Silverstein and Hopper Chapter 7: SIRS, MODS, and Sepsis
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
ACCP/SCCM Working Definition of SIRS
2 of any of the 4 clinical findings
Hyper/hypothermia
Tachycardia
Tachypnea (or hyperventilation)
Leukocyte count abnormalities in the absence of other known causes such as exercise or chemotherapy
Evolution of Definitions of Sepsis
2001 Sepsis-2
Recommendation to adopt the PIRO scheme (Predisposition, Insult/infection, response, organ dysfunction)
2016 Sepsis-3
Sepsis - life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
Organ dysfunction, rather than clinical features of inflammation, was recognized as a hallmark feature of sepsis syndrome
Can be characterized clinically by various scoring systems
SOFA score and the quick SOFA (qSOFA) score were identified as the most clinically useful methods
SOFA Score
Based on the combined clinical assessment of cardiopulmonary (blood pressure, P/F ratio), neurologic (Glasgow Coma Score), renal (serum creatinine), hepatic (serum bilirubin), and coagulation (platelet count) system functions, with deviations from normal scored on a 5-point scale
Score (from 0-4) assigned to a patient is the value of the highest subscore in the schema
Patients are assumed to have a baseline score of 0 unless there is known preexisting disease
A score of 2 or more or an increase in the score by a value of 2 or greater in infected patients has defined human sepsis since the Sepsis-3 conference
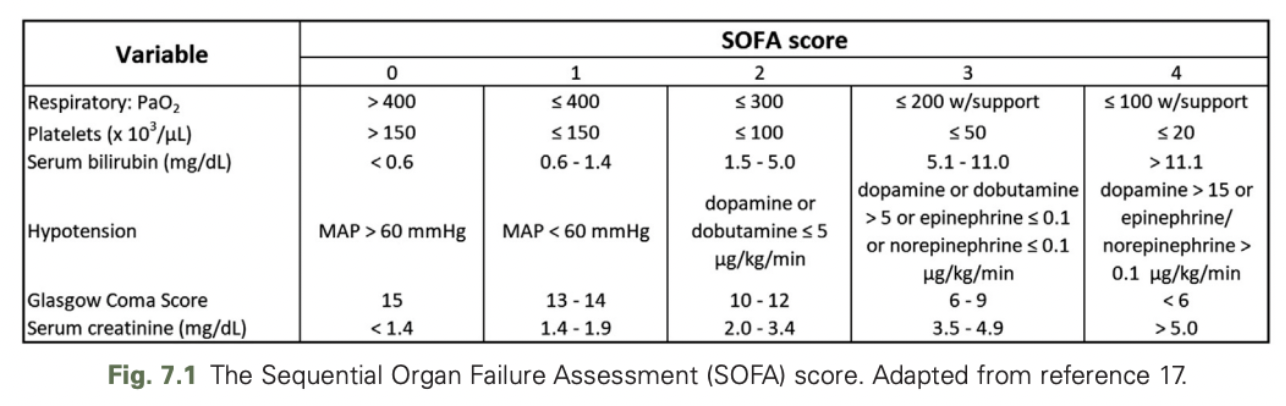
What accompanies a SOFA score of 2 ore more in humans hospitalized with infection?
