biochem 3: hepatic metabolism
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
in basal fasting state, _____ is the primary source of serum glucose, and _______ provide additional energy.
glycogen and fatty acids
______ becomes important as the fast progresses
gluconeogenesis
In the starved fasting state, _____ is provided by gluconeogenesis. _______ become a significant source of energy for the brain, and other tissues rely largely on ______
glucose, ketone bodies, and other tissues rely largely on fatty acids
Defects in energy metabolism are generally inherited in an _______ and most often present in ________.
autosomal recessive manner, infancy or early childhood.
If not successfully treated, most of these can result in _____ due to ____ or _____
permanent brain damage due to severe hypoglycemia or liver damage.
carbohydrate disorders include
galactosemia
essential fructosuria
heritable fructose intolerance
glycogen storage diseases
pyruvate kinase deficiency
lipid disorders
medium-chain acyl coA dehydrogenase deficiency
Defects in galactose metabolism are detected in the _______
first few days after birth
symptoms include
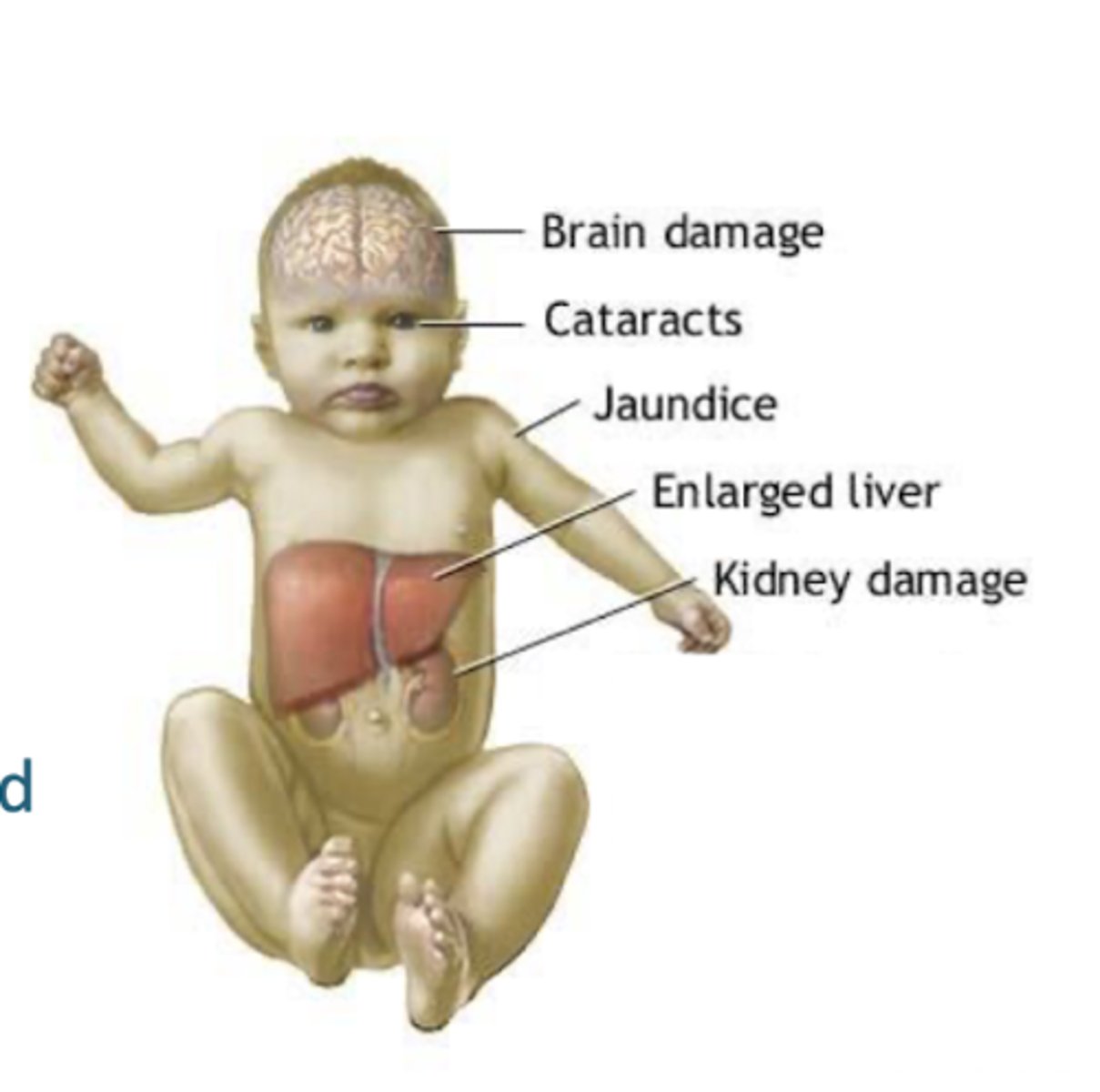
vomiting, refusal to eat, jaundice, and cataracts (if treatment is not begun soon enough).
