Cerebellum
Primary deficit is incoordination
slow & slurred speech, irregular articulatory breakdowns, distorted vowels, excess & equal stress, prolonged phonemes
etiologies: cerebellar stroke/injury/atrophy
Hypokinetic Dysarthria
Basal ganglia (dopamine depletion; extrapyramidal tract)
Primary deficit is rigidity and decreased ROM
rapid rate/short rushes of speech, DDKs fast & imprecise, reduced loudness, reduced stress
etiologies: Parkinson’s
Hyperkinetic Dysarthria
Basal Ganglia (excess dopamine; extrapyramidal)
Primary deficit is involuntary movement
involuntary movements at rest, voice stoppages, prolonged phonemes, variable rate, inappropriate silences
etiologies: Huntington’s
Unliateral UMN
Unilateral UMN
Primary deficit is weakness, incoordination, spasticity
unilateral facial weakness, harsh voice, articulatory imprecision, slow rate
etiologies: Unilateral CVA