Biology (5.3): Neuronal communication
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
sensory receptors
cells/sensory nerve endings that respond to a stimulus in the internal or external environment of an organism and can create action potentials
transducer
a cell that converts one form of energy into another
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with a change in light intensity? (2)
light sensitive cells (rods and cones) in the retina
light to electrical
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with a change in temperature? (2)
temperature receptors in the skin and hypothalamus
heat to electrical
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with a change in pressure on the skin? (2)
Pacinian corpuscles in the skin
movement to electrical
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with a change in sound? (2)
vibration receptors in cochlea of the ear
movement to electrical
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with movement? (2)
hair cells in inner ear
movement to electrical
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with a change in length of muscle?
muscle spindles in skeletal muscles
movement to electrical
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with chemicals in the air?
olfactory cells in epithelium lining the nose
detect a chemical and create an electrical nerve impulse
What is the sensory receptor and energy change involved with chemicals in food? (2)
chemical receptors in taste buds on tongue
detect a chemical and create an electrical nerve impulse
Pacinian corpuscles
a pressure sensor that detects change in pressure on the skin
What kind of receptor is a Pacinian corpuscle?
mechanoreceptor
Characteristics of a corpuscle (2)
oval-shaped structure
series of cocentric rings of connective tissue wrapped around the end of a nerve cell
What happens to a Pacinian corpuscle when the pressure on the skin changes?
it deforms the rings of connective tissue, which push against the nerve ending
What happens to the corpuscle when the pressure is constant?
it stops responding
What are the two kinds of specialised channel proteins found in cells associated with the nervous system?
sodium and potassium channels
What kind of sodium channels are found in a Pacinian corpuscle?
stretch-mediated
What happens when the rings are deformed?
the sodium ion channels open and sodium ions diffuse into the cell, creating a generator potential
When is an action potential triggered?
If the generator potential reaches the threshold value
What do sodium potassium pumps do?
actively pump sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell
How many sodium ions are pumped out for every two potassium ions that are pumped into the cell?
3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions in
Why do potassium ions leak out of the cell?
because the membrane is permeable to potassium ions
What is the potential gradient formed across the membrane?
cell more negatively charged than outside the cell
What is the cell called when it is inactive?
polarised (-vely charged inside compared with the outside)
depolarisation
the inside of the cell becomes less negative compared with the outside (due to the movement of ions across the membrane)
What happens to the membranes to cause an action potential?
if enough gates are opened and enough sodium ions enter the cell, the potential difference across the membrane changes significantly and will initiate an impulse (action potential)
sensory neurones
carry the action potential from a sensory receptor to the CNS
relay neurones
connect sensory and motor neurones
motor neurones
carry action potentials from the CNS to an effector
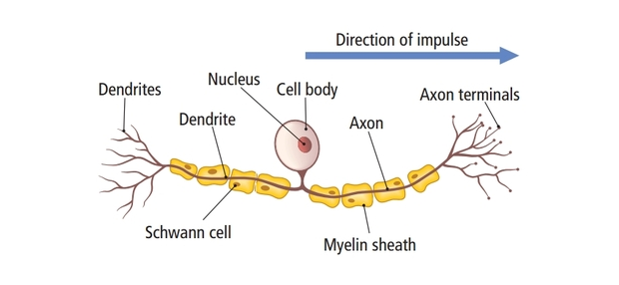
What type of neurone is this?
sensory neurone

What type of neurone is this?
motor
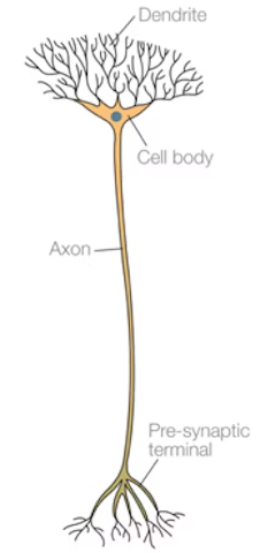
What type of neurone is this?
relay
Axon
carries impulses away from the cell body
What does the cell body of a neurone contain?
nucleus, many mitochondia and ribosomes
Dendrites
carry impulses towards the cell body
myelinated neurones
are insulated by the myelin sheath
motor neurone (structural differences) (2)
cell body in CNS
long axon (that carries AP to effector)
sensory neurone (structural differences) (2)
long dendron
short axon
relay neurone (structural differences) (2)
many short dendrites
short axon
Schwann cells
make up the myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in between the Schwann cells
What does myelination do to the AP?
