6A Stimuli and Response
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is a stimulus?
A change in the internal or external environment.
What is a receptor?
Cells or proteins on cell membranes that detect a stimulus.
What are effectors?
Cells that bring about a response to a stimulus
How do receptors communicate with effectors?
Via the nervous system or hormonal system
What are the three types of neurones?
sensory neurones- transmit electrical impulses from receptors to the CNS.
motor neurones- transmit electrical impulses from the CNS to effectors
relay neurones- transmit electrical impulses between sensory neurones and motor neurones.
What is the central nervous system?
The brain and spinal cord.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The neurones that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
It is split into the somatic nervous system, which controls conscious activities, and the automatic nervous system, which controls unconscious activities.
The automatic nervous system is then split into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system gets the body ready for actions; the parasympathetic nervous system calms the body down.
What is a reflex?
A rapid, unconscious response to a stimulus.
Describe a simple reflex arc for a hand touching something hot.
thermoreceptors in the hand detect the heat stimulus.
the sensory neurones carries impulses to the relay neurone.
the relay neurone connects and passes the impulses to the motor neurone.
the motor neurone sends impulses to the effector- your bicep.
the bicep contracts to draw the hand away from the heat and prevent damage.
When is it possible to override a reflex?
If there is a relay neurone involved in the reflex arc, eg. then your brain could tell your hand to withstand the heat.
What are the 3 factors of nervous system communication?
It is localised, short-term and rapid.
What is a tropism?
The response of a plant to a directional stimulus.
How do plants respond to directional stimuli?
Using growth factors- chemicals that speed up or slow down plant growth.
What is IAA?
An auxin- it is produced in the shoots of flowering plants and moves by diffusion, active transport and through the phloem around the plant.
How does phototropism occur?
IAA moves to more shaded parts of the shoots/roots, causing uneven growth.
In shoots, the shaded parts elongate, causing the plant to bend towards the light.
In roots, growth is inhibited in the shaded parts, causing the root to bend away from the light.
How does gravitropism occur?
IAA moves to the underside of roots and shoots.
In shoots, IAA concentration increases on the lower side, causing cells to elongate and the shoots to bend upwards.
In roots, IAA concentration increases on the lower side, inhibiting growth so the root bends downwards.
What is a tactic response?
taxis- the organisms move towards or away from a directional stimulus. Eg. woodlice move away from a light source.
What is a kinetic response?
kinesis- the organisms’ movement is affected by a non-directional stimulus. Eg. in high humidity, woodlice move slower and turn less often so they will stay where they are in the desirable conditions.
What can be used to investigate animal responses to stimulus?
A choice chamber
How do receptor cells that communicate via the nervous system work?
when a receptor is in its resting state, there is a difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell. Therefore there is a potential difference across the membrane.
when a stimulus is detected, the cell membrane is excited and becomes more permeable, allowing more ions to move in and out of the cell, altering the potential difference. The change in potential difference is the generator potential.
if the generator potential is big enough, an action potential will be triggered. This is an electrical impulse along a neurone, and is only triggered if the generator potential reaches a threshold level.
What happens if the stimulus is too weak?
the generator potential won’t reach the threshold so an action potential will not be triggered.
How is the strength of the stimulus measured?
Action potentials are all the same size, so strength of stimulus is the frequency of action potentials.
What are the pressure receptors in your skin known as?
Pacinian corpuscles
Describe a pacinian corpuscle.
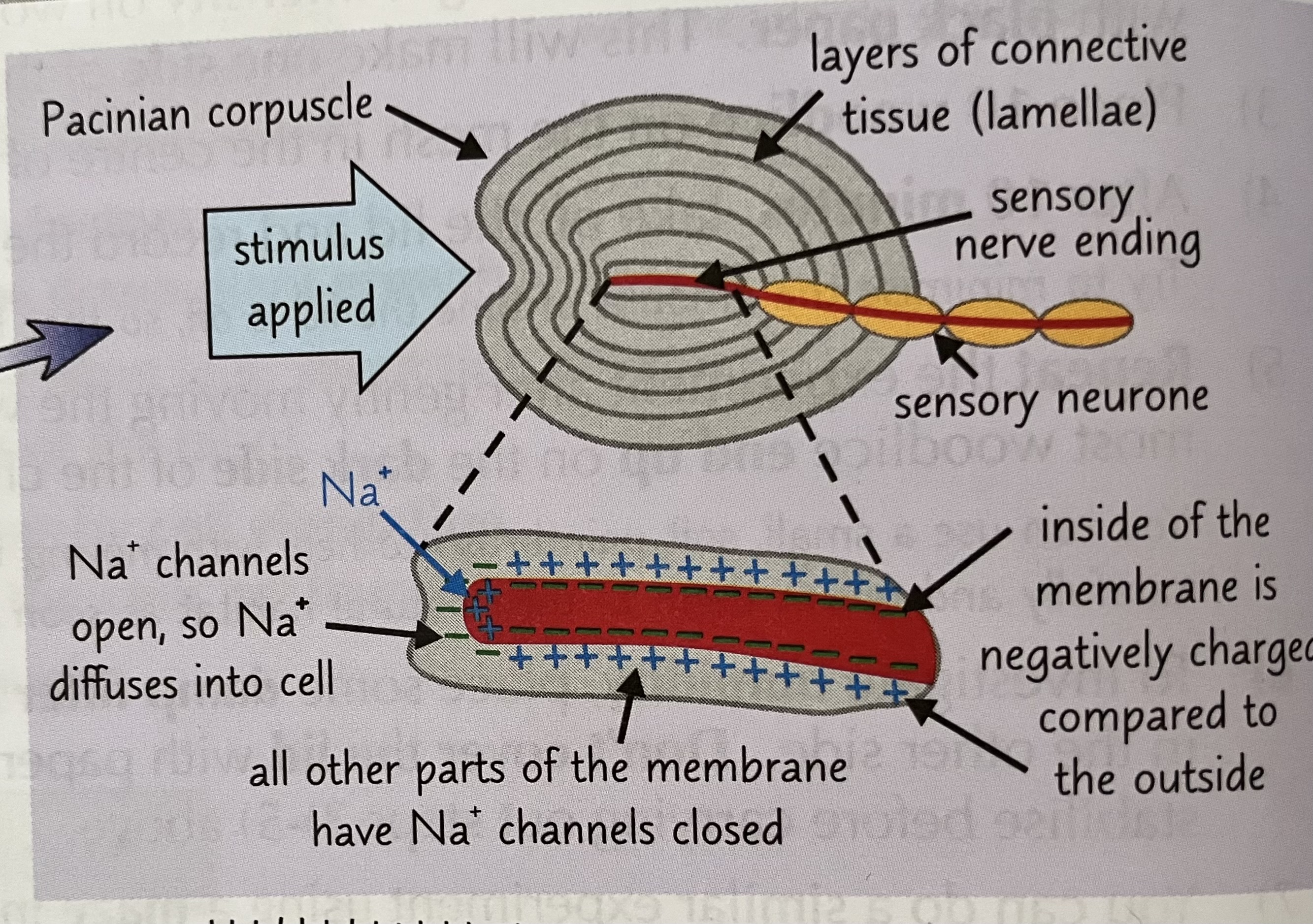
a mechanoreceptor found in the skin. They contain a sensory nerve ending wrapped in lamellae. When the corpuscle is stimulated, the lamellae are deformed and press on the nerve ending. This causes the sensory neurone’s cell membrane to stretch, deforming the sodium ion channels so they open and sodium ions move into the cell and create a generator potential. If the generator potential reaches the threshold, an action potential is triggered.