Galactose accumulates in both forms of galactosemia, and is converted to ______ in most tissues. Result is ______ leading to cataracts and possible _______
galactitol, osmolar imbalance, cataracts and kidney damage
in classic glactosemia, ________ also accumulates, which is toxic to the _______
galactose 1-phosphate, liver
treatment of galactosemia - Dietary restriction of _____. patients are at higher risk for deficiencies in ____ and ____
lactose dairy products; At higher risk for deficiencies in Calcium and Vitamin D
what mechanism is shut down in classical galactosemia? _____ to ____ with _____
Galactose 1 phosphate to glucose 1 phosphate with galactose 1-phosphate uridylytransferase
what mechanism is shut down in non-classical galactosemia
galactose --> galactose 1 phosphate with galactokinase
Fructose metabolism occurs almost exclusively in the _____, and is not subject to regulation except at ______
liver and is not subject to regulation, except at pyruvate kinase
fructose catabolism produces high quantities of ______ and _____, which combine to form ______
glycerol phosphate and fatty acids, which combine to form TAG
fructose consumption is associated with
hypertriglyceridemia
TG can be exported in VLDL, or remain in the liver and cause
steatosis
rapid and unregulated _________ by fructokinase with low concentrations of ________ result in high quantities of_____
unregulated conversion of ATP to ADP by fructokinase, together with low concentrations of inorganic phosphate (Pi) result in production of high quantities of uric acid
hyperuricemia is associated with
gout, kidney stones, HTN, CVD, insulin resistance
Defects in fructose metabolism are generally not detected until after
a child begins to wean.
Hereditary fructose intolerance can cause ________, while essential fructosuria is ________
severe hypoglycemia, while essential fructosuria is asymptomatic.
what mechanism is shut down in essential fructosuria
fructose --> fructose 1 P using fructokinase
what mechanism is shut down in hereditary fructose intolerance?
fructose 1 P --> glyceraldehyde with aldolase B
essential fructosuria
fructokinase
hereditary fructose intolerance -
aldose b deficiency
fructose 1 phosphate is toxic to the _____. it ties up _____, thus inhibiting ______ and ______
liver; phosphate, thus inhibiting ATP synthesis, and it inhibits glycogen phosphorylase
glycogen is a ______ structure and that synthesis involves _____ and _______
highly branched structure, and that synthesis involves glycogen synthase and branching enzyme
glycogenolysis requires the activity of
glycogen phosphorylase and debranching enzyme
glucose-6-phosphatase is required for release of
glucose from hepatocytes
there are several glycogen storage diseases (GSD) that can cause severe _______ and can often be treated by _______
severe fasting hypoglycemia, can often be treated by dietary modification
type 0 will be a deficiency in
glycogen synthase
glycogen synthase causes
fasting hypoglycemia and fed state hyperglycemia
type 1a is a deficiency in
glucose 6 phosphatase
type 1a deficiency causes
fasting hypoglycemic, glycogen accumulation in liver, hyperlipidemia
type III is a def in
debranching enzyme
type III causes
fasting hypoglycemia, glycogen accumulation in liver, glycogen with short outer branches
type IV is a def in
branching enzyme
type IV will cause
fasting hypoglycemia, glycogen accumulation in liver, glycogen with long outer branches
type VI is a def in
glycogen phosphorylase
type VI will cause
gasting hypoglycemia, glycogen accumulation in liver
dietary modifications for glycogen storage disease (GSD)
Avoid fasting
Low carb diet
Uncooked cornstarch or intragastric feeding at night
Decrease amount of glycogen stored in liver
The most common inborn error in metabolism is a defect in ______, called _____
fatty acid catabolism; medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.