Makes the AP jump from one node to the next, so conduction is more rapid
Advantages of myelination (2)
can transmit AP quickly over long distances
enables rapid response to stimulus
action potential
a brief reversal of the potential across the membrane of a neurone causing a peak of +40 mV compared to the resting potential of -60 mV
resting potential
the potential difference across the membrane while the neurone is at rest
What kind of response are action potentials?
all-or-nothing
Stages of an action potential (13)
membrane in resting state (polarised), Na+ conc outside>inside & K+ conc inside>outside
Na ion channels open
Na ions diffuse into cell
membrane depolarises
voltage-gated sodium ion channels open
cell becomes more positively charged inside
p.d reaches +40(ish)mV (inside of cell positive compared to outside)
Na ion channels close
K ion channels open
K ions diffuse out of cell
p.d back to -ve inside compared with outside (repolarisation)
p.d overshoots, cell hyperpolarised
original p.d restored & cell returns to resting state
refractory period
period of recovery during hyperpolarisation when the ion channels are closed
How are local currents formed?
when Na ions move along the neurone towards regions where their conc is lower (causing slight depolarisation of the membrane)
Steps in the formation of local currents (6)
Na ion channels open
Na ions diffuse into neurone
localised increases in Na ion conc inside neurone (AP)
Na ions diffuse along axon/dendron
Na gate open due to movement of Na ions
AP moves along neurone as more Na ions enter
What is it called when the action potentials appear to jump from one node to the next?
saltatory conduction
Advantage of saltatory conduction
speeds up transmission of AP along the neurone
How does the brain determine the intensity of a stimulus?
from the frequency of APs arriving in the sensory region of the brain
A higher frequency of APs means …
a more intense stimulus
Synapse
junction between 2 or more neurones where one neurone can communicate with, or signal to, another neurone
What is the small gap between 2 neurones called?
synaptic cleft
Cholinergic synapse
a synapse that uses acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter
neurotransmitter
a chemical used as a signalling molecule between two neurones in a synapse
Specialised features of the pre-synaptic bulb (4)
many mitochondria
large amount of SER (packages neurotransmitter into vesicles)
lots of vesicles
voltage-gated Ca ion channels
What does the post-synaptic membrane contain? (2)
Na ion channels
receptor sites with complementary shape to neurotransmitter
Stages of the transmission across a synapse (12)
AP arrives at synaptic bulb
voltage-gated Ca ion channels open
Ca ions diffuse into synaptic bulb
Ca ions cause synaptic vesicles to fuse with pre-synaptic membrane
ACh released by exocytosis
ACh molecules diffuse across cleft
ACh binds to receptor sites on Na ion channels in post-synaptic membrane
Na ion channels open
Na ions diffuse across post-synaptic membrane into post-synaptic neurone
GP created
if sufficient GPs combine potential reaches threshold potential
new AP created in post-synaptic neurone
acetylcholinesterase
an enzyme found in the synaptic cleft that hydrolyses acetylcholine to ethanoic acid and choline
What happens to the ethanoic acid and choline?
They are recycled (re-enter the synaptic bulb by diffusion and are recombined to ACh using ATP)
When does summation occur?
when the effects of several excitatory post-synaptic potentials (EPSPs) are added together
excitatory synapse
neurotransmitters depolarise the postsynaptic membrane, making it fire an AP if the threshold is reached
inhibitory synapse
when neurotransmitters bind to the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, they hyperpolarise the membrane (more -ve) preventing an AP from being fired
synaptic divergence
when one neurone connects to many neurones so information is dispersed to different parts of the body
synaptic convergence
when many neurones connect to one neurone so information is amplified
spatial summation
when neurones converge, so several pre-synaptic neurones contribute to producing an AP in the post-synaptic neurone
temporal summation
two or more nerve impulses arrive in quick succession from the same presynaptic neurone
Habituated
After repeated stimulation a synapse may run out of vesicles containing the neurotransmitter so the nervous system no longer responds to the stimulus