Describe how light acts as a stimulus in the eye.
light enters through the pupil. The amount of light that enters is controlled by the muscles of the iris. Light rays are focused by the lens onto the retina, which contains photoreceptor cells that detect light. The fovea is an area of the retina with many photoreceptors.
Nerve impulses are carried from the retina to the brain by the optic nerve. There is a blind spot where the optic nerve meets the eye as there are no photoreceptors here.
How do photoreceptors convert light into an electrical impulse?
light hits the photoreceptors and is absorbed by light-sensitive optical pigments.
light bleaches the pigments, causing a chemical change that alters the membrane permeability and creates a generator potential.
if the threshold is reached, a nerve impulse is sent along a bipolar neurone that connects to the optic nerve and sends impulses to the brain.
Describe rods.
rods are mainly found in the peripheral part of the retina and only give information in black and white.
rods are very sensitive to light because many rods join one neurone, so many weak generator potentials combine to reach the threshold and trigger an action potential.
rods give low visual acuity because many rods join the same neurone, which means lights from two points close together can’t be told apart.
describe cones.
cones are found packed together in the fovea. they give trichromatic vision- there are three types of cone that each contain a different optical pigment so there are red-sensitive, green-sensitive and blue-sensitive cones.
cones are less sensitive to light because one cone connects to one neurone so it takes more light to reach the threshold and trigger an action potential.
cones give high visual acuity because cones are close together and one cone joins one neurone, so two points close together can be distinguished as two separate points.
How is the beating of the heart controlled?
MYOGENIC
The sinoatrial node in the wall of the right atrium sets the rhythm of the heartbeat by sending out regular waves of electrical acitivity.
This causes the left and right atria to contract at the same time.
A band of non-conducting collagen tissue prevents the waves from being passed directly to the ventricles.
The waves are transferred to the atrioventricular node that then passes the electrical activity to the Bundle of His.
The bundle of His splits into purkyne tissue that carries waves of electrical activity into the muscular walls of the ventricles and causes them to contract simultaneously.
Why is there a slight delay before the AVN reacts to the waves of electrical activity?
to make sure the atria have emptied before the ventricles contract
What is purkyne tissue?
fine muscle fibres
Where are pressure receptors for the cardiovascular system found?
baroreceptors- in the aorta and the carotid arteries. They are stimulated by high and low blood pressure.
Where are chemical receptors of the cardiovascular system found?
chemoreceptors- found in the aorta, carotid arteries and the medulla. They monitor carbon dioxide concentration and pH.
How would the heart respond to high blood pressure?
detected by baroreceptors
impulses are sent to the medulla, which sends impulses along the parasympathetic neurones. These secrete acetylcholine which binds to receptors on the SAN.
Heart rate slows down to reduce blood pressure.
How would the heart respond to low blood pressure?
detected by baroreceptors
impulses sent to the medulla, which sends impulses along sympathetic neurones. These secrete noradrenaline, which binds to receptors on the SAN.
heart rate speeds up to increase blood pressure back to normal.
How would the heart respond to high oxygen or low carbon dioxide?
What pH would give the same response?
detected by chemoreceptors.
impulses are sent to the medulla, which sends impulses along the parasympathetic neurones. These secrete acetylcholine, which binds to receptors on the SAN.
Heart rate decreases to return blood levels back to normal.
high pH would give the same response.
How would the heart respond to low oxygen or high carbon dioxide?
Which pH would give the same response?
detected by chemoreceptors.
impulses are sent to the medulla, which sends impulses along the sympathetic nervous system. This secretes noradrenaline, which binds to receptors on the SAN.
Heart rate increases to return blood levels back to normal.
Low pH would give the same response.
Which pigment is found in the rods?
rhodopsin
Which pigment is found in the cones?
iodopsin