deficiency in MCAD causes
Decreased ability of hepatocytes to generate energy for gluconeogenesis from fatty acids
Decreased ability of hepatocytes to generate ketone bodies
Accumulation of medium chain fatty acids in the liver
Decreased ability of hepatocytes to generate energy for gluconeogenesis from fatty acids, leading to
fasting hypoglycemia
Decreased ability of hepatocytes to generate ketone bodies leading to
leading to fasting hypoketonemia
Accumulation of medium chain fatty acids in the liver -
- these appear to be toxic to the mitochondria and can cause liver damage.
dietary management to MCAD
High carb diet & frequent feeding
the liver is the prinicpal site of ______ in humans
AA synthesis
liver contains all pathways for _____ of all ____, can convert the ___ to either ____ or _____
catabolism if all amino acids, and can convert the carbon skeletons to either glucose or fatty acids/ketone bodies
liver contrains the urea cycle, which converts ______ generated in AA metabolism (in liver AND extrahepatic tissues) to ______
Contains the urea cycle, which converts toxic ammonium ions generated in amino acid metabolism (in the liver AND extrahepatic tissues) to urea for excretion in the urine.
liver processes _____ generated in the gut by enteric and bacteralial catabolism of _______
Processes ammonium ions generated in the gut (by enteric and bacterial catabolism of glutamine)
liver produces nitrogen containing compounds, such as
nucleotides and heme
liver synthesizes the majority of
serum proteins
Hyperammonemia is a symptom of
urea cycle defects and certain liver diseases.
Liver cirrhosis also increases
serum levels of various amino acids.
In newborns with hyperammonemia, a ______ should be considered.
urea cycle defect
________ is the result of increased ammonia due to _______
Hepatic encephalopathy is the result of increased ammonia (and possibly other neural toxins, including some amino acids) due to cirrhosis of the liver.
Portosystemic shunting in cirrhosis decreases ________ and _______. generally, _____ and ____ are elevated
hepatic uptake of amino acids (which may be elevated to begin with due to a hypercatabolic state) and enteric ammonium ions. Generally, aromatic amino acids and methionine are elevated.
defects in ____ and ____ catabolism are associated with a number of diseases
phe and tyr
Phe is hydroxylated to Tyr by _______. Deficiencies in the hydroxylase or its cofactor, ______, results in ______
phenylalanine hydroxylase; tetrahydrobiopterin, result in PKU.
Accumulated phe inhibits transport of _________ causing altered _______ and leading to problems in ________
other large hydrophobic amino acids into the brain; neurotransmitter synthesis leading to problems in psychomotor development.
PKU will also cause decreased synthesis of ______, which may also cause _______ in older patients
catecholamines, mood disorders in older patients
phenypyruvate, produced by _______, accumulates in the serum and urine and causes a _______
transamination of phe, causing musky odor
Tyr is the precursor of
melanin - albinism
treatment involves
Restriction of dietary phe, and sometimes supplementation with large hydrophobic amino acids.
Phe is an
essential amino acid
tyrosinemia I and II and alcaptonuria are more rare than
PKU
tyrosinemia I and II present in _____.
infancy
tyrosinemia type I is associated with ______, ______, and death within the first year of life
liver failure, cabbage-like body odor, and death within the first year of life.
tyrosinemia I mechanism -
homogentisate --> fumarate and acetoacetate via fumarylacetoaetate hydrolase
type II may cause _____ and _____ problems
eye and skin lesions and neuro problems
tyrosinemia II occurs from what mechanism?
tyrosine --> p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate via tyrosine aminotransferase
alcaptonuria results in accumulation of _______, which oxidizes in ______ causing it to turn ______
homogentisate, which oxidizes in urine, causing it to turn dark red.
mechanism of alcaptonuria -
homogentisate --> fumarate and acetoacetate via homogentisate oxidase
later in life, accumulation in _____ may cause ______
cartilage may cause arthritic joint pain
in maple syrup disease, a _______ is deficient
alpha-keto dehydrogenase
the _____ and their _____ products accumulate
The branched chain amino acids and their alpha-keto transamination products accumulate.
maple syrup disease affects the bodys ability to break down certain amino acids -
leucine, isoleucine, and valine —
inability to breakdown certain AA will lead to their
toxic buildup in the blood and brain.
accumulation of ____ leads to ______ and death within _____ if untreated.
alpha-keto acids leads to severe neurological problems (death within 1 year if untreated)
treatment requires restriction of
dietary branched chain amino acids
careful management of hypercatabolic states (avoid fasting)
what diet is treatment for maple syrup disease
Low protein diet with carefully managed levels of leucine, isoleucine, and valine.