Central Dogma
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
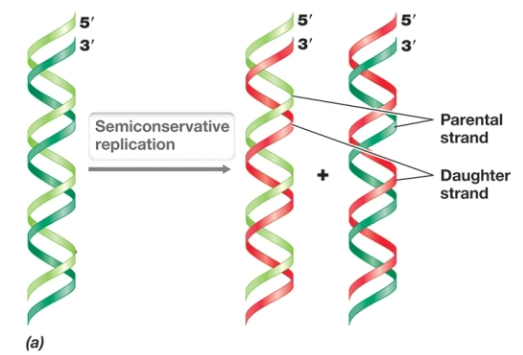
DNA replication
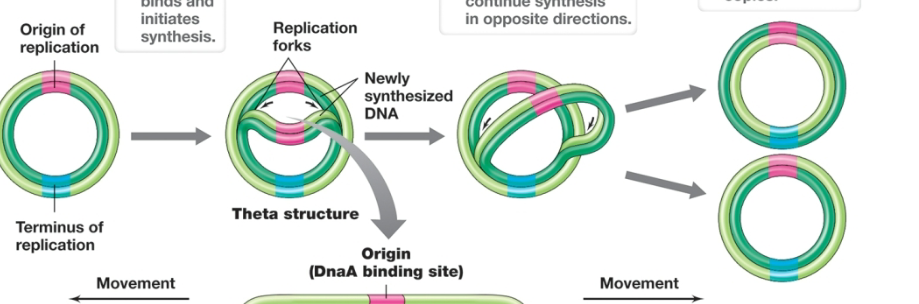
DNA replication for circular DNA
Replisome binds and initiates synthesis
replication forks continue synthesis in opposite directions
replication forks hit terminus of replication and collide releasing two chromosome copies
Replication fork
zone of unwound DNA where replication occurs
DNA synthesis
new DNA always goes from 5’ to 3’
RNA primer
beginning of DNA synthesis
primase makes the primer
DNA polymerase III
can’t remove RNA primer
can proofread
DNA polymerase I
can remove RNA primer
can proofread
Ligase
connects 3’ to 5’ to seal the Okazaki fragments (seals nicks in the backbone of DNA)
Replisome
complex of multiple proteins involved in replication
Proofreading
begins at time of nucleotide insertion
mismatched nucleotide is excised from growing DNA strand
correct nucleotide inserted into growing DNA strand
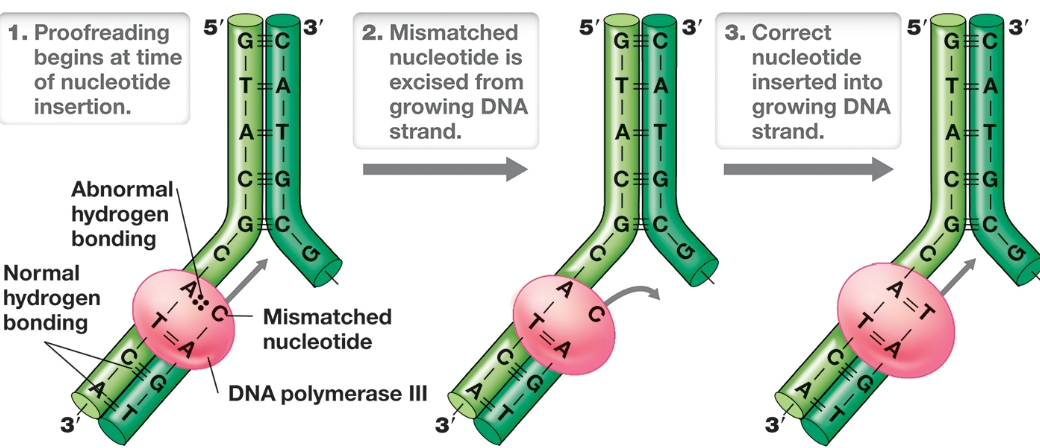
How is proofreading achieved
Polymerase can detect mismatch through incorrect hydrogen bonding
mRNA
carry information to ribosome
have short half-lives (a few minutes)
tRNA
convert mRNA information to amino acid sequence
rRNA
catalytic and structural ribosome components
Transcription
DNA is transcribed into a single stranded RNA
RNA polymerase
recognizes DNA sites called promoters
Promoters
site of initiation of transcription
Transcription terminators
transcription stops at these sites
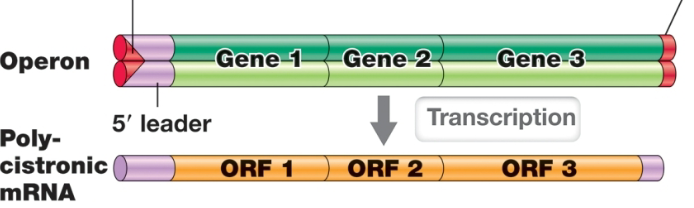
Operon
a group of related genes cotranscribed on a polycistronic mRNA
Exon
coding sequences in Eukarya
Introns
intervening sequences in Eukarya
RNA capping
addition of methylated guanine to 5’ end of mRNA
Poly(A) tail
stabilizes mRNA and required for translation
Translation
the synthesis of proteins from RNA
Protein structure
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
What are the components needed for Translation
mRNA with RBS and start codon
transfer RNA
the ribosome
what is tRNA used for
one tRNA per amino acid
each contains an anticodon
charging of tRNA
anticodon
three bases that recognize codon
charging of tRNA
tRNA and cognate (correct) amino acid brought together by aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis
The wobble concept
irregular base pairing allowed at third position of tRNA
The 3 stages of translation
Initiation
elongation
termination