Science Laboratory
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
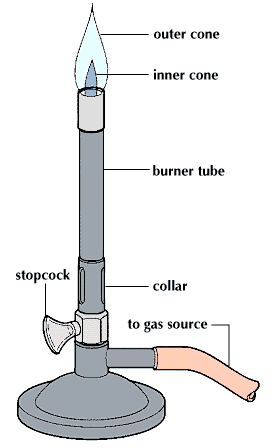
Bunsen Burner
To raise a flame above the table surface high enough for heating. It is a type of ambient air gas burner used for burning, sterilization, and combustion.
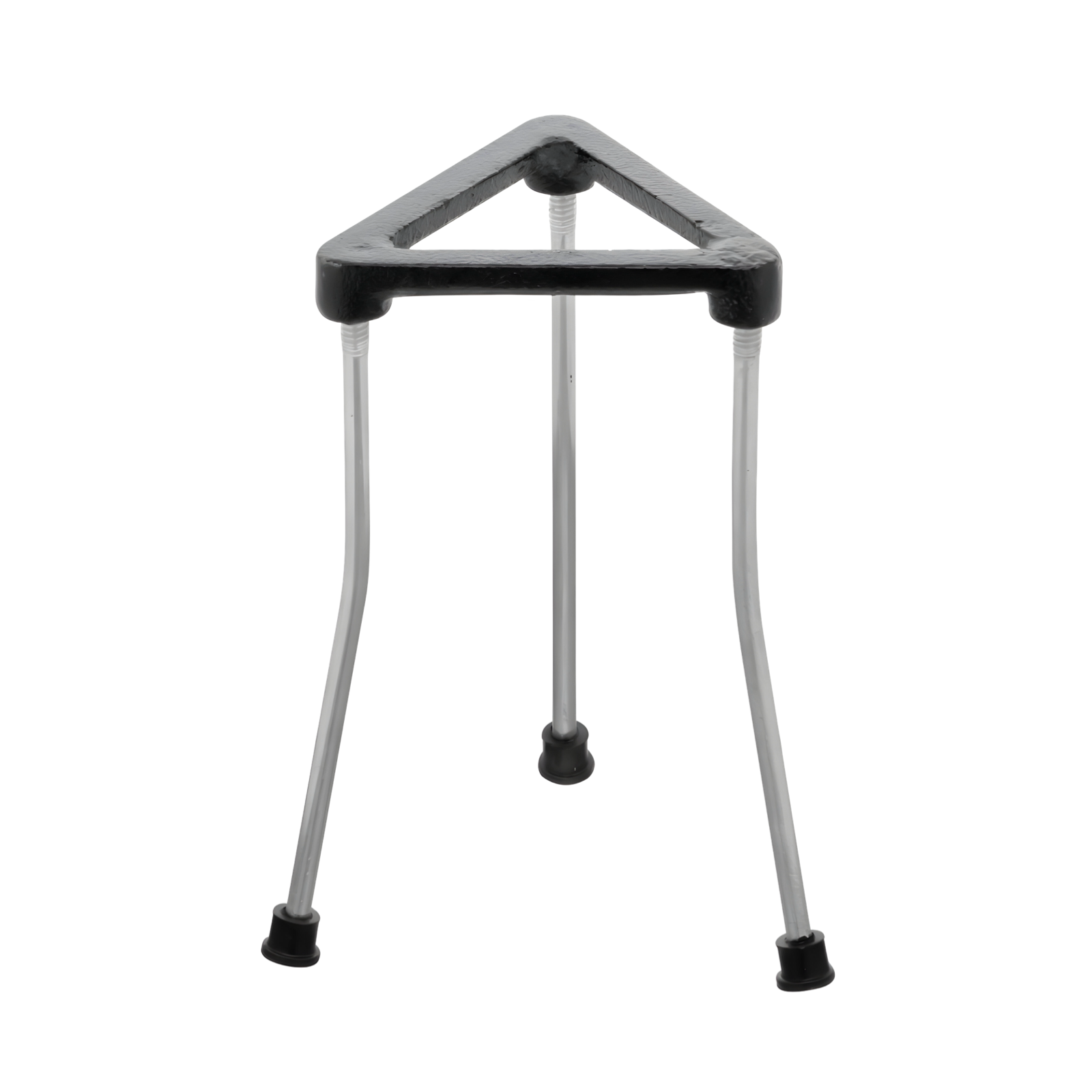

Tripod Stand
To support the apparatus during heating. To stabilize glassware and equipment during experiments, providing a stable base for beakers, flasks, and other items.

Retort Stand
To support apparatus during experiments. To securely hold and support various pieces of glassware and equipment, for measuring, filtration, and etc.

Test Tube
Test tubes are to contain or mix chemicals together and to mix solutions and liquids. They are also used for heating small amounts of chemicals or biological samples. They are very thin and long — but unsuitable for burning.

Beaker
To contain chemicals and to contain liquids. They are also used for holding, mixing, heating and measuring liquids.
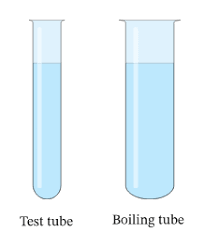
Boiling tubes
To contain chemicals for strong heating and to collect and hold liquids. It’s a type of laboratory glassware whereas they are used for heating substances, often in the flame of a bunsen burner. They are thicker, longer and bigger.
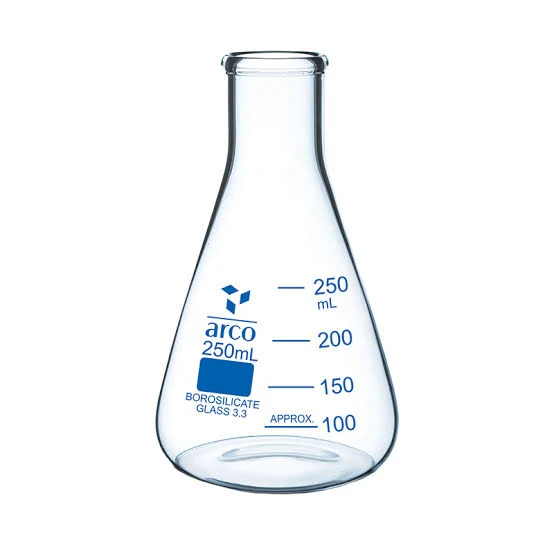

Conical flask
Conical flasks are to contain and mix chemicals and liquids. They are also used for transporting liquids without splashing — allowing for swishing and swirling inside of the flask.

Filter funnel
To transform liquids into containers with a small opening, and to separate solids from liquids. It is usually used in a separating method called filtration.

Bell jar
Bell jars are to separate the set up of an experiment from its surroundings. It is to create and maintain a vacuum environment, allowing for experiments involving gases, chemical reactions, and etc under controlled conditions.

Evaporating dish
The evaporating dish is to evaporate the liquid in a solution over a Bunsen burner. Mainly used to leave behind a solid residue inside of the dish.

Gas jar
Gas jars are usually to collect gas, also to store, transport, and examine specimens. Used to study the behaviour of gases in a controlled environment.