At least a 10% mortality risk
qSOFA
Uses three elements (altered mentation, systolic blood pressure of 100 mmHg or less, respiratory rate of 22 or more) to create a scale or 0-3 with each abnormality assigned 1 point
Sepsis-3 conference recommendations include using qSOFA as a screening tool for sepsis outside of the ICU
qSOFA score of 2 or more increases the likelihood of a poor outcome and warrants further investigation to rule out sepsis
qSOFA tool may have more value for animals with sepsis as opposed to other causes of severe illness, but accurate assessment of the tool's utility to identify either will require prospective trials
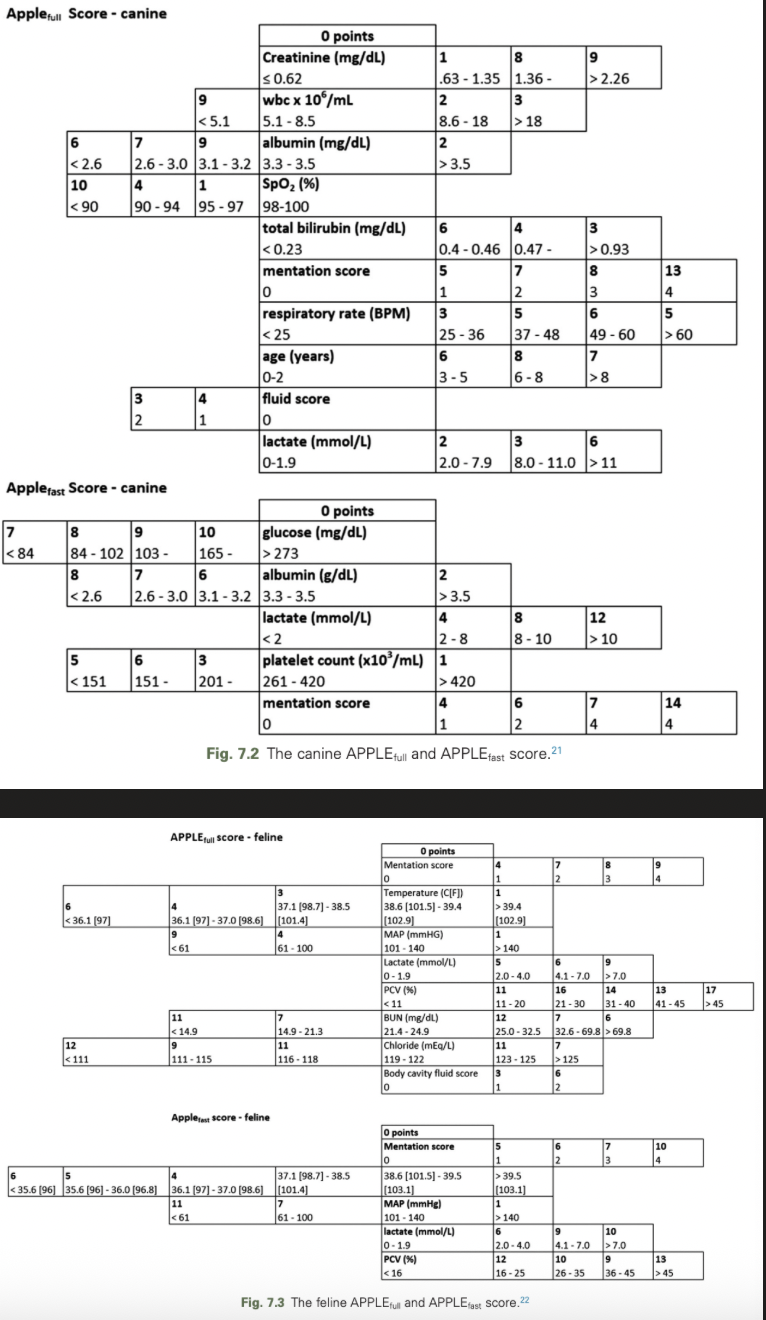
The APPLE Score
Acute Patient Physiologic and Laboratory Evaluation (APPLE) Score
Most comprehensive validated illness severity scoring system to characterize organ dysfunction and risk of death in dogs and cats
The individually weighted scores add up to a maximum possible score of 80 (APPLEfull) or 50 (APPLEfast)
Assessment of Animals with SIRS or MODS
Hyper/hypothermia, unexplained sinus tachy- or bradycardia, and tachypnea are significant features of critical illness in companion animals, particularly when accompanies by other physical examination findings such as depressed mentation or abnormal mucus membrane color, skin temperature, and femoral pulse quality
Low specificity of SIRS criteria for predicting outcome means that a prognosis should not be offered based on the presence of the syndrome alone
Treatment of suspected bacterial sepsis should utilize intravenous antibiotics administered at the upper end of the therapeutic dosage range, adhering to principles of time- or concentration-dependent drug administration
Time-dependent antibiotics may best be administered as a loading dose followed by a continuous rate intravenous infusion to maintain tissue concentrations above the minimal inhibitory concentration for the target organism