AQA GCSE DT - Polymers
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Core technical principles + specialist technical principles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the 2 types of polymers?
Thermosetting + thermoforming polymers
What is a thermoforming polymer?
= type of polymer that can be reheated and reshaped multiple times
What are the main properties of a thermoforming polymer? (Name 3)
Recyclable
Pliable (flexible & easy to bend)
Good impact resistance
What are 4 examples of thermoforming polymers?
Acrylic (PMMA)
Polypropylene (PP)
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
Polyethylene (PE)
What are thermosetting polymers?
= type of polymers that cannot be reshaped after heating and shaping it once
What are some properties of thermosetting polymers? (Name 4)
Heat-resistant
Electrical insulators
Durable
Brittle
What are 3 examples of thermosetting polymers?
Epoxy resin
Urea formaldehyde
Melamine formaldehyde
What is the primary source of most polymers?
Crude oil
How is crude oil refined?
Through fractional distillation
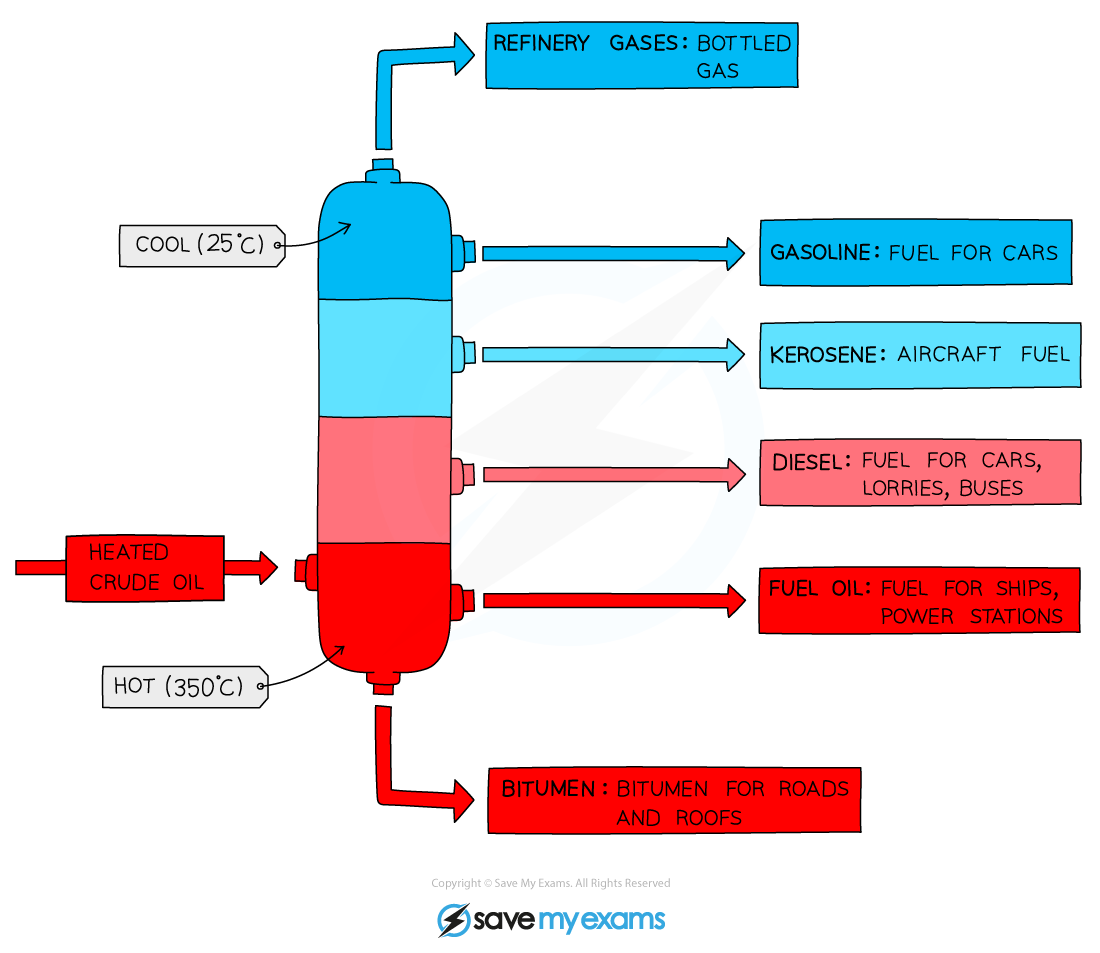
Outline the 5 main steps of fractional distillation
Crude oil is heated until it becomes a vapour
Vapours rise up the distillation column
Column cools and different hydrocarbons condense at different temps
Seperated into different fractions & drawn off for further processing
What is cracking?
= breaking down large hydrocarbons into smaller ones used in polymer production (eg. Propylene)
What type of polymer is best suited for seating and why? (name 3 properties it must have)
Polypropylene:
Flexibility - user can adjust in seat without breaking it
Impact resistance - prevents damage from sudden force (sitting on it abruptly)
Heat resistance - can withstand temp changes (outdoor use/exposure to sun)
What type of polymer is best suited for electrical fittings and why? (name 3 properties it must have)
Urea formaldehyde:
Insulating properties - avoids risk of short circuits or shocks
Rigidity - electrical components can maintain shape under stress & pressure
Heat resistance - can withstand high temperatures from electrical components
What are polymer stabilisers & what are they used for?
= additives to prevent degradation & discolouration from UV sunlight exposure
When are polymer stabilisers commonly used?
Outdoor products - improves durability
What equipment can be used for cutting/drilling polymers?
Saws
Laser cutters
Standard drill bits
What is polymer casting? + what type of polymer is it used for?
Liquid polymer poured into moulds - used for thermosetting polymers
What is polymer deforming?
= heating thermoforming polymers to reshape them (eg. Vacuum forming)
What is polymer welding? + what are the 3 main types?
= joining polymers through: heat welding, solvent welding, ultrasonic welding
Outline the process of injection moulding in 4 main steps
Granules held in a hopper
Granules are heated and melted along a heating chamber via Archimedean screw
Melted polymer pushed into mould with a hydraulic ram
Mould cools, polymer solidifies and product is ejected
Outline the process of extrusion in 4 main steps
Granules held in a hopper
Granules are heated and melted along a heating chamber via Archimedean screw
Melted polymer pushed through a die mould
After cooling in cooling chamber, extruded plastic is cut to desired length
Outline 3 surface finishes that can be applied to polymers
Vinyl decals = adhesive vinyl decals applied for custom designs/brand logos
Polishing = smooths & enhances gloss of (mainly) thermoforming polymers
Printing = adding decorative/informational text - methods eg. screen printing, laser printing
What are 2 environmental issues caused by using polymers?
Most are non-biodegradable → disposal contributes to pollution
Fractional distillation & cracking are very energy extensive → high CO2 emissions
What are 2 challenges to consider when recycling polymers?
Contamination: If polymers aren’t sorted/cleaned properly → affects quality of recycled material
Downcycling: Recycled polymers often have inferior properties compared to virgin plastics → leading to lower-quality products
What are some alternatives to traditional polymers?
Bioplastics: Made from renewable sources such as plant materials instead of fossil fuels.
Plant based polymers: such as PHA
What are 3 ways to reduce polymer use?
Design for the Environment: designing products that use less material & can be recycled
Longevity and Reusability: Creating durable products that can be reused
Legislation: introducing plastic bans (e.g., banning single-use plastic bags or straws)