Body Fluid Compartments
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Sources of water intake
1) Ingested in form of liquid and food (2.1L)
2) Produced during metabolism (0.2L)
Total water intake
2.3L
Factors affecting water intake
Climate, habit and amount of physical activity
Sources of loss of water
1) Insensible loss (700ml) through skin and lungs (350ml each)
2) Fluid loss in sweat (100ml)
3) Water loss in feces (100ml)
4) Water loss in kidney (1400)
Insensible water loss through skin prevented by
Cholestrol filled cornified layer of skin (Incase of burns the layer is disrupted so leads to 3-5L body fluid loss)
Dryness in winter due to
Increased insensible water loss through lungs
Factors affecting fluid loss through sweat
Physical activity and temperature
Transcellular fluid
Synovial, peritoneal, pericardial, intraocular space fuids and CSF. It constitutes abt 1-2L
Body Fluid Distribution
¾ Intracellular fluid(40% body wt)
¼ Extracellular fluid(20% body wt)
Extracellular is further divided into interstitial fluid(11L), plasma(3L) and transcellular fluid
Factors affecting the contribution of fluids to body weight
Age, gender and degree of obesity
Body fluid contribution more in
1) males or females
2) Newborns or old people
3) Skinny or obese
1) Men
2) Newborns
3) Skinny
Higher protein in interstitial fluid or plasma
Protein
Blood Volume
Plasma(3L)+ RBC(2L)= 5L
Hematocrit
Fraction of blood composed of RBCs
Normal hematocrit
0.40 in males n 0.36 in females
Donnan effect
More positive charge in plasma than interstitial fluid
Composition of intracellular fluids
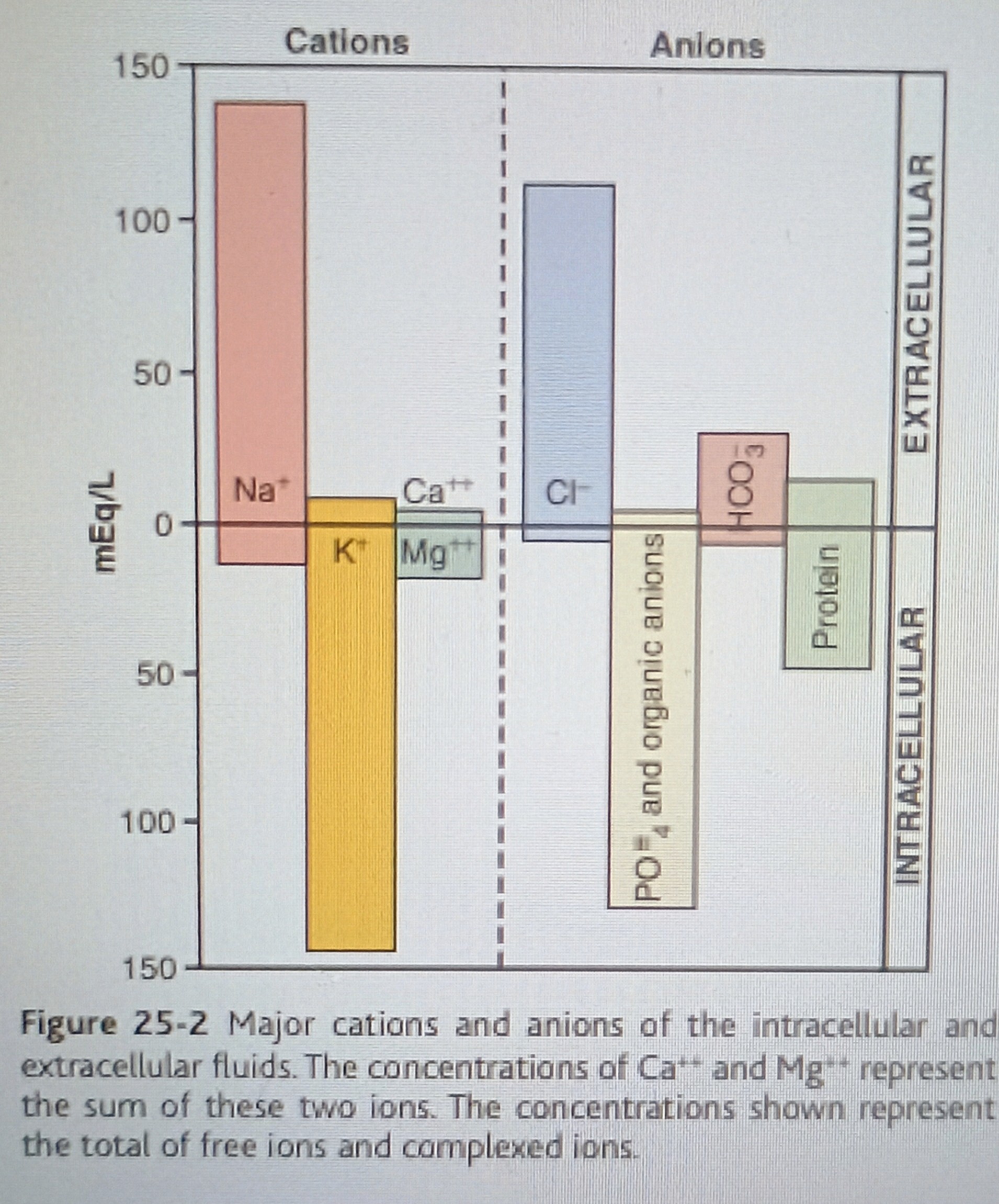
K+, Mg++, Na+(very little), PO4 3- n organic anions, protein, little cl- n HCO3-
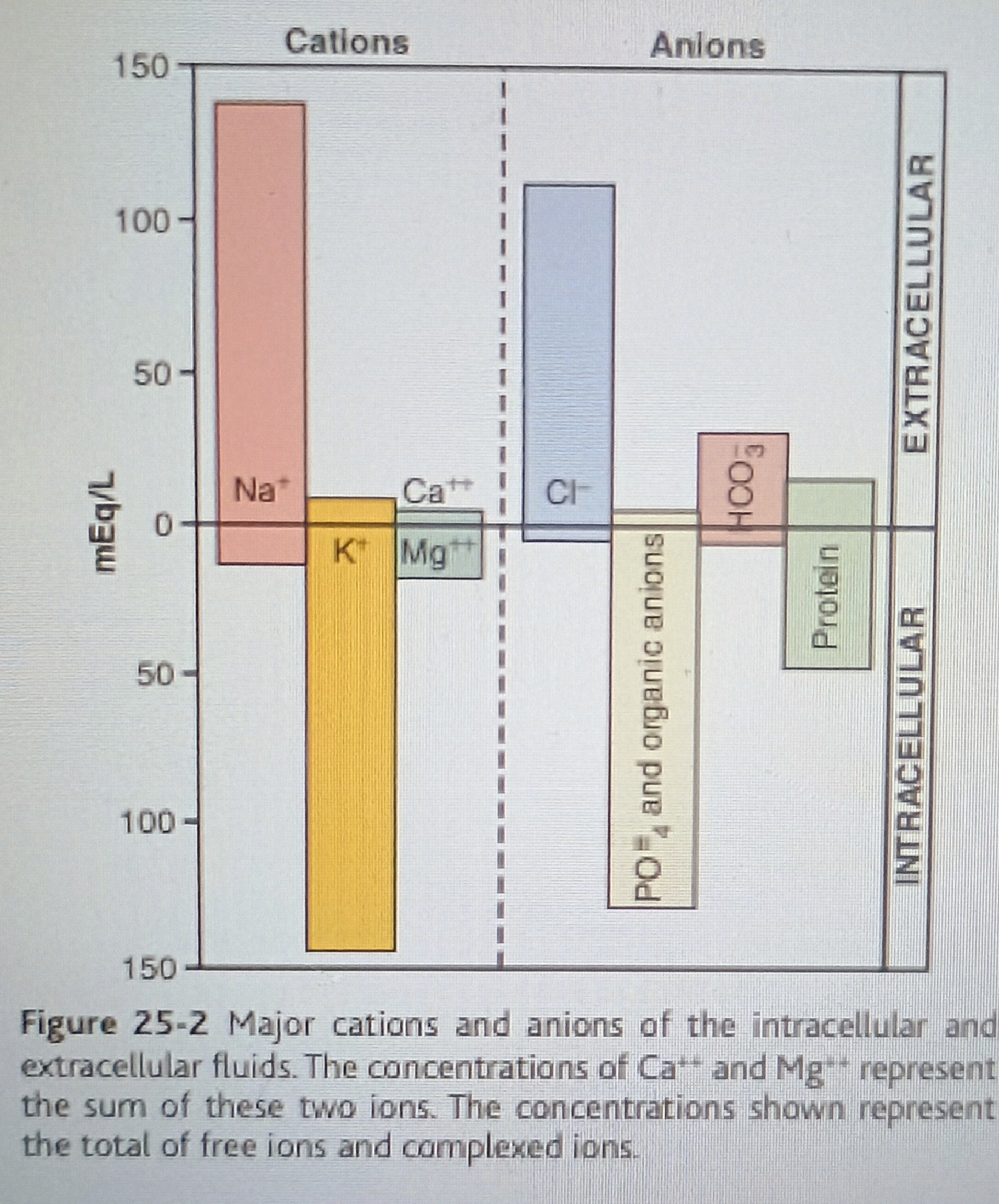
Composition of Extracellular fluid
Na+, Ca2+, K+ a little
Dye to measure total body water
Radioactive water, heavy water, antipyrine
Dye for Measurement of Extracellular fluid volume
Radioactive Na, radioactive chloride, radioactive iothalamate, thiosulphate kon, inulin
Intracellular fluids Volume
Calculated
Volume(intracellular fluid= Total body fluid-extracellular fluid
Dye for Measurement of plasma volume
Serum albumin labelled with radioactive iodine, Evans blue dye
Interstitial fluid volume
Extracellular fluid volume - plasma volume
Blood Volume
Blood Volume= Plasma volume/(1-hematocrit)
RBC labelled with radioactive materials like radioactive chromium
Osmosis
Net diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to that has lower water concentration
Osmoles
The number of osmotically active particles
Osmolality
Number of osmoles per kilogram of solvent(water)
Osmolarity
Number of osmoles per litre of solution
Higher osmotic pressure(20mm Hg greater) and osmolarity(1 higher) in plasma due to
Plasma